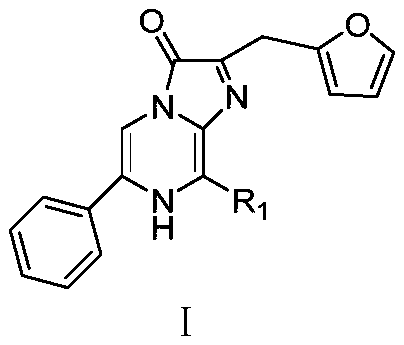
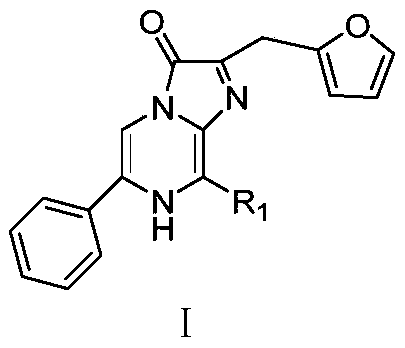
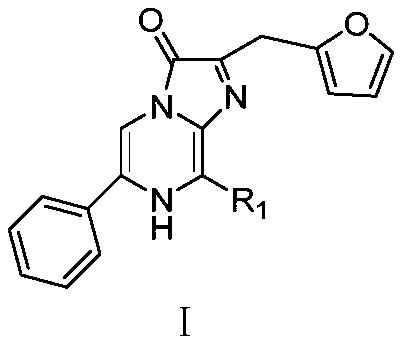
Phenyl imidazopyrazinone compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of phenylimidazole and compound, which is applied to phenylimidazopyrazinone compounds and the fields of preparation and application, can solve the problems of improving background signal, short emission wavelength, poor stability and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Example 1: Study on in vitro enzymatic activity of NanoLuc-type derivatives and NanoLuc luciferase.
[0076] 1. Determination of bioluminescence intensity and calculation of kinetic constants of enzymatic reactions: the measured values were calculated using GraphPad Prism to calculate the reaction kinetic constants and half life of different compounds. Based on the test results of Furimazine (2 μM), the relative bioluminescent intensity values of all compounds were converted.
[0077] 2. Determination of the maximum wavelength of bioluminescence: Add 0.5ml NanoLuc (0.6μg / ml) to 0.5ml of different target compounds dissolved in Tris-HCl (50mM, pH=7.42) and Furimazine (25μM), respectively, and use F- The 2500 fluorescence spectrophotometer is in the lamp off luminescence mode, the response time is set to 0.4s, and the emission spectrum is scanned to obtain the maximum biological emission wavelength.
[0078] Table 1. In vitro bioluminescent properties of NanoLuc-type ...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2: Study on the luminous intensity of NanoLuc-type derivatives and Renilla luciferase in vitro.
[0082] Add 50 μL of the target compound and Furimazine at different concentrations (0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 25 μM) dissolved in Tris-HCl (50 mM, pH=7.42) to 50 μL of Renilla fluorescent Sulfase (1 μg / ml) was placed in a black 96-well plate, and the intensity of bioluminescence was measured with the IVIS Kinetic small animal in vivo imaging system.
[0083] Table 2. In vitro bioluminescence intensities of NanoLuc-type derivatives and Renilla luciferase
[0084]
[0085] The results showed that all the target compounds gradually increased the luminescence intensity with the increase of the concentration, but were far lower than the luminescence intensity (lower three orders of magnitude) under NanoLuc luciferase, which also indicated that the target compound had a strong effect on NanoLuc luciferase. With high selectivity, it can be used as a probe to specifica...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Example 3: Study on the luminescence intensity of NanoLuc-type derivatives and Gaussisa luciferase in vitro.
[0087] Add 50 μL of the target compound and Furimazine at different concentrations (0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 25 μM) dissolved in Tris-HCl (50 mM, pH=7.42) to 50 μL of Gaussisa luciferase (0.5 μg / ml) in a completely black 96-well plate, the bioluminescence intensity was measured with the IVIS Kinetic small animal in vivo imaging system.
[0088] Table 3. In vitro bioluminescence intensity of NanoLuc type derivatives and Gaussisa luciferase
[0089]
[0090]
[0091] The results showed that compared with Furimazine, A1 and A2 exhibited stronger bioluminescence under the action of Gaussisa luciferase; however, the luminescence intensity of all compounds was much lower than that of NanoLuc luciferase, which indicated that the target compound had a strong NanoLuc luciferase is highly selective.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com