Timing controller for dead-time control
A timing control and control circuit technology, which is applied in the direction of control/regulation systems, conversion equipment and instruments without intermediate conversion to AC, and can solve the problems of reduced benefits of GaN devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
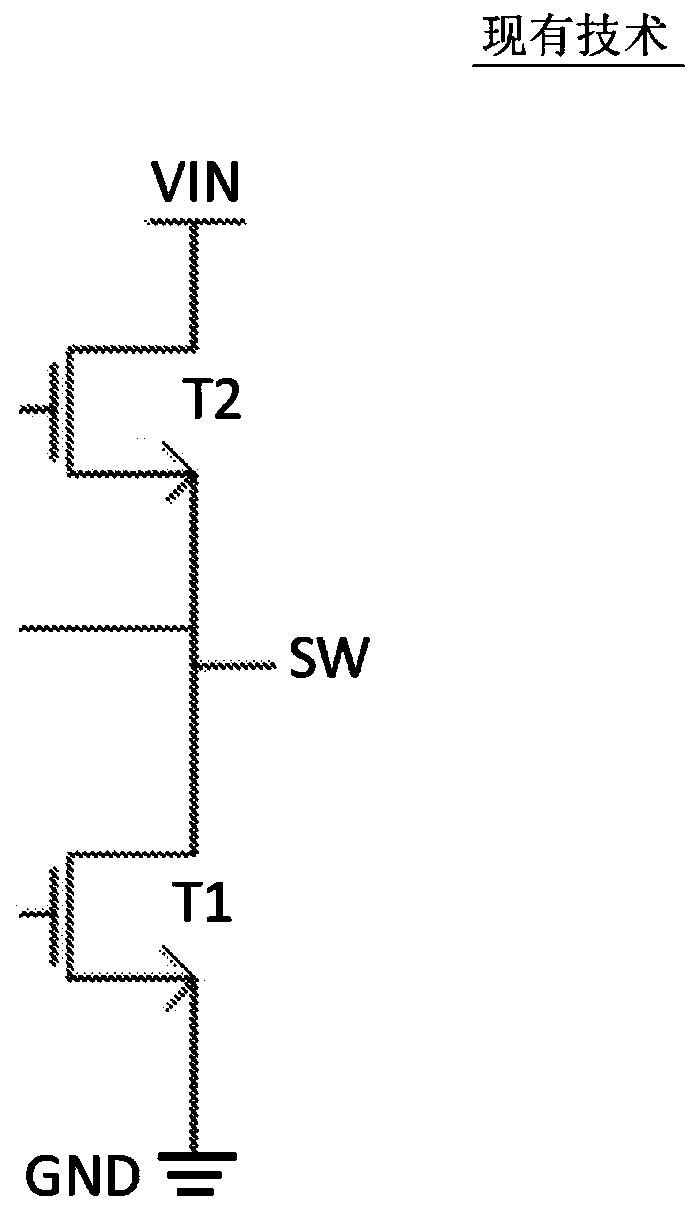
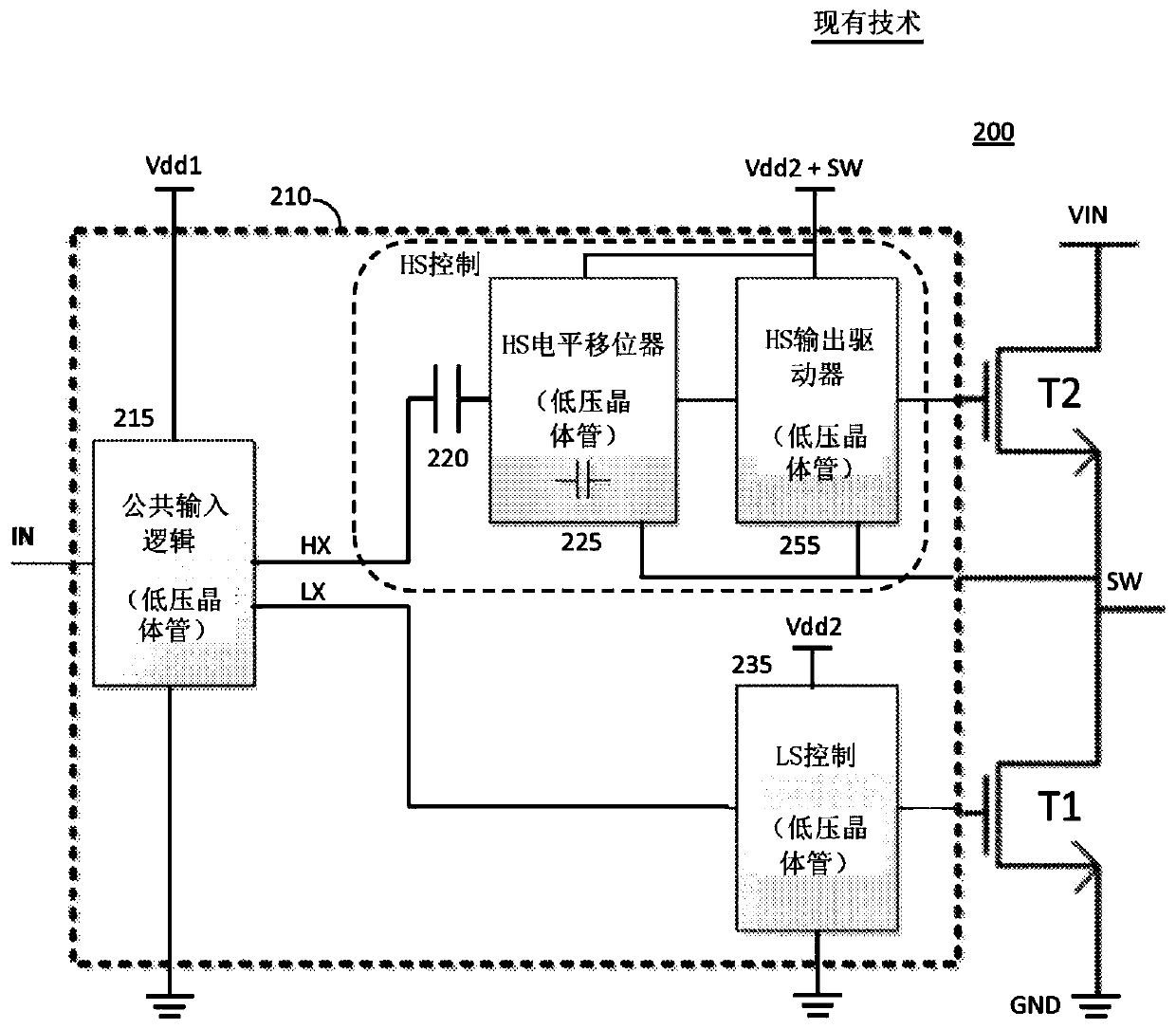
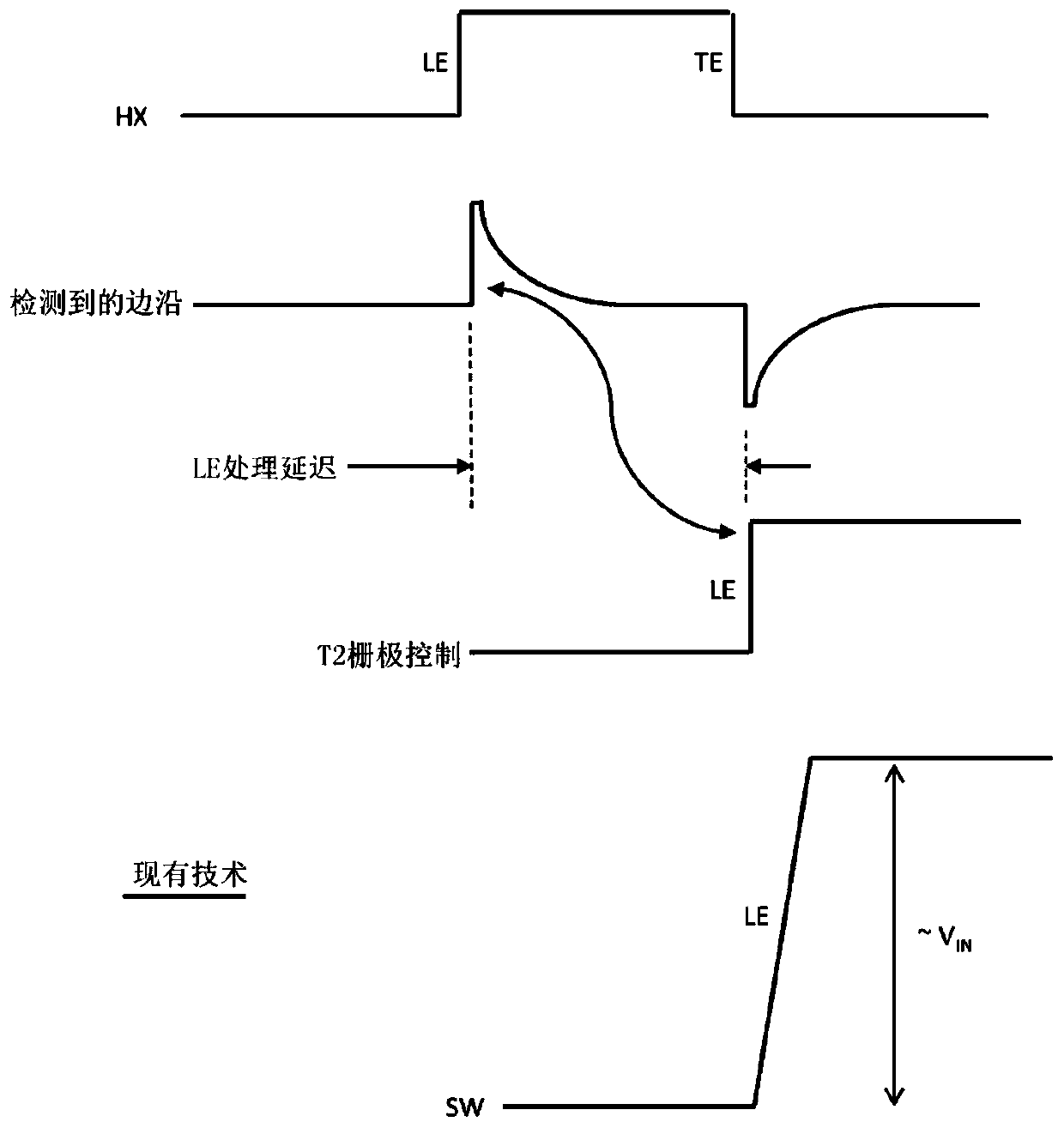
[0043] As used in this disclosure, the figure of merit (FOM) of a switching transistor (e.g., a transistor that can have a conducting ON state and a non-conducting OFF state)—also simply referred to as FOM—refers to the ON (conducting pass) resistance R on and transistor gate charge Q g product of . A lower FOM may indicate higher switching performance of the transistor. Having a low FOM—especially at high withstand voltages—is a unique characteristic of GaN transistors, which can handle up to 100 volts at a FOM that is about one-tenth that of a high-voltage MOSFET.
[0044] As used in this disclosure, a low-voltage device or low-voltage transistor refers to a semiconductor transistor device with a low breakdown voltage that can withstand and block (e.g., in the OFF state) less than 10 volts and more typically significantly less than 10 volts A DC voltage (eg, less than 3.3 volts to 5 volts) (typically applied between the source and drain terminals of a transistor, or betwe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com