Design method of ultra-low noise radio frequency receiver based on Rydberg atomic transition
A radio frequency receiver, ultra-low noise technology, applied in the field of laser communication, can solve the problem of not being able to receive signals lower than thermal noise power, etc., and achieve the effects of large signal-to-noise ratio, large transition dipole moment and long life.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] The embodiments and effects of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0026] A kind of design method of the ultra-low noise radio frequency receiver based on Rydberg atomic transition of the present invention, implement according to the following steps:
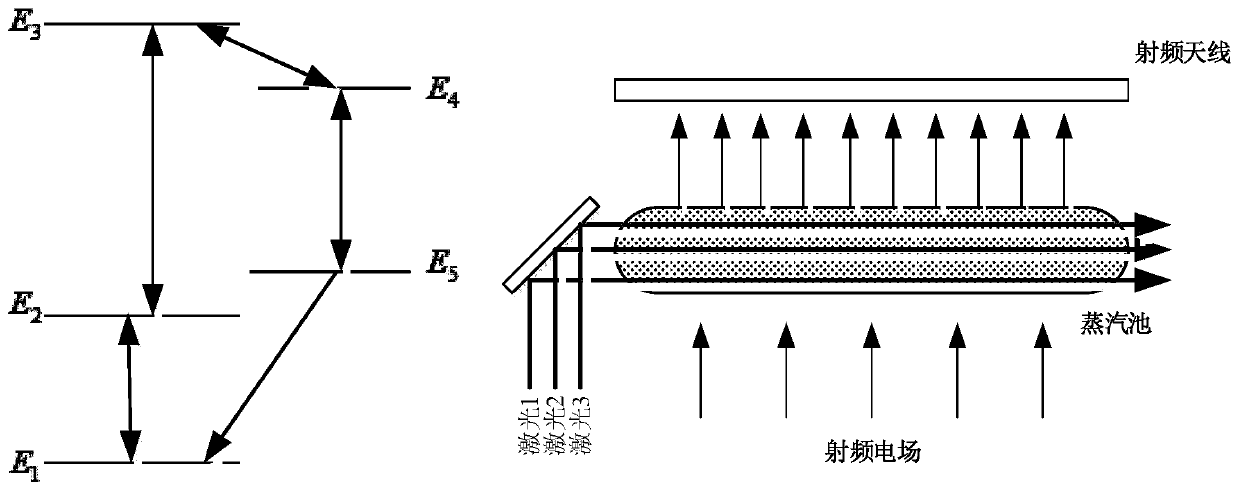
[0027] Step 1, according to the mechanism of the Rydberg atomic transition to receive the signal, set the Rydberg steam pool at the front end of the traditional radio frequency antenna; determine the type and angular frequency of the radio frequency signal of the receiver;
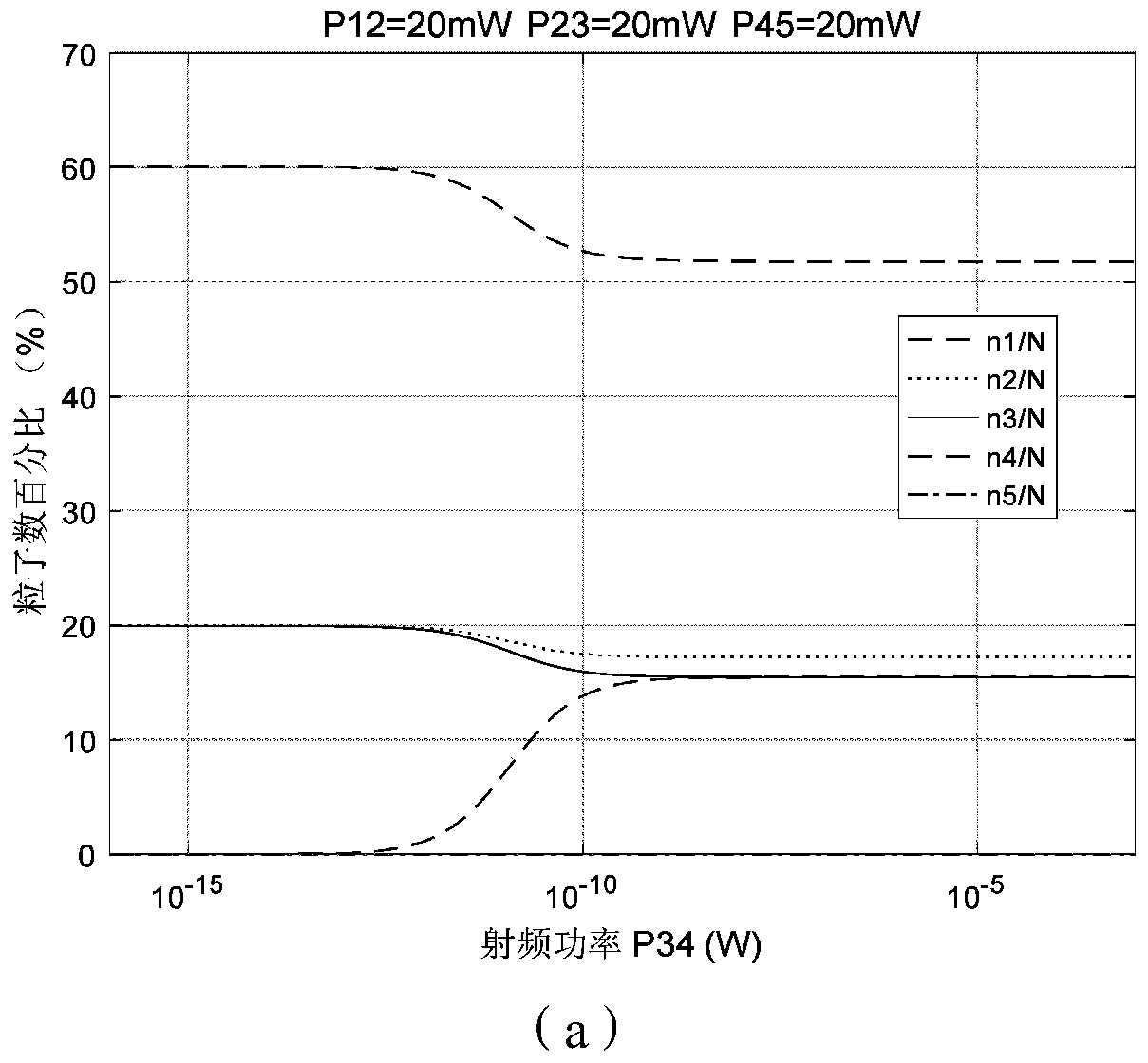
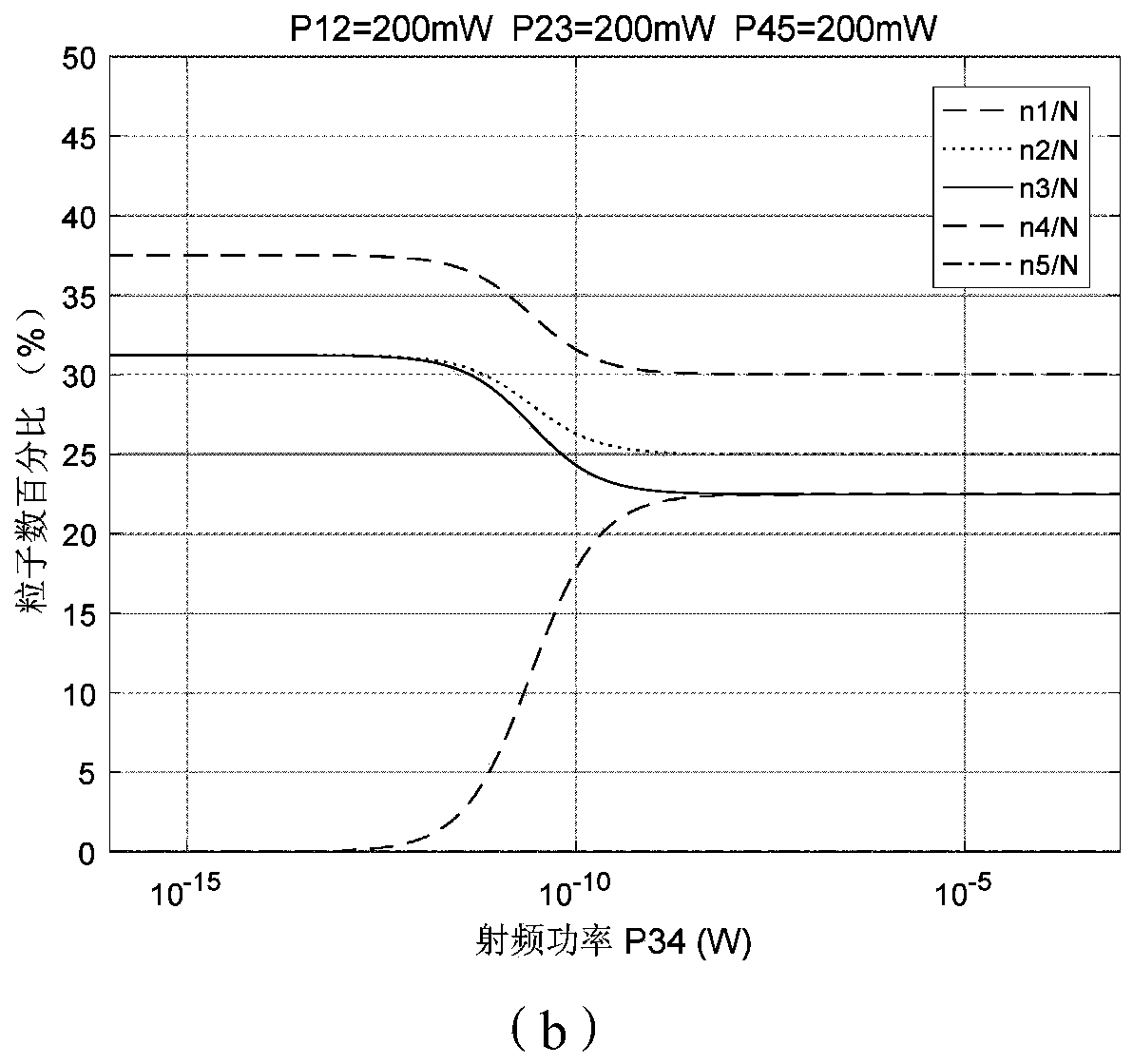
[0028] refer to figure 1 , taking 5 energy levels as an example: a Rydberg steam cell is set at the front end of a traditional radio frequency antenna, so that the weak radio frequency electric field is amplified through the steam pool, and the steam pool is excited by three laser beams, so that the particles in the steam pool are in different In terms of energy levels, thes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com