Light load detection and power tube partial conduction control method and circuit
A conduction control circuit, conduction control technology, applied in control/regulation systems, output power conversion devices, DC power input conversion to DC power output, etc. Problems such as poor load regulation rate, to achieve the effect of suppressing the output voltage floating, reducing the output voltage drop, and reducing the output voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
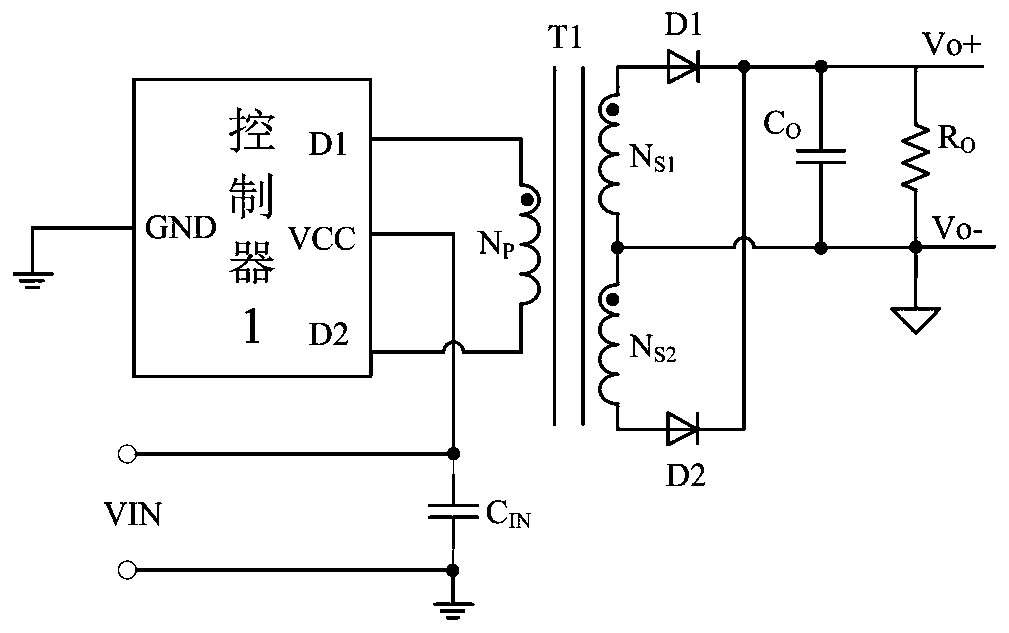
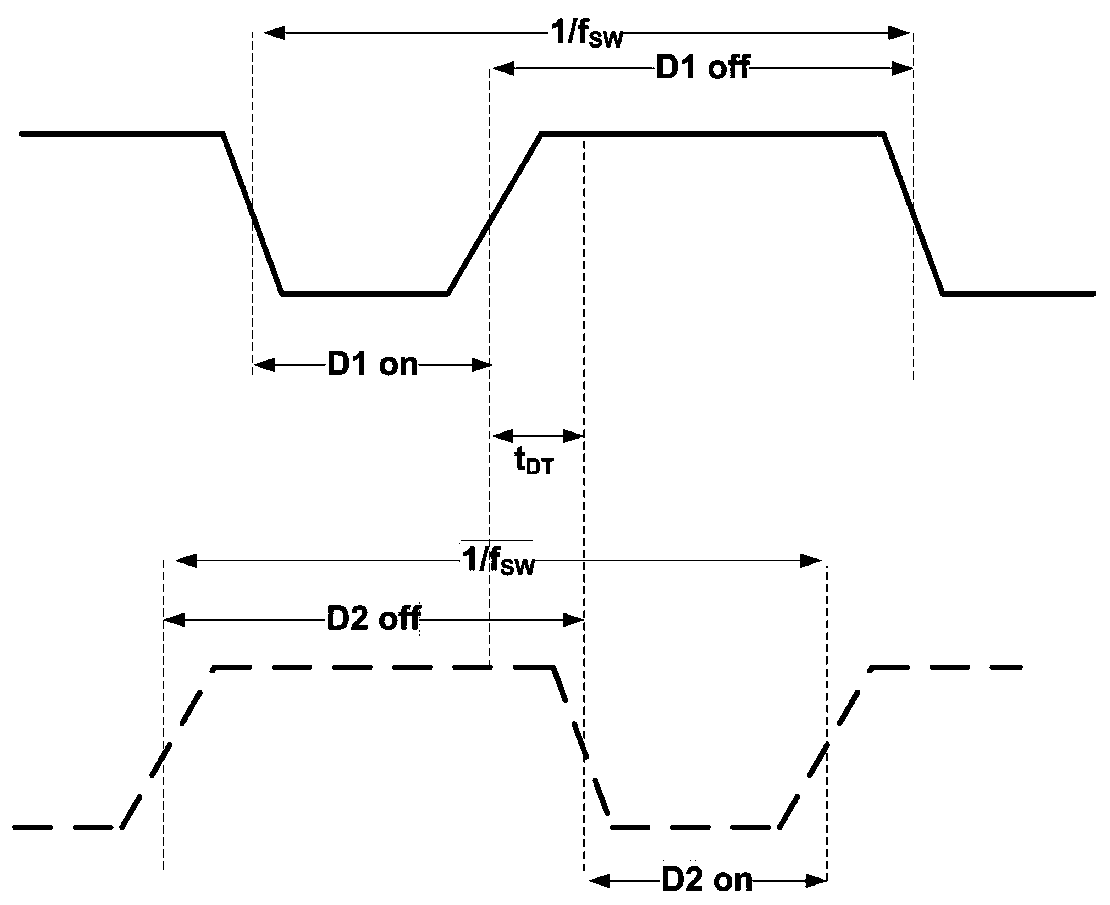
[0086] like Figure 4 Shown is a schematic circuit diagram of the application of the controller applying the light load detection and power tube partial conduction control circuit of the present invention to the driver of the full bridge converter. like Figure 4 As shown, the GND port of the controller 100 is connected to the ground, the D1 port is connected to the drains of the power transistors PM1_m, PM1_n, NM1_m, and NM1_n inside the controller 100, and connected to the drains of the winding N P Similarly, the D2 port is internally connected to the drains of the power transistors PM2_m, PM2_n and NM2_m, NM2_n, and externally connected to the winding N P The other end of the connection, the input filter capacitor C IN It is connected between the voltage input terminal VCC of the controller 100 and the ground to filter the input voltage VIN, and the anodes of the output rectifier diodes D1 and D2 are respectively connected to the two terminals of the secondary coil Ns1 an...
no. 2 example
[0122] The circuit principle diagram of the light load detection and power tube partial conduction control circuit in the controller 200 of the second embodiment of the present invention and Figure 5 The same, so no repeated drawing.
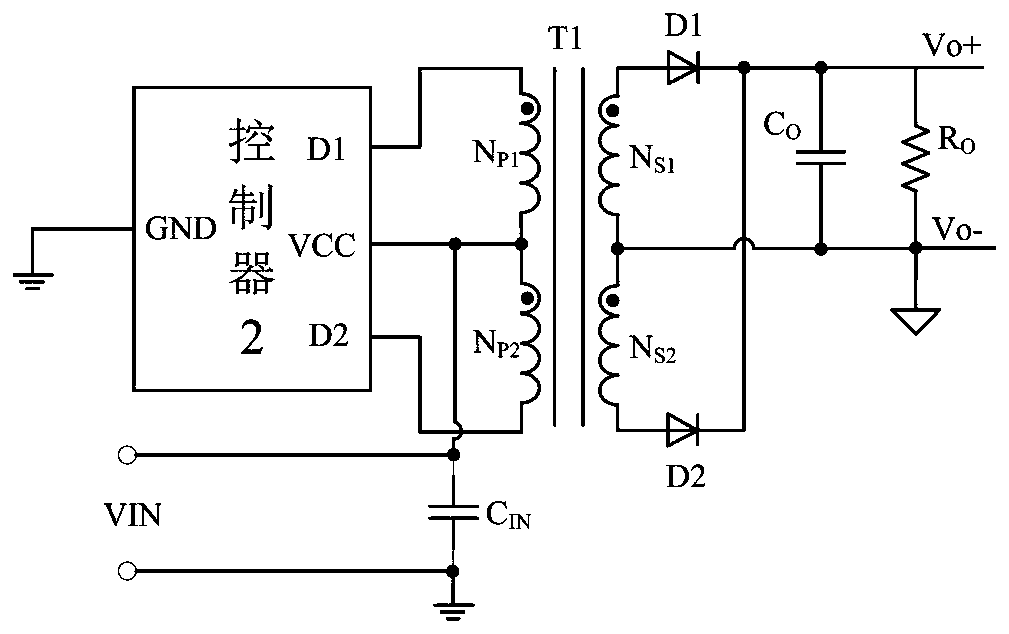
[0123] like Figure 17 Shown is a schematic circuit diagram of a push-pull driver application of a controller applying the light load detection and power tube partial conduction control circuit of the present invention. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that the VCC port of the controller 200 and the coupling transformer T1 Primary coil N p1 and N p2 The center tap connection of the controller 200, the D1 port is connected with the drains of the power transistors NM1_m and NM1_n inside the controller 200, the D2 port controller 200 is connected with the drains of the power transistors NM2_m and NM2_n, and its D1 and D2 ports are respectively connected with the coupling transformer T1 The primary coil N p1 and N p2 The two ends of the con...
Embodiment 2
[0127] The specific circuit principles and beneficial effects of the second embodiment are the same as those of the first embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
[0128] The above are only preferred embodiments of the present invention. It should be noted that the above-mentioned preferred embodiments should not be considered as limiting the present invention, and it should also be recognized that the present invention can be applied in other wider scopes. In addition, the present invention It is also applicable to a DC-DC isolation converter with only one power tube, but the power tube unit at this time outputs a power tube drain voltage signal. Compared with the first embodiment, the voltage detection unit needs to reduce one channel, due to the number of power tubes If it is reduced, the number of driving signal paths that the driving control unit needs to generate will also be correspondingly reduced. According to the above content of the present invention, using commo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com