<99>Mo sub-critical production device and method based on accelerator driving
An accelerator-driven, production device technology, which is applied in radiation-converting chemical element devices, reactor/accelerator external conversion, nuclear engineering, etc., can solve problems such as high cost and complex process, achieve reduction of radioactive waste, simple post-processing, and avoidance of Effects of nuclear proliferation risk
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
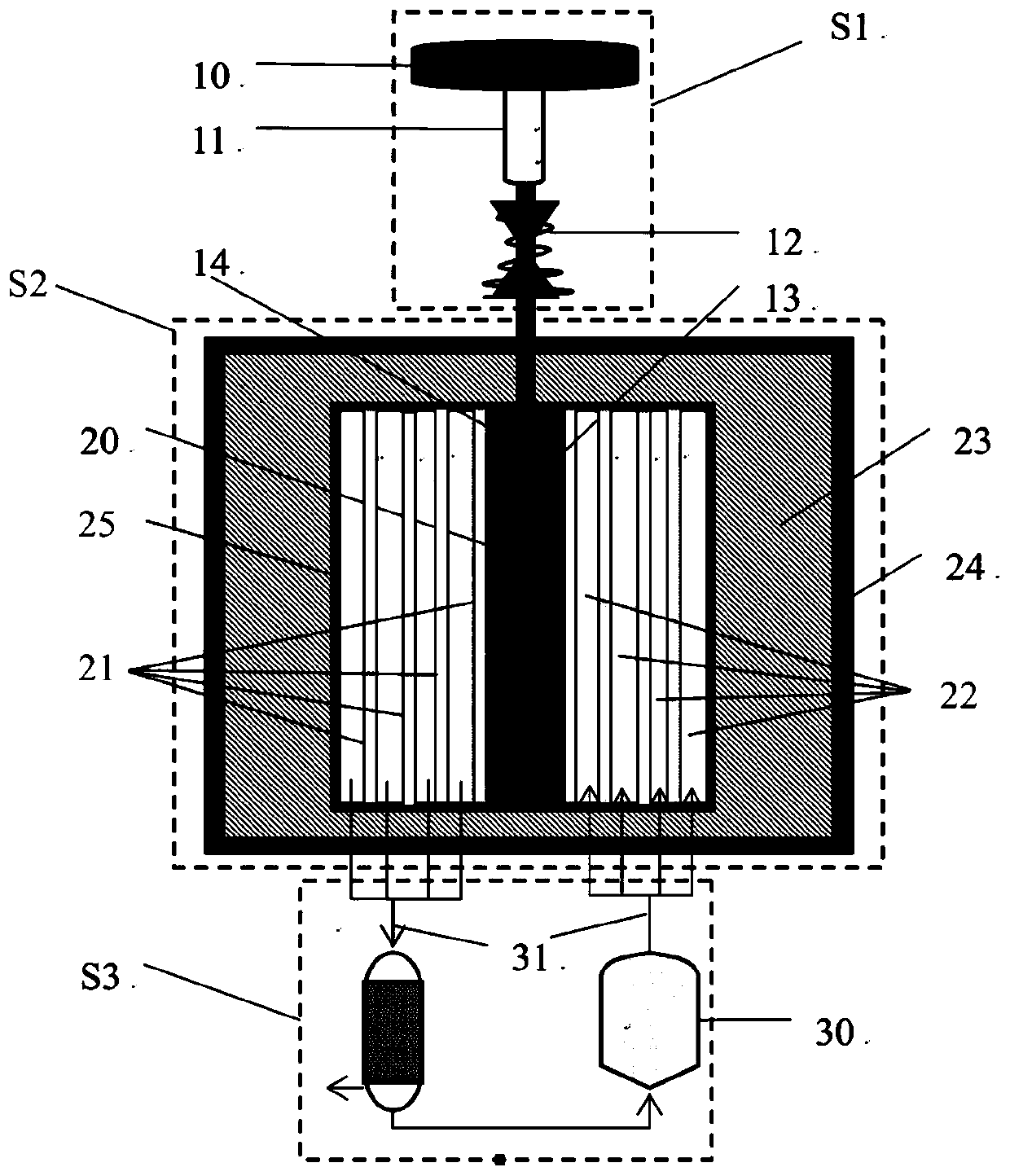
[0036] See Figure 1-2 : An accelerator-based drive of this embodiment 99 Mo subcritical production device, including accelerator unit: S1, irradiation production unit S2, and separation and purification unit S3;
[0037] The accelerator unit S1 includes a high-energy particle source 10, a collimator 11, an accelerator 12, a target 13, and a target cavity 14, from the output direction. The high-energy particle source 10 passes through the collimator 11 and the accelerator 12 to accurately bombard the irradiation production unit. The target 13 in the target cavity 14 in the center of S2 generates neutron emission;
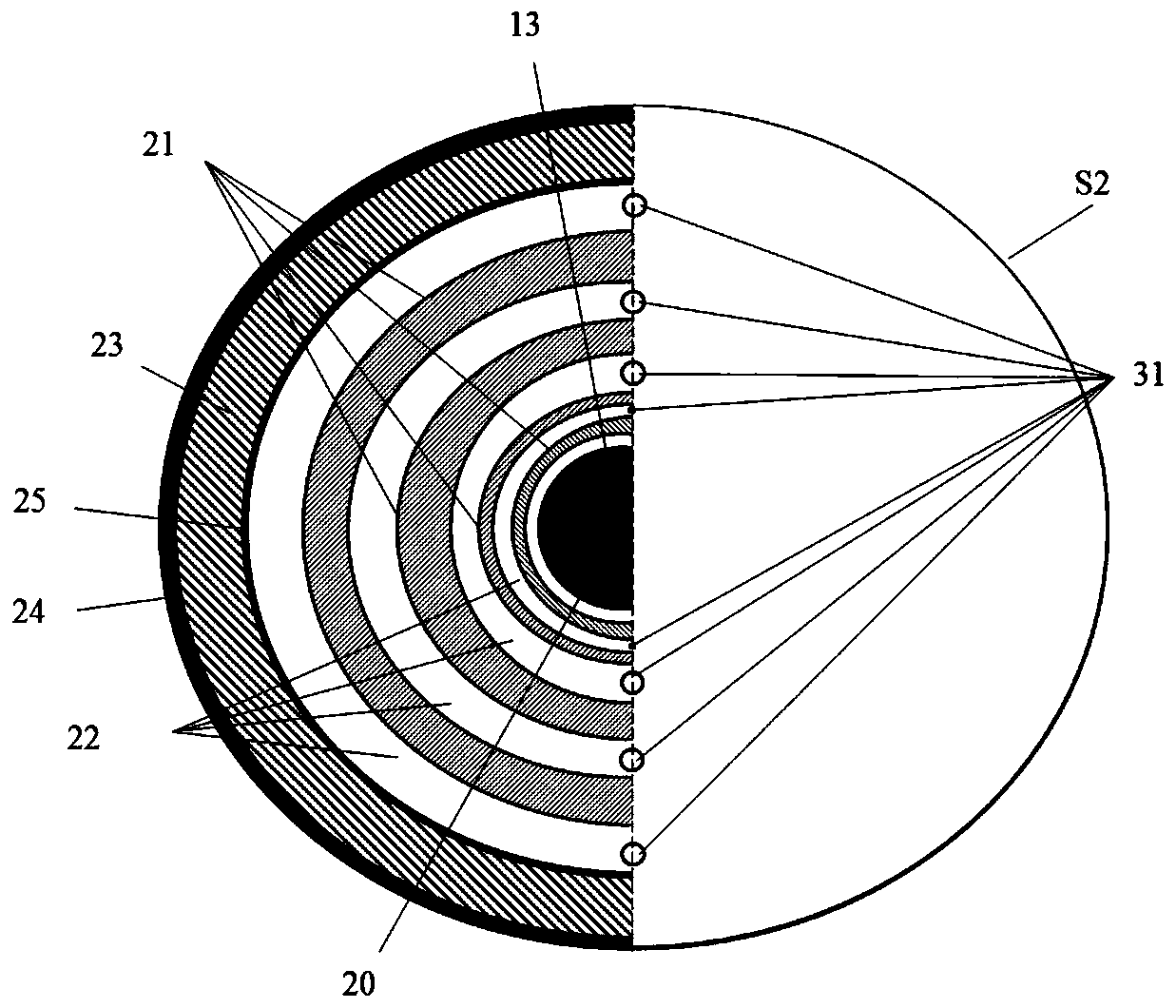
[0038] The irradiation production unit S2 is a concentric cylindrical structure, which includes a neutron moderation layer 20, a neutron multiplier layer 21, a low-enriched uranium salt solution 22, a neutron reflection layer 23, and a shielding layer 24 from the inside to the outside. , The low-enriched uranium salt solution 22 is placed in the fission reaction vessel ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] This embodiment 2 also discloses an accelerator-based 99 The Mo subcritical production method includes the following steps:
[0049] First, the accelerator unit generates an accelerated particle beam (proton beam or deuterium ion beam) to bombard a heavy nuclear target (lead, mercury, tungsten), or a gaseous deuterium target (or tritium target) in the target chamber, causing heavy nuclear fission, or deuterium Deuterium fusion (or deuterium-tritium fusion) reaction emits neutrons;
[0050] The high-energy neutrons generated above enter the neutron moderation layer surrounding the target chamber, and part of them are slowed down to the thermal neutron zone. 235 U has a larger fission cross-section; among them, the moderator layer material used is polyethylene, or water, or heavy water, or graphite, or beryllium, or zirconium hydride;
[0051] The neutron beam passing through the moderating layer enters the neutron multiplication layer I, which is made of bismuth, or lead, or le...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com