Electrolytic corrosion resistance method for M-Bus wet-type photoelectric direct-reading water meter
A technology of photoelectric direct reading and electrolytic corrosion, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, liquid/fluid solid measurement, etc., and can solve problems such as meter failure, shrinkage, and deepening of electrolytic corrosion of M-Bus wet photoelectric direct reading water meters, etc. , to achieve the effects of long power-on time, large resistance between conductors, and insensitive power-on time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
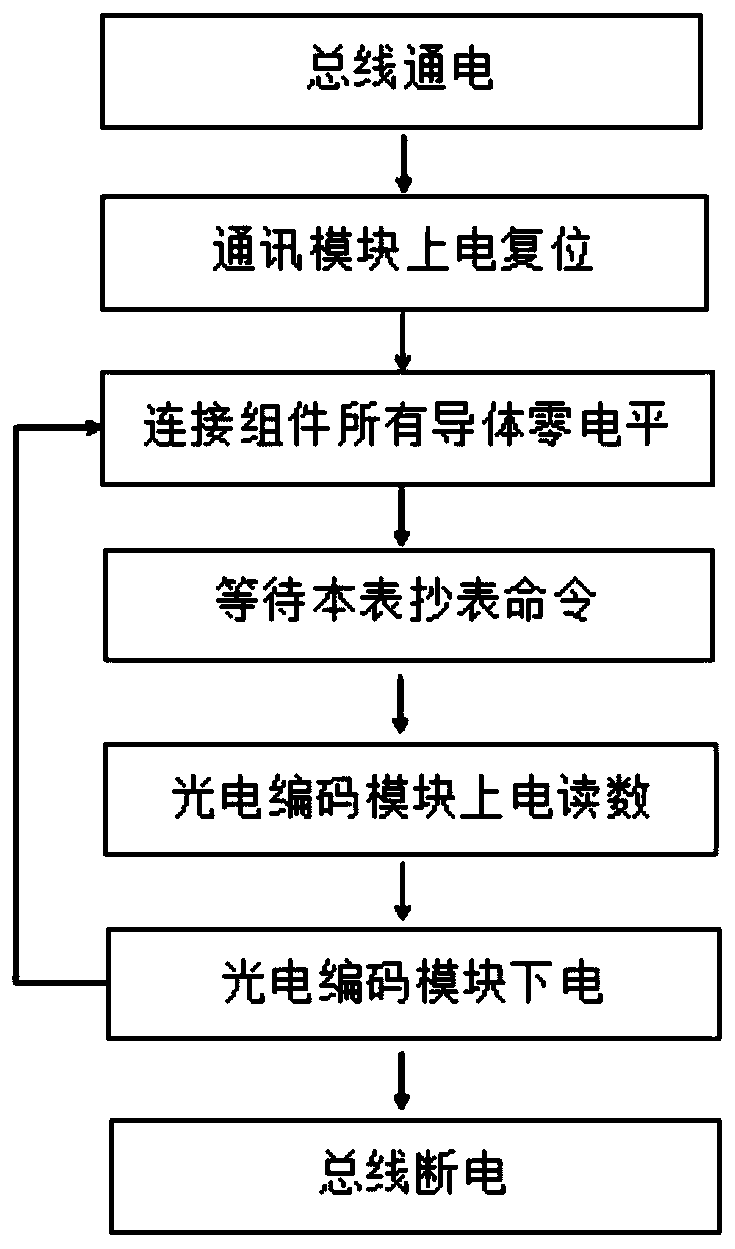
[0036] Example 1, such as figure 1 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention provides an M-Bus wet-type photoelectric direct-reading water meter anti-electrolytic corrosion method, comprising the following steps:
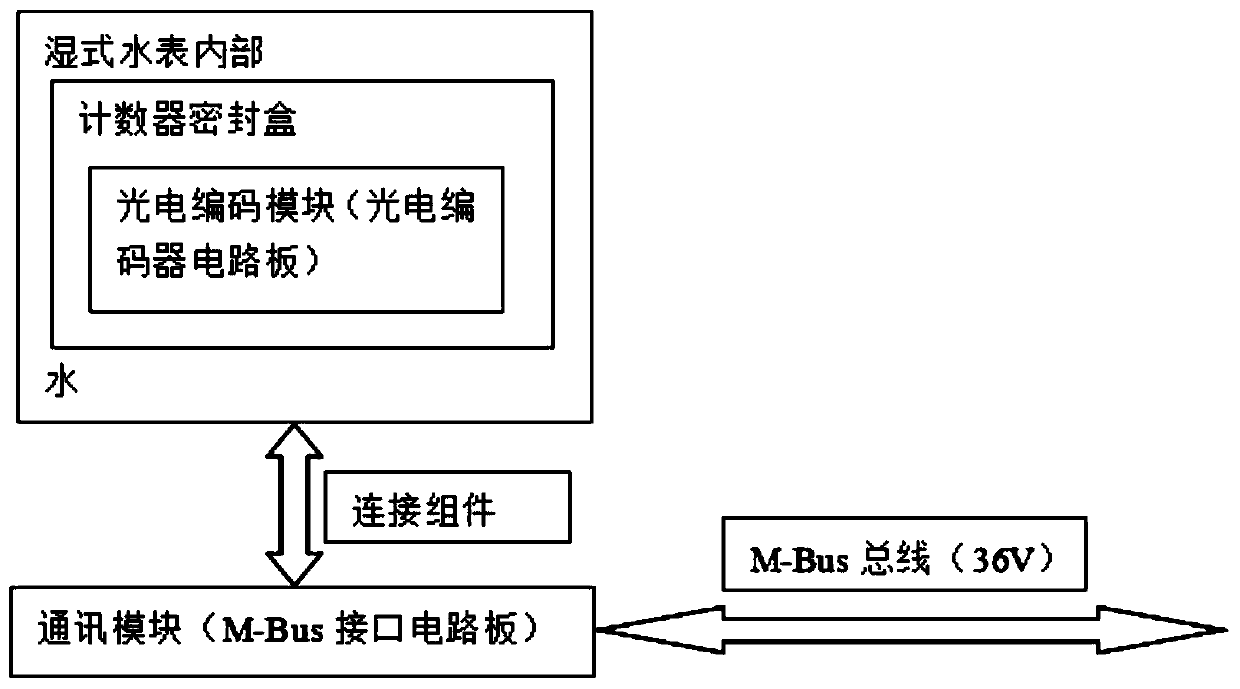
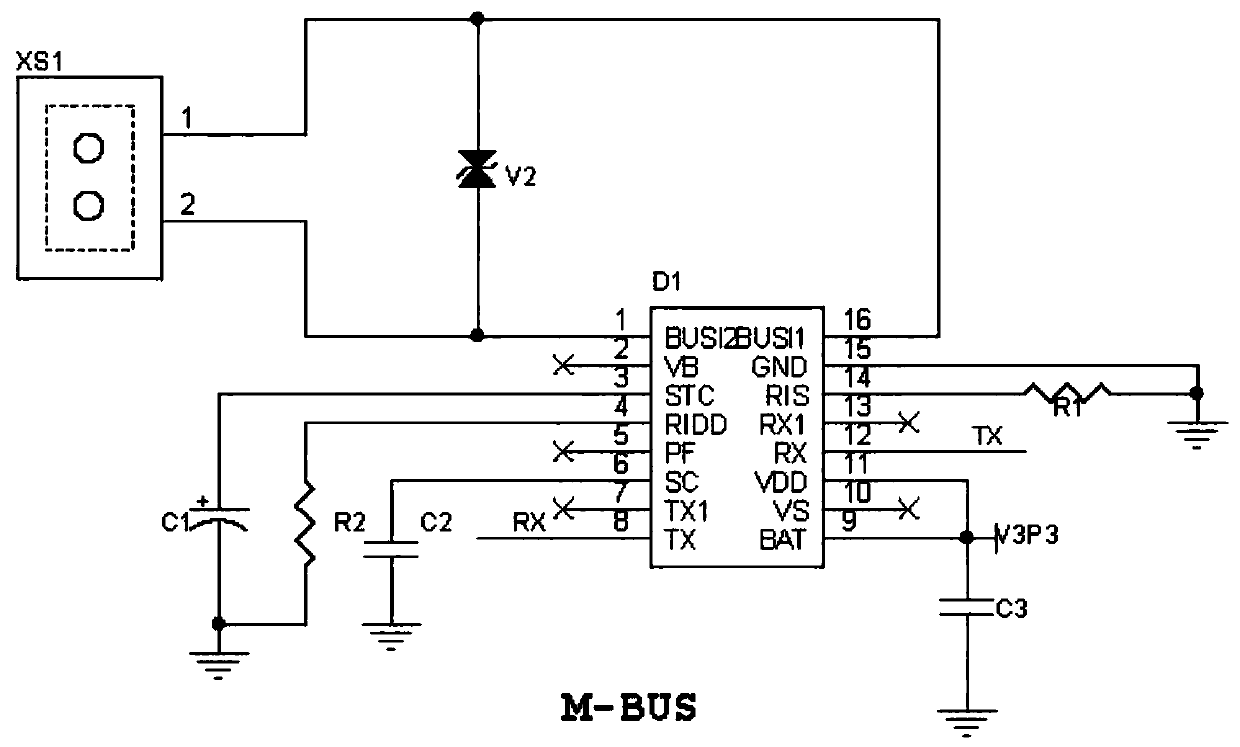
[0037] Step 1. Divide the internal circuit of the water meter counter into two parts: a communication module and a photoelectric coding module. The photoelectric coding module is located on the counter inside the water meter. The communication module is moved out of the water meter and is located outside the water meter with a relatively good environment. The communication module and The M-Bus bus is connected, and the communication module and the photoelectric encoding module are connected through a connecting component;
[0038] Step 2. Power on the M-Bus bus, power on and reset the communication module to start working, and do not power on the photoelectric encoding module, and all the electrical connection conductors in the connection components are at z...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com