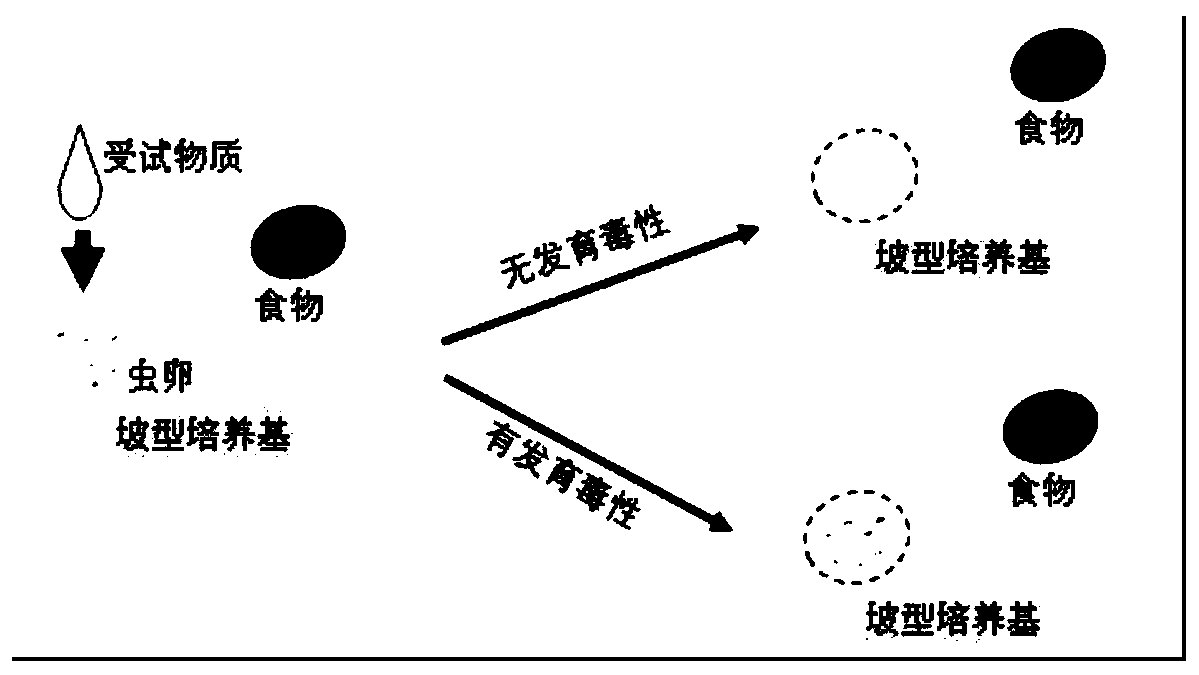
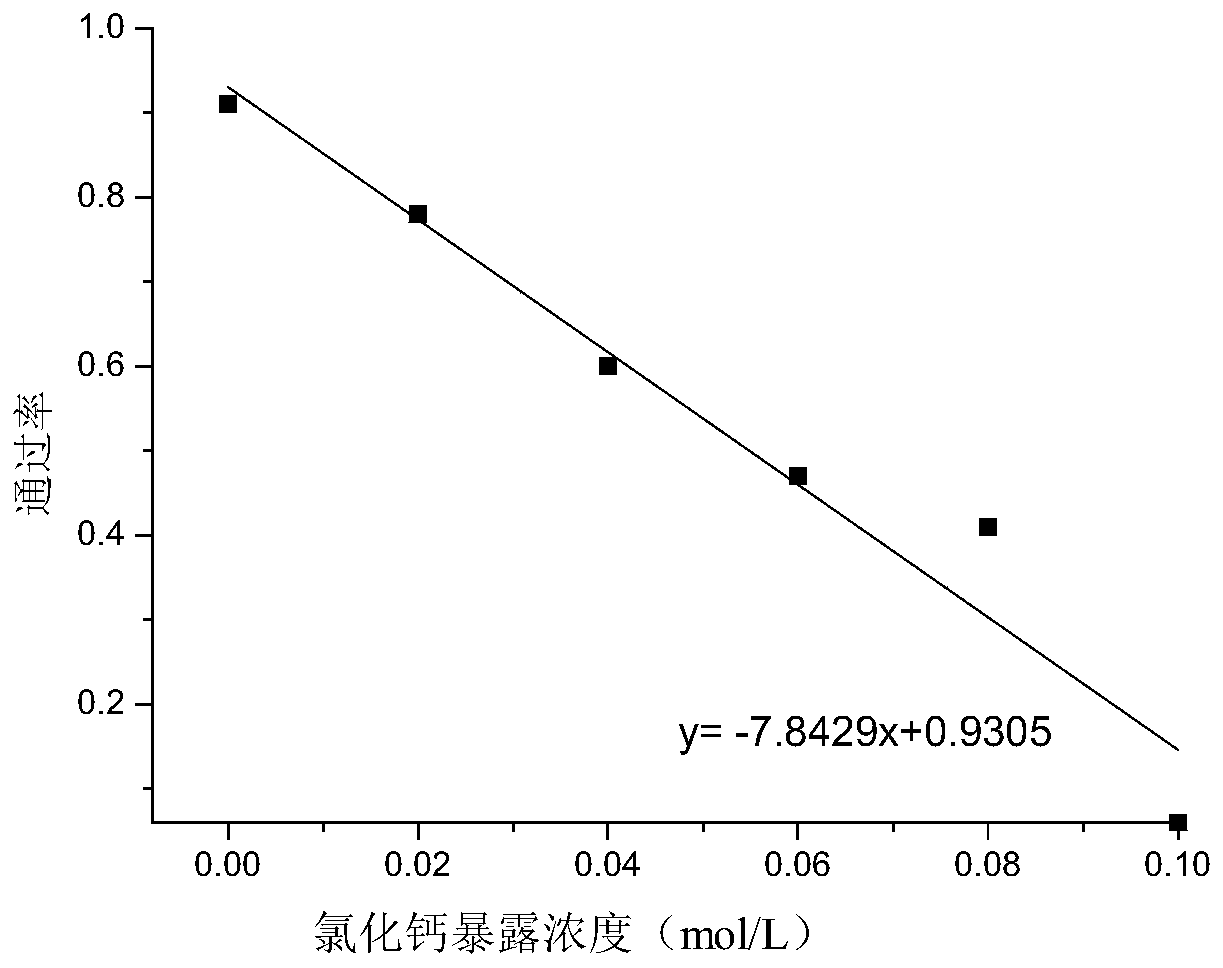
Method for detecting developmental toxicity by using caenorhabditis elegans
A Caenorhabditis elegans, toxicity technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, measuring devices, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of long detection cycle, low detection accuracy, etc., to shorten detection time, omit transfer Steps, the effect of speeding up the convenience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0026] In this embodiment, the method for detecting the developmental toxicity of calcium chloride using Caenorhabditis elegans comprises the following steps:
[0027] a. Preparation of bacteria solution: culture uracil-deficient Escherichia coli (ie E.coli OP50) for 24 hours with Escherichia coli liquid medium at 37°C and 200rpm, mix well and pour into a sterilized 15mL centrifuge tube, Centrifuge at 4000rpm for 5min, discard the supernatant, keep the bacteria that sink to the bottom, add 8mL sterile potassium solution and mix evenly, use a 24-well plate as a container, and use an enzyme-linked immunoassay instrument as a detection instrument to measure the concentration of the mixed solution per 300μL Absorbance at 570nm, if the absorbance value is less than 1.1 or greater than 1.3, centrifuge the mixture again, discard the supernatant, keep the bacteria that sink to the bottom, add 6mL or 10mL sterile potassium solution and mix, and measure the concentration of the mixture a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com