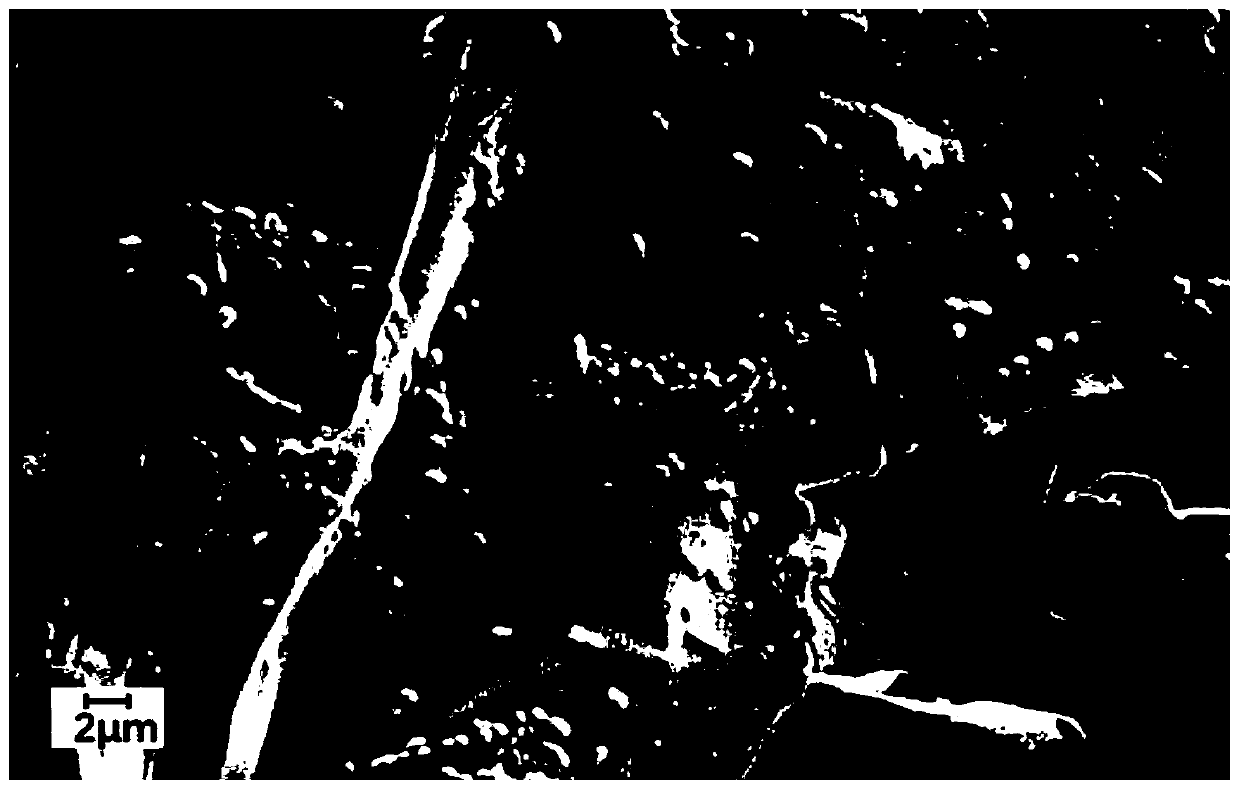
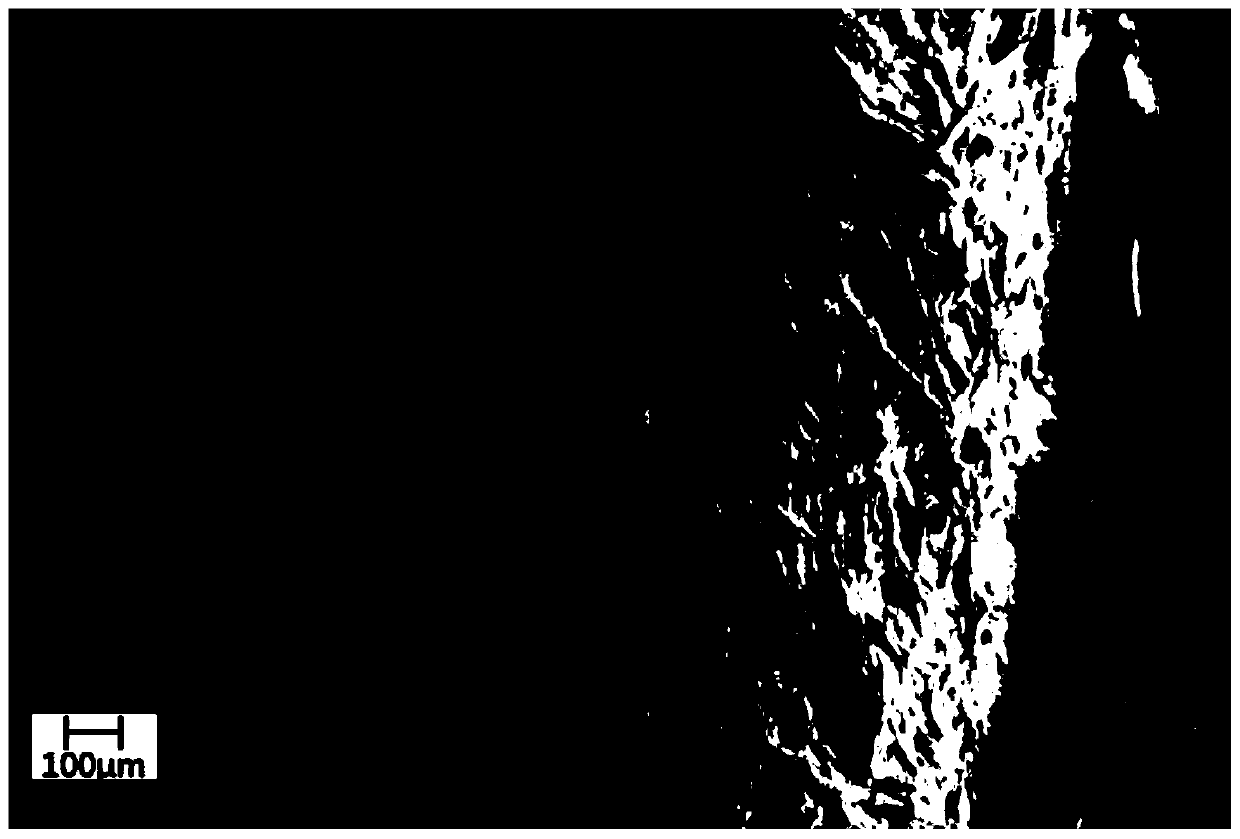
Nano-crystalline cellulose based 3D printing lactobacillus embedding material as well as preparation method and application thereof
A nanocellulose, 3D printing technology, applied in applications, dairy products, milk preparations, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient viscoelasticity of 3D printing ink, and achieve excellent 3D printing performance, efficient continuous cyclic fermentation, and effective embedding. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] A preparation method of a nanocellulose-based 3D printed lactic acid bacteria embedding material, comprising the steps of:
[0046] (1) At room temperature, add 0.2g of sodium alginate powder to 20g of nanocellulose solution with a concentration of 0.03g / mL, mix well, then pour into the 3D printing syringe, and centrifuge to eliminate air bubbles. The speed is 2000rpm, and the centrifugation time is 1min to obtain the mixed solution;
[0047] (2) Add 0.01g of chitosan into 10mL of pure water, stir evenly to disperse the chitosan evenly in the water, then add 0.05mL of glacial acetic acid, mix well to completely dissolve the chitosan, and obtain a chitosan solution;
[0048] (3) Add 2g of lactic acid bacteria powder to the chitosan solution described in step (2), and mix evenly to obtain chitosan-lactic acid bacteria suspension;
[0049] (4) Use the mixture described in step (1) as the outer layer material, and the chitosan-lactic acid bacteria suspension described in s...
Embodiment 2
[0053] A preparation method of a nanocellulose-based 3D printed lactic acid bacteria embedding material, comprising the steps of:
[0054] (1) At room temperature, add 0.3g of sodium alginate powder to 20g of nanocellulose solution with a concentration of 0.04g / mL, mix well, then pour it into a 3D printing syringe, and centrifuge to eliminate air bubbles. The speed is 3000rpm, and the centrifugation time is 3min to obtain the mixed solution;
[0055] (2) Add 0.03g chitosan into 10mL pure water, stir evenly to disperse chitosan evenly in the water, then add 0.07mL glacial acetic acid, mix well, completely dissolve chitosan, and obtain chitosan solution;
[0056] (3) Add 1.5 g of lactic acid bacteria powder to the chitosan solution described in step (2), and mix evenly to obtain chitosan-lactic acid bacteria suspension;
[0057] (4) Use the mixture described in step (1) as the outer layer material, and the chitosan-lactic acid bacteria suspension described in step (3) as the in...
Embodiment 3
[0061] A preparation method of a nanocellulose-based 3D printed lactic acid bacteria embedding material, comprising the steps of:
[0062] (1) At room temperature, add 0.4g of sodium alginate powder to 20g of nanocellulose solution with a concentration of 0.05g / mL, mix well, then pour it into the 3D printing syringe, and centrifuge to eliminate air bubbles. The speed is 4000rpm, and the centrifugation time is 5min to obtain the mixed solution;
[0063] (2) Add 0.05g chitosan into 10mL pure water, stir evenly to disperse the chitosan evenly in the water, then add 0.1mL glacial acetic acid, mix well, completely dissolve the chitosan, and obtain a chitosan solution;
[0064] (3) Add 1.0 g of lactic acid bacteria powder to the chitosan solution described in step (2), and mix evenly to obtain chitosan-lactic acid bacteria suspension;
[0065] (4) Use the mixture described in step (1) as the outer layer material, and the chitosan-lactic acid bacteria suspension described in step (3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com