A cp*co(co)i 2 Preparation method of cobalt-doped zinc oxide photoanode nanoarray
A nano-array, photoanode technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, organic compound/hydride/coordination complex catalysts, etc., can solve problems such as no related reports, and achieve good electron transfer efficiency, rapid separation and transport, and improved oxygen adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
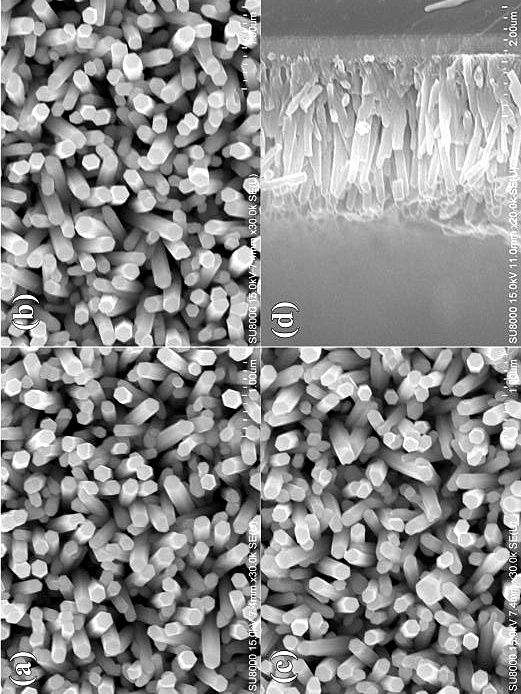
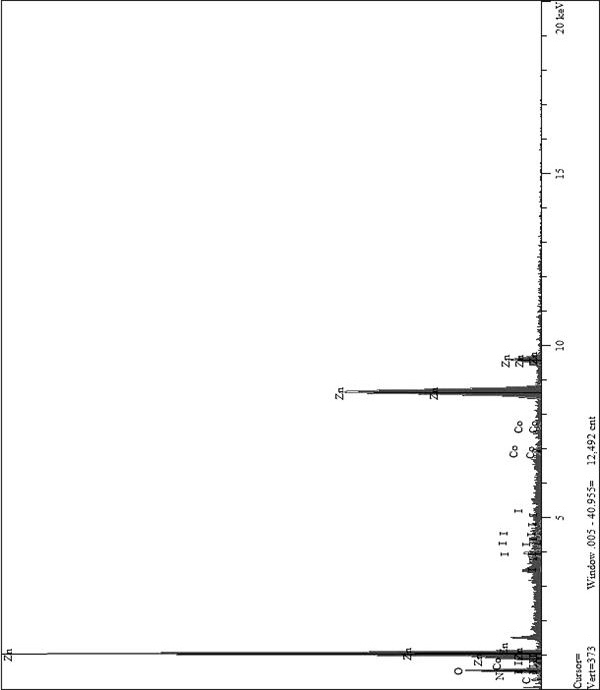
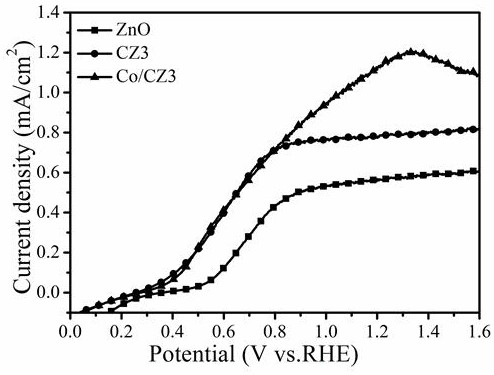
[0020] Take 10~200μL of 10mM zinc acetate ethanol solution and drop-coat it on the cleaned FTO substrate, 2500~3500 rpm for 30 seconds. Transfer to a muffle furnace, heat up to 300° C. for 2.5 hours for calcination over 40 minutes to obtain a zinc oxide seed layer. Put the above substrate into a polytetrafluoroethylene autoclave, add 0.01M Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O and 0.01M hexamethylenetetramine, 80mL mixed solution with a molar ratio of 1:1, were hydrothermally reacted at 90°C for 6h to obtain ZnO photoanode nanoarrays. Cobalt nitrate with a molar ratio of Co / Zn=1% was added to the hydrothermal reaction solution, and CZ1 photoanode nanoarrays were obtained under the same conditions. The prepared Co-ZnO photoanode nanoarrays were immersed in Cp*Co(CO)I at room temperature in the dark 2 N,N-dimethylformamide solution for 10h, and finally washed with ethanol and water to obtain Co / CZ1 photoanode nanoarrays.
Embodiment 2
[0022] Take 10~200μL of 10mM zinc acetate ethanol solution and drop-coat it on the cleaned FTO substrate, 2500~3500 rpm for 30 seconds. Transfer to a muffle furnace, heat up to 300° C. for 2.5 hours for calcination over 40 minutes to obtain a zinc oxide seed layer. Put the above substrate into a polytetrafluoroethylene autoclave, add 0.05M Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O and 0.05M hexamethylenetetramine, 80mL mixed solution with a molar ratio of 1:1, were hydrothermally reacted at 90°C for 6h to obtain ZnO photoanode nanoarrays. Cobalt nitrate with a molar ratio of Co / Zn=3% was added to the hydrothermal reaction solution, and CZ3 photoanode nanoarrays were obtained under the same conditions. The prepared Co-ZnO photoanode nanoarrays were immersed in Cp*Co(CO)I at room temperature in the dark 2 N,N-dimethylformamide solution for 10h, and finally washed with ethanol and water to obtain Co / CZ3 photoanode nanoarrays.
Embodiment 3
[0024] Take 10~200μL of 10mM zinc acetate ethanol solution and drop-coat it on the cleaned FTO substrate, 2500~3500 rpm for 30 seconds. Transfer to a muffle furnace, heat up to 300° C. for 2.5 hours for calcination over 40 minutes to obtain a zinc oxide seed layer. Put the above substrate into a polytetrafluoroethylene autoclave, add 0.25M Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O and 0.25M hexamethylenetetramine, 80mL mixed solution with a molar ratio of 1:1, were hydrothermally reacted at 90°C for 6h to obtain ZnO photoanode nanoarrays. Cobalt nitrate with a molar ratio of Co / Zn=5% was added to the hydrothermal reaction solution, and the CZ5 photoanode nanoarray was obtained under the same conditions. The prepared Co-ZnO photoanode nanoarrays were immersed in Cp*Co(CO)I at room temperature in the dark 2 N,N-dimethylformamide solution for 10 h, and finally rinsed with ethanol and water to obtain Co / CZ5 photoanode nanoarrays.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com