Treatment agent for epidermolysis bullosa
A technology for bullous and lysis, which is applied in the field of cell preparations, can solve problems such as undisclosed treatment effects, and achieve the effect of improving or restoring skin symptoms and having good safety.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0124] Example 1: Evaluation of full-thickness trauma model mice
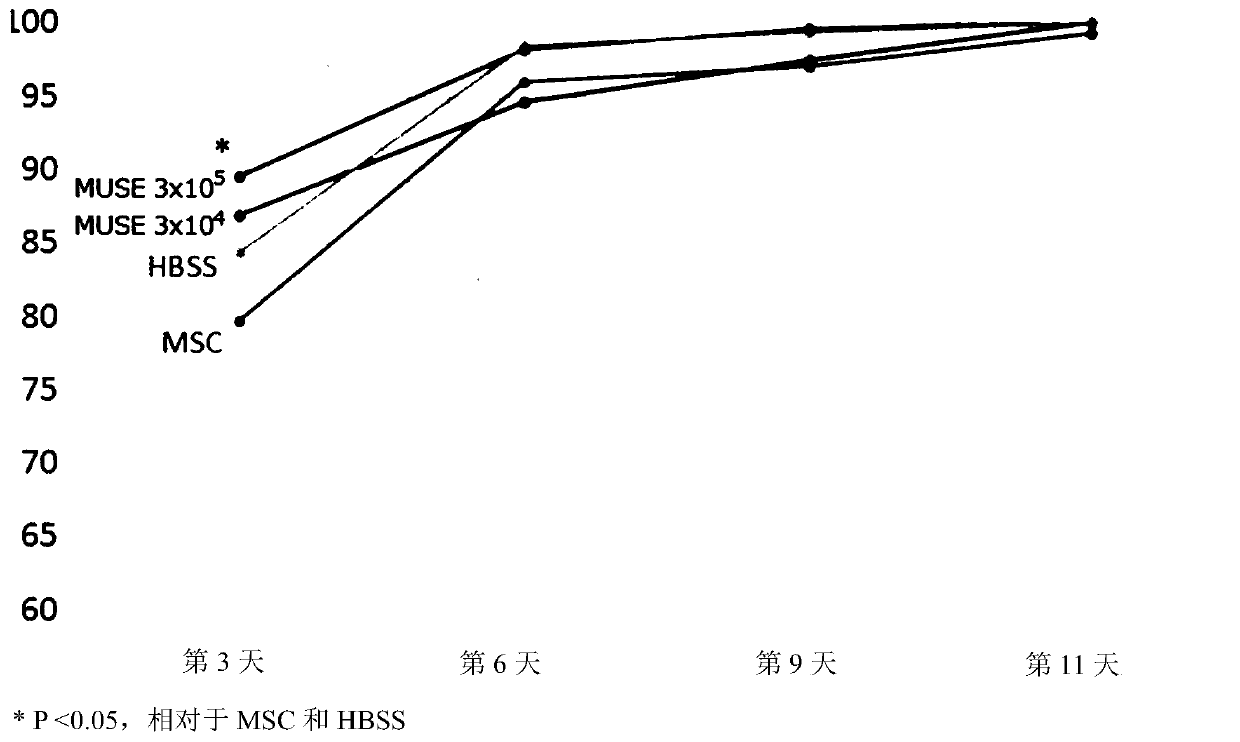
[0125] Adult C57BL / 6 mice were used as a model by performing full-thickness wounds on the back. Within 30 minutes from the implementation of the full-thickness wound, the Muse cells prepared above (3×10 5 / mouse or 3 x 10 4 / mouse), MSC (3×10 5 / mouse) or HBSS 200μl for tail vein injection to test the therapeutic effect.
[0126] In addition, the epithelialization rate was calculated as follows.
[0127] Use a ruler and a digital camera to take pictures of the back skin at the time of wound creation and the 3rd, 6th, 9th, and 11th day after wounding, and use Image J software (version 1.50i) to calculate the respective skin ulcer areas (mm 2 ). Taking the area at the time of wound creation as a reference value, the percentage (%) of area reduction rate was calculated.
[0128] [Formula 1]
[0129]
[0130] The result is as figure 1 with figure 2 shown. In either group, wounds healed over time, but ...
Embodiment 2
[0132] Example 2. Evaluation of COL17 knockout epidermolysis bullosa model mice
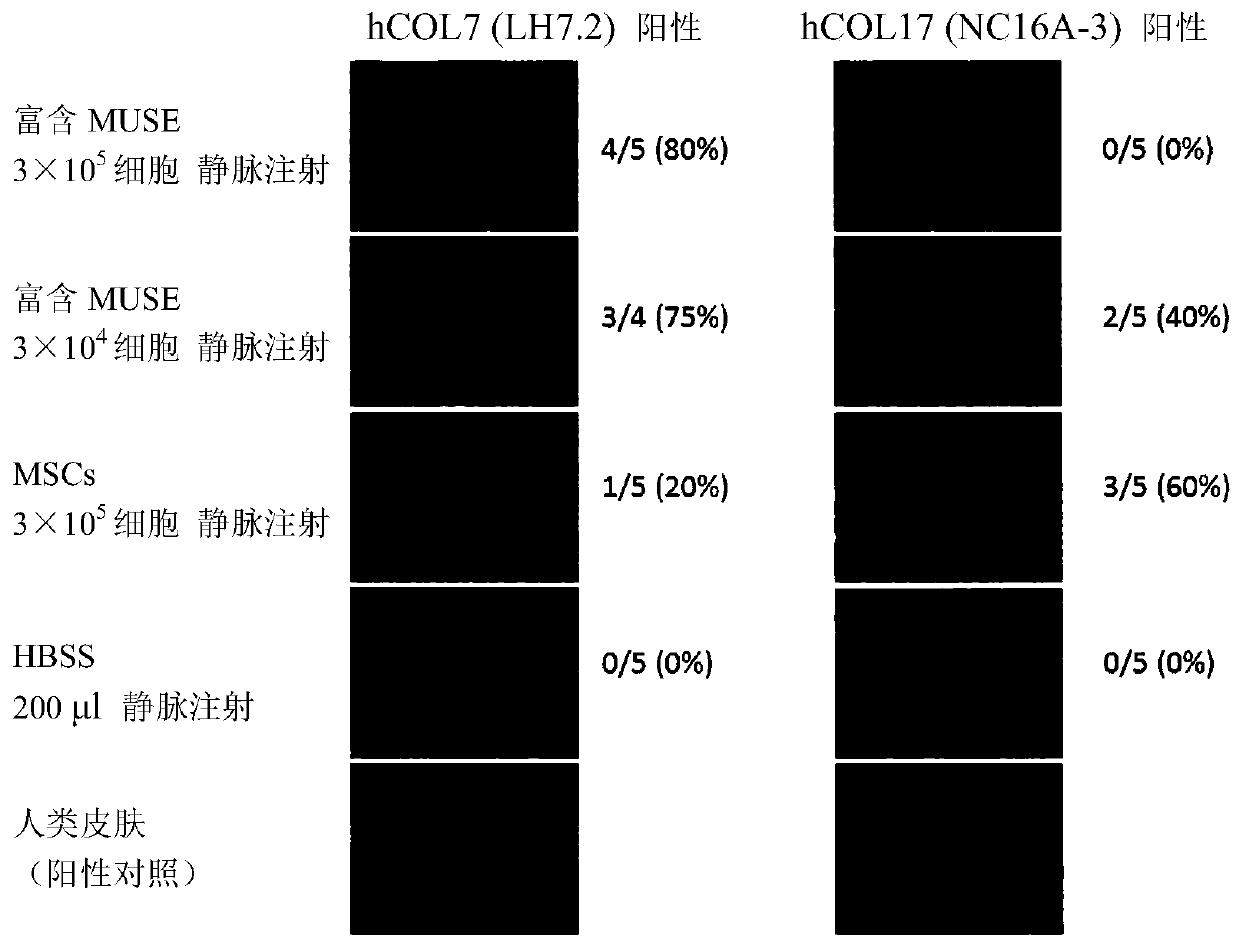
[0133] In COL17 knockout mice (reference Nat Med. 2007 Mar; 13(3): 378-83.) (3 to 4 weeks old), blisters are formed by rubbing the epidermis, and injected through the tail vein within 30 minutes from the formation of blisters Muse cells (3×10 5 / mouse). As a result of observing the state of the skin after one month, as Figure 4 As shown, in the control mice administered with HBSS, the state of the coat was poor, and the formation of wounds and mucosal erosions was widely confirmed, but in the mice administered with Muse cells, the state of the coat and the formation of wounds were relatively poor. light. In addition, skin tissue one month after the application was isolated, RNA was extracted therefrom, and expression of human-derived COL7 gene and COL17 gene was examined by RT-PCR. The result is shown in 5. As a result, the presence of human COL7 and human COL17 was confirmed in mice admini...
Embodiment 3
[0134] Example 3. Induction of differentiation of Muse cells into keratinocytes
[0135] Differentiation into keratinocytes was induced by culturing Muse cells according to the following procedure.
[0136] Inoculation of Muse cells on day 0
[0137] On the first day, culture with DMEM low glucose medium + 10% FBS + KGF (10ng / ml) + EGF (20-30ng / ml) for 3 days
[0138] On day 4, culture with DMEM low glucose medium + 10% FBS + KGF (10ng / ml) + EGF (20-30ng / ml) + HGF (10ng / ml) + IGF2 (60ng / ml), every other day Replace the medium once and culture for 8-14 days
[0139] The result is as Figure 7-9 shown. Such as Figure 7 As shown, cells at day 8 of differentiation exhibited a keratinocyte-like morphology. In addition, if Figure 8 with Figure 9 As shown, differentiation-induced cells showed expression of keratinocyte markers at both protein and mRNA levels.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com