Method for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates by using acetic acid or butyric acid
A technology of polyhydroxyalkanoate and acetic acid, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve the problems of restricting large-scale industrial production and application, high production cost of PHA, etc., achieves good industrial application prospects, reduces fermentation costs, and has great economic advantages Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] Embodiment 1, utilize acetic acid to produce polyhydroxyalkanoate (shaking flask culture) with Neptunomonas
[0073] 1. Production of polyhydroxyalkanoate from acetic acid by Neptunonas bacterium
[0074] 1. Aseptically prepare Neptunonas seed solution
[0075] (1) Activation of bacteria
[0076] Take a glycerol tube of strains stored in a -80°C refrigerator, streak and inoculate it on a TYS medium plate, and incubate at 37°C for 12-24h.
[0077] (2) First-class seeds
[0078] Pick a single colony from the plate that has completed step (1), inoculate it in liquid TYS medium, and cultivate it at 37° C. with shaking at 200 rpm for 10-12 hours.
[0079] (3)Secondary seed
[0080] Take the primary seed liquid obtained in step (2), inoculate it in liquid TYS medium according to the inoculum amount of 1%, add 10 g / L acetic acid as carbon source, and culture at 37°C and 200 rpm for 10-12 hours with shaking.
[0081] 2. Prepare liquid TYS medium, add acetic acid to a final...
Embodiment 2
[0101] Embodiment 2, utilize butyric acid to produce polyhydroxyalkanoate (shake flask culture) with Neptunomonas
[0102] 1. Production of polyhydroxyalkanoate from butyric acid by Neptunomonas
[0103] 1. Aseptically prepare Neptunonas seed solution
[0104] (1) Activation of bacteria
[0105] Take a glycerol tube of strains stored in a -80°C refrigerator, streak and inoculate it on a TYS medium plate, and incubate at 37°C for 12-24h.
[0106] (2) First-class seeds
[0107] Pick a single colony from the plate that has completed step (1), inoculate it in liquid TYS medium, and cultivate it at 37° C. with shaking at 200 rpm for 10-12 hours.
[0108] (3)Secondary seed
[0109]Take the primary seed liquid obtained in step (2), inoculate it in liquid TYS medium according to the inoculum amount of 1%, add 10 g / L butyric acid as a carbon source, and culture at 37°C and 200 rpm for 10-12 hours with shaking.
[0110] 2. Prepare liquid TYS medium, add butyric acid to a final conc...
Embodiment 3
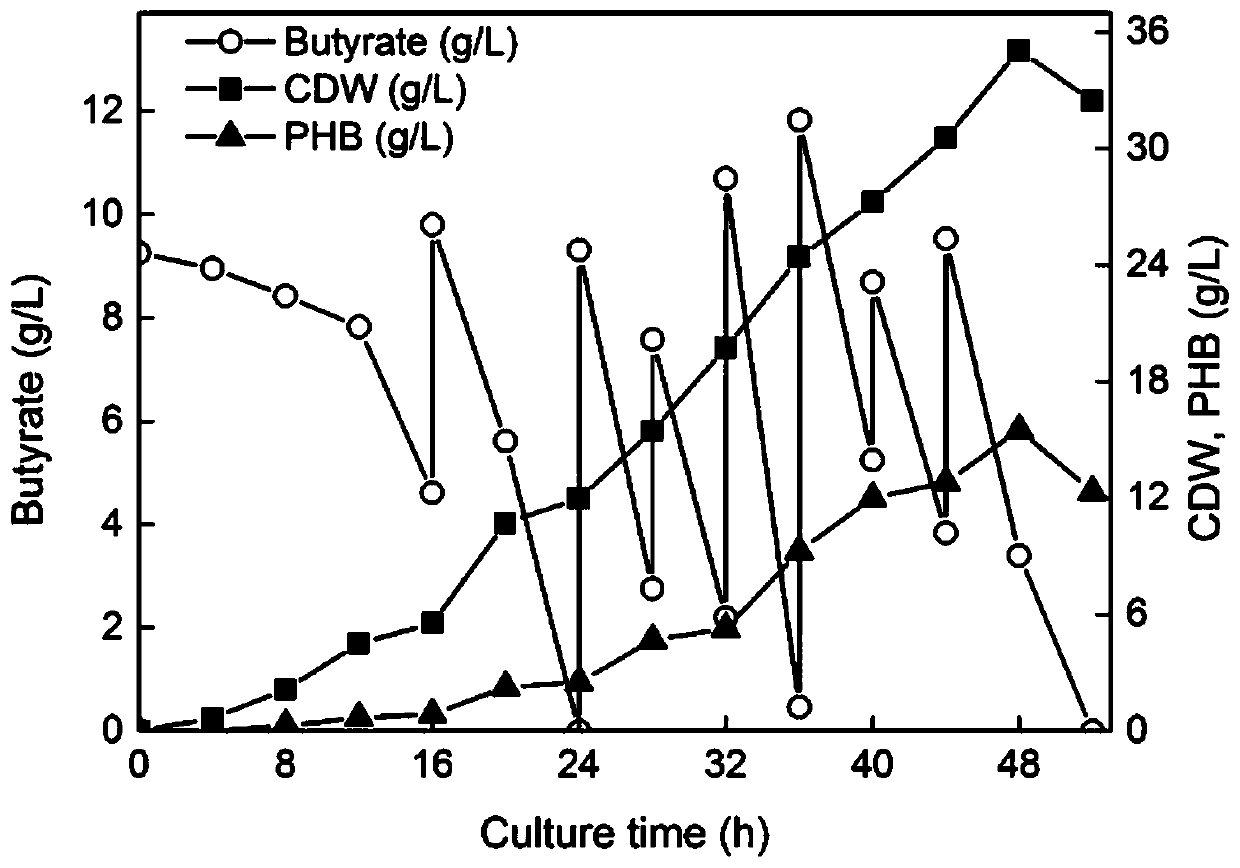
[0121] Embodiment 3, utilize butyric acid to produce polyhydroxyalkanoate (fermenter cultivation) with Neptunomonas
[0122] 1. Production of polyhydroxyalkanoate from butyric acid by Neptunomonas
[0123] 1. Aseptically prepare Neptunonas seed solution
[0124] (1) Activation of bacteria
[0125] Take a glycerol tube of strains stored in a -80°C refrigerator, streak and inoculate it on a TYS medium plate, and incubate at 37°C for 12-24h.
[0126] (2) First-class seeds
[0127] Pick a single colony from the plate that has completed step (1), inoculate it in liquid TYS medium, and cultivate it at 37° C. with shaking at 200 rpm for 10-12 hours.
[0128] (3)Secondary seed
[0129] Take the primary seed liquid obtained in step (2), inoculate it in liquid TYS medium according to the inoculum amount of 1%, add 10 g / L butyric acid as a carbon source, and culture at 37°C and 200 rpm for 10-12 hours with shaking. A total of 300ml of secondary seed liquid is required for fermenter ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com