Automobile brake system high-speed switch valve development test method
A technology for automotive braking systems and high-speed switching valves. It is applied in mechanical valve testing, circuit breaker testing, and by measuring fluid growth and deceleration rates. It can solve problems such as high labor intensity, lack of testing procedures, and reduced testing efficiency. Achieve the effects of improving pressure control accuracy, reducing product noise, and reducing testing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
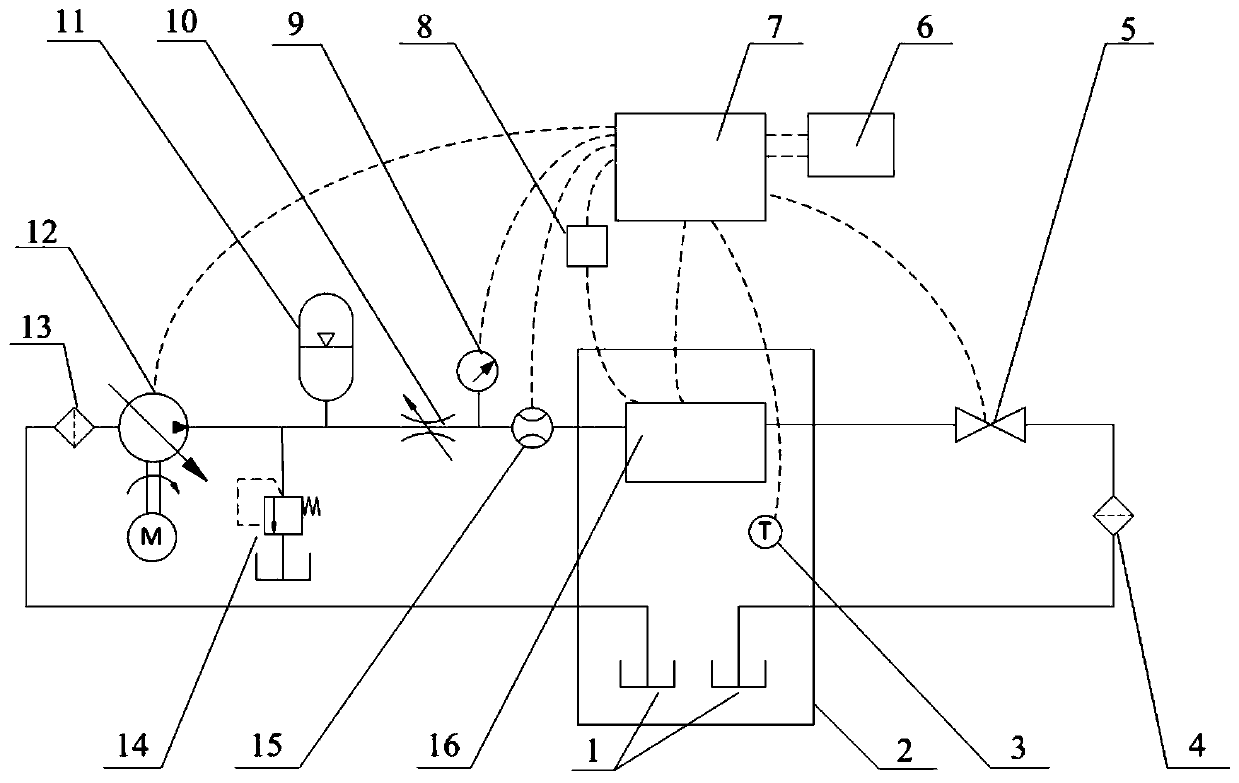
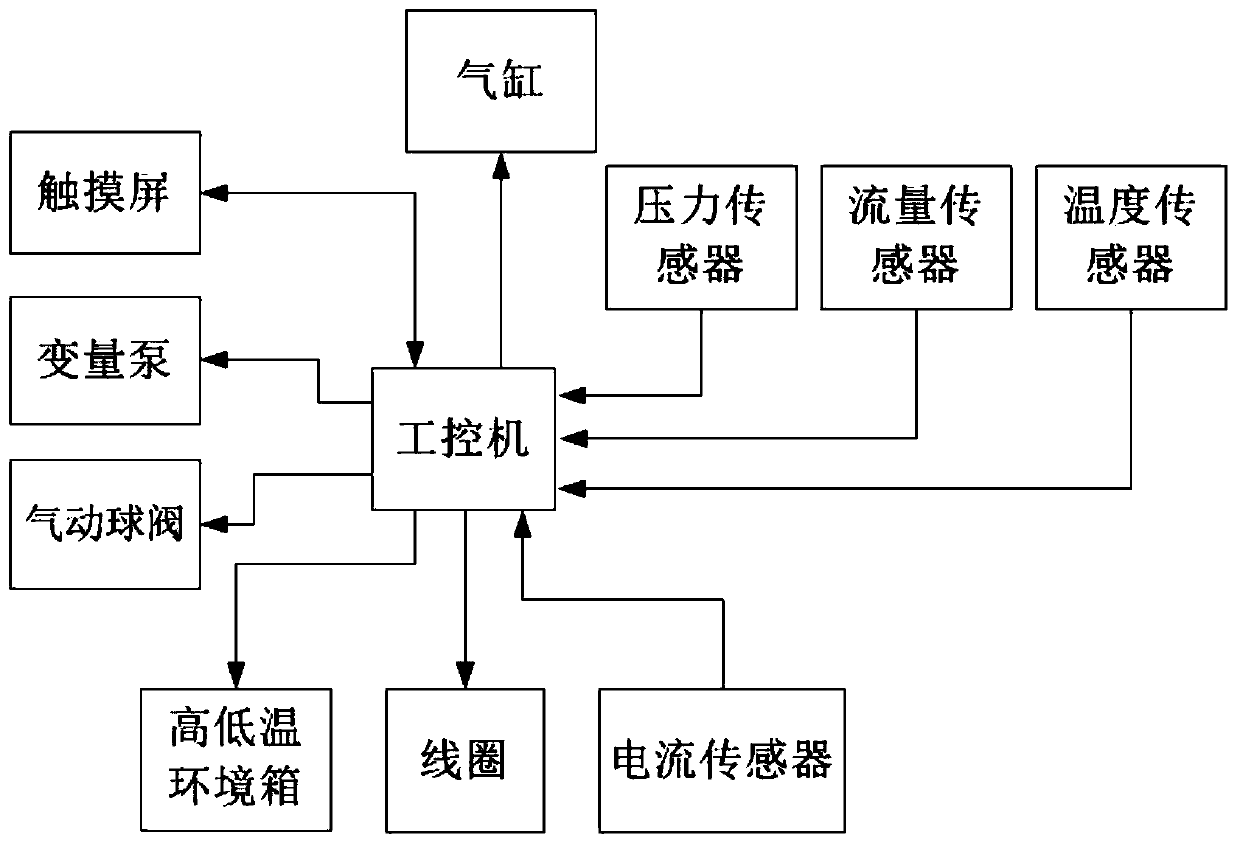
[0099] Embodiment 1: sealing self-test method, such as Figure 7 shown, including the following steps:
[0100] S001. Preset the pipeline tightness holding time Tp, the valve port sealing time Tv and the allowable pressure drop ΔPp within the pipeline sealing time Tp and the valve sealing time Tv through the touch screen 6 Allowable pressure drop ΔPv, and set tightness test pressure Ps;
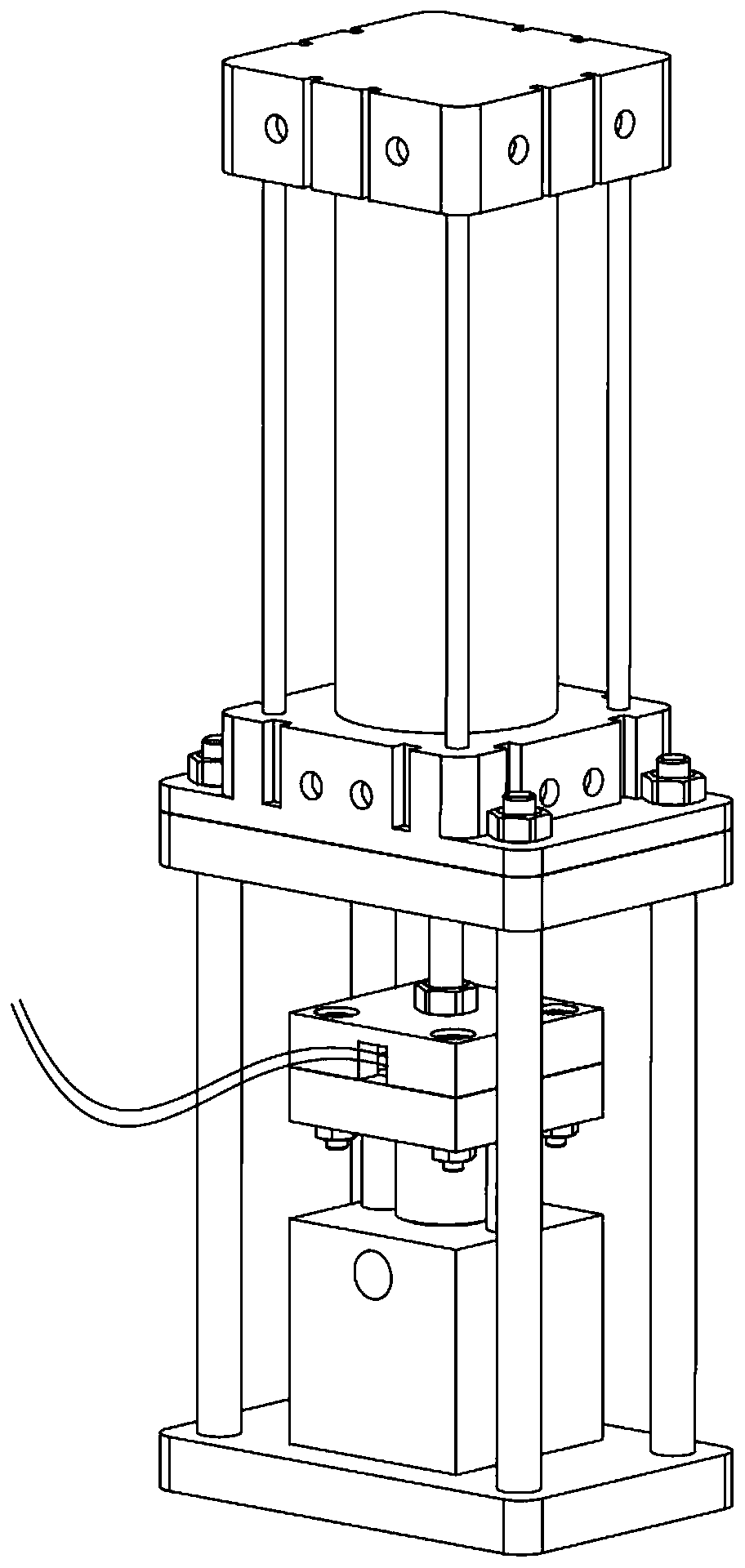
[0101] S002. Control the cylinder shaft 32 of the cylinder 23 to protrude downward through the control box 7, drive the upper pressure plate 27 to press the high-speed switch valve 29, control the closing of the pneumatic ball valve 5 through the control box 7, and establish a pipeline sealing test circuit;
[0102] S003, start the variable pump 12 through the control box 7, and close the variable pump 12 through the control box 7 after the pressure increases to Ps, record the value P1 of the pressure sensor 15 at this time, and start timing;
[0103] S004, record the value P2 of the pressu...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Embodiment 2: proportional flow test method, such as Figure 8 shown, including the following steps:
[0112] S020, set the ambient temperature Tg inside the high and low temperature environmental chamber 2, the valve inlet pressure Pg tested by the pressure sensor, the PWM frequency Fg, the initial value of the PWM duty ratio Dg0, the end value of the PWM duty ratio Dgn, and the value of a single test cycle through the touch screen. Coil energization duration Tgon, coil power-off duration Tgoff of a single test cycle, incremental duty cycle tolerance K of each test cycle, initial value of the number of tests i=1, total number of tests N;
[0113] The outlet of the valve is connected to the oil tank, and the outlet pressure of the valve is atmospheric pressure Pout (0.1MPa). The difference between the inlet and outlet pressure of the valve in this group of tests is the pressure difference of the valve port to be measured (Pg-Pout). In the actual vehicle ECU software cont...
Embodiment 3
[0121] Embodiment 3: proportional pressure test method, such as Figure 9 shown, including the following steps:
[0122] S030, set the ambient temperature Ty, the variable pump pressure Py, the PWM frequency Fy, the initial value of the PWM duty cycle value Dy0, the end value of the PWM duty cycle value Dyn, the coil energization time of a single test cycle Tyon, and The duration of coil power-off and power-on Tyoff for a single test cycle, the incremental duty cycle tolerance K of each test cycle, the initial value of the number of tests i=1, and the total number of tests N;
[0123] S031, the high and low temperature environment box 2 adjusts the temperature in the box to the ambient temperature Tg, and collects the temperature in the box through the temperature sensor 3;
[0124] S032, control the cylinder shaft 32 to extend through the control box 7, the upper pressing plate 27 presses the coil support, and the coil support presses the high-speed switching valve 29 to est...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com