Screening method and screening device of microsatellite sites pertinent to genome stability, and application
A genome stability, microsatellite locus technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, recombinant DNA technology, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problem of low accuracy of test results, achieve high accuracy, sensitivity and highly specific effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
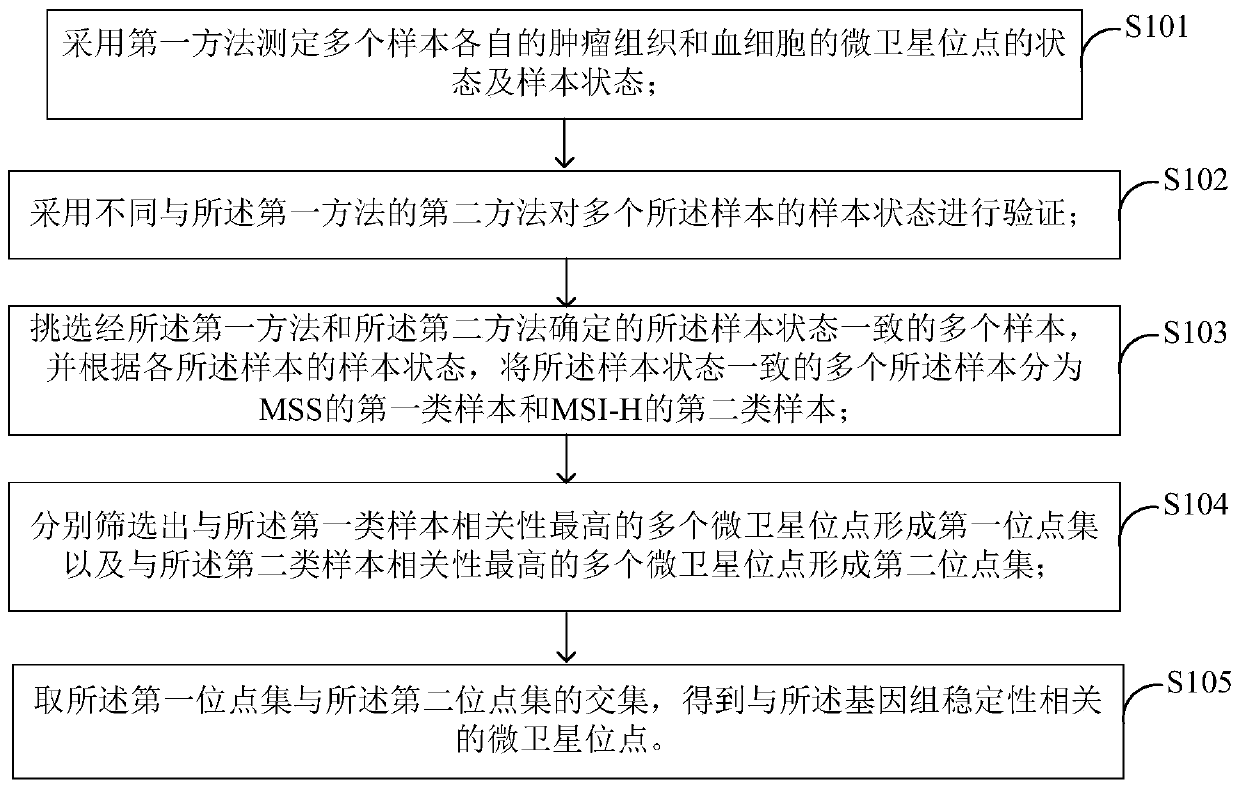
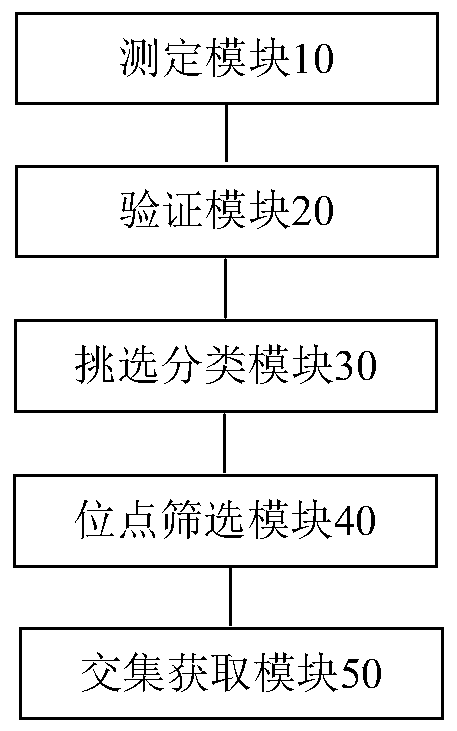
[0047] In a preferred embodiment of the present application, a method for screening microsatellite sites related to genome stability is provided, figure 1 is a flowchart of a method according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown, the screening method includes:
[0048] Step S101, using the first method to measure the state of microsatellite sites and sample state of tumor tissues and blood cells in multiple samples;
[0049] Step S102, using a second method different from the first method to verify the sample states of multiple samples;
[0050] Step S103, selecting a plurality of samples with the same sample status determined by the first method and the second method, and according to the sample status of each sample, classifying the multiple samples with the same sample status into the first type of MSS (i.e. MSS) samples and MSI-H (MSI-H) of the second category of samples;
[0051] Step S104, respectively selecting a plurality of microsatellite loci with ...
Embodiment 2
[0066]This embodiment provides a method for screening colorectal cancer tissue-specific microsatellite loci, and using this method to detect and verify the status of the samples. Specific steps are as follows:
[0067] 1. Obtain tumor tissue and white blood cell DNA from several colorectal cancer patients.
[0068] 2. Use the high-throughput microarray capture method to obtain the genome sequence of patient sample tumor and leukocyte control sample.
[0069] 3. Align the sequence obtained by sequencing with the human hg19 reference genome sequence, and remove the repeated sequence and the sequence aligned to multiple positions in the alignment result.
[0070] 4. Use the MSIsensor tool to scan the human hg19 reference genome sequence to obtain the distribution of microsatellite loci within the human genome.
[0071] 5. From the microsatellite sites distributed in the whole human genome, select all the microsatellite sites covering the capture interval of the chip.
[0072] ...
Embodiment 3
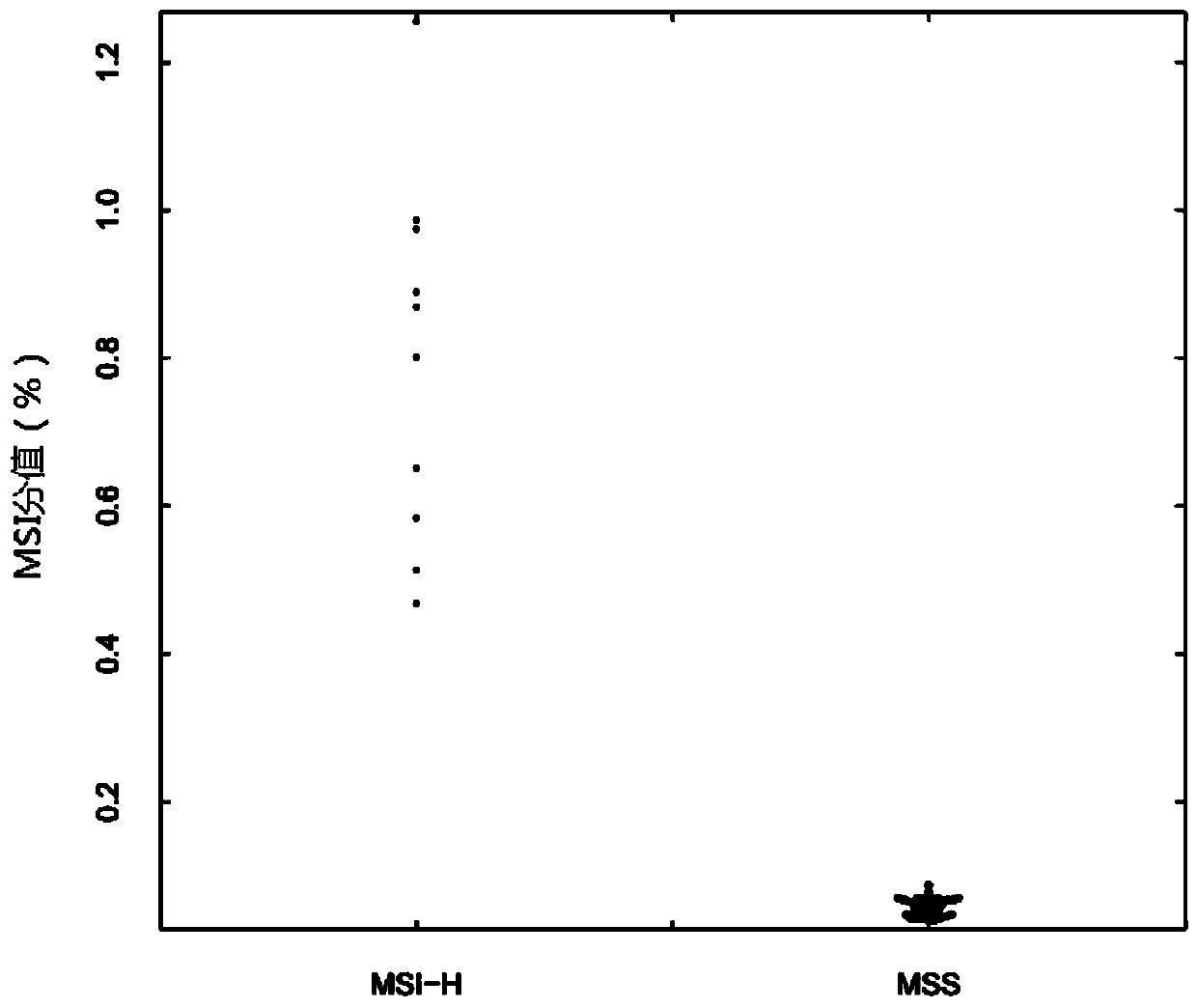
[0084] In this embodiment, a microsatellite site for detecting genome stability is provided, and the microsatellite site is screened by any of the above screening methods. The microsatellite sites screened by the above method of the present application are highly correlated with the unstable state of the microsatellite, so the stability state of the sample to be tested can be accurately distinguished, and the detection sensitivity and specificity are high (verified by MSI-PCR 64 cases of colorectal cancer samples, including 14 cases of MSI-H samples, 50 cases of MSS samples, using the microsatellite loci screened by the method of this application for genome stability detection, the method is correctly detected, sensitivity and specificity All of them are 100%, see Table 2 below for details.
[0085] Table 2:
[0086]
[0087] In a preferred embodiment, the microsatellite locus is a marked microsatellite locus of colorectal cancer tissue, and preferably the microsatellite l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com