Electronic brake control method for electric motorcycle
A technology of electric motorcycles and electronic brakes, applied in brakes, bicycle accessories, bicycle brakes, etc., can solve the problems of reduced battery life, potential safety hazards, waste of braking energy, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
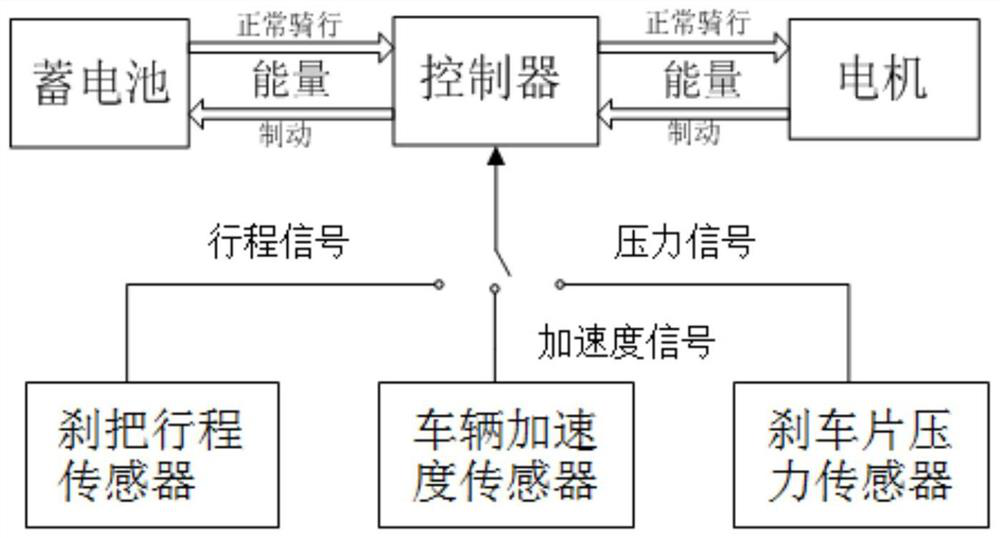
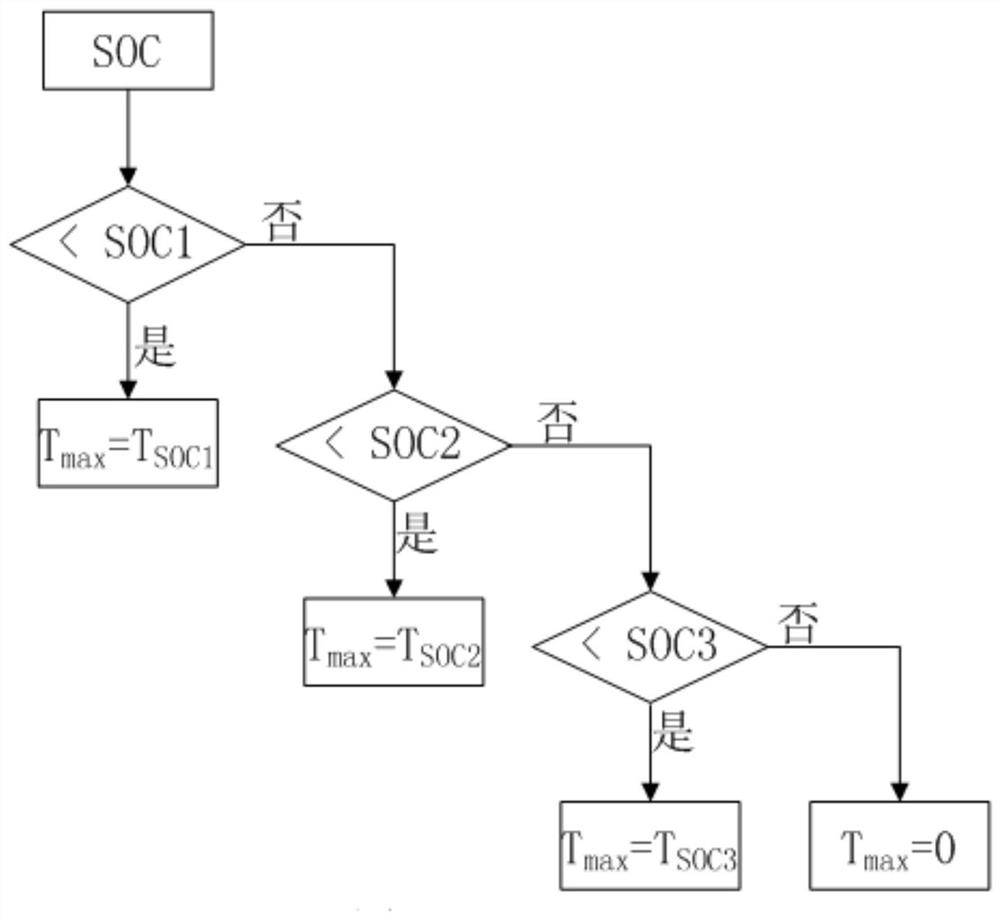
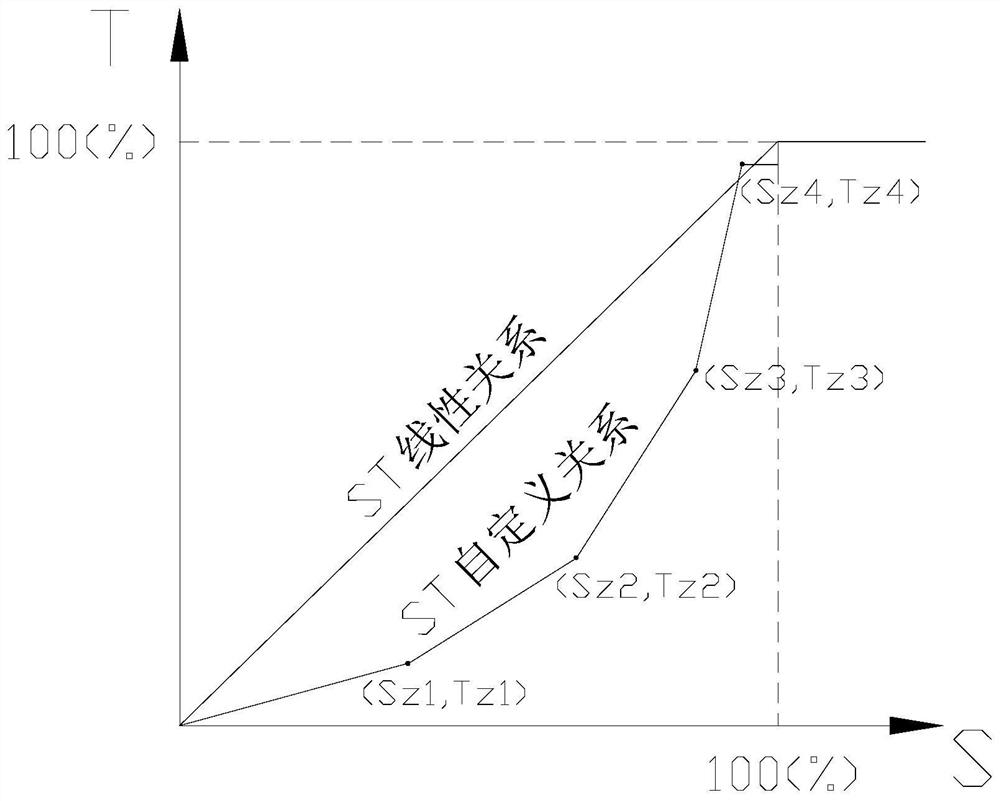
[0022] See attached Figure 1-3 As shown, an electronic brake control method for electric motorcycles of the present invention includes the following steps: step S1, the controller collects the brake signal of the mechanical brake through the signal acquisition unit; step S2, the controller according to the real-time SOC threshold of the battery Determine the maximum electromagnetic braking force Tmax that is allowed to be output by the motor; step S3, the controller constructs a braking signal conversion model according to the maximum electromagnetic braking force Tmax in S2; step S4, the controller converts the braking signal collected by S1 into The target electromagnetic braking force Tt; step S5, the controller controls the motor to output the target electromagnetic braking force Tt.
[0023] In step S1, when the vehicle is mechanically braked, the human hand will press the brake lever. At this time, the brake pad will be under corresponding pressure, and the acceleration...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com