New purpose of sodium polyacrylate to modified starch or starch base foods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
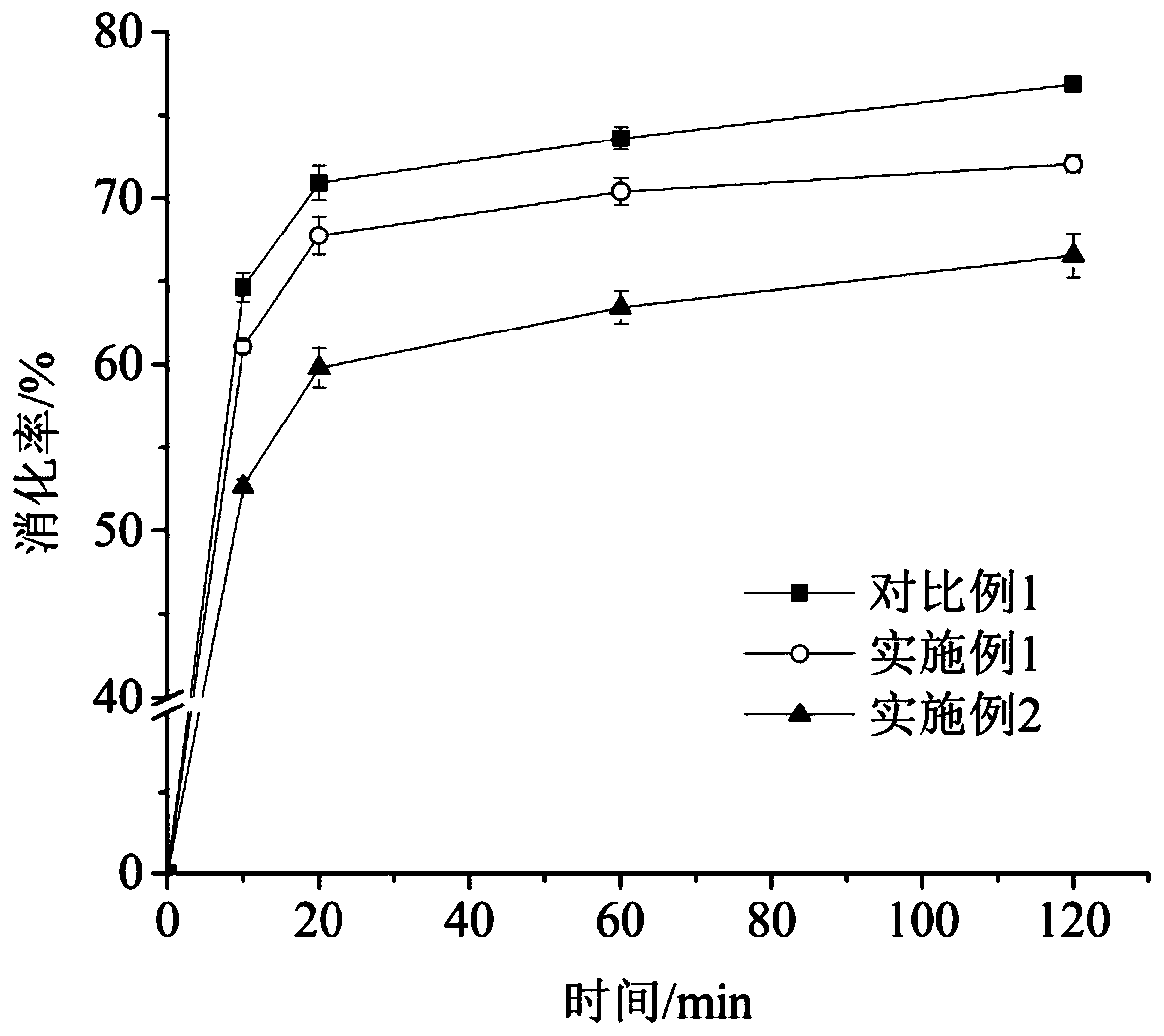
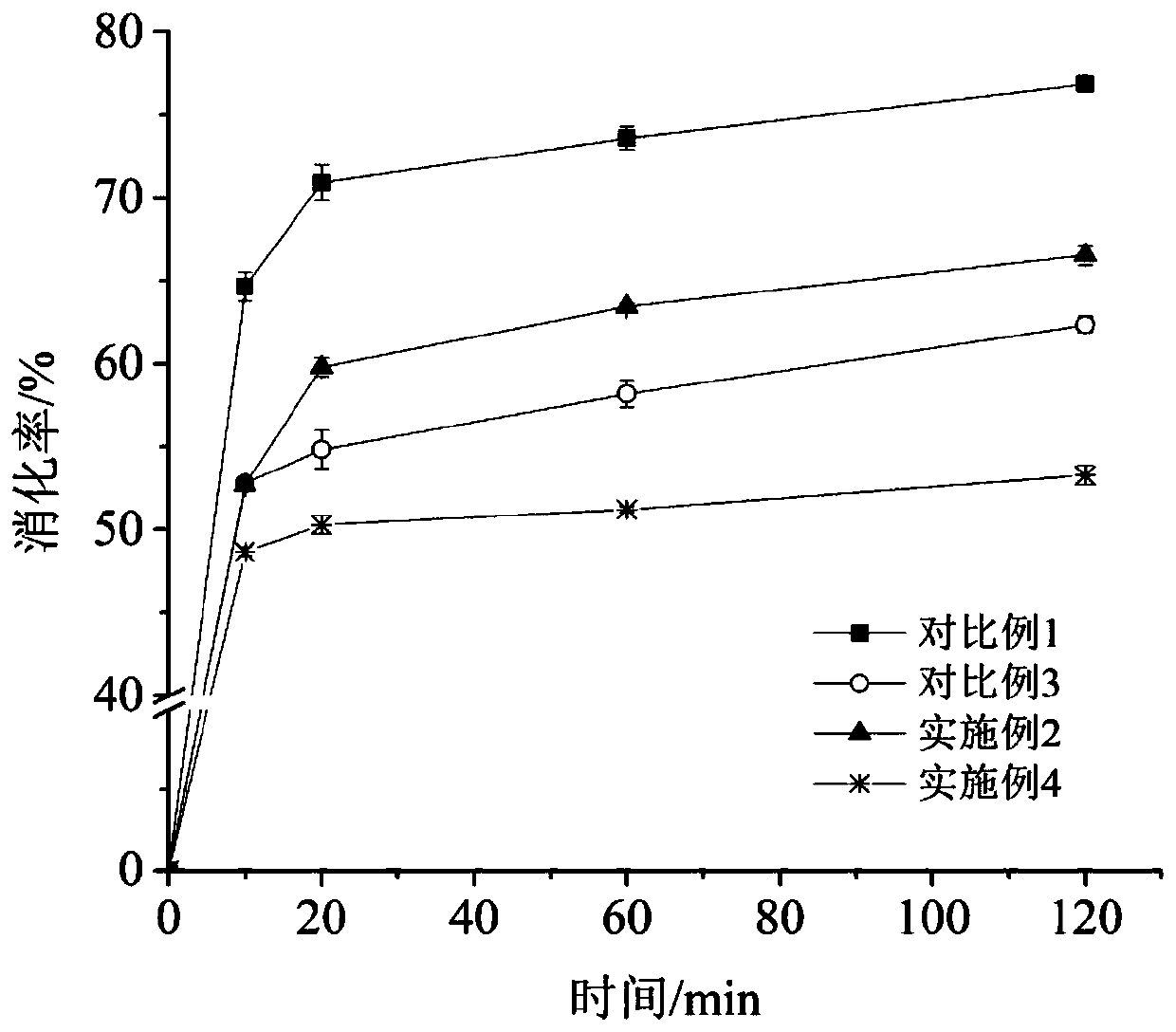
[0046] Fully dissolve 10 mg of food-grade sodium polyacrylate and 0.4 g of potato starch in 15 mL of pH 5.2 sodium acetate buffer to form a uniform mixed system. Put the mixed system in a boiling water bath and heat for 5 minutes, stir while heating. After complete gelatinization, cool at 0°C for 2 minutes, place on a shaker at 37°C to preheat for 20 minutes, add amylase for in vitro digestion test, the results are as follows figure 1 . Compared with Comparative Example 1, the digestibility at 10, 20, 60, and 120 minutes decreased by 3.58%, 3.16%, 3.19%, and 4.81%, respectively, which delayed the digestibility of potato starch as a whole and increased the RS content. The results showed that sodium polyacrylate had a significant inhibitory effect on the digestion of gelatinized potato starch, and theoretically speaking, sodium polyacrylate should have more significant resistance to digestion of raw potato starch. Therefore, sodium polyacrylate can be applied in slow digestible...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Fully dissolve 30 mg of food-grade sodium polyacrylate and 0.4 g of potato starch in 15 mL of pH 5.2 sodium acetate buffer to form a uniform mixed system. Put the mixed system in a boiling water bath and heat for 5 minutes, stir while heating. After complete gelatinization, cool at 0°C for 2 minutes, place on a shaker at 37°C to preheat for 20 minutes, add amylase for in vitro digestion test, the results are as follows figure 1 . Compared with Comparative Example 1, the digestibility at 10, 20, 60, and 120 minutes decreased by 11.94%, 11.12%, 10.15%, and 10.31%, respectively, which delayed the digestibility of gelatinized potato starch as a whole and increased the RS content. And with the increase of sodium polyacrylate addition, the decrease rate of the digestibility of this embodiment is greater than that of Example 1, indicating that the influence of sodium polyacrylate on starch digestibility is concentration-dependent. The results showed that sodium polyacrylate h...
Embodiment 3
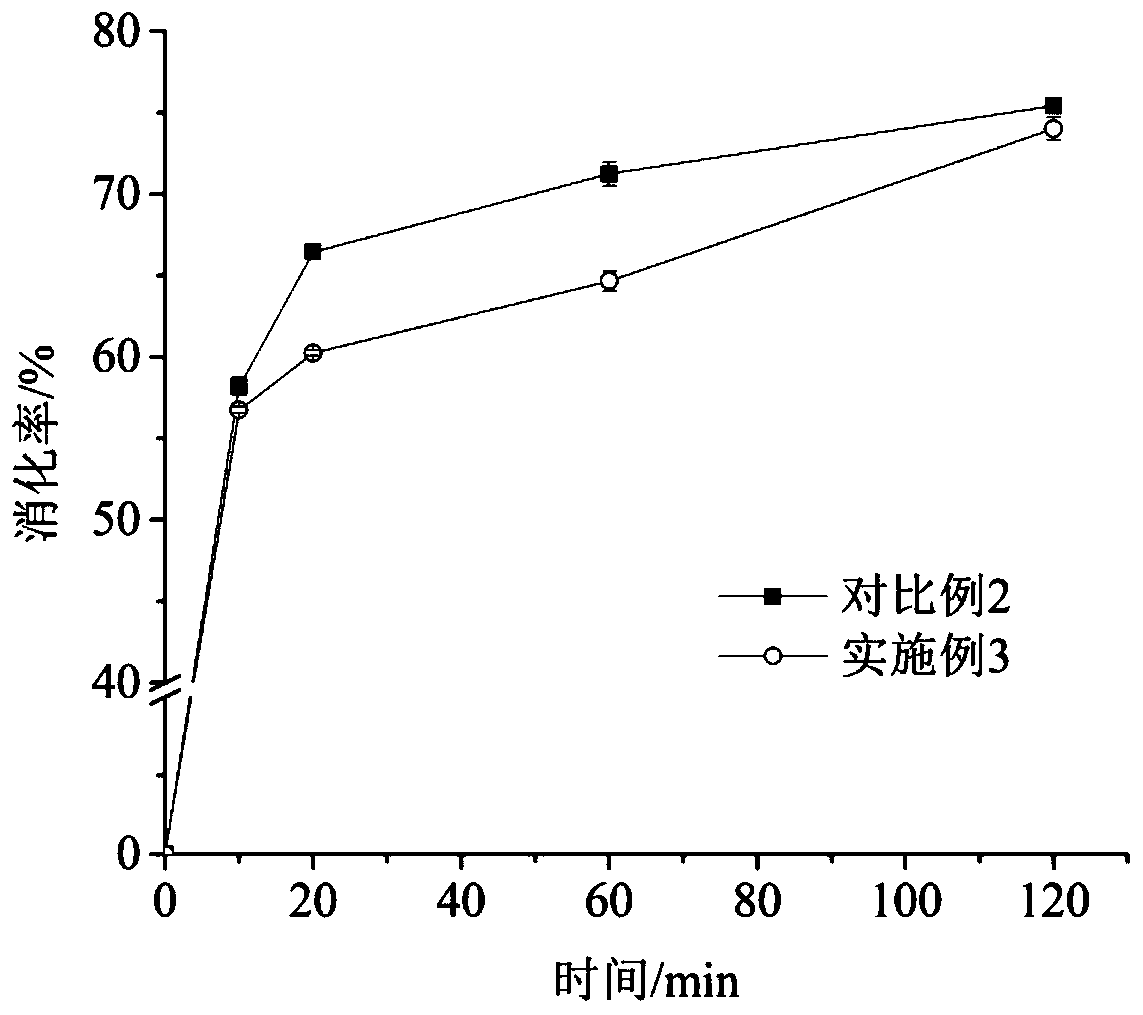
[0050] 30 mg of food-grade sodium polyacrylate and 0.4 g of glutinous rice starch were fully dissolved in 15 mL of pH 5.2 sodium acetate buffer to form a uniform mixed system. Put the mixed system in a boiling water bath and heat for 5 minutes, stir while heating. After complete gelatinization, cool at 0°C for 2 minutes, place on a shaker at 37°C to preheat for 20 minutes, add amylase for in vitro digestion test, the results are as follows figure 2 . Compared with Comparative Example 2, the digestibility at 10, 20, 60, and 120 minutes decreased by 1.44%, 6.22%, 6.58%, and 1.4%, respectively, and the inhibitory effect of sodium polyacrylate on the digestion of gelatinized glutinous rice starch was mainly manifested in the Halfway through, increase the SDS content from 8.96% to 13.78%. The inhibitory effect of sodium polyacrylate on the digestibility of gelatinized glutinous rice starch is different from that of gelatinized potato starch, which may be attributed to the differe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com