Method for identifying whether non-milk powder type exogenous protein is adulterated in honey or not
A protein and honey technology, applied in the field of food testing, analysis and testing, can solve the problem of difficult detection of adulterated honey, and achieve the effect of being suitable for promotion, improving competitiveness and low detection limit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
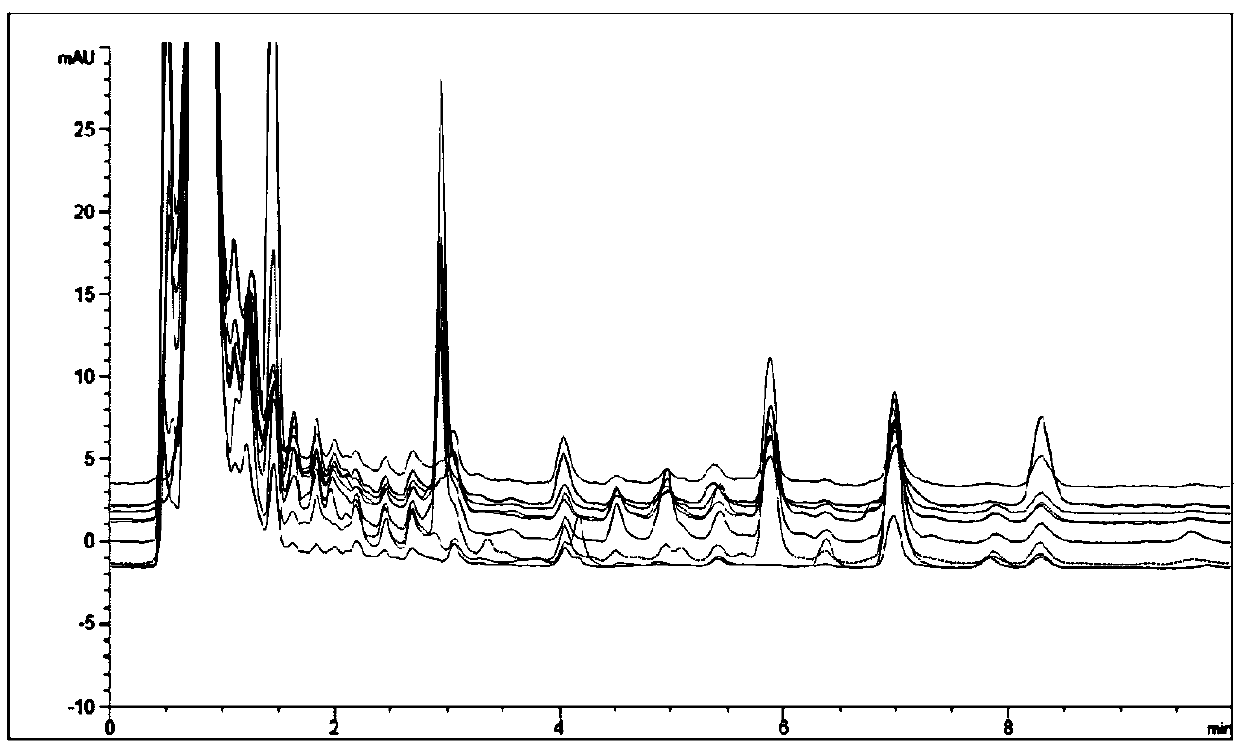
[0022] Example 1 Determination of characteristic detection peaks of non-milk powder class exogenous proteins
[0023] First, collect pure honey from different regions and different types. There are 161 pure honeys, including: acacia honey, rapeseed honey, vitex honey, linden honey, jujube honey, sunflower honey, buckwheat honey, vetch honey, cotton honey, lychee honey, longan honey, wolfberry honey and potpourri honey, The origin of honey includes: Xinjiang, Sichuan, Inner Mongolia, Hubei, Liaoning, Jiangsu, Henan, Hebei, Jilin, Shaanxi, Shandong, Gansu and other provinces.
[0024] These samples can cover all types of honey that are common today.
[0025] The above-mentioned samples are respectively marked as pure honey sample 1, pure honey sample 2, pure honey sample 3, ... pure honey sample n.
[0026] Adulterated honey spiked with exogenous proteins other than milk powder is then collected. These honeys have the following two characteristics: first, these honey samples ...
Embodiment 2
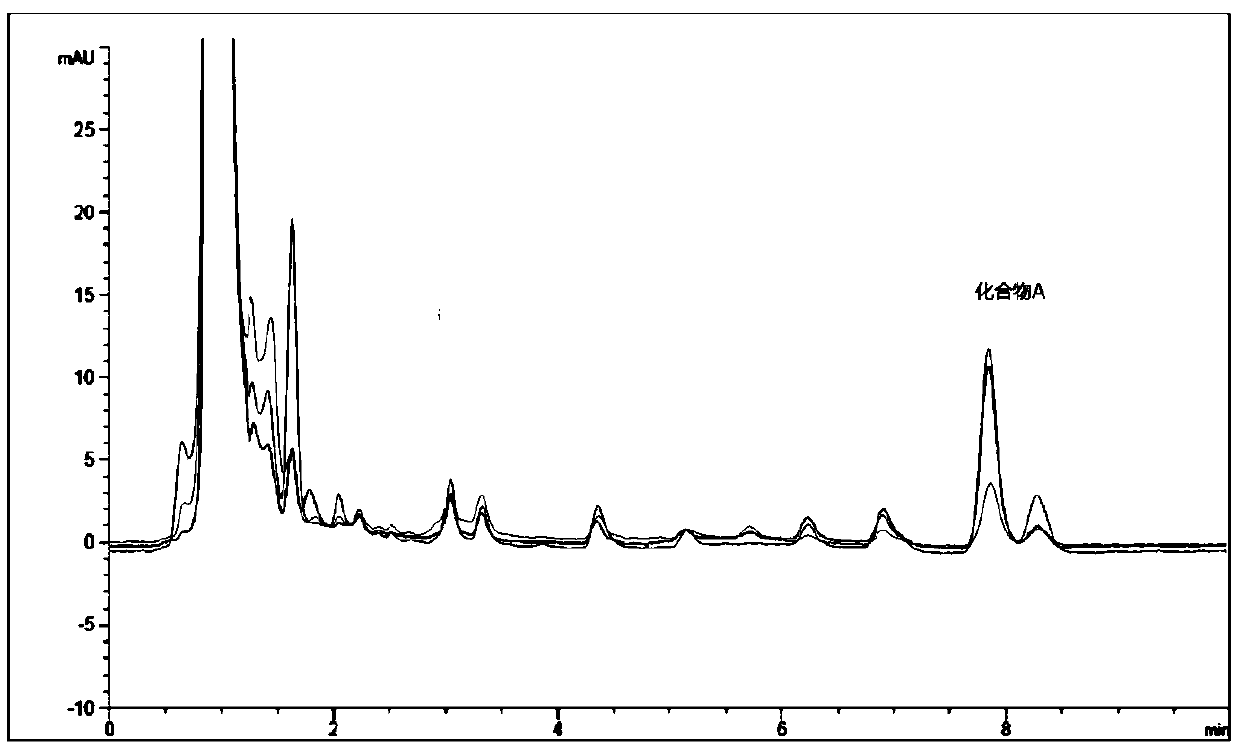
[0039] Preparation of Characteristic Substance Compound A
[0040] Compound A, as a characteristic substance of non-milk powder adulterated protein, has a relatively high content. Take 100g of a non-milk powder adulterated protein and pre-treat it as a honey sample. 7.8 ± 0.2min of the compound (hereinafter referred to as compound A), a total of 1.6g after drying. That is, the content of characteristic compound A in non-milk powder adulterated protein is 16g / kg.
[0041] After the characteristic substance Compound A was prepared, it was tested for stability test for 6 months, and it was found that the substance existed stably in non-milk powder adulterated protein during 6 months.
Embodiment 3
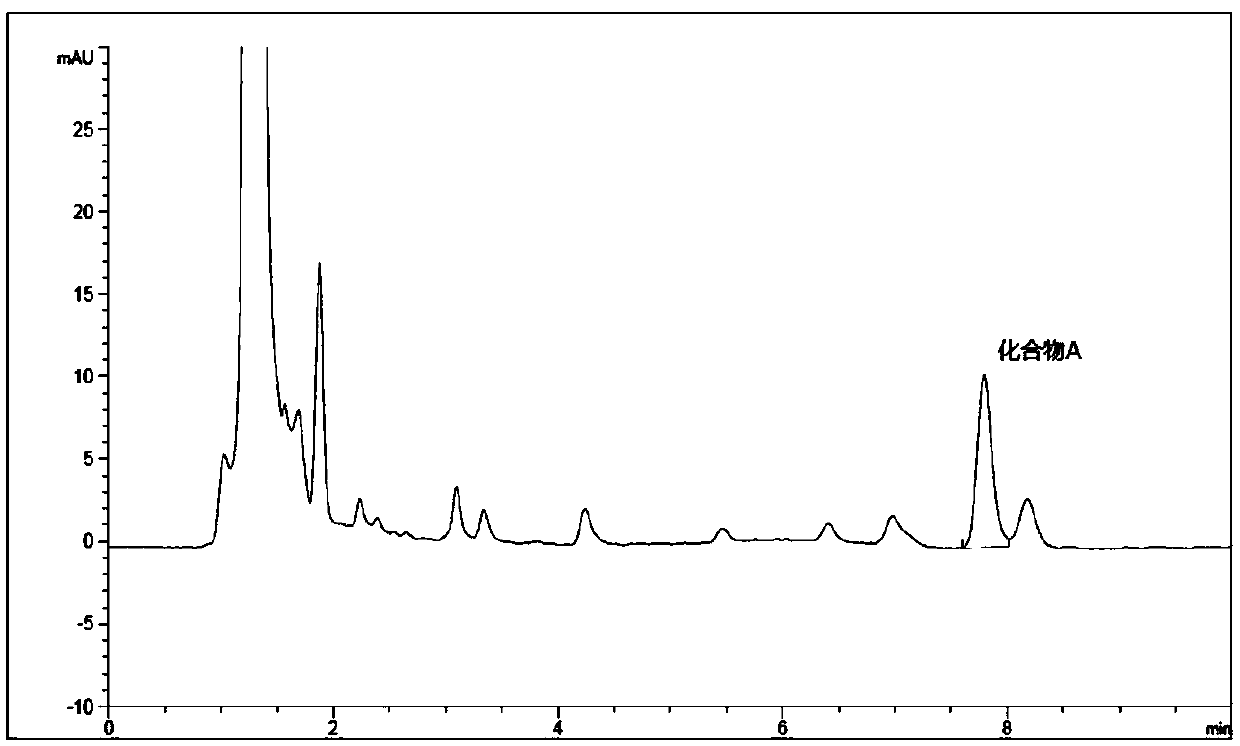
[0043] Determination of detection method for characteristic substance compound A of non-milk powder exogenous protein
[0044] 1. Pretreatment
[0045]Weigh about 2.0g of sample into a 50mL centrifuge tube, add 1mL of 0.1mol / L phosphoric acid solution and 4mL of ethanol, vortex and dissolve in a water bath at 60°C for 10min; then transfer to a 10mL volumetric flask, add mobile phase (acetonitrile: 0.1% phosphoric acid aqueous solution = 30:70 (volume ratio)) and set the volume to the mark; filter through 0.45 μm organic phase and aqueous phase filter membranes into the sample bottle for testing.
[0046] 2. Instrument Analysis Conditions
[0047] Chromatographic conditions: chromatographic column is Kinetex C18 column (100mm×4.6mm, 2.6μm)
[0048] Column temperature: 40°C
[0049] Injection volume 5μL
[0050] Mobile phase: A is acetonitrile, mobile phase B is 0.1% phosphoric acid aqueous solution, isocratic elution, mobile phase ratio A:B=30:70
[0051] Flow rate: 0.2mL·...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com