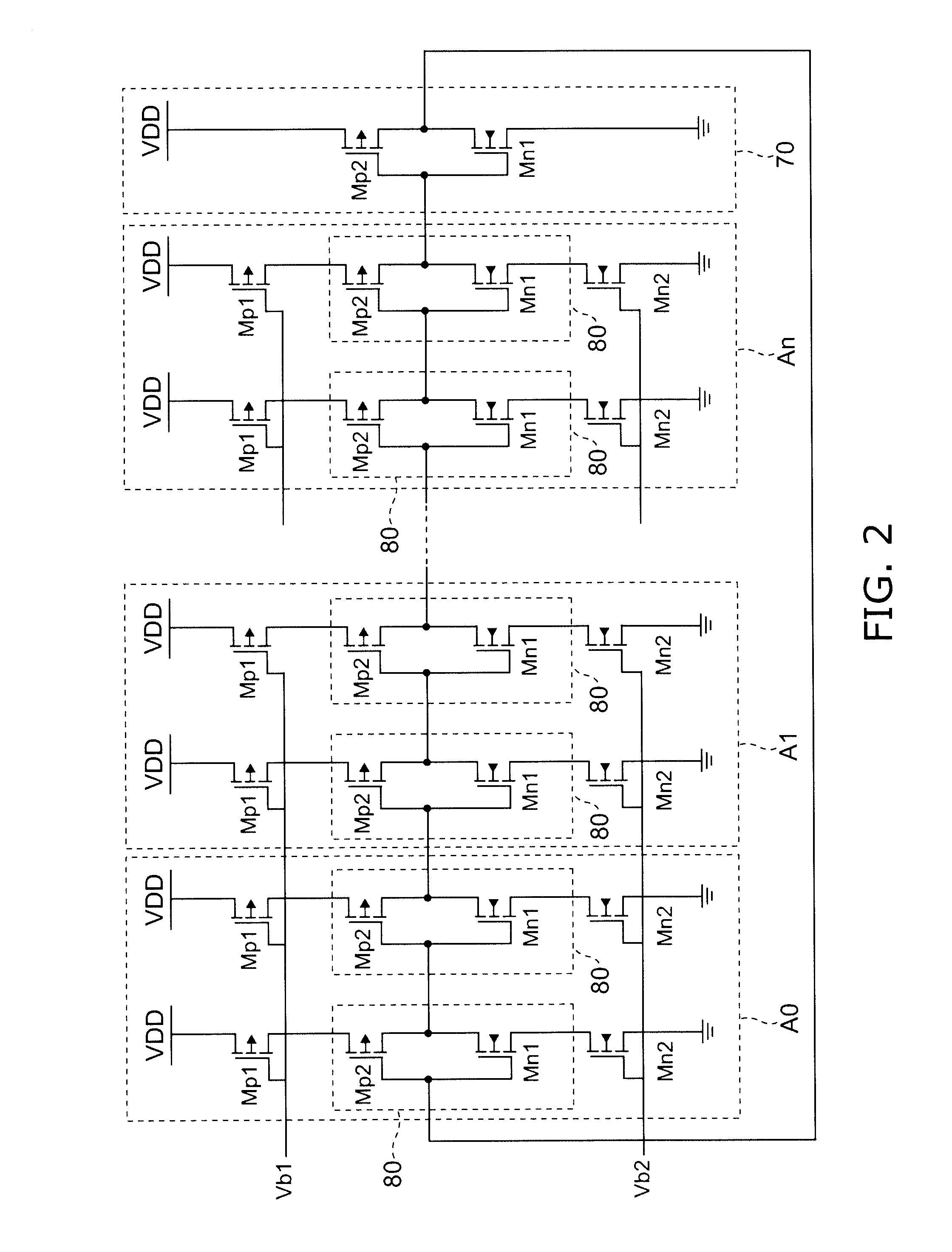
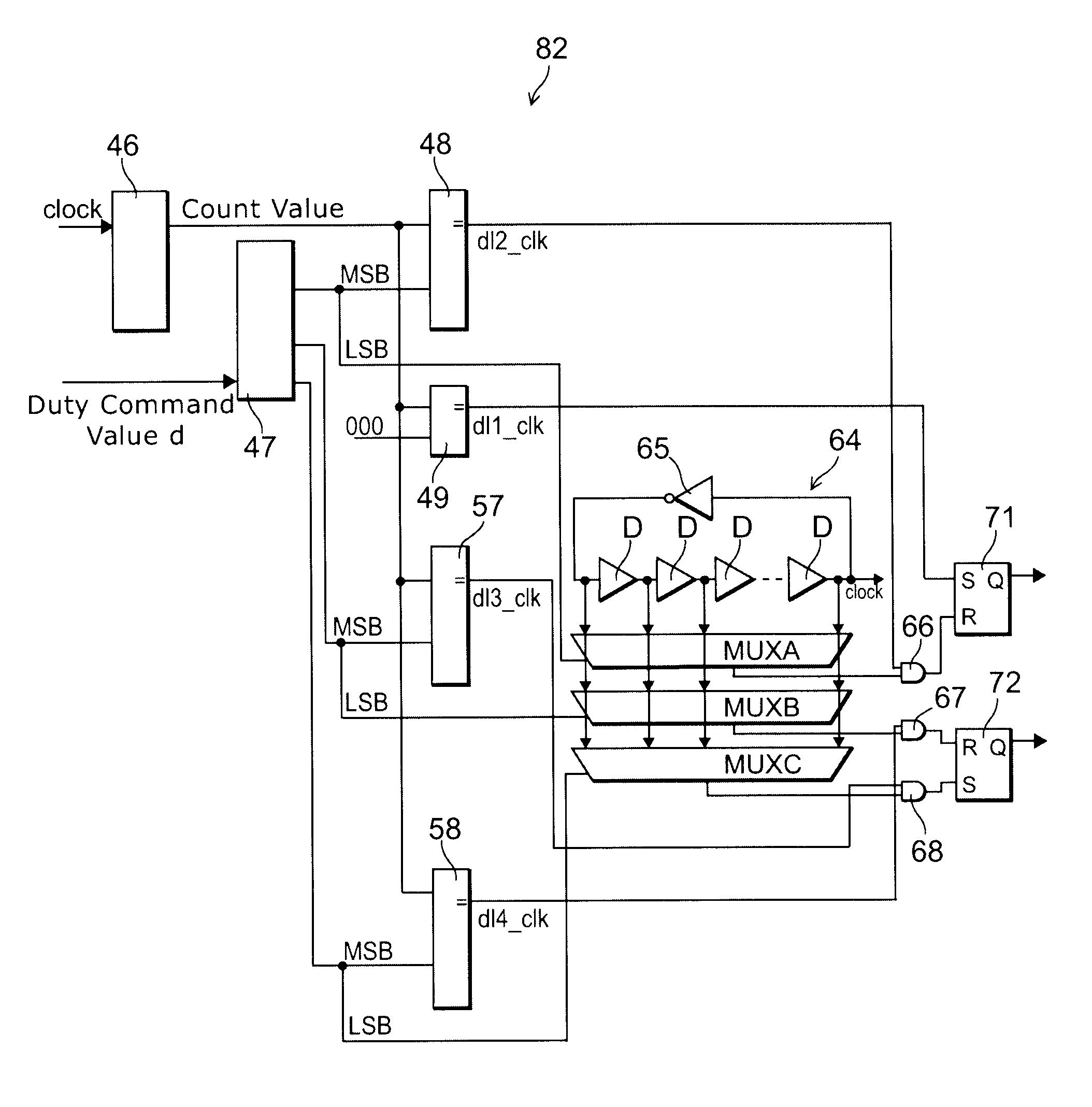
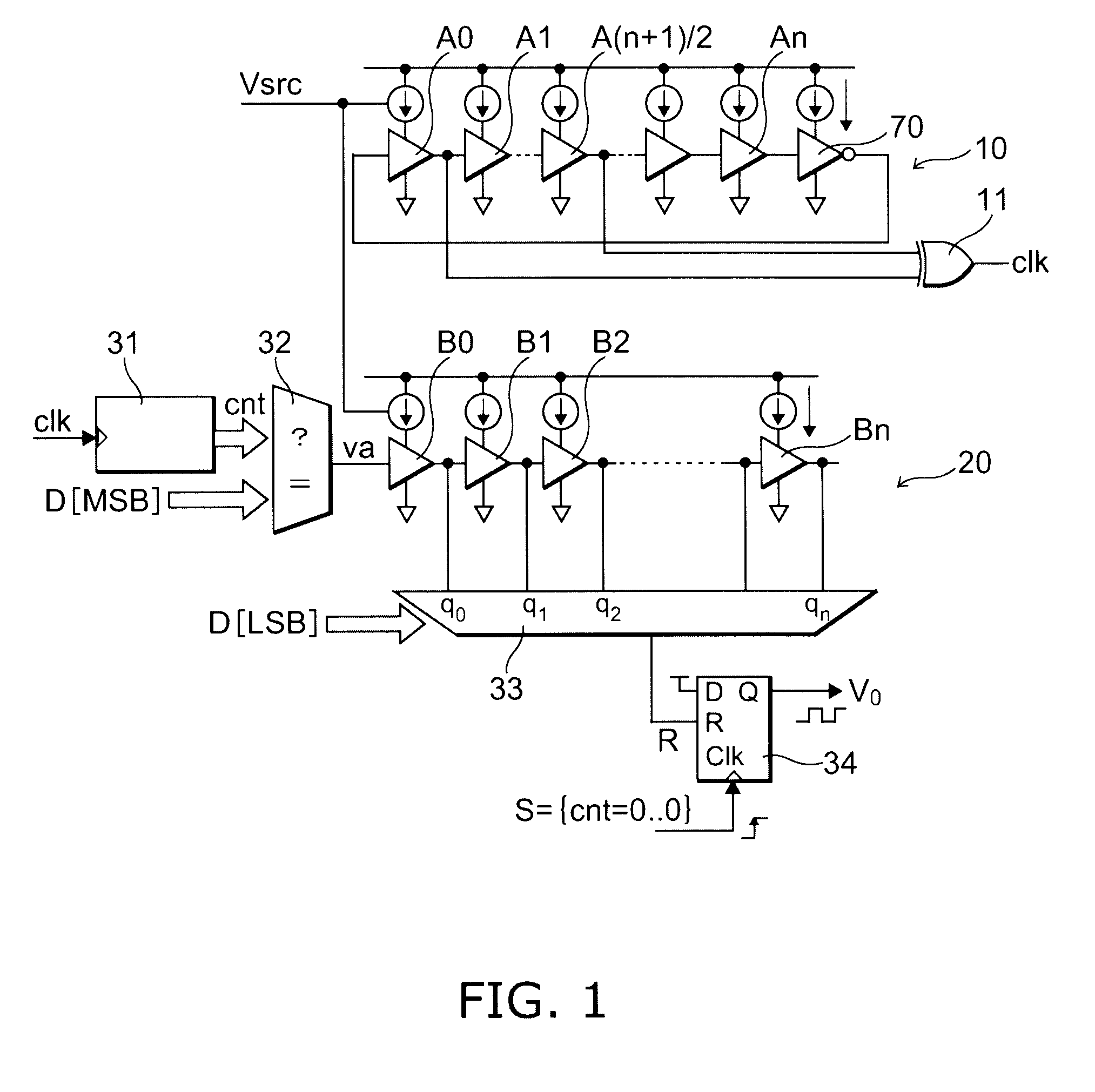
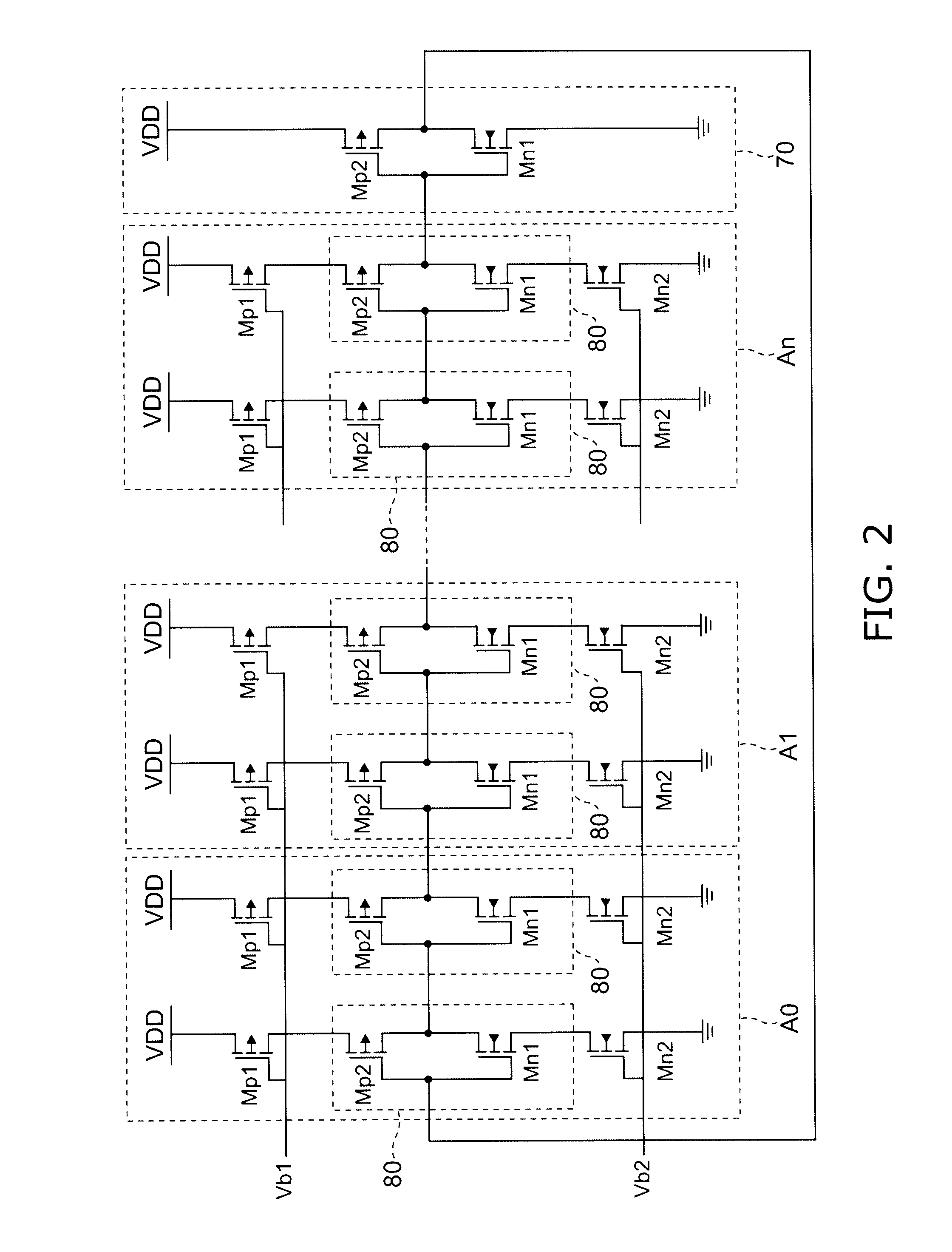
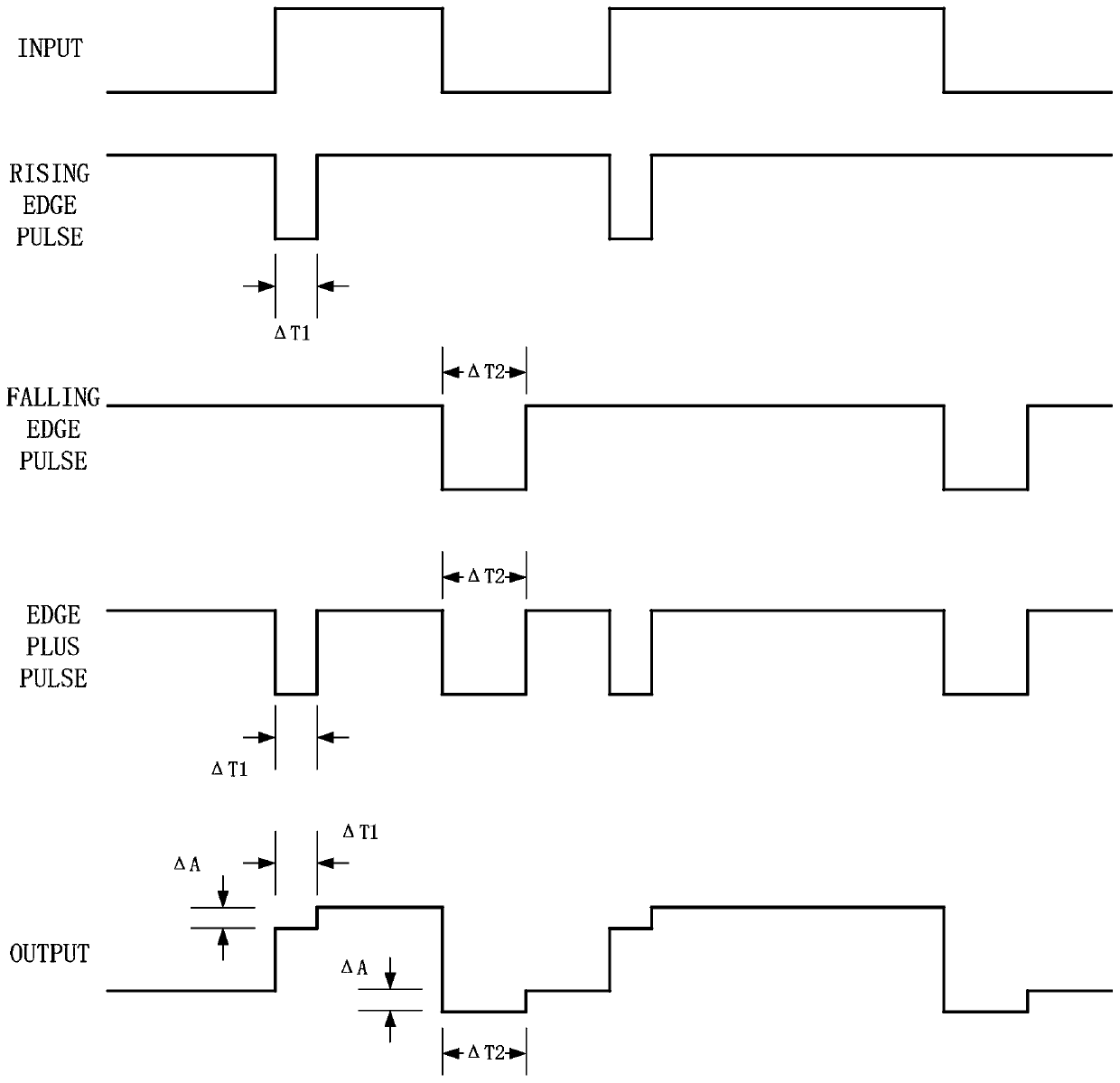
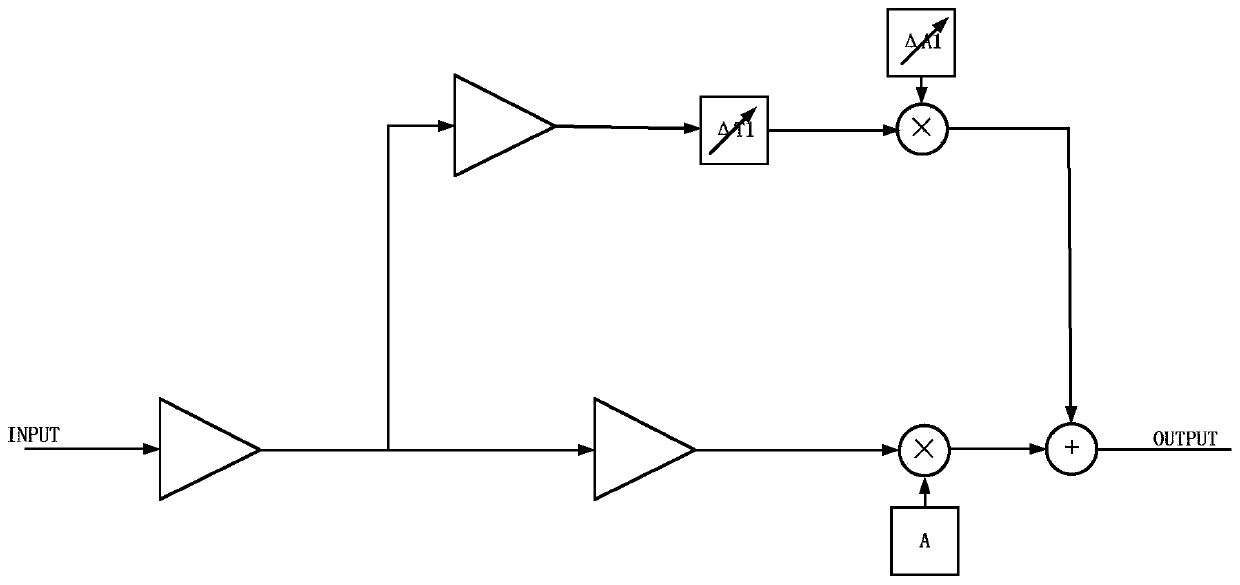
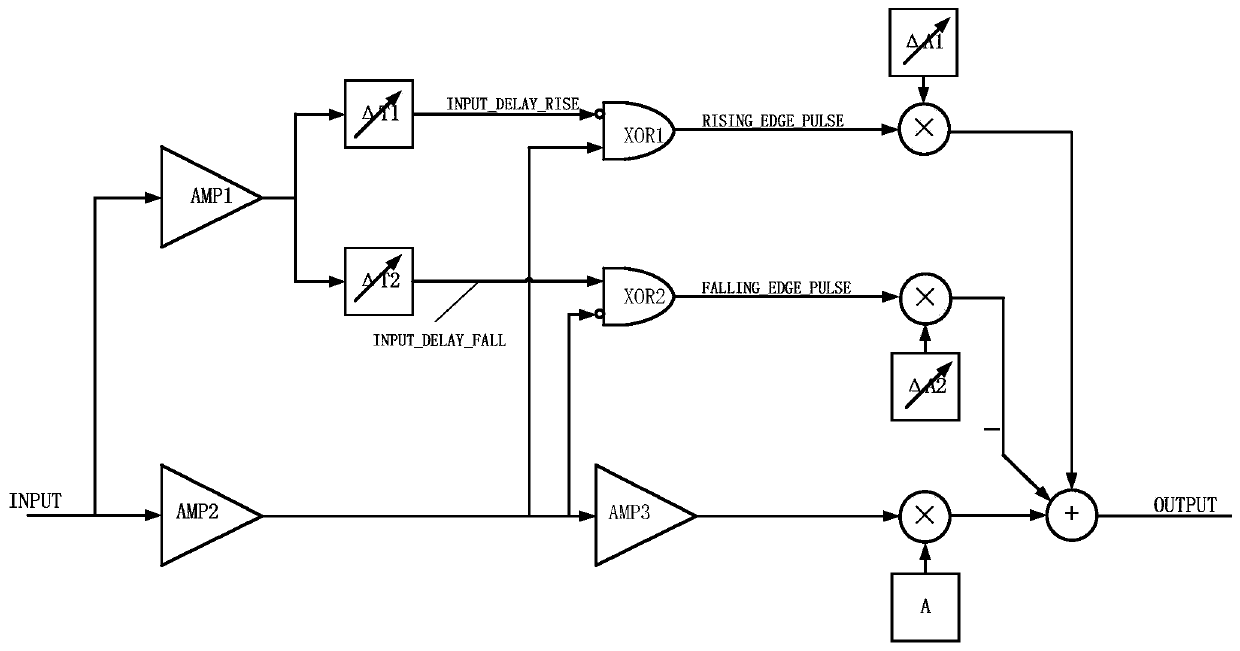
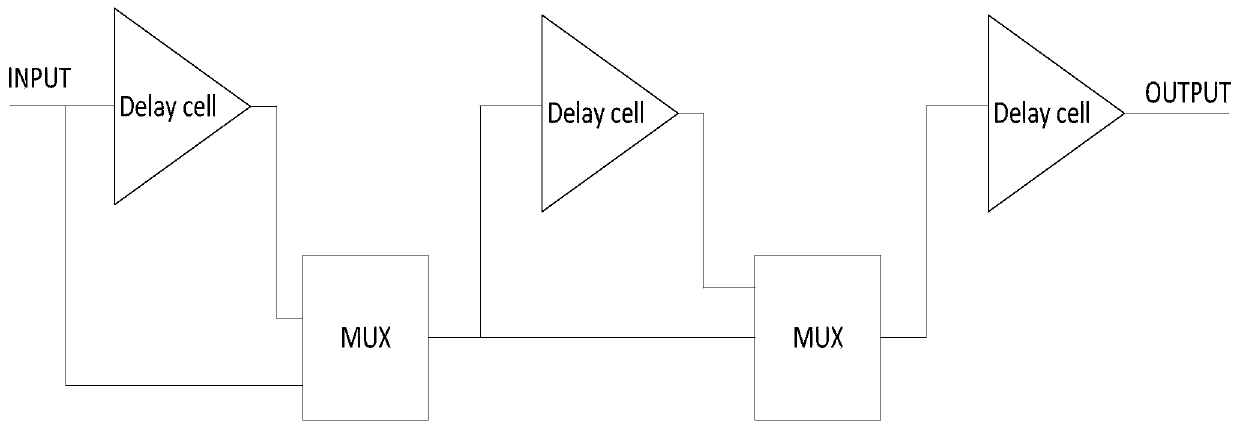
Patents
Literature
53results about "Manipulation with delayed output pulse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
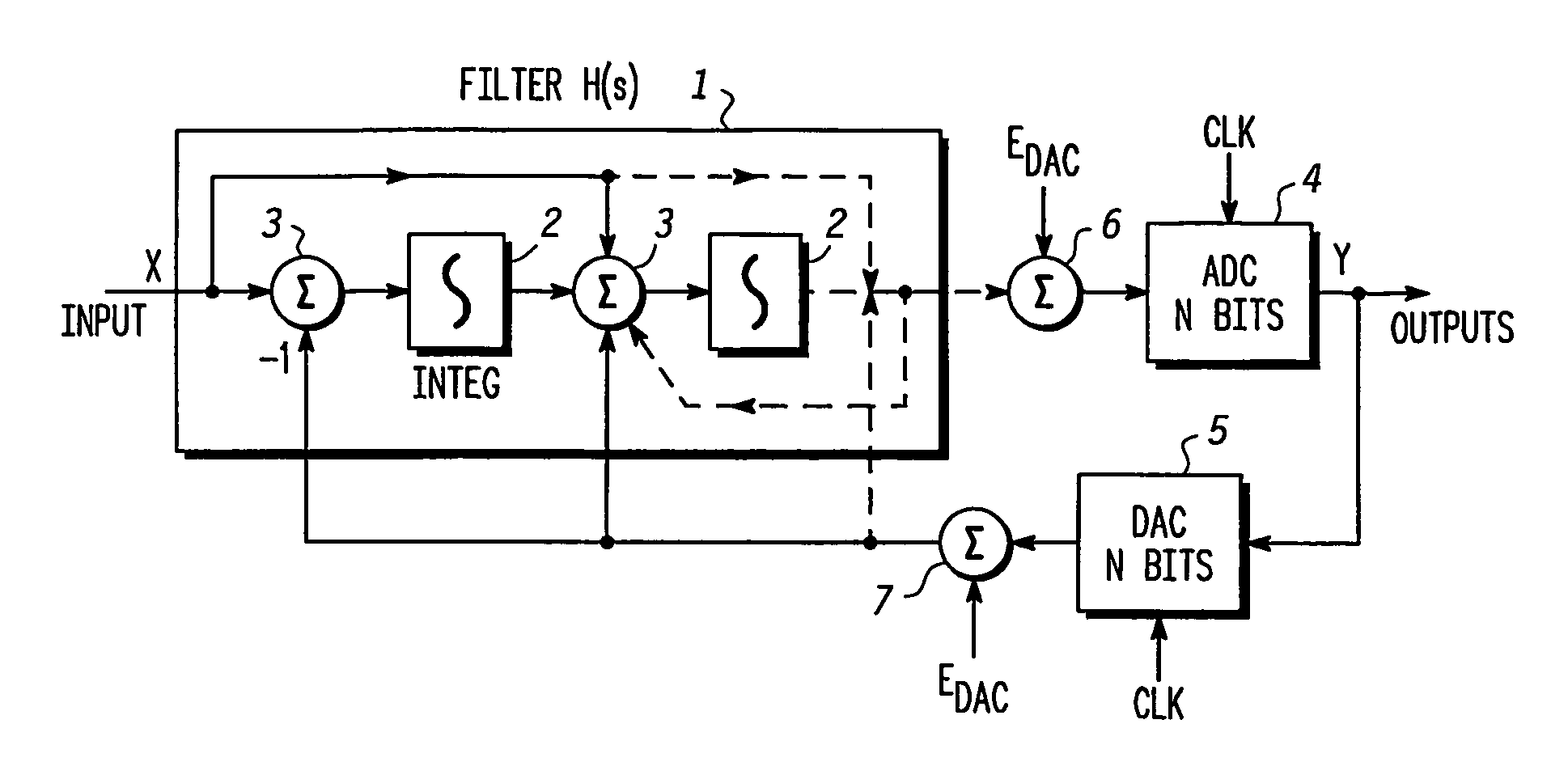
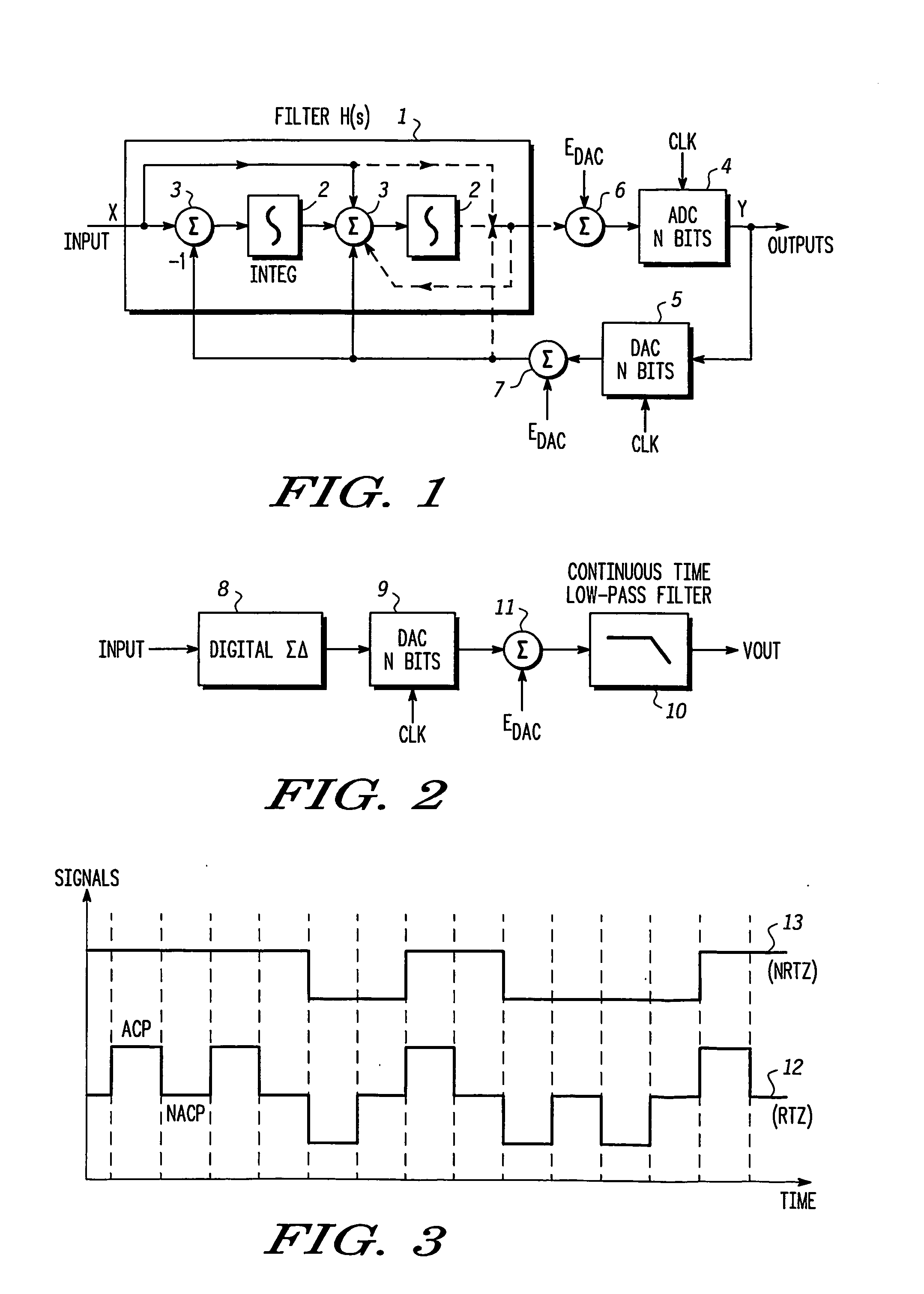
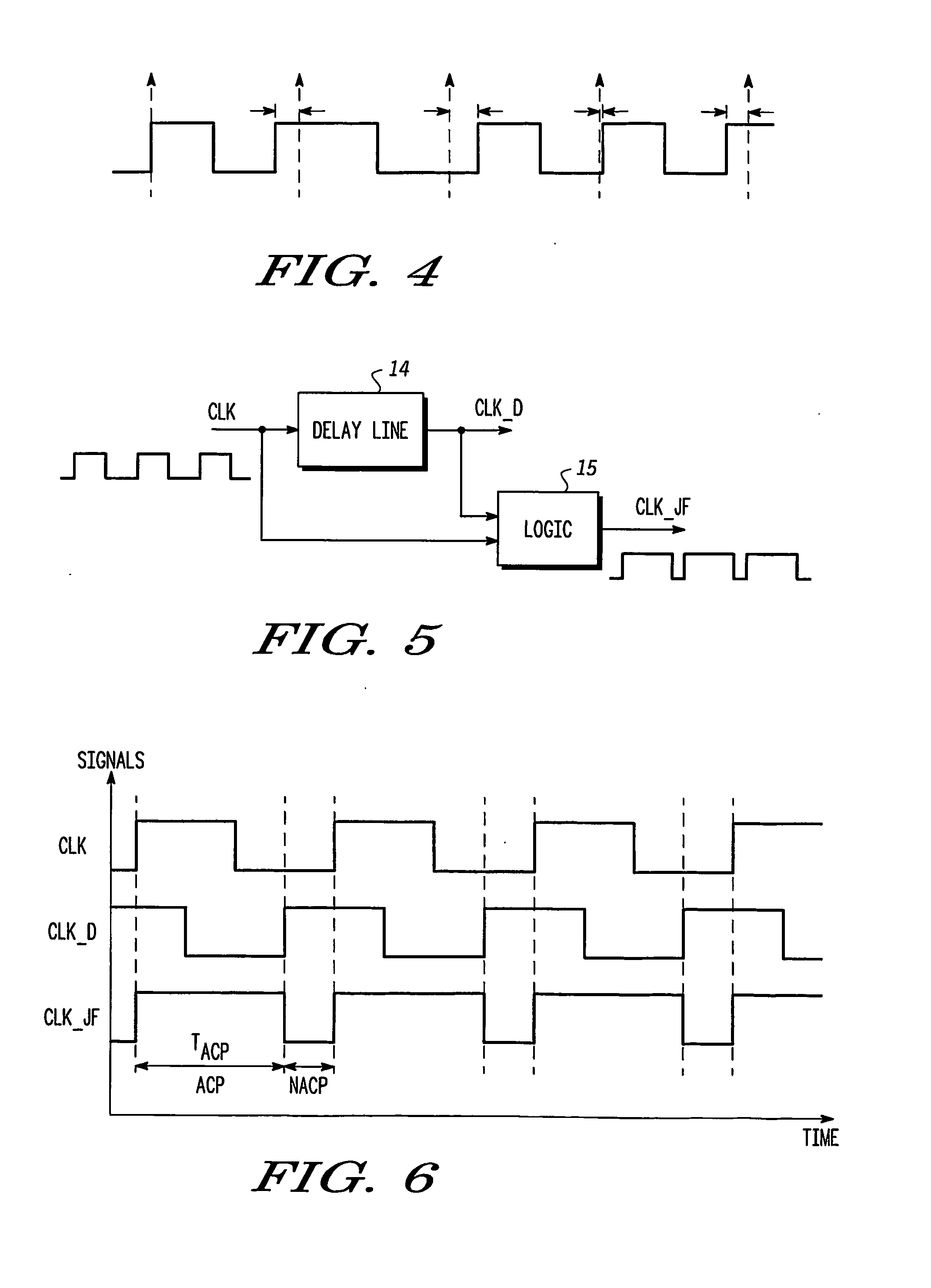
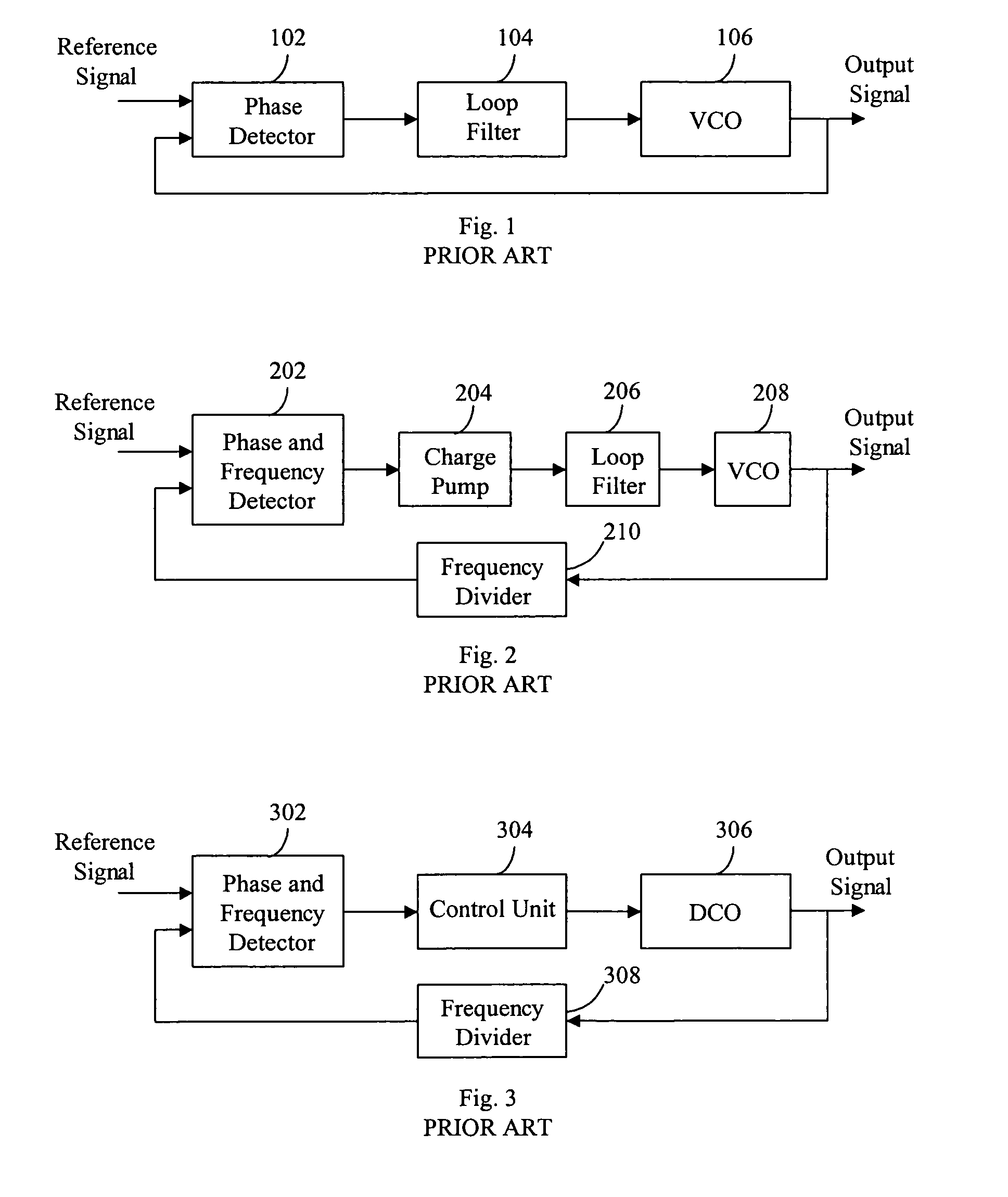
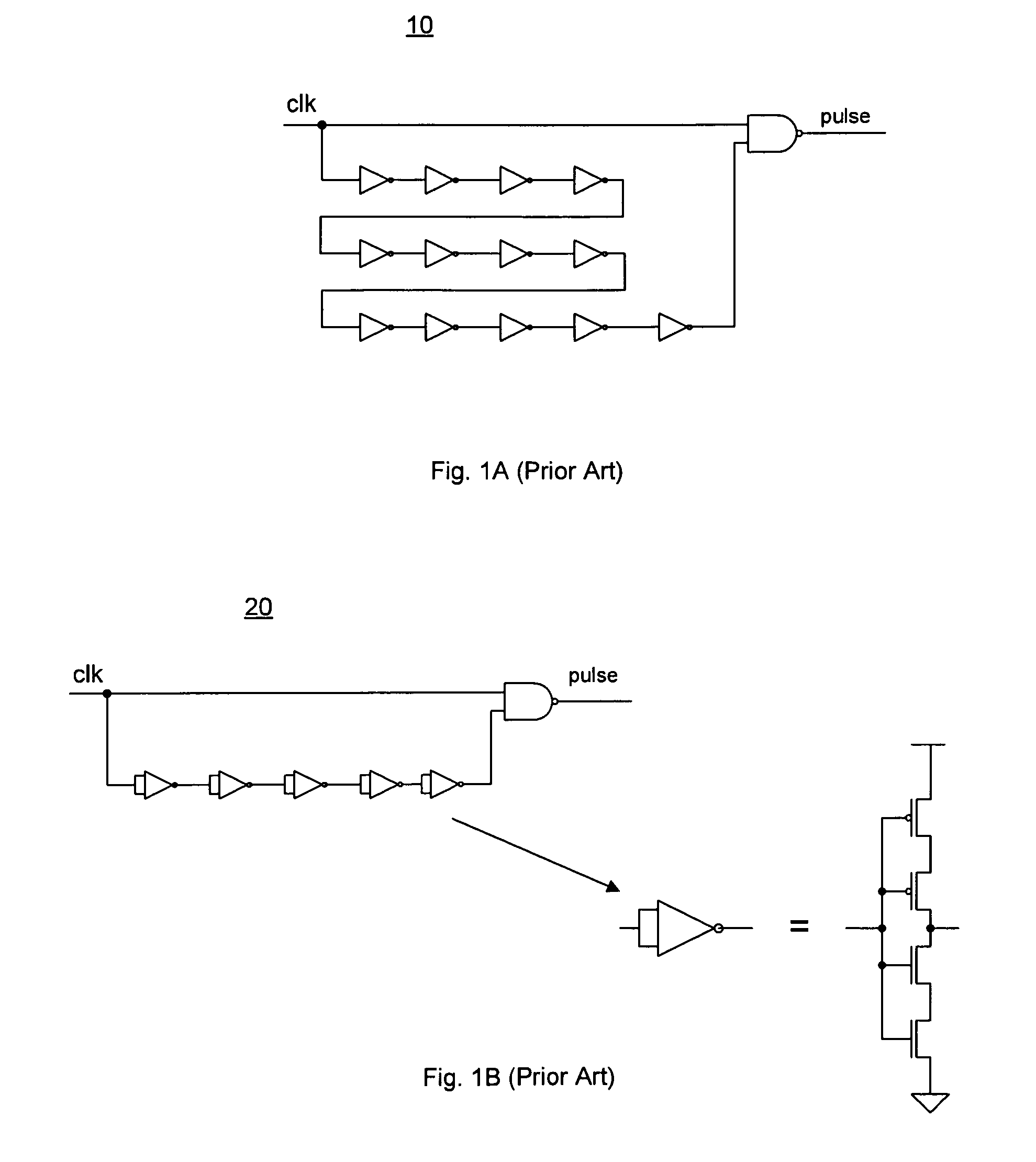
Clock pulse generator apparatus with reduced jitter clock phase
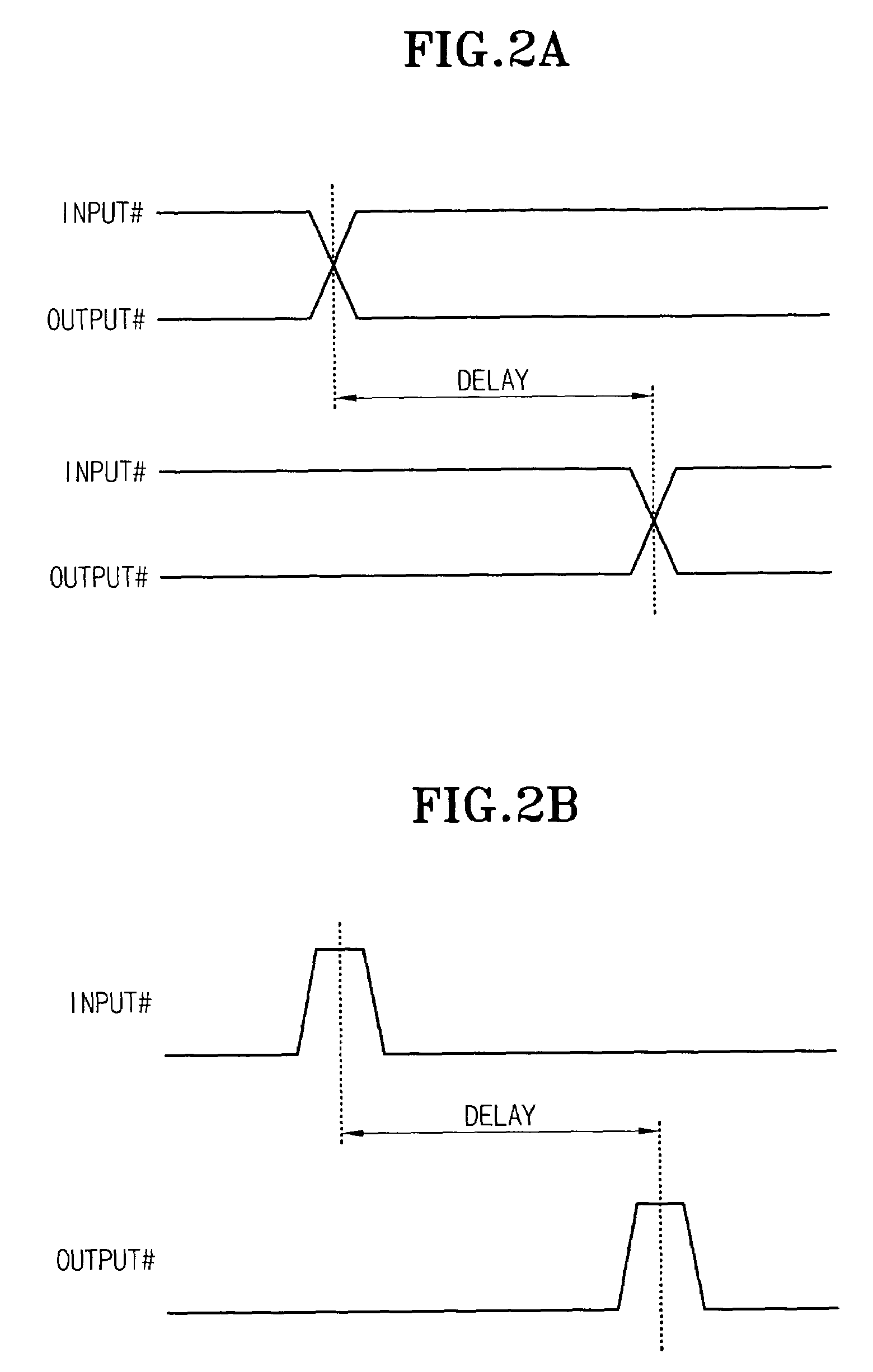
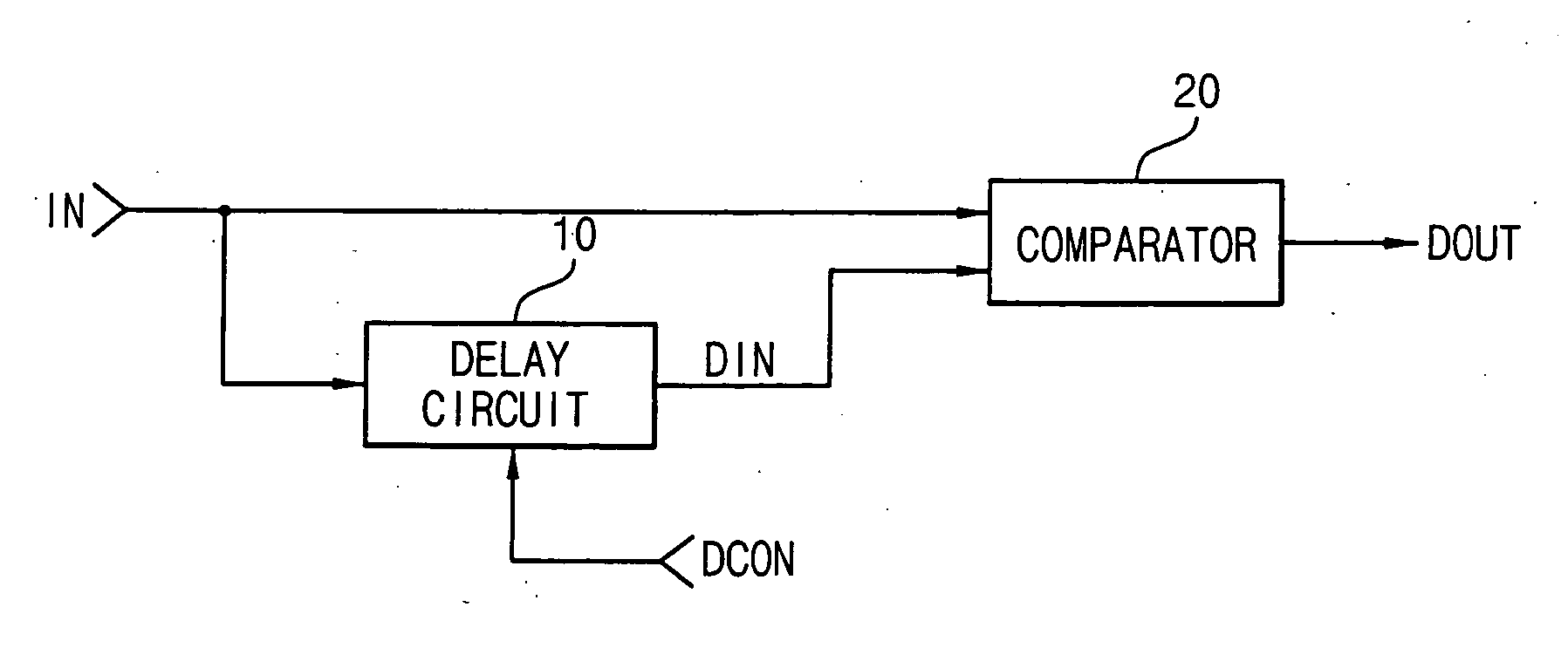
Clock pulse generator apparatus comprising a clock pulse generator for generating a train of primary clock pulses having leading and trailing edges. A delay line produces a train of delayed clock pulses presenting delayed edges whose timing relative to corresponding edges of the primary clock pulses is defined by the delay line. A logic circuit produces a train of combined clock pulses presenting leading and trailing edges defined alternately by one of the delayed edges and the corresponding edge of the primary clock pulse, so that the combined clock pulses comprise active clock phases having widths defined by the delay line; the variability of the widths of the active clock phases is smaller than the variability of the positions of the leading and trailing edges of the primary clock pulses.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
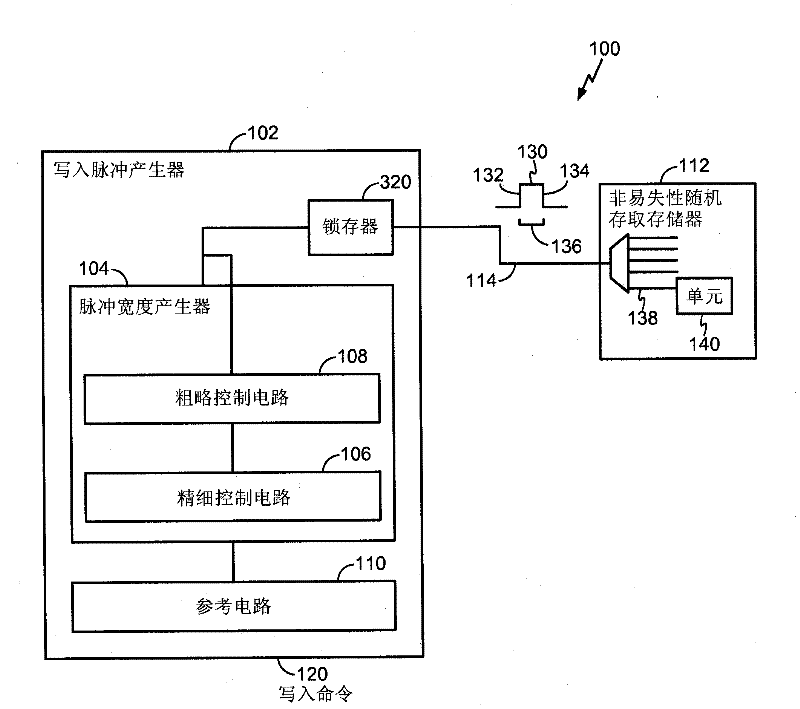
Pulse generation system and method
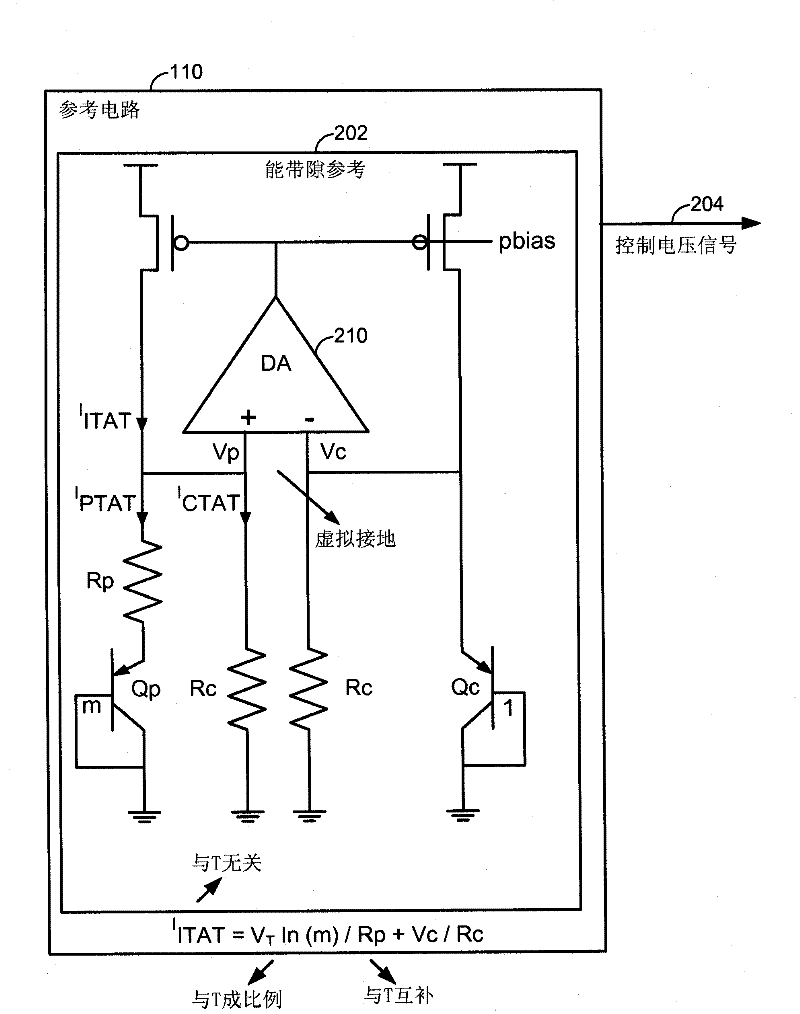
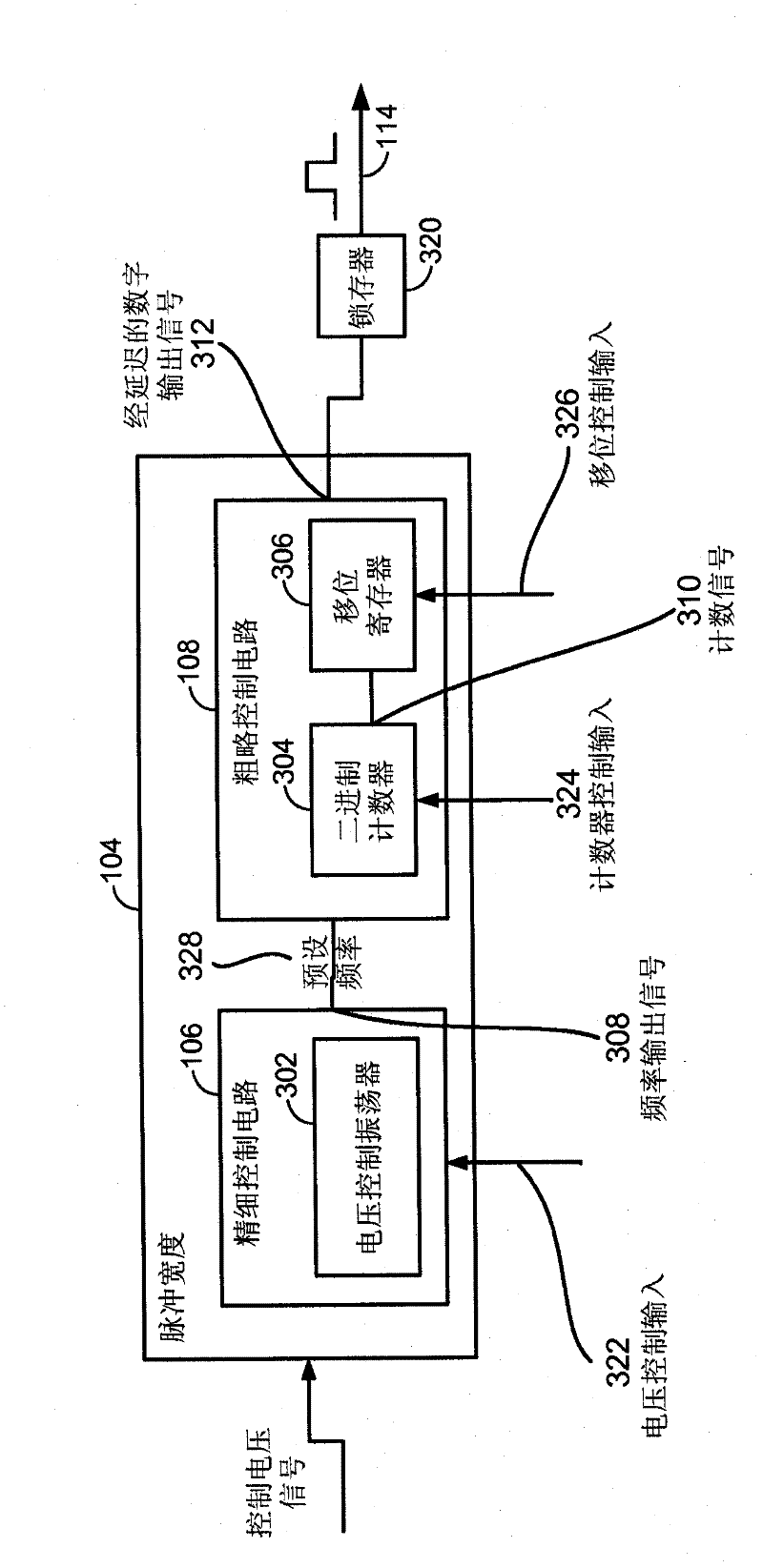
InactiveCN102301423ASave electricityRead-only memoriesDigital storageVoltage referenceElectrical current
In a particular embodiment, an apparatus (102) includes a reference voltage circuit (110) for generating a controlled voltage. The device includes: a frequency circuit (106) configured to generate a frequency output signal (328) having a preset frequency; and a counter (304) to generate a count signal (310) based on the preset frequency. The device also includes a delay circuit (306) coupled to receive the count signal and generate a delayed digital output signal (312); and a latch (320) to generate a pulse (130). The pulse has a first edge (132) in response to a write command and a trailing edge (134) formed in response to the delayed digital output signal. In a particular embodiment, the pulse width of the pulse corresponds to an applied current level that exceeds a critical current enabling data to be written to an element of the memory, but does not exceed a predetermined threshold.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090179681A1Short timeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVoltage regulationVoltage control
A semiconductor device includes: a voltage-control-type clock generation circuit having a plurality of stages of first delay elements and whose oscillation frequency is controlled according to a control voltage applied to the first delay elements; a delay circuit having a plurality of stages of second delay elements connected serially; and a selection circuit selecting one from pulse signals output by the plurality of stages of respective second delay elements. The first delay elements and the second delay elements have a same structure formed on a same semiconductor substrate, and a delay amount of the second delay elements is adjusted according to the control voltage.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS7893744B2Electric signal transmission systemsSolid-state devicesVoltage regulationEngineering
A semiconductor device includes: a voltage-control-type clock generation circuit having a plurality of stages of first delay elements and whose oscillation frequency is controlled according to a control voltage applied to the first delay elements; a delay circuit having a plurality of stages of second delay elements connected serially; and a selection circuit selecting one from pulse signals output by the plurality of stages of respective second delay elements. The first delay elements and the second delay elements have a same structure formed on a same semiconductor substrate, and a delay amount of the second delay elements is adjusted according to the control voltage.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
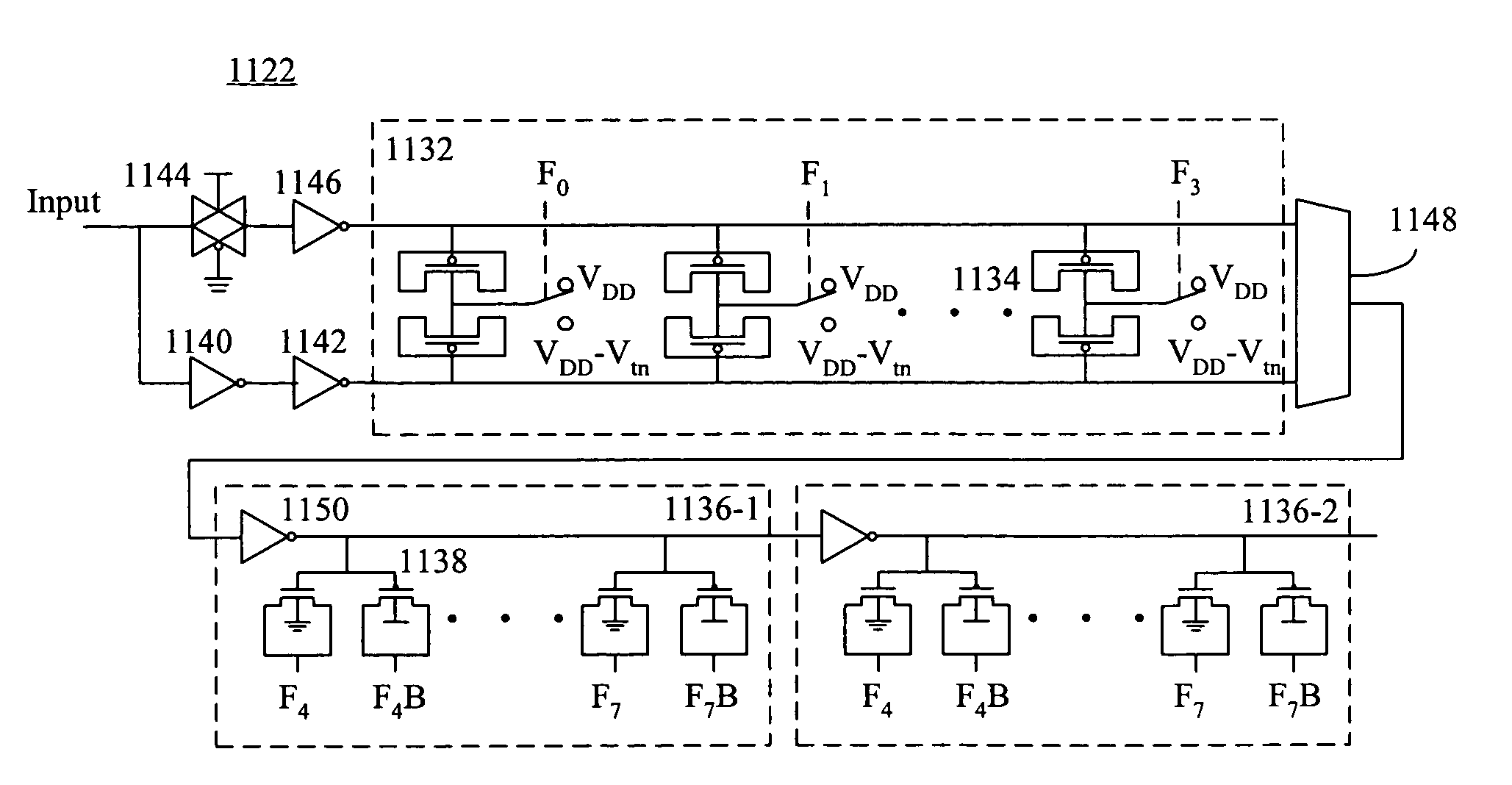
High-resolution varactors, single-edge triggered digitally controlled oscillators, and all-digital phase-locked loops using the same
A digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) includes a pulse generator for generating a pulse signal upon an edge of a trigger signal, and at least one delay circuit coupled to delay the pulse signal generated by the pulse generator. The pulse generator is coupled to receive one of the delayed pulse signal from the at least one delay circuit and an enable signal as the trigger signal. A digitally controlled varactor (DCV) includes a transistor having a gate, a source, a drain, and a substrate, wherein at least one of the gate, the source, the drain, and the substrate is coupled to receive one of two or more voltages, wherein at least one of the two or more voltages is not a power supply voltage or ground.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Apparatus and method for generating pulses
An apparatus for generating pulses includes: (a) A delay unit having an input delay locus for receiving a delay unit input signal and an output delay locus for presenting an output delay signal. The delay unit output signal is delayed by a delay interval with respect to the input delay signal. (B) A latch coupled with the delay unit to selectively keep the delay unit input signal at at least one predetermined signal level.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
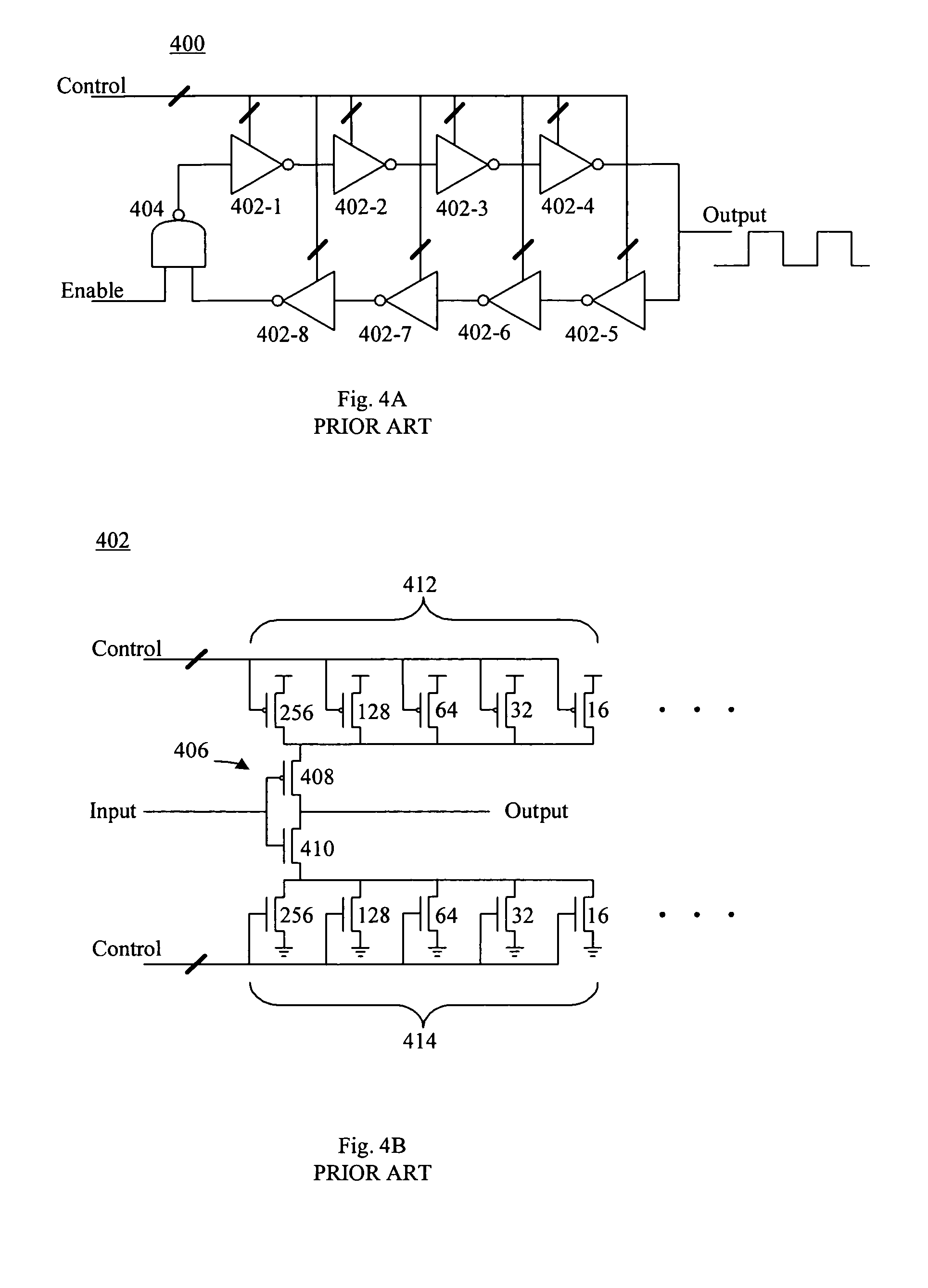
Dual edge programmable delay unit
InactiveUS6914467B2Fast setting timeShort timeElectrical measurement instrument detailsInstant pulse delivery arrangementsCapacitanceFall time
A method and device program a dual edge programmable delay unit, that responds to an input signal with a rise time and a fall time, includes a buffer which receives the input signal and provides an output signal with programmed variable delays between the rise and fall times of the output signal. Programmable control sources (PCS) provide separate control inputs to a buffer. The FTPCS charges a capacitor in the buffer when the input signal changes from high to low to adjust time delay before the fall of the buffer output signal. The RTPCS discharges the capacitor in the buffer when the input signal changes from low to high to adjust time delay before the rise of the buffer output signal.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Delay circuit and method for driving the same
ActiveUS20110291727A1Guaranteed uptimePulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A delay circuit includes a pulse generation unit configured to generate a pulse signal, which is activated in response to an input signal and has a pulse width corresponding to delay information, and an output unit configured to activate a final output signal in response to a deactivation of the pulse signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Apparatus and method for extracting a maximum pulse width of a pulse width limiter
InactiveUS7358785B2Reduce the amount requiredContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationElectric pulse generatorEngineeringDelay unit
An apparatus and method for extracting a maximum pulse width of a pulse width limiter are provided. The apparatus and method of the illustrative embodiments performs such extraction using a circuit that is configured to eliminate the majority of the delay cells utilized in the circuit arrangement described in commonly assigned and co-pending U.S. patent application Ser. No. 11 / 109,090 (hereafter referred to as the '090 application). The elimination of these delay cells is made possible in one illustrative embodiment by replacing an OR gate in the circuit configuration of the '090 application with an edge triggered re-settable latch. The replacement of the OR gate with the edge triggered re-settable latch reduces the amount of chip area used in addition to the power consumption of the circuit.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
High-resolution varactors, single-edge triggered digitally controlled oscillators, and all-digital phase-locked loops using the same
A digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) includes a pulse generator for generating a pulse signal upon an edge of a trigger signal, and at least one delay circuit coupled to delay the pulse signal generated by the pulse generator. The pulse generator is coupled to receive one of the delayed pulse signal from the at least one delay circuit and an enable signal as the trigger signal. A digitally controlled varactor (DCV) includes a transistor having a gate, a source, a drain, and a substrate, wherein at least one of the gate, the source, the drain, and the substrate is coupled to receive one of two or more voltages, wherein at least one of the two or more voltages is not a power supply voltage or ground.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
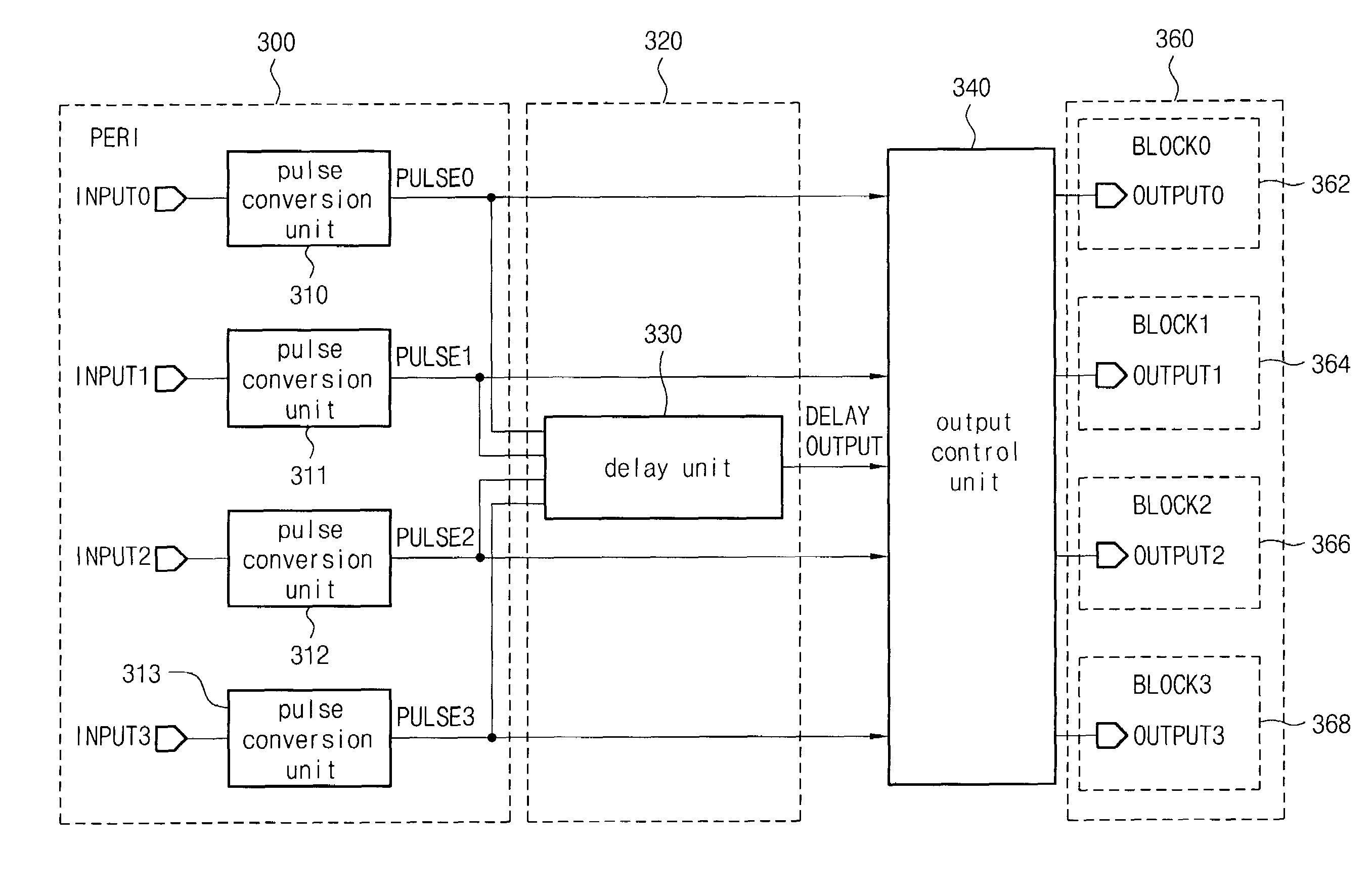
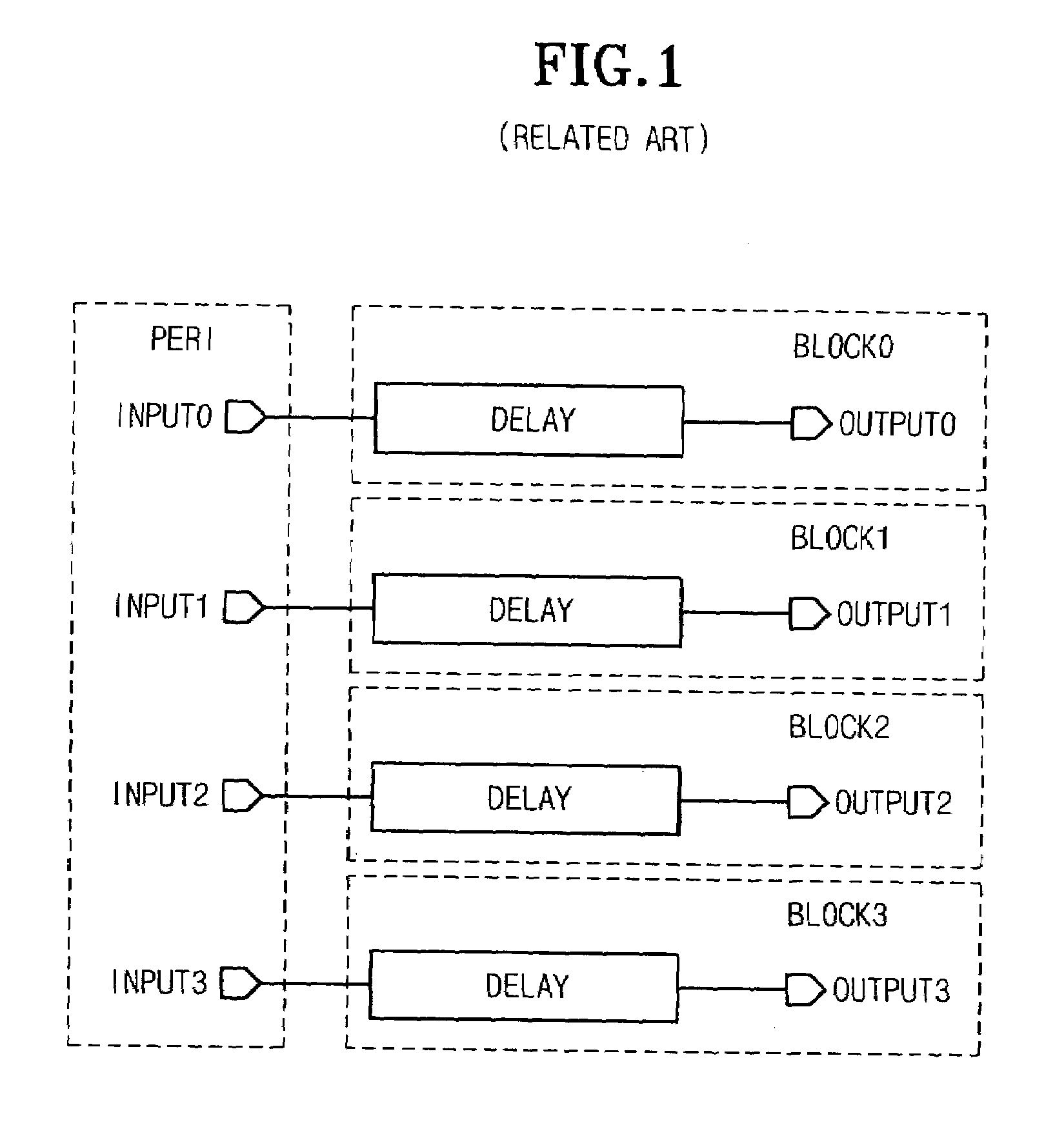
Shared delay circuit of a semiconductor device
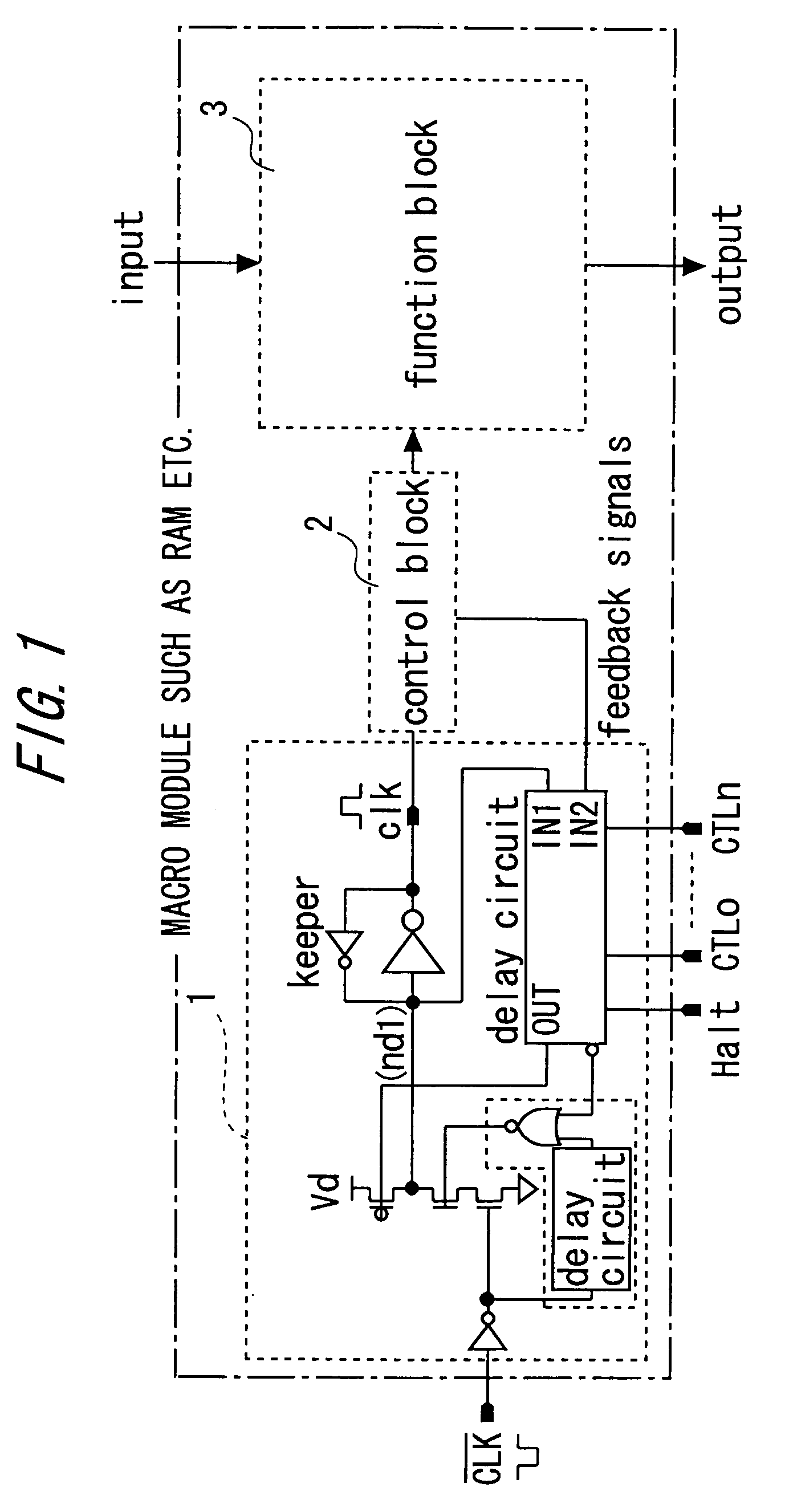
A shared delay circuit of a semiconductor device can share a plurality of delay elements having the same function by integrating the delay elements. The shared delay circuit includes an input signal conversion unit for converting a plurality of input signals into a plurality of pulse signals, a delay unit for delaying the pulse signals outputted from the input signal conversion unit for a predetermined time to output the delayed pulse signal, and a switch and output control unit for receiving the pulse signals outputted from the input signal conversion unit and the delayed pulse signals delayed for the predetermined time through the delay unit, and outputting the delayed pulse signals in the same form as the input signals inputted to the input signal conversion unit. According to the shared delay circuit, the repeated arrangement of circuits having the same function can be avoided by sharing the delay circuits in the semiconductor device and thus the installation area of the delay circuits can be reduced.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Circuit and method of controlling a delay of a semiconductor device
ActiveUS20060158238A1Multiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse automatic controlDevice materialCircuit delay
A delay control circuit capable of controlling a delay time is disclosed. The delay control circuit includes a delay detecting circuit, a first pulse generator, a counter control circuit and a counter. The delay detecting circuit delays an input signal by a first time in response to an output signal and compares the input signal and the delayed input signal to generate a first signal. The first pulse generator generates a second signal in response to the input signal. The counter control circuit generates a count-up signal and a count-down signal in response to the first signal and the second signal. The counter generates the output signal in response to the count-up signal and the count-down signal to divide the first time by 2n intervals, wherein n is a positive integer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
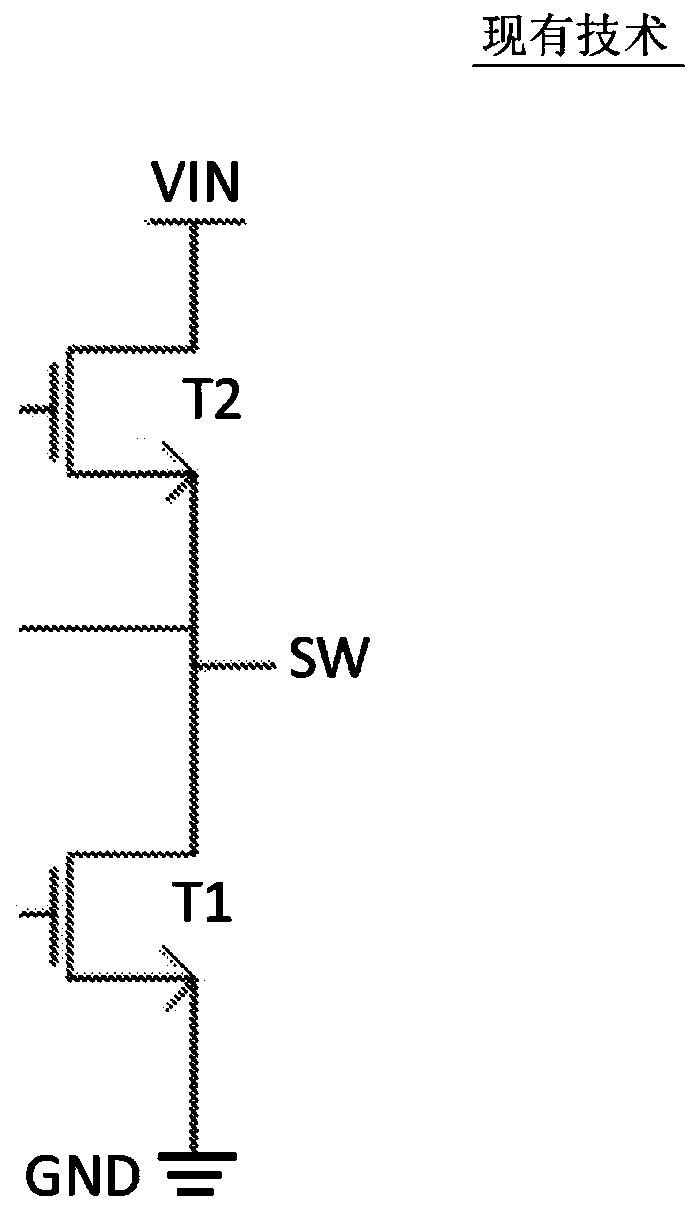
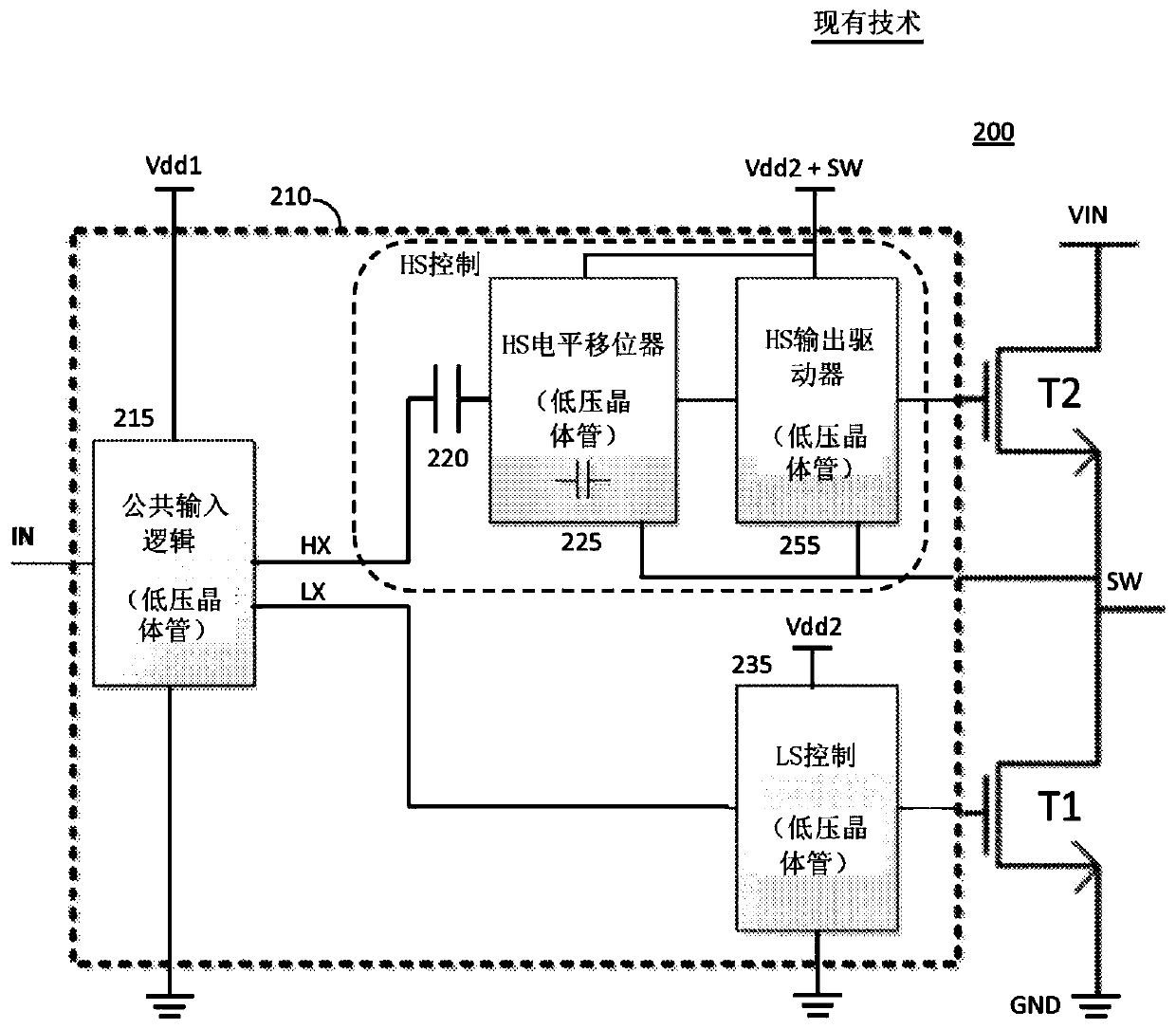
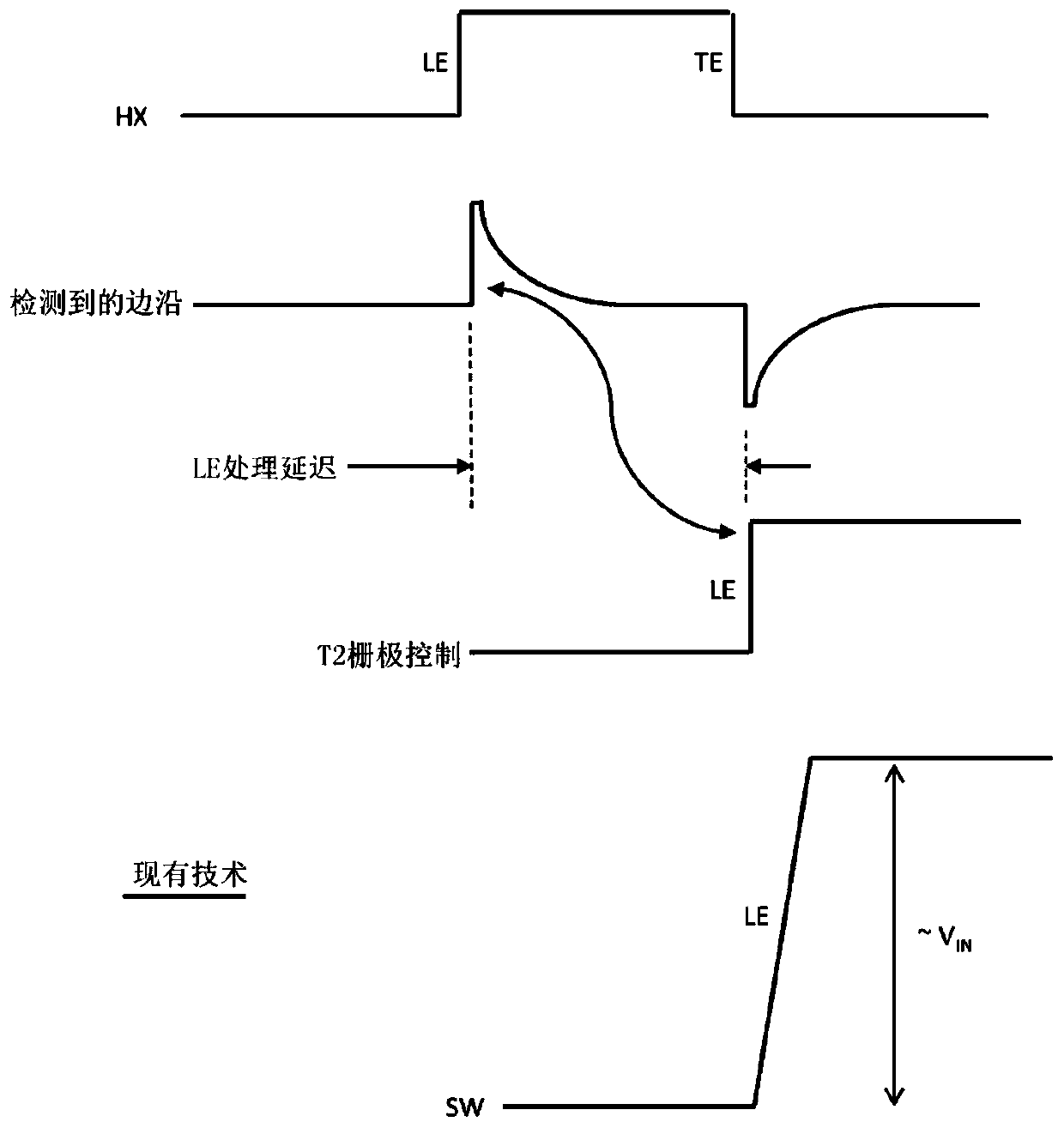
Timing controller for dead-time control
Systems, methods, and apparatus for use in biasing and driving high voltage semiconductor devices (T1, T2) using only low voltage transistors (inside 410) are described. The apparatus (410) and methodare adapted to control multiple high voltage semiconductor devices (T1, T2) to enable high voltage power control, such as power amplifiers, power management and conversion (e.g. DC / DC) and other applications wherein a first voltage (Vin) is large compared to the maximum voltage handling of the low voltage control transistors (Vdd1, Vdd2). According to an aspect, timing control of edges (fig. 4: 215, fig.14a: 1410 ) of a control signal (IN) to the high voltage semiconductor devices (T1, T2) is provided by a basic edge delay circuit (fig. 4: inside 215, fig. 14a: 1410) that includes a transistor, a current source and a capacitor. An inverter can be selectively coupled, via a switch, to an input and / or an output of the basic edge delay circuit to allow for timing control of a rising edge ora falling edge of the control signal.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Multi-dimensional signal eye pattern compensation circuit
PendingCN110896327AQuality improvementGood symmetryPulse shapingElectromagnetic transmittersSignal onSignal Pathways
The invention provides a multi-dimensional signal eye pattern compensation circuit, and the circuit is characterized in that a rising edge adjustment path and a falling edge adjustment path are respectively provided with detection circuits which are used for extracting a rising edge / falling edge pulse signal with a certain width in an input signal; a rising edge / falling edge pre-emphasis compensation signal or a rising edge / falling edge de-emphasis compensation signal is generated after the rising edge / falling edge pulse signal with a certain width passes through the MUX selector; and the rising edge / falling edge pre-emphasis compensation signal or the rising edge / falling edge de-emphasis compensation signal is weighted with the input signal on the high-speed main signal path, and the amplitudes of the rising edge and the falling edge of the input signal at the corresponding rising edge / falling edge pulse signal are adjusted. According to the multi-dimensional signal eye pattern compensation circuit, the phases, the amplitudes and the pre-emphasis directions of the rising edge and the falling edge of the eye pattern can be adjusted respectively, four-dimensional eye pattern compensation is presented, and the opening degree and the symmetry of the eye pattern are improved.
Owner:XIAMEN UX HIGH SPEED IC
High-speed rising edge/falling edge adjustable circuit with programmable amplitude and phase
PendingCN110896304AEasy to openImprove matchPulse shapingElectromagnetic transmittersHemt circuitsControl theory
The invention provides a high-speed rising edge / falling edge adjustable circuit with programmable amplitude and phase. A rising edge adjusting circuit and a falling edge adjusting circuit are respectively provided with a delay phase adjusting module for controlling phase positions of a rising edge and a falling edge to be subjected to amplitude adjustment; the phase positions of the rising edge and the falling edge subjected to amplitude adjustment are subjected to logical exclusive-OR operation with the input signal through a high-speed exclusive-OR module to generate a rising edge adjustmentphase signal and a falling edge adjustment phase signal; the rising edge adjusting circuit and the falling edge adjusting circuit are respectively provided with a phase amplitude adjusting module, and the rising edge adjusting phase signal and the falling edge adjusting phase signal perform logical OR operation with the phase amplitude adjusting module to control the amplitude of amplitude adjustment of the rising edge and the falling edge; the input signal also generates an original signal through a high-speed main path; and logic AND operation is performed on the original signal, the risingedge adjustment phase signal and the falling edge adjustment phase signal, and the amplitude of the main signal at the phase position is adjusted.
Owner:XIAMEN UX HIGH SPEED IC
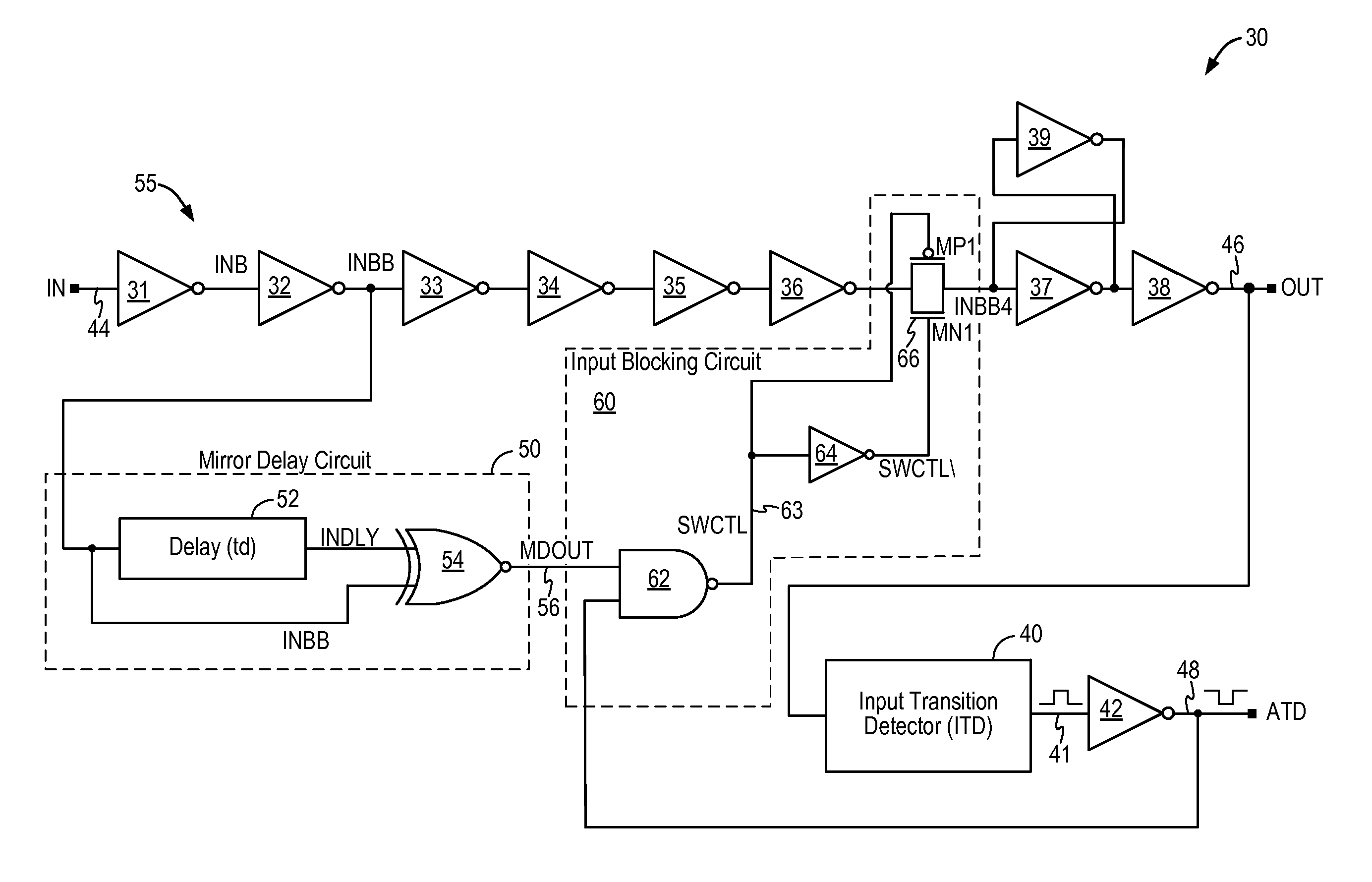
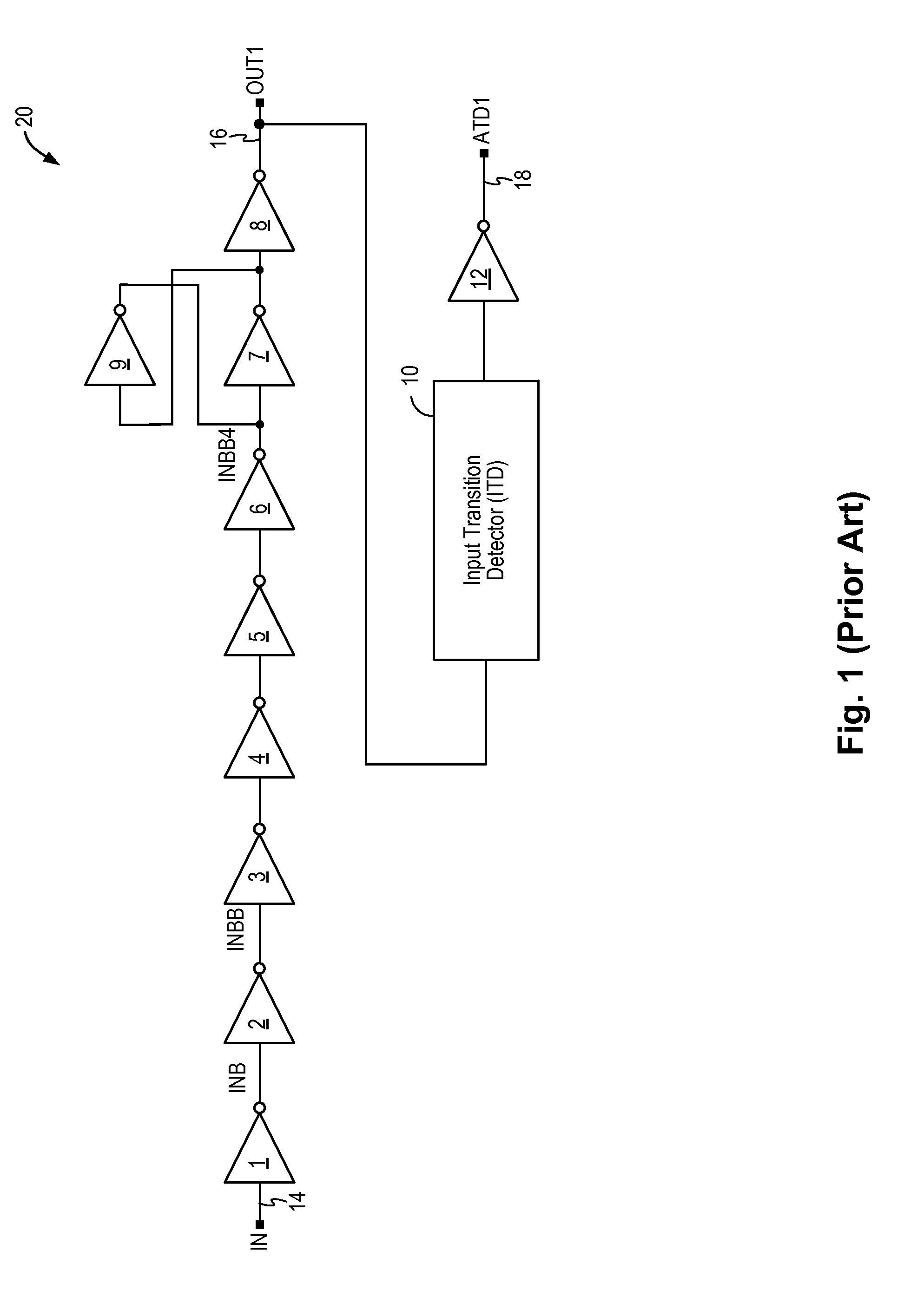
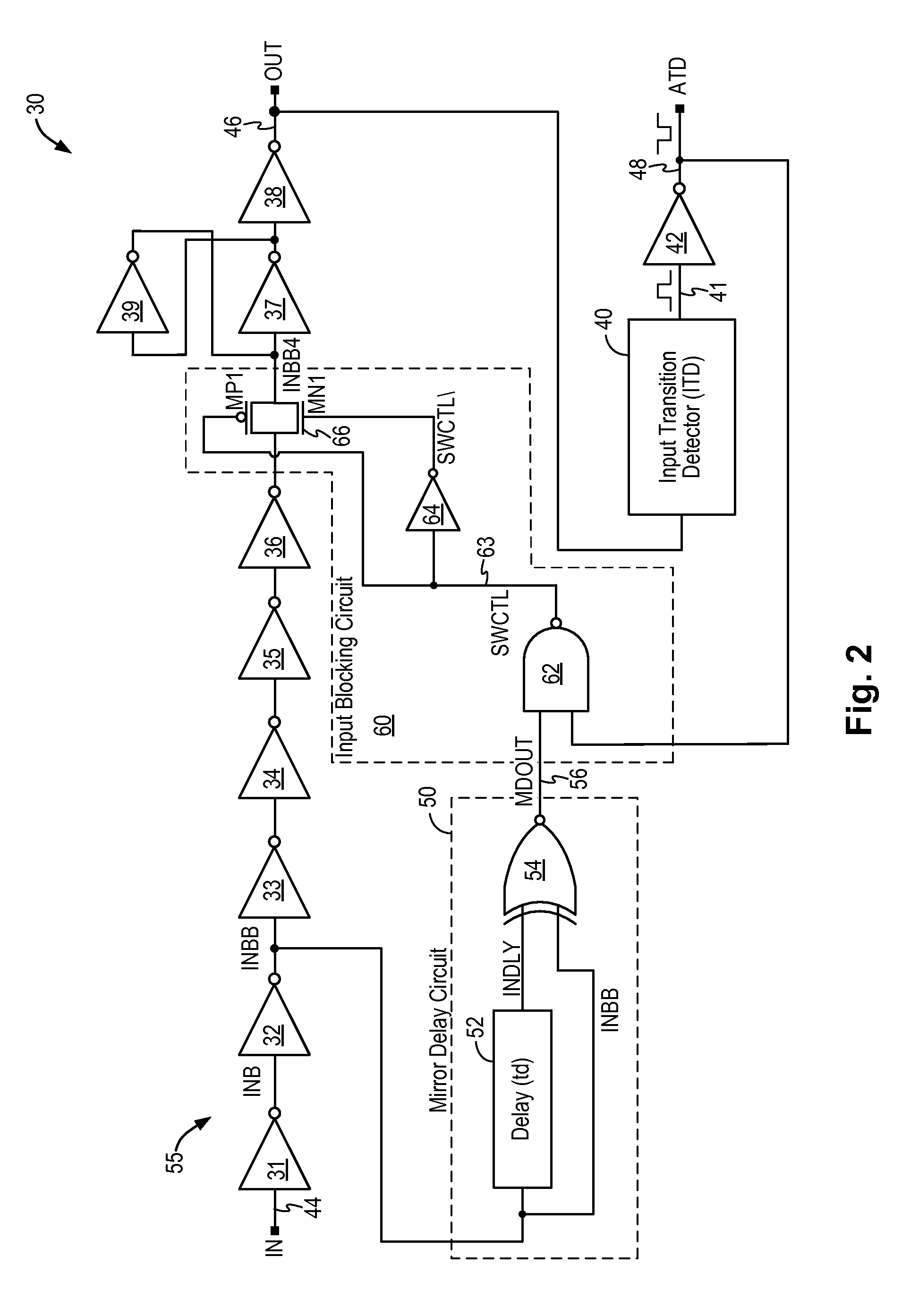
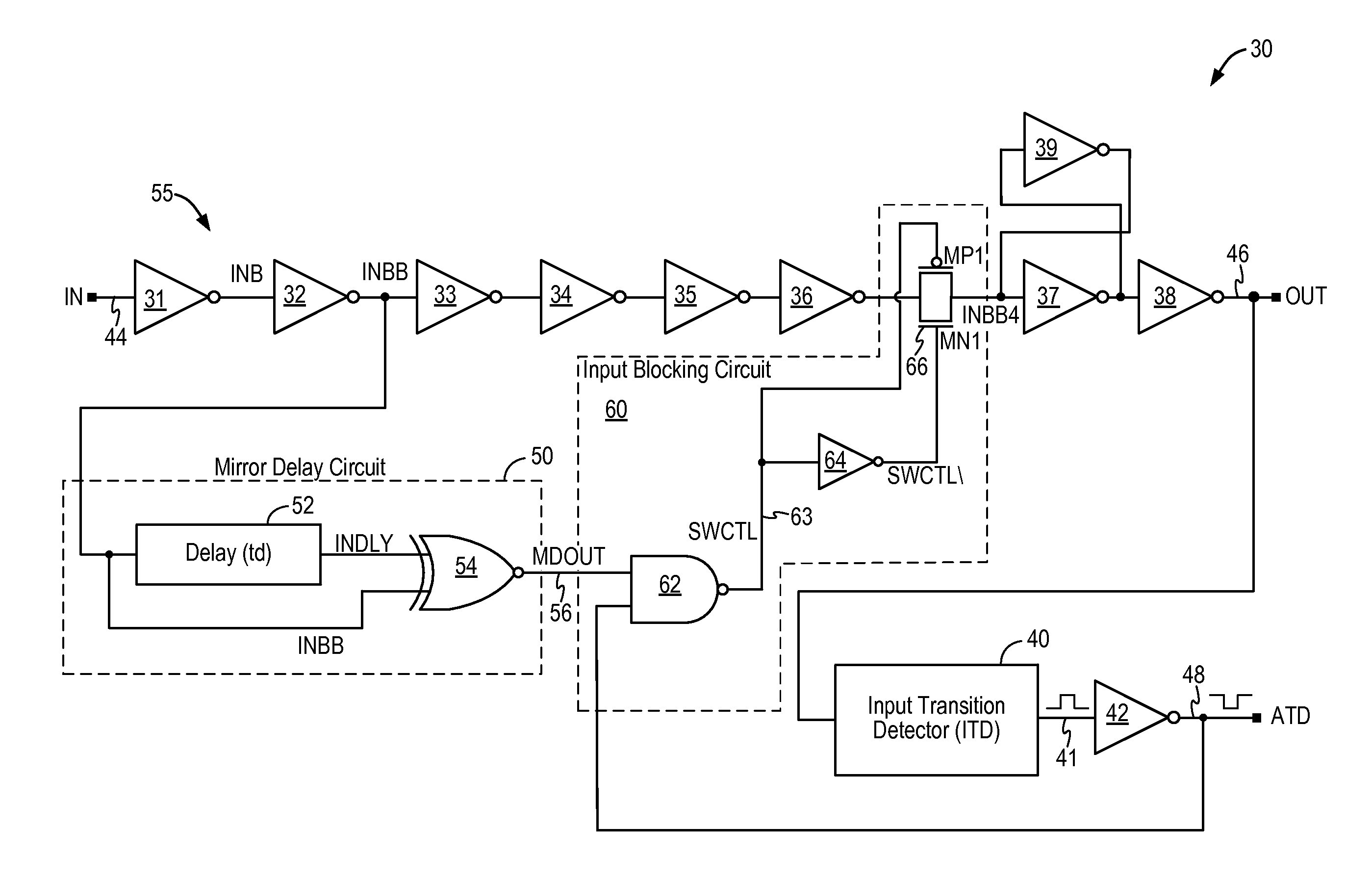
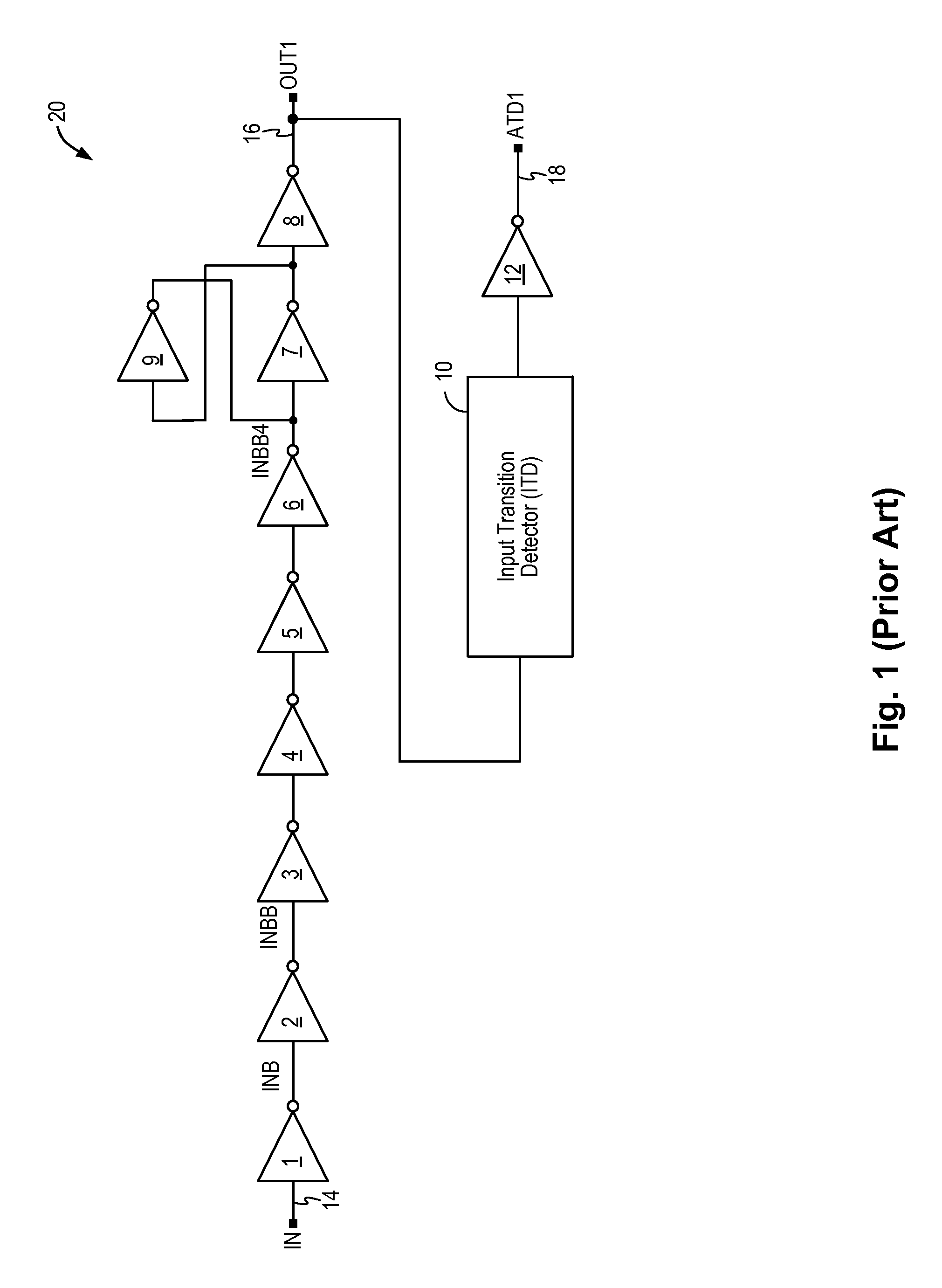
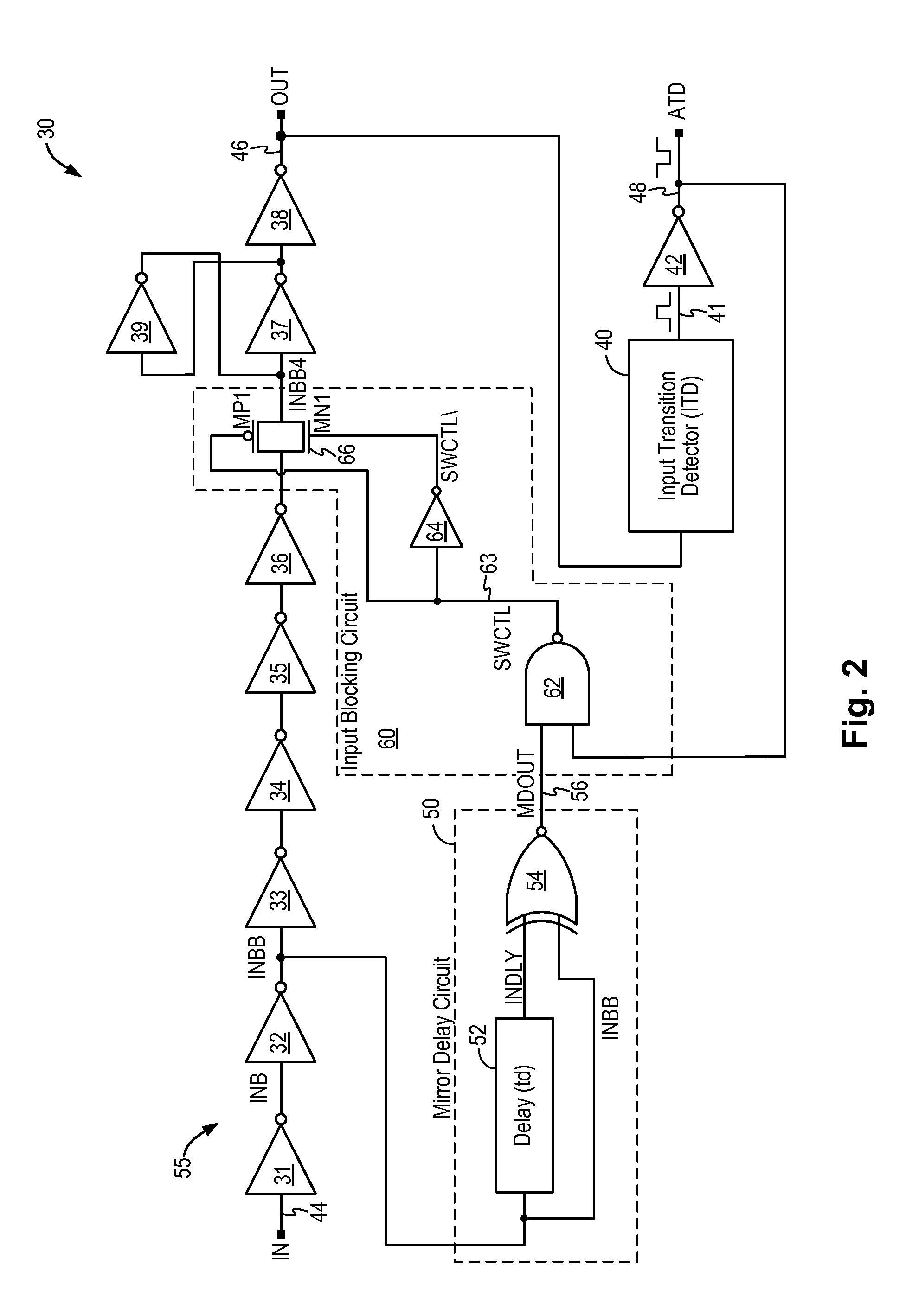
Glitch-free input transition detector
ActiveUS8890575B1Current/voltage measurementDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationSignaling nodesGlitch
A circuit for detecting a signal transition on an input signal includes a mirror delay circuit and an input blocking circuit to prevent signal glitches or undesired signal pulses from being passed to the output signal node, thereby preventing signal distortions from being detected as a valid signal transition. The input transition detection circuit generates stable and correct transition detection pulses having a consistent pulse width.
Owner:INTEGRATED SILICON SOLUTION
Glitch-free input transition detector
A circuit for detecting a signal transition on an input signal includes a mirror delay circuit and an input blocking circuit to prevent signal glitches or undesired signal pulses from being passed to the output signal node, thereby preventing signal distortions from being detected as a valid signal transition. The input transition detection circuit generates stable and correct transition detection pulses having a consistent pulse width.
Owner:INTEGRATED SILICON SOLUTION
Dual edge programmable delay unit
InactiveUS20050122151A1Improve performanceSetting changedElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingCapacitanceFall time
A method and device program a dual edge programmable delay unit, that responds to an input signal with a rise time and a fall time, includes a buffer which receives the input signal and provides an output signal with programmed variable delays between the rise and fall times of the output signal. Programmable control sources (PCS) provide separate control inputs to a buffer. The FTPCS charges a capacitor in the buffer when the input signal changes from high to low to adjust time delay before the fall of the buffer output signal. The RTPCS discharges the capacitor in the buffer when the input signal changes from low to high to adjust time delay before the rise of the buffer output signal.
Owner:IBM CORP
Pulse generation circuit
InactiveUS20060097768A1High voltage levelSingle output arrangementsElectric pulse generatorEngineeringTransistor
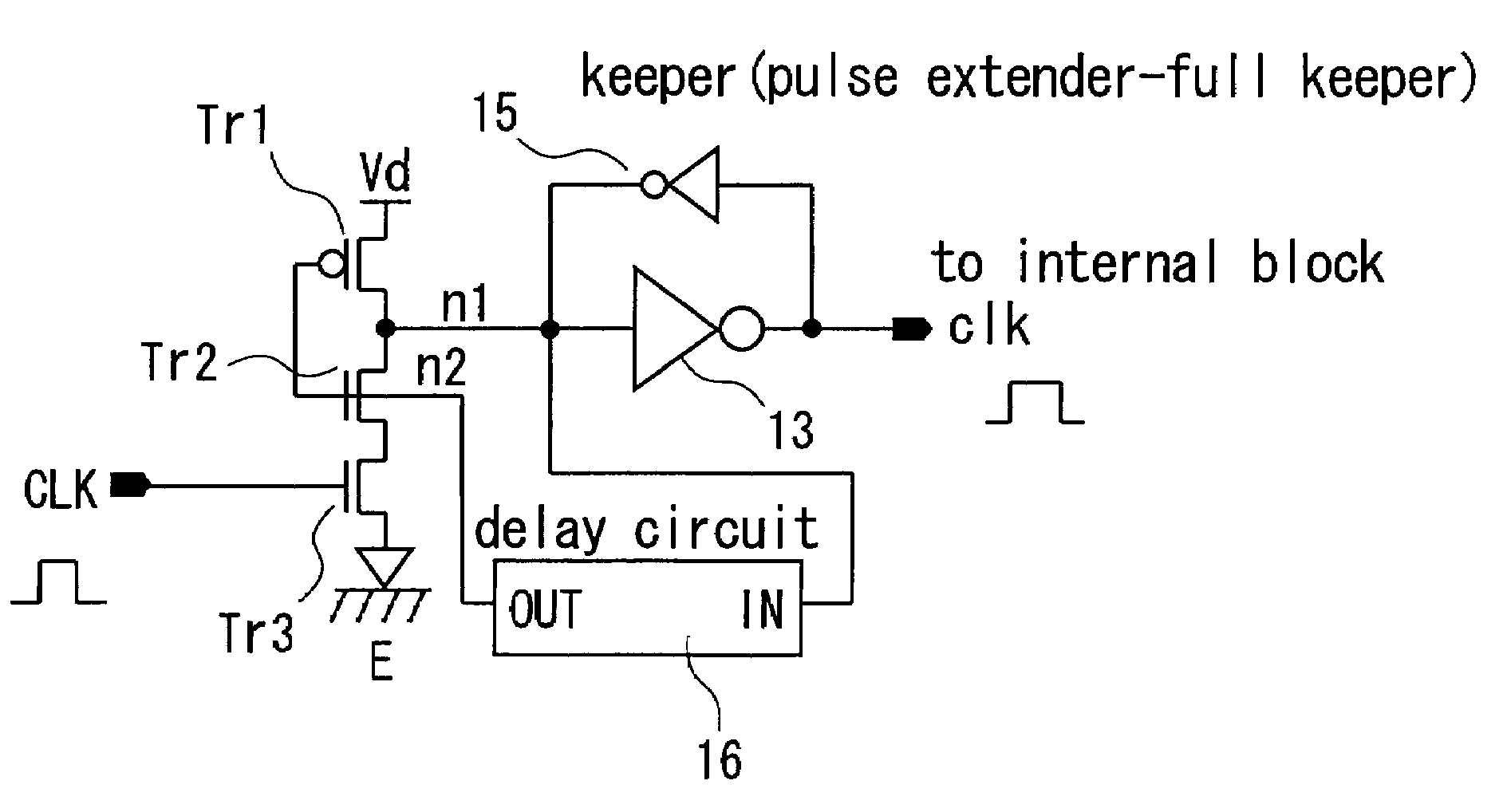
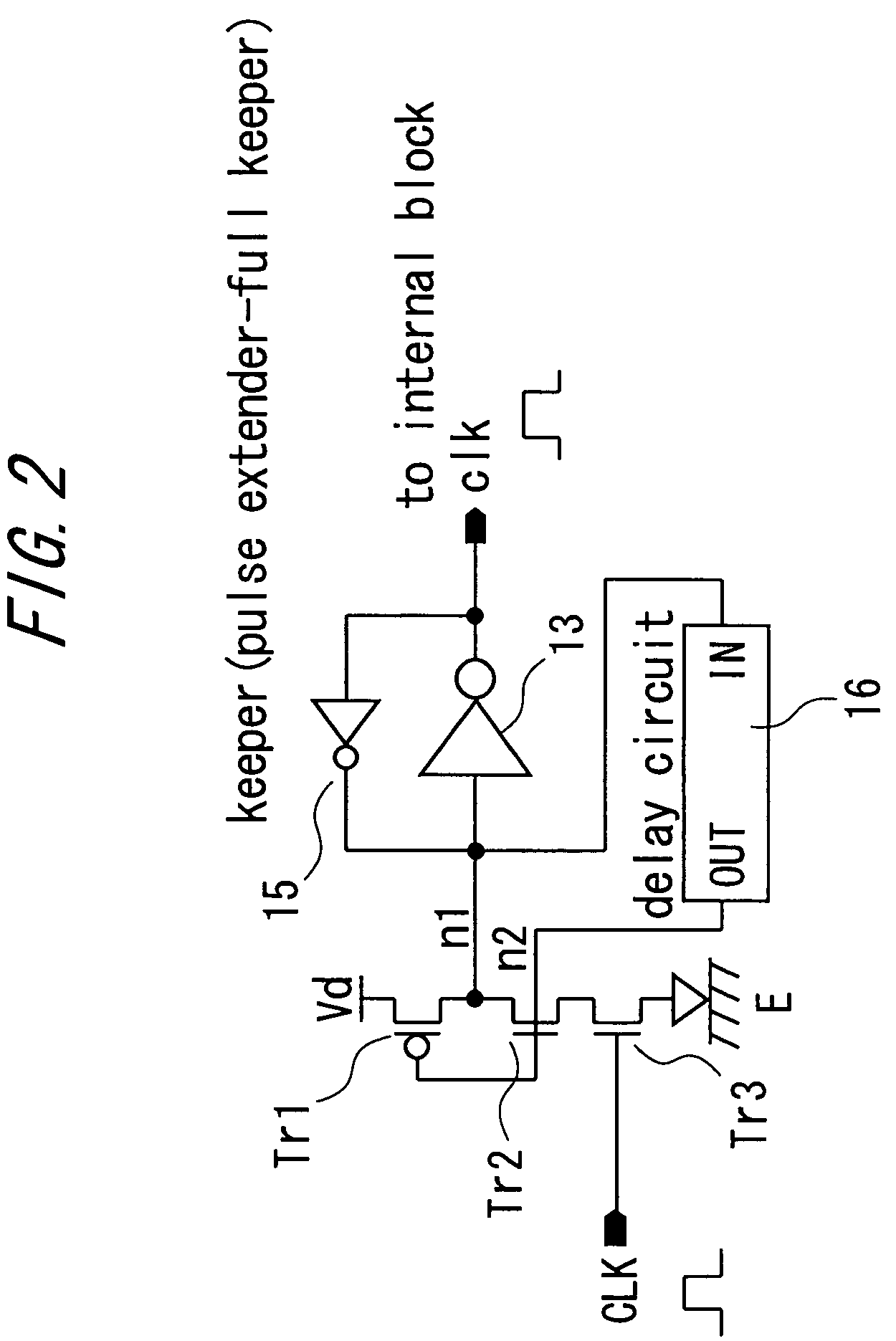
There is provided a pulse generation circuit having a small input load and capable of self-reset. The pulse generation circuit includes: a P-MOS transistor having a drain electrode connected to a first power source line; a first N-MOS transistor having a drain electrode connected to the source electrode of the P-MOS transistor; a second N-MOS transistor having a drain electrode connected to the source electrode of the first N-MOS transistor, a gate electrode connected to the input line to which an input pulse signal is input, and a source electrode connected to the second power source line; a delay circuit having an input terminal connected to the source electrode of the P-MOS transistor and the drain electrode of the first N-MOS transistor and an output terminal connected to the gate electrode of the P-MOS transistor and the gate electrode of the first N-MOS transistor; an inverter having an input terminal connected to the source electrode of the P-MOS transistor and the drain electrode of the second N-MOS transistor and an output terminal connected to the output line for outputting a generated pulse; and a keeper for keeping the voltage level of the line connected to the input terminal of the inverter.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
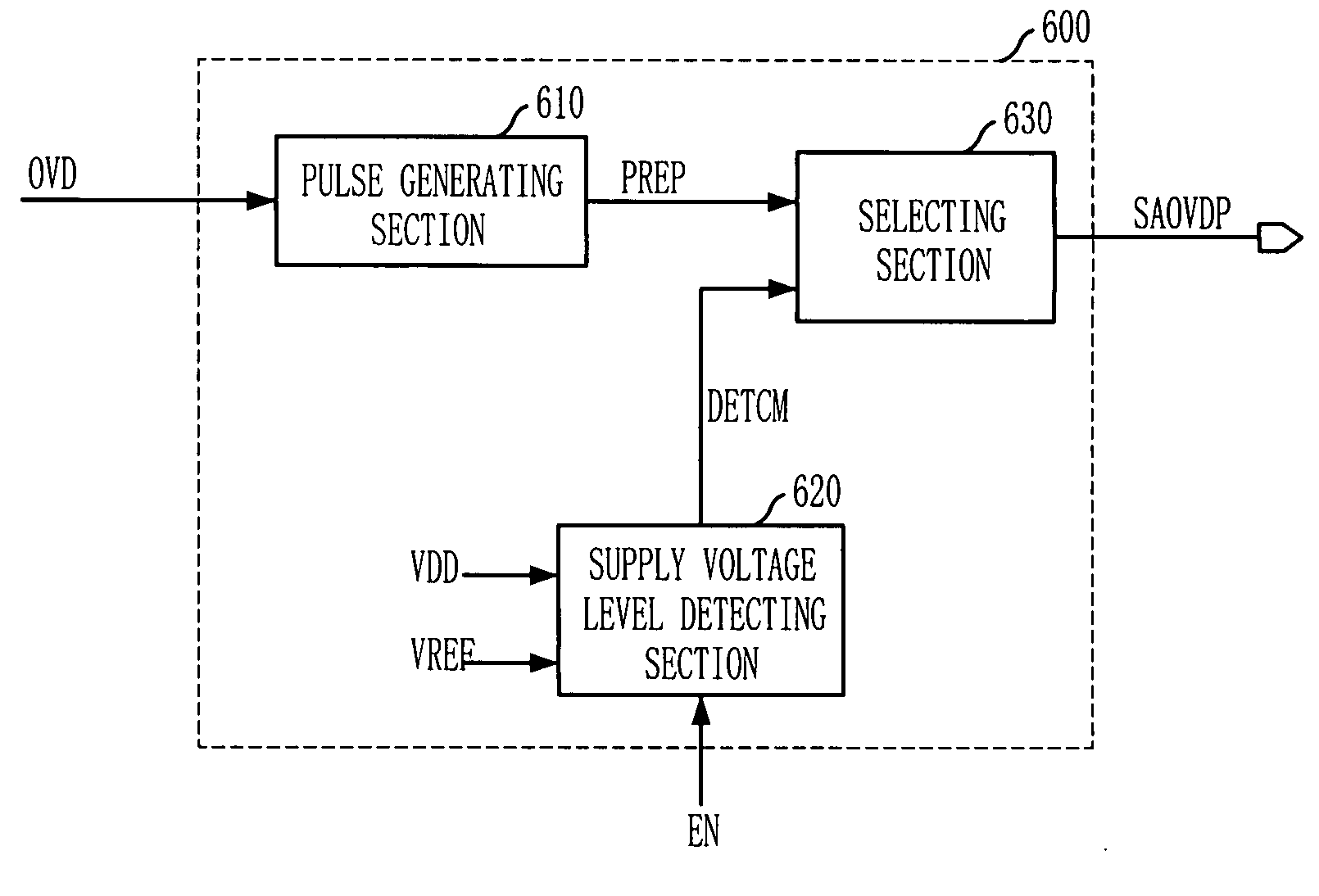
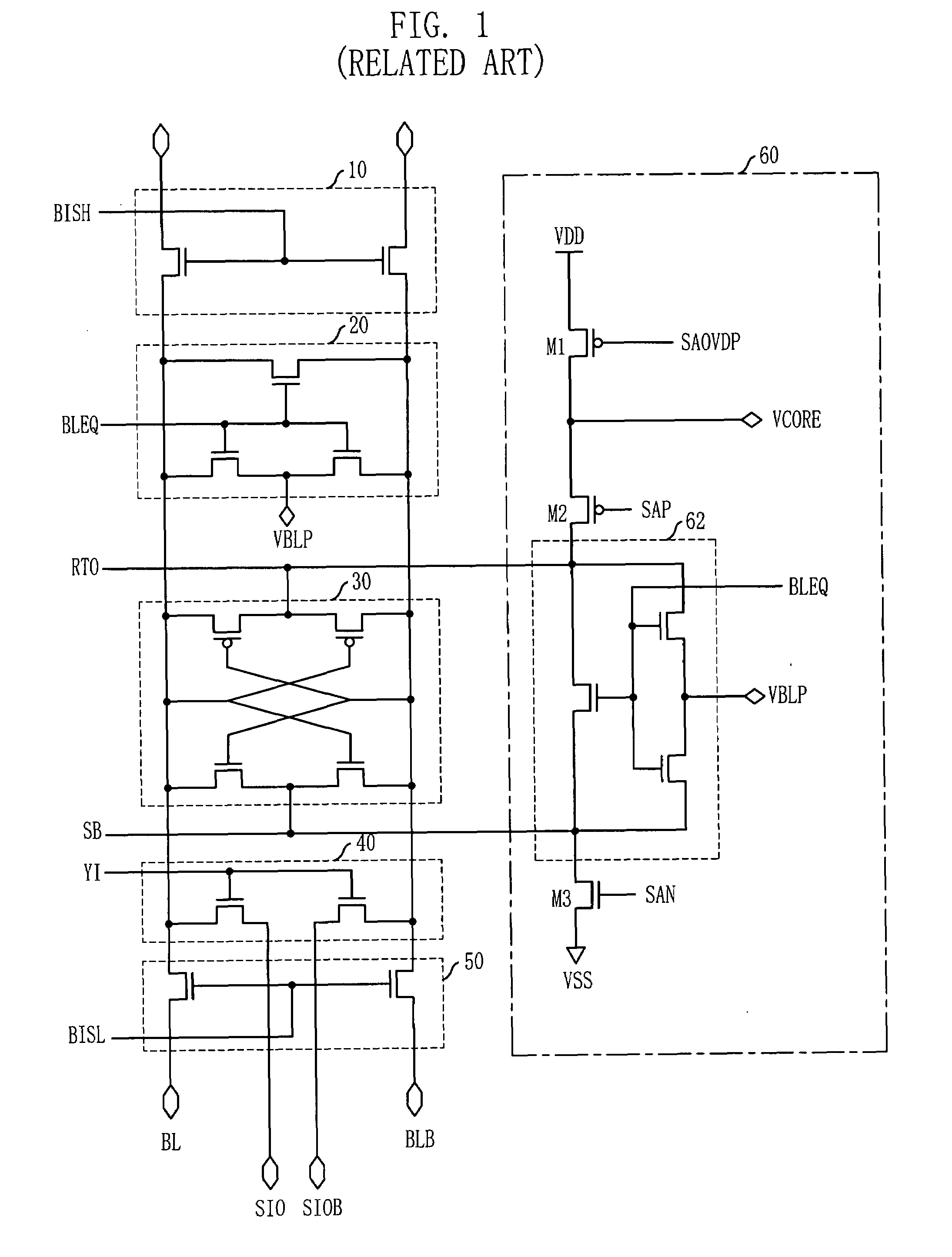
Over driver control signal generator in semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS20080079472A1Stable voltage levelCurrent/voltage measurementDigital storageBit lineControl signal
An over-driver control signal generating apparatus includes a pulse generating unit for generating a pulse signal having a pulse width corresponding to a desired over-driving interval in response to an over-driving signal; a supply voltage level detecting unit for detecting a voltage level of a supply voltage to generate a detecting signal; and a selecting unit for outputting the pulse signal as a bit line over-driver control signal in response to the detecting signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Over driver control signal generator in semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS7573777B2Stable voltage levelCurrent/voltage measurementDigital storageBit lineControl signal
An over-driver control signal generating apparatus includes a pulse generating unit for generating a pulse signal having a pulse width corresponding to a desired over-driving interval in response to an over-driving signal; a supply voltage level detecting unit for detecting a voltage level of a supply voltage to generate a detecting signal; and a selecting unit for outputting the pulse signal as a bit line over-driver control signal in response to the detecting signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
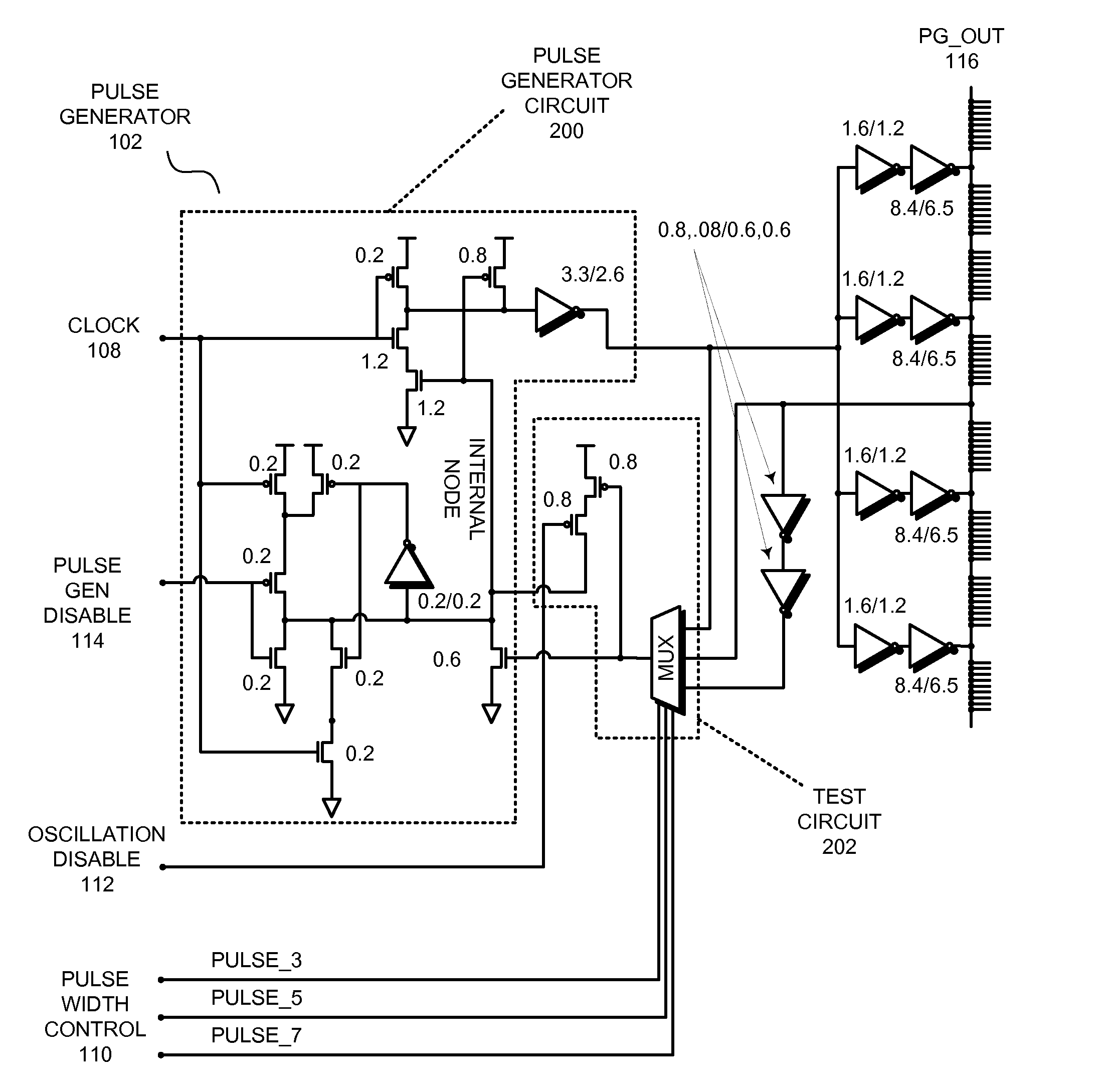
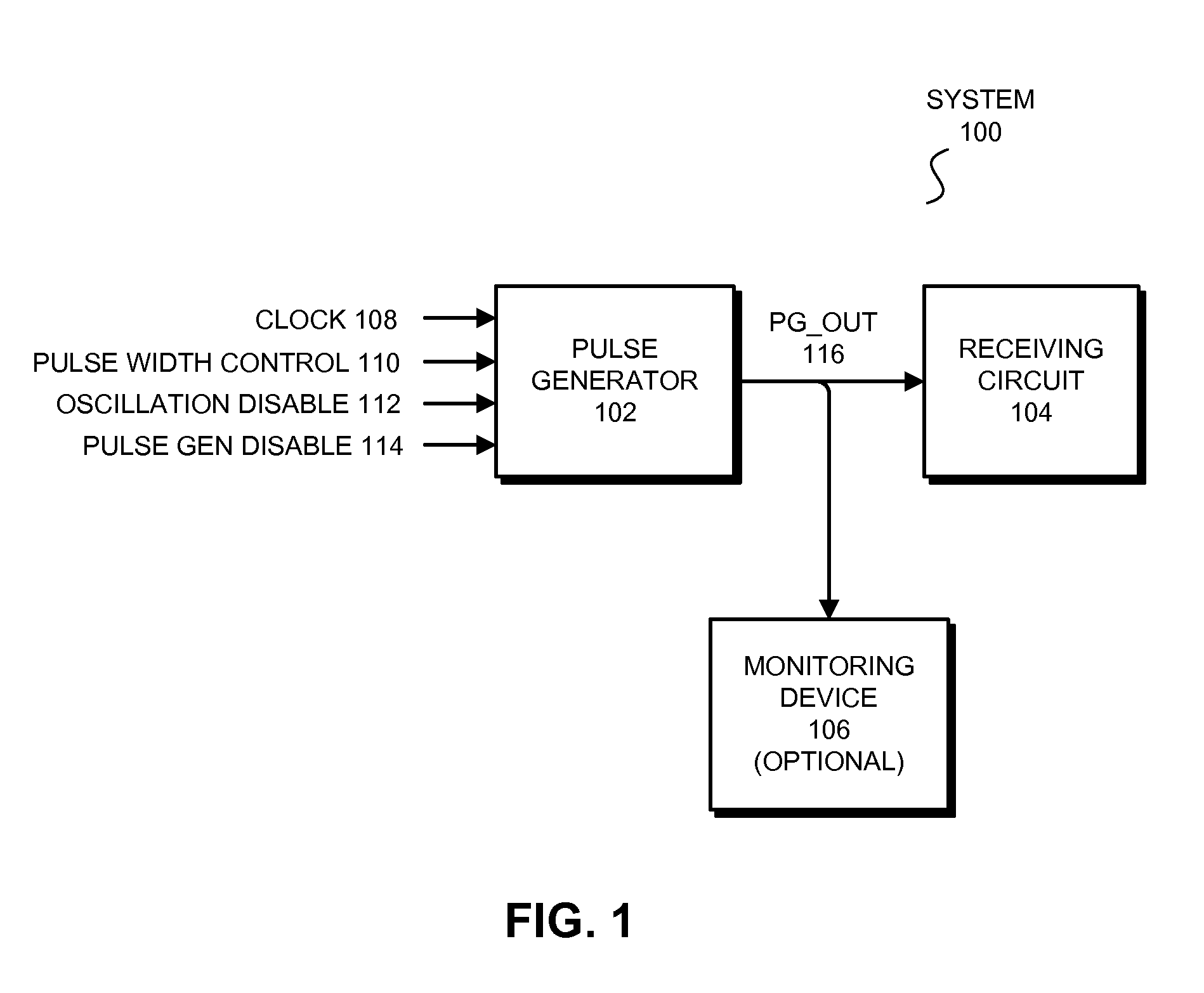
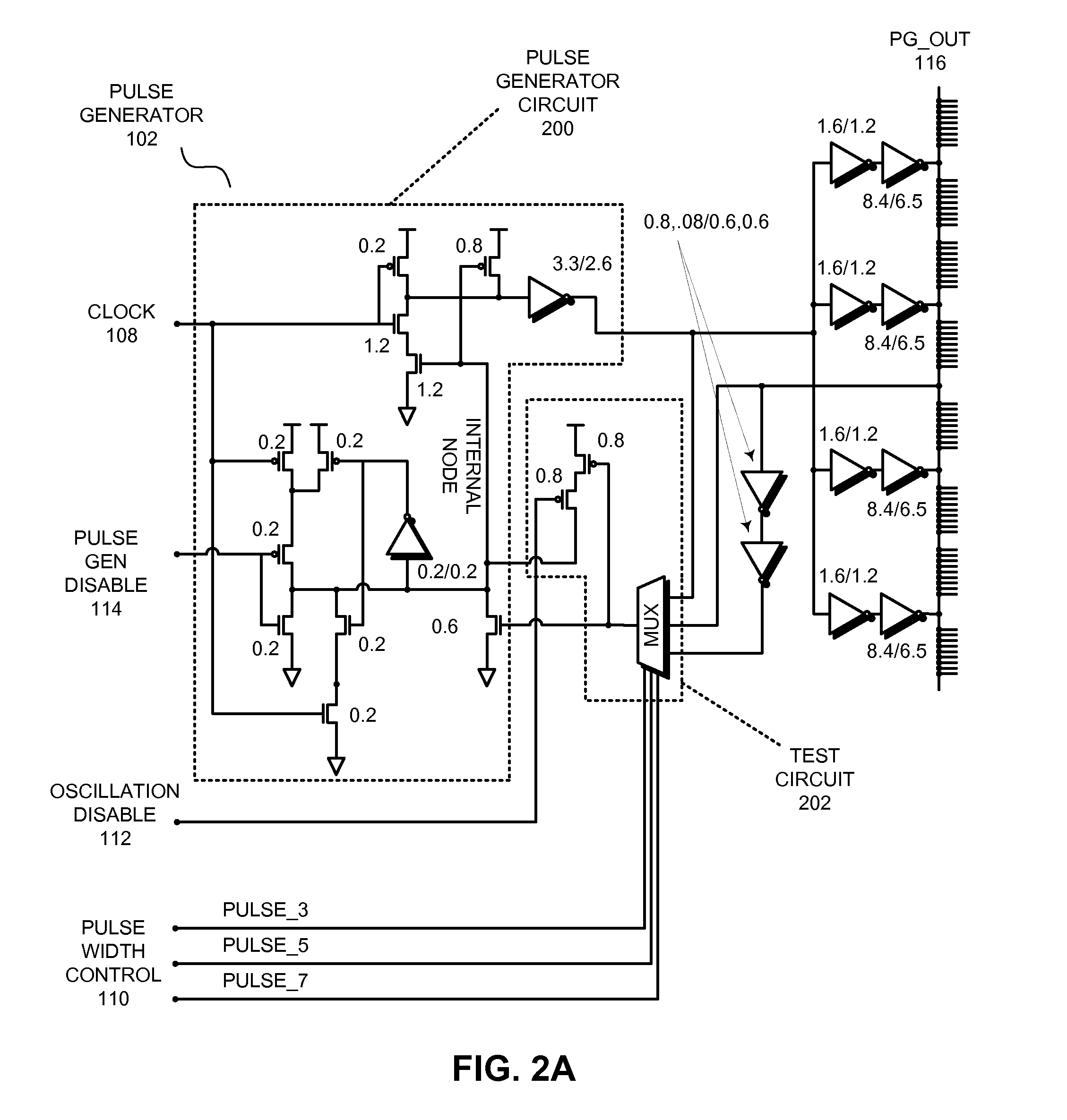
Configurable pulse generator
ActiveUS20100327937A1Electric pulse generatorGenerating/distributing signalsElectrical and Electronics engineeringDuration time
The described embodiments provide a circuit that can be configured as a pulse generator or as an oscillator. The circuit includes a pulse generator circuit and a test circuit that is coupled to the pulse generator circuit. In the described embodiments, an disable signal is coupled to the test circuit. When the disable signal is asserted, the test circuit is disabled, and the pulse generator circuit outputs pulses of a predetermined duration. In contrast, when the disable signal is deasserted, the test circuit is enabled, and the pulse generator circuit outputs an oscillating signal.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
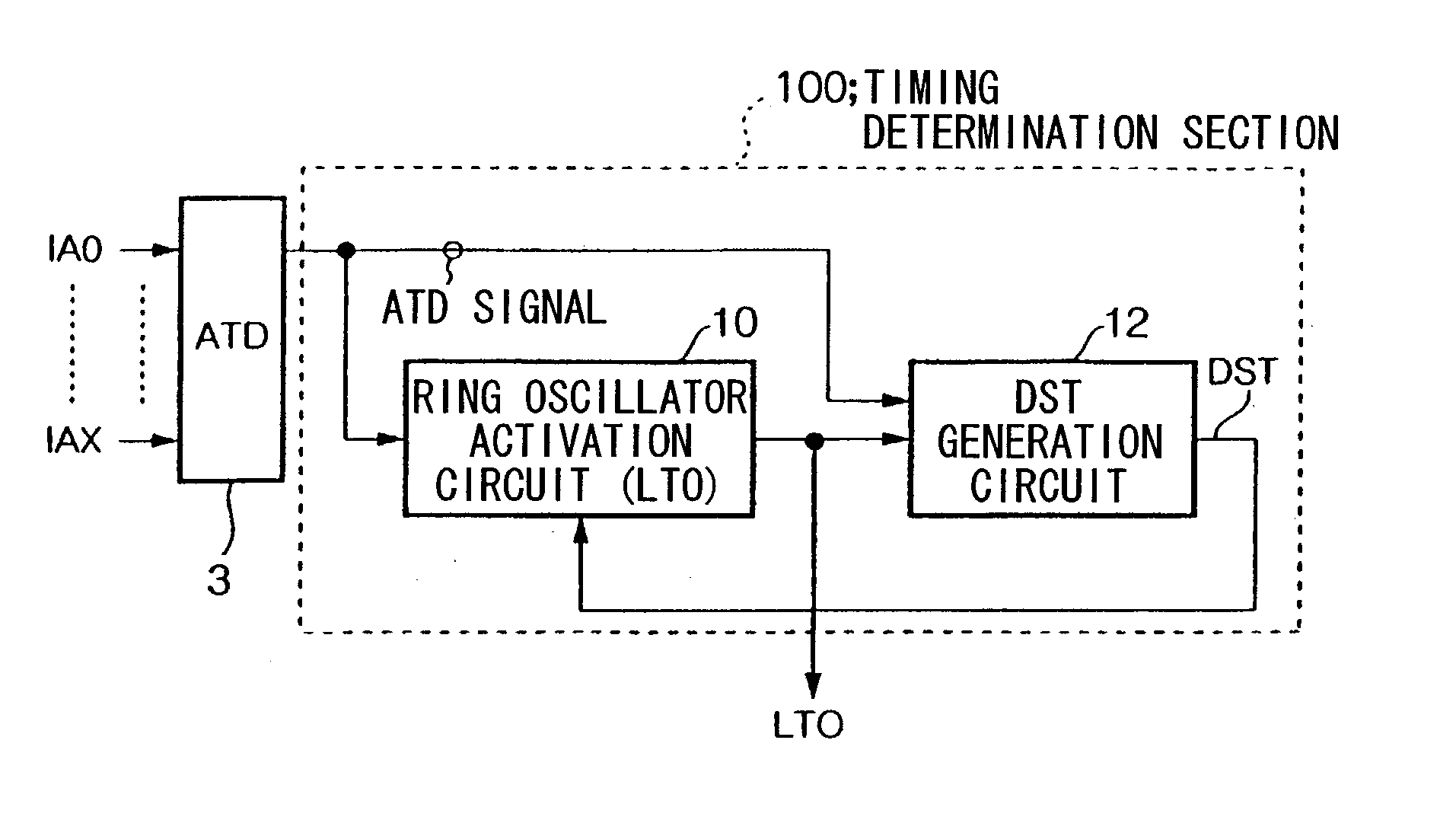
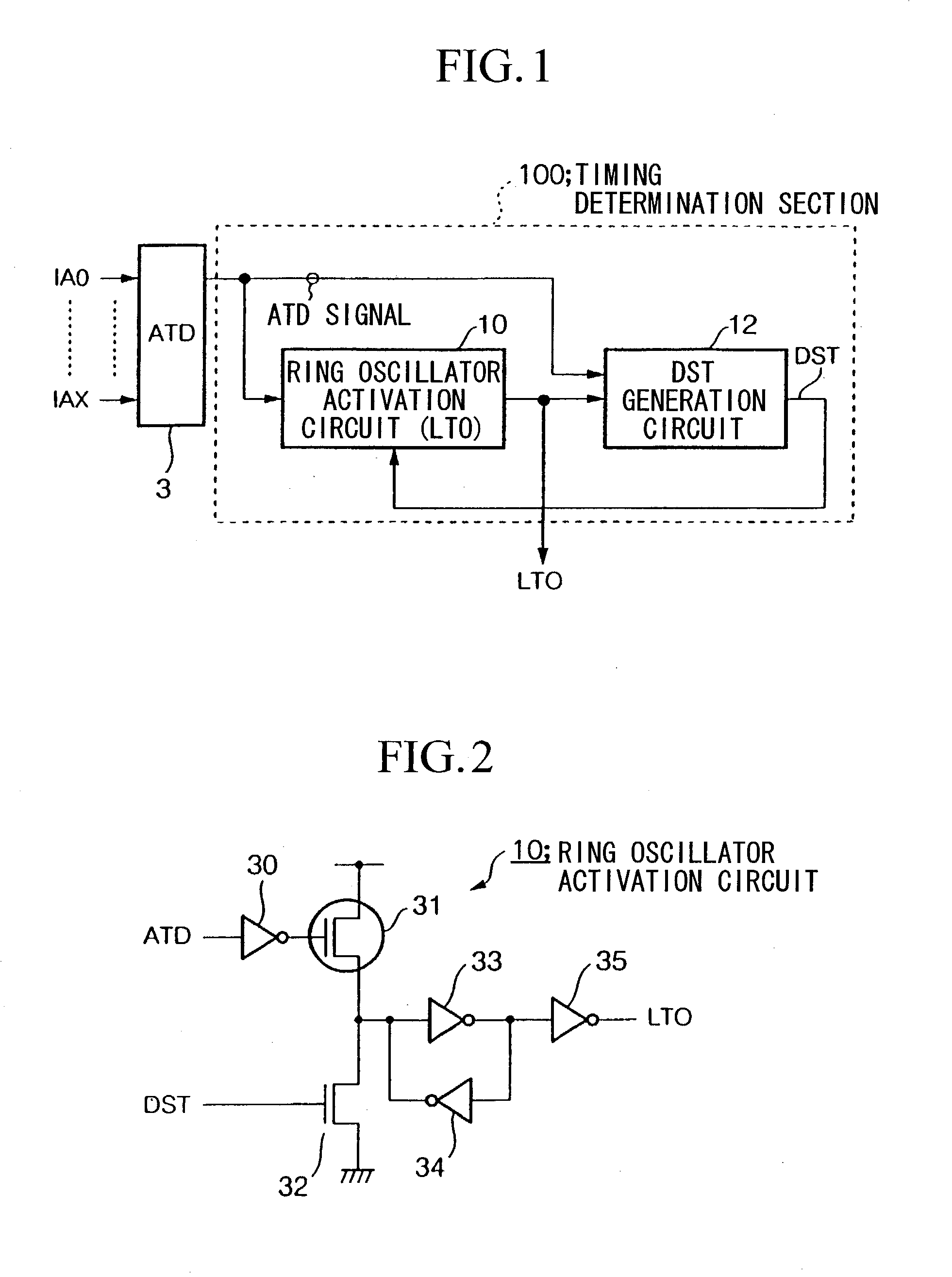
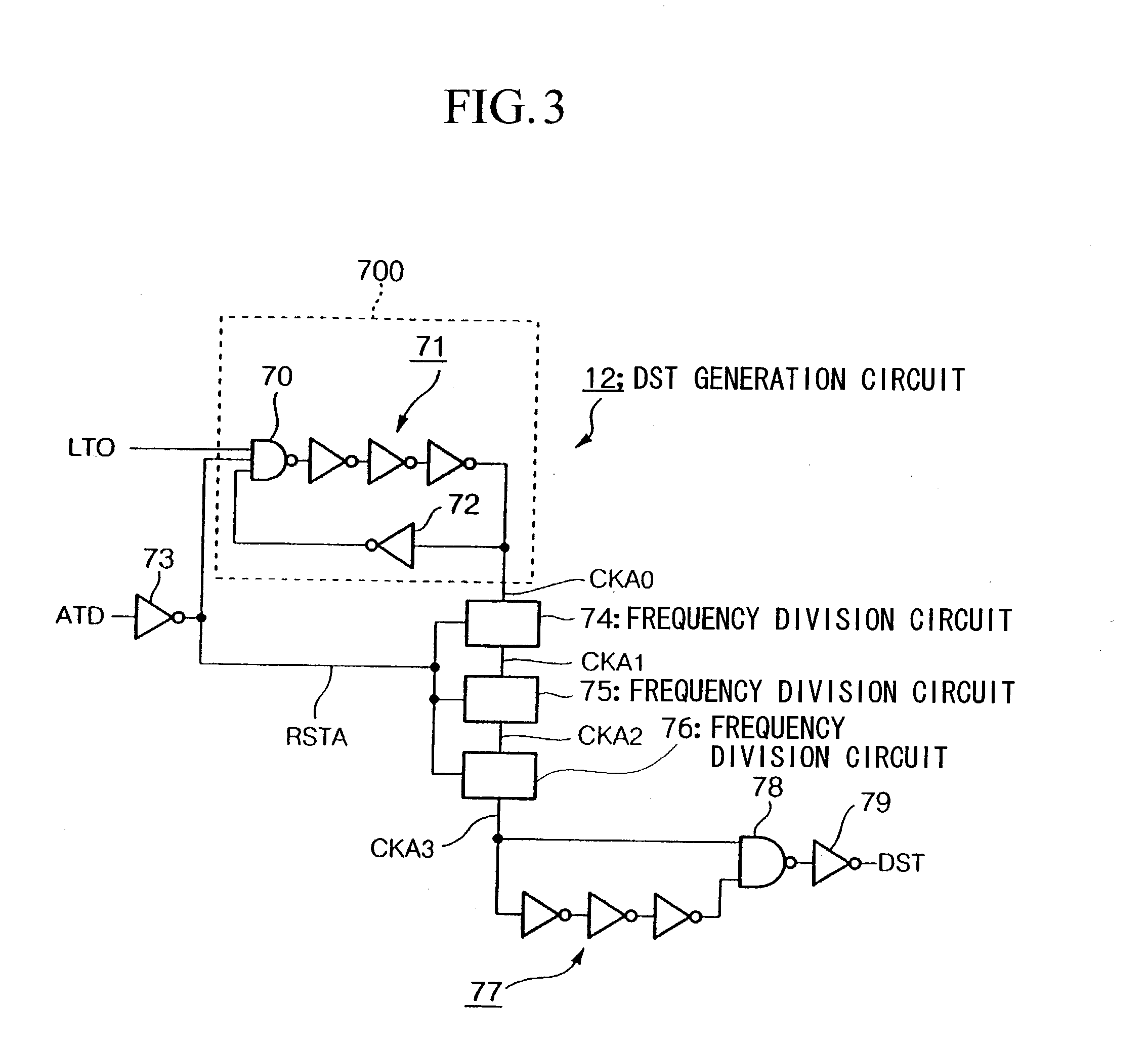
One-shot signal generating circuit
InactiveUS20030090954A1Easy to adjustReduce chip areaDigital storageElectric pulse generatorEngineeringOne shot
A one-shot signal generation circuit is provided which makes it easy to adjust pulse width and to deal with variation of skew of an ATD signal, and can reduce chip area. A timing determination section (100) is reset by an edge of a first detected signal among a plurality of address transition detection signals (ATD signals) which have arrived within the skew period of an address signal, measures a first predetermined time by taking an edge of a second detected signal as start instant, and outputs a signal DST which reflects the result of this measurement. A timing determination section (110) measures a second predetermined time by taking an edge of the first detected signal as start instant, and outputs a signal PG which reflects the result of this measurement. An LC generation circuit (14) outputs a one-shot signal (LC) whose start instant is determined by the signal PG and whose end instant is determined by the signal DST.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Pulse generation circuit
InactiveUS7446589B2High voltage levelSingle output arrangementsElectric pulse generatorTransistorAND gate
Pulse generation circuit has a P-MOS transistor having a drain electrode connected to a first power source; a first N-MOS transistor having a drain electrode connected to the source electrode of the P-MOS transistor; a second N-MOS transistor having a drain electrode connected to the source electrode of the first N-MOS transistor, a gate electrode receiving an input pulse signal, and a source electrode connected to the second power source; a delay circuit having an input terminal connected to the source electrode of the P-MOS transistor and the drain electrode of the first N-MOS transistor and an output terminal connected to gate electrode of the P-MOS transistor and gate electrode of the first N-MOS transistor; an inverter input connected to the source electrode of the P-MOS transistor and the drain electrode of the second N-MOS transistor for outputting a generated pulse; and a keeper keeping voltage level to the inverter.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
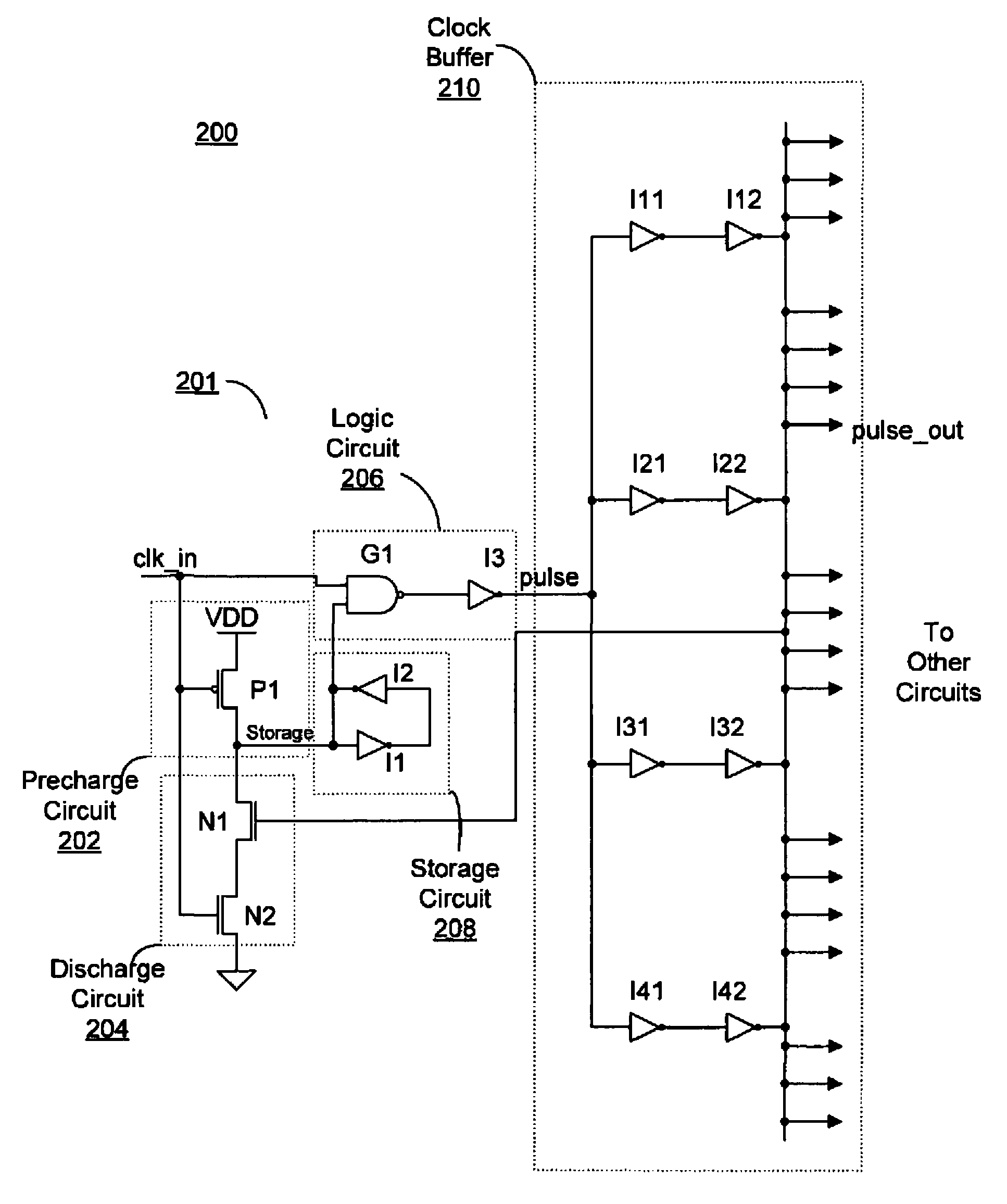
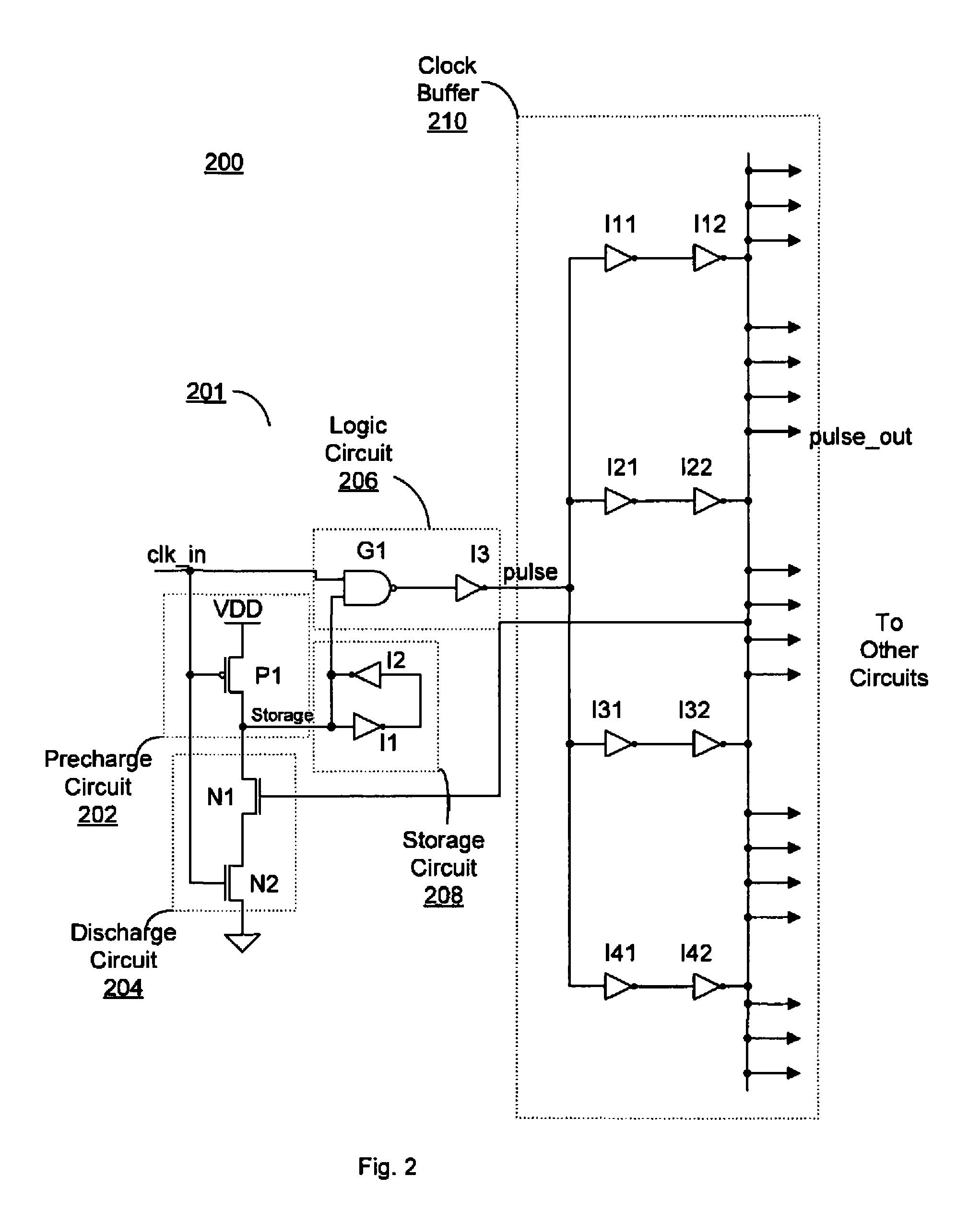
Precision pulse generator
A pulse generator circuit. The pulse generator circuit includes a precharge circuit coupled to receive a clock signal alternating between a first logic level and a second logic level, a storage circuit having a storage node, wherein the precharge circuit is configured to precharge the storage node when the clock signal is at the first logic level, a logic circuit having an output, a first input node coupled to receive the clock signal, and a second input node coupled to the storage node and configured to produce a pulse at the second logic level responsive to the clock signal transitioning to the second logic level, and a discharge circuit configured to discharge the storage node at a predetermined delay time subsequent to the clock signal transitioning to the second logic level, wherein the output of the logic circuit transitions to the first logic level responsive to discharging the storage node.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
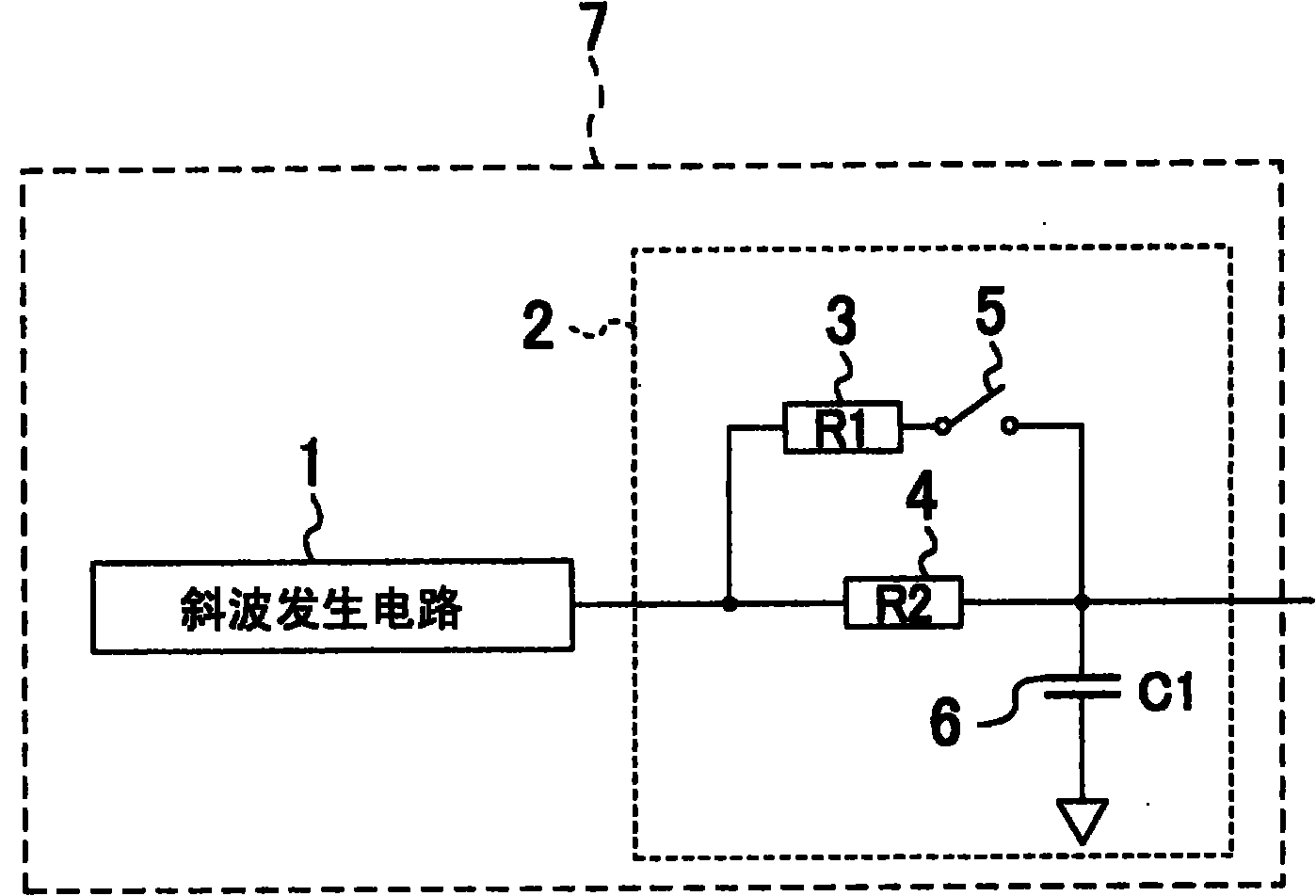
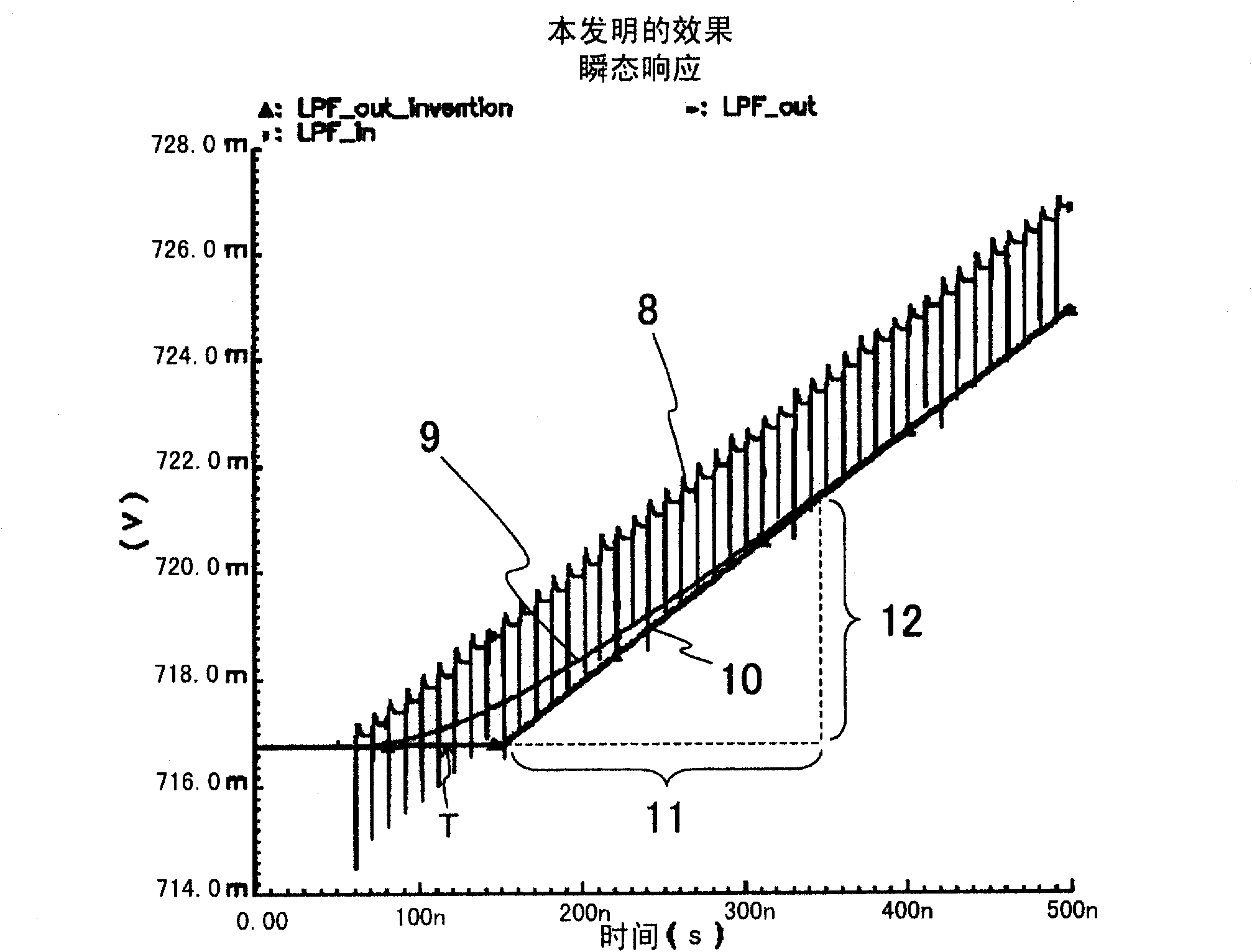
Ramp wave output circuit, analog/digital conversion circuit, and camera
A ramp wave output circuit includes a ramp wave generation circuit (1) which generates a ramp wave and a low-pass filter (2) having a variable cut-off frequency for receiving the ramp wave. The low-pass filter (2) operates with a first cut-off frequency for a predetermined time from the reception of the ramp wave and operates with a second cut-off frequency greater than the first cut-off frequency after a predetermined time has elapsed.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Circuit and method of controlling a delay of a semiconductor device
ActiveUS7271637B2Multiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse automatic controlDevice materialCircuit delay
A delay control circuit capable of controlling a delay time is disclosed. The delay control circuit includes a delay detecting circuit, a first pulse generator, a counter control circuit and a counter. The delay detecting circuit delays an input signal by a first time in response to an output signal and compares the input signal and the delayed input signal to generate a first signal. The first pulse generator generates a second signal in response to the input signal. The counter control circuit generates a count-up signal and a count-down signal in response to the first signal and the second signal. The counter generates the output signal in response to the count-up signal and the count-down signal to divide the first time by 2n intervals, wherein n is a positive integer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Circuit arrangement for producing short electrical pulses
ActiveUS8253439B2Reduced transit timeReduce complexityReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionLogic gateTransmission time
A circuit arrangement for producing short electrical pulses, including a logic gate (1) with a very short gate transit time and having a clock signal being supplied to a trigger input (2) of the logic gate (1) as a trigger signal. An output signal based on the trigger signal is generated as a short electrical pulse at an output (3) or at one output (3 or 4) or at both outputs (3 and 4) of the logic gate (1).
Owner:KROHNE MESSTECHNICK GMBH & CO KG
Apparatus and method for transferring multiple asynchronous clock signals over a single conductor
ActiveUS20150171850A1Avoid overlapSynchronisation information channelsTime-division multiplexElectrical conductorClock signal
Methods and systems for transferring two clock signals over a single conductor are disclosed. According to various disclosed embodiments, first and second input clock signals are generated at a first module. The rising and falling edges of a generated reference clock signal are used to transfer the two clock signals from the first module to a second module over the single conductor.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Constant-ratio timing circuit for trailing edge timing
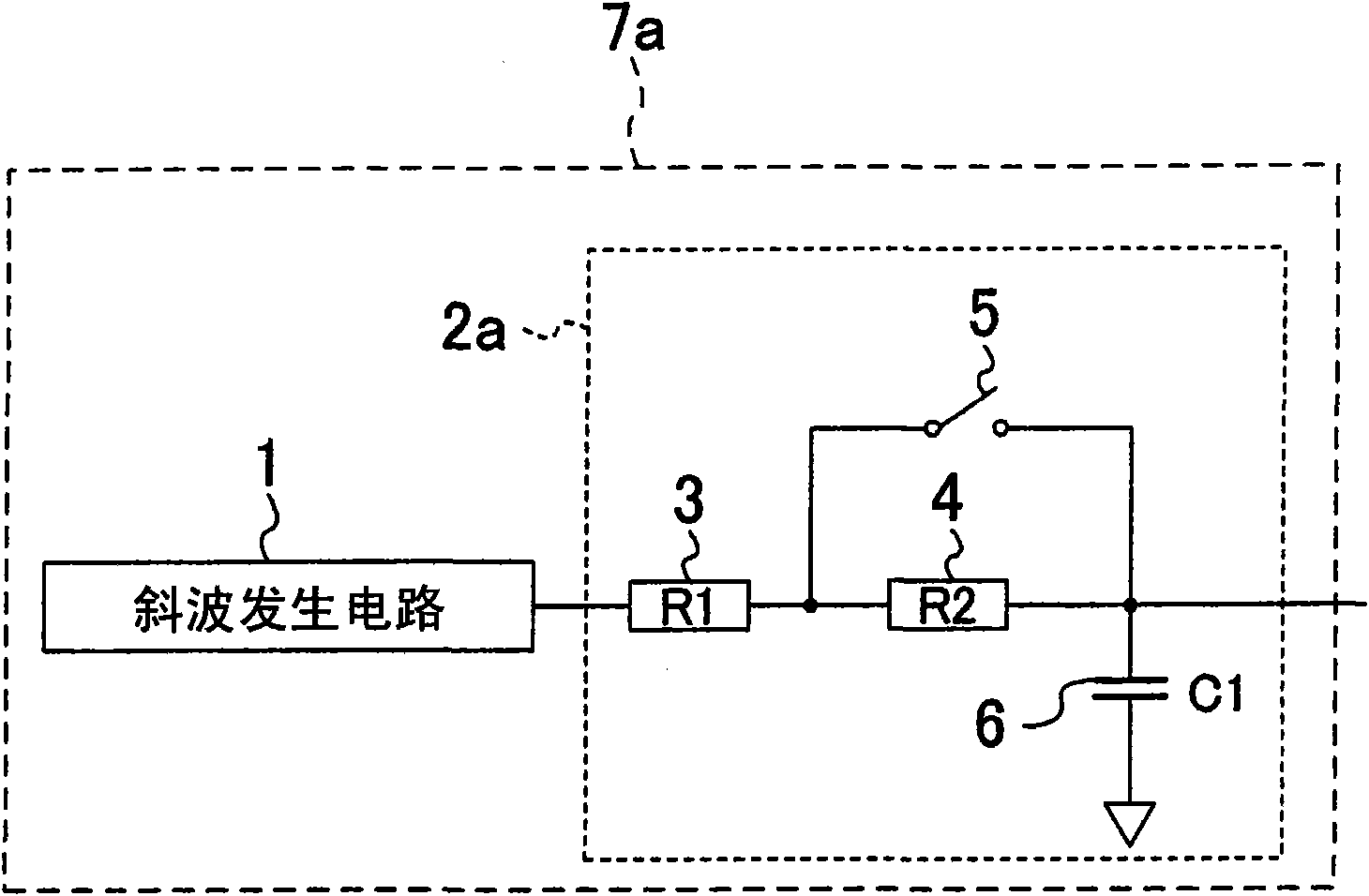
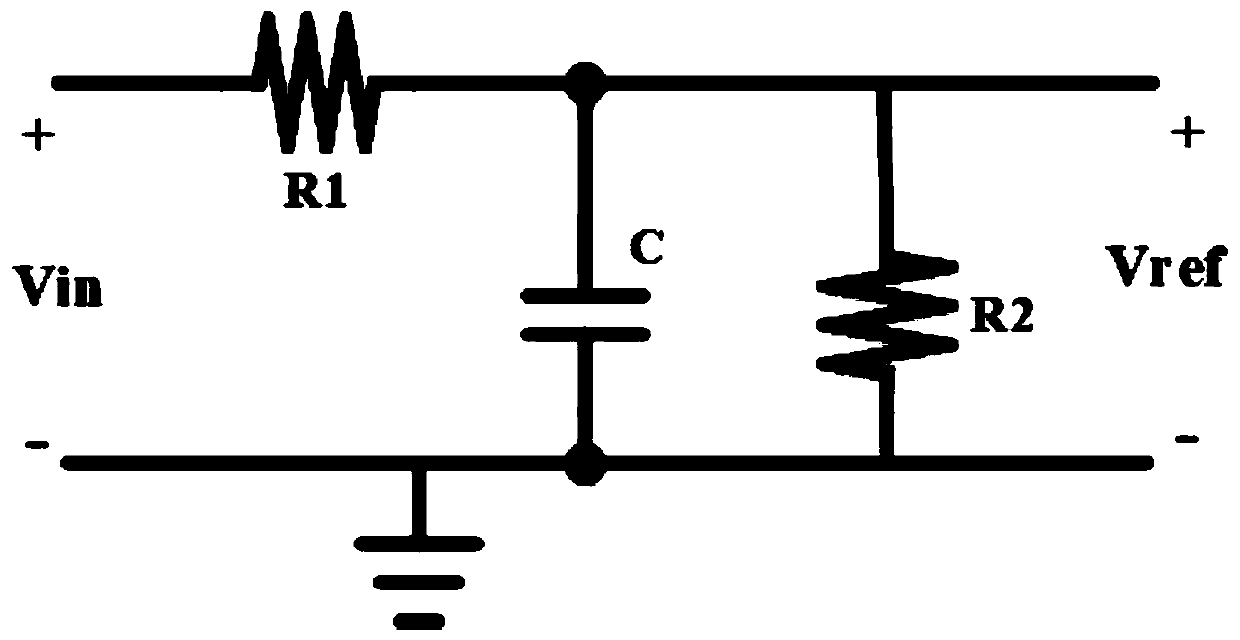
ActiveCN110492871AImprove stabilityAchieving attenuationManipulation with delayed output pulseUltrasound attenuationCapacitance
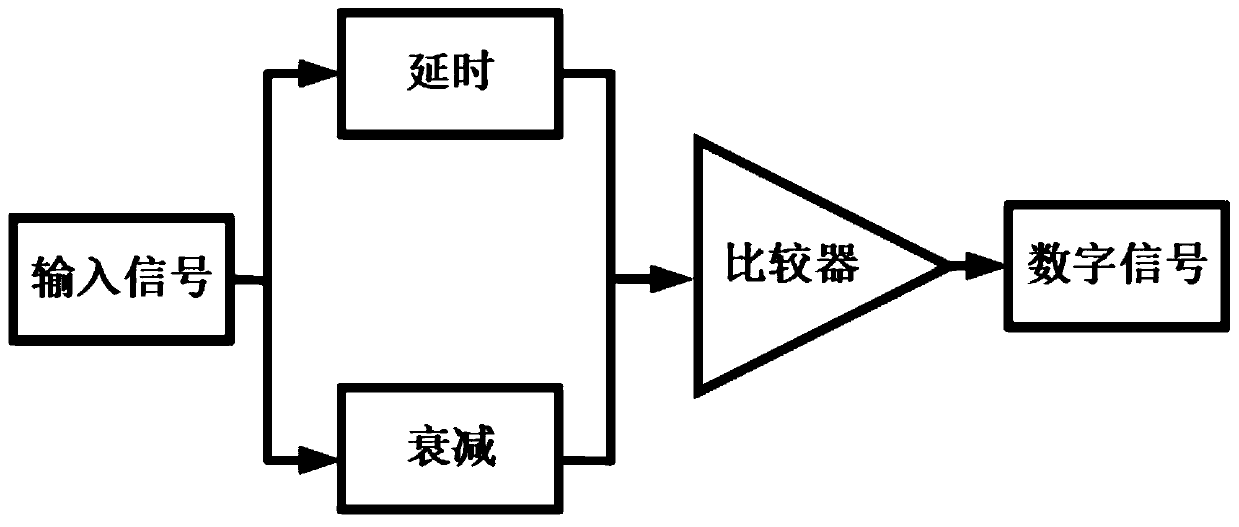
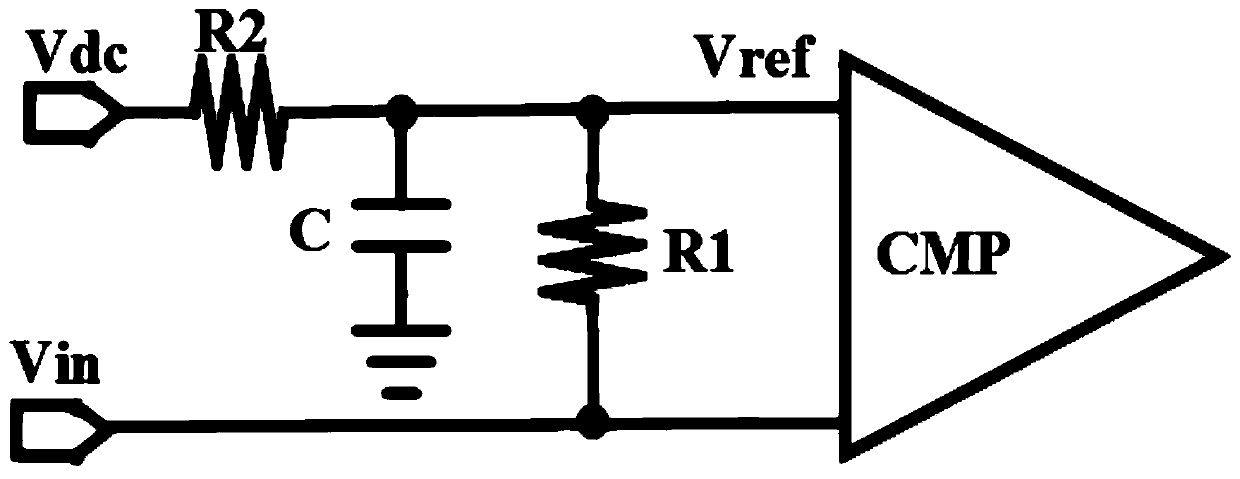
The invention provides a constant-ratio timing circuit for trailing edge timing. The circuit comprises a first resistor, a second resistor, a capacitor and a comparator. One end of the second resistoris connected with a direct-current power supply, and the other end of the second resistor is connected with one end of the first resistor and the first input end of the comparator and then grounded through the capacitor. A second input end of the comparator is connected with the other end of the first resistor and an input signal of the constant-ratio timing circuit. An output end of the comparator serves as an output end of the constant-ratio timing circuit. The direct-current power supply and the input signal have the same direct-current component. According to the invention, only the pulsesignal is attenuated, and the direct current component remains unchanged, so that the stability of the circuit is improved compared with the attenuation of the direct current component and the pulsesignal in the traditional constant-ratio timing circuit. In addition, the attenuation and the time delay are achieved only through one RC network. Compared with a traditional constant-ratio timing circuit in which quantity signals are divided into two paths to be attenuated and delayed respectively, the structure is simpler.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com