Foot-type robot terrain perception method based on virtual sensor
A virtual sensor and terrain perception technology, applied in the field of robot perception, can solve problems such as the impact of the robot's movement performance, the inability to complete predetermined tasks, and the reduction of system robustness. Dynamically responsive effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
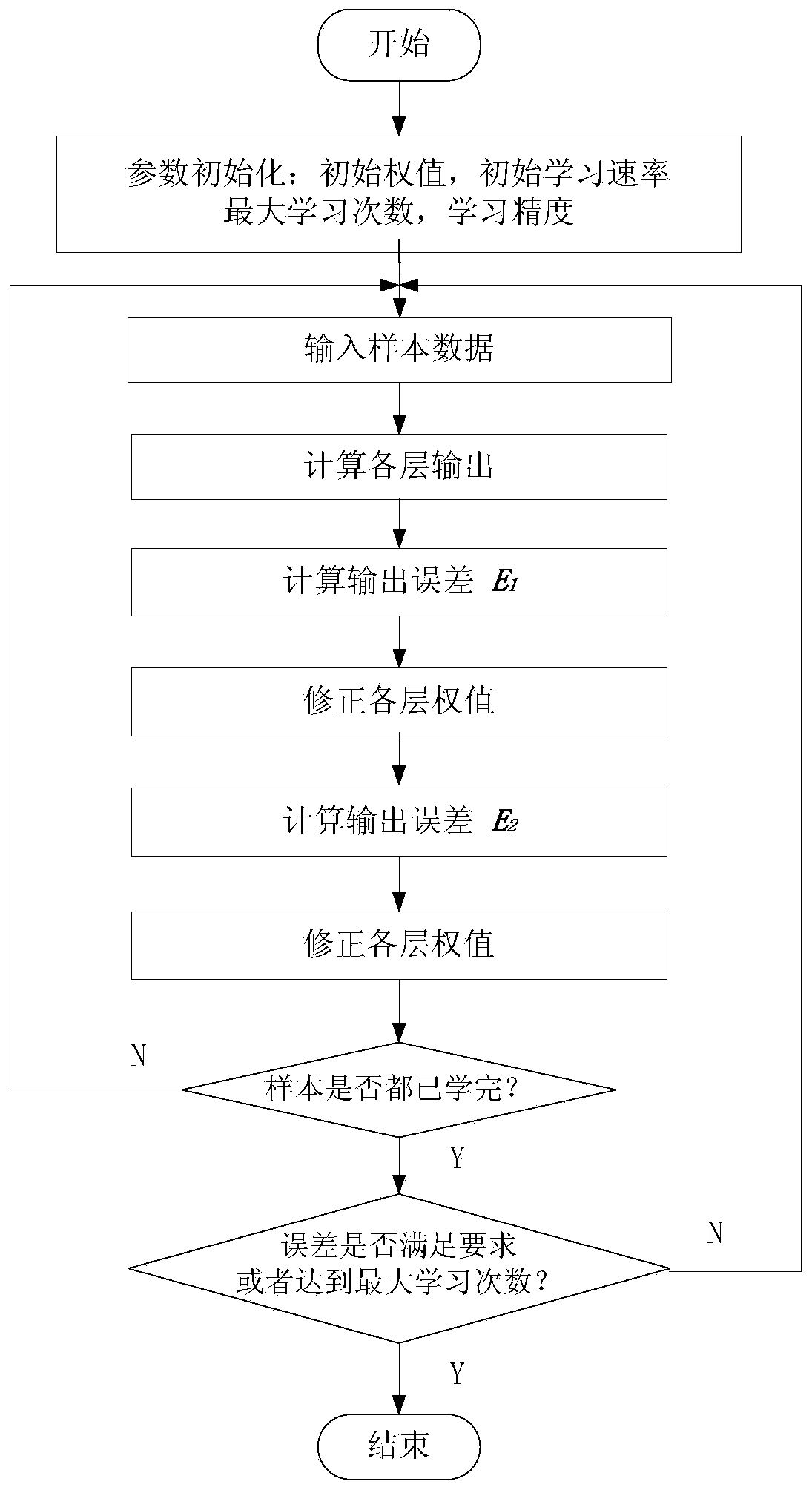
[0040] Step (1) Modeling of terrain-aware machine learning model
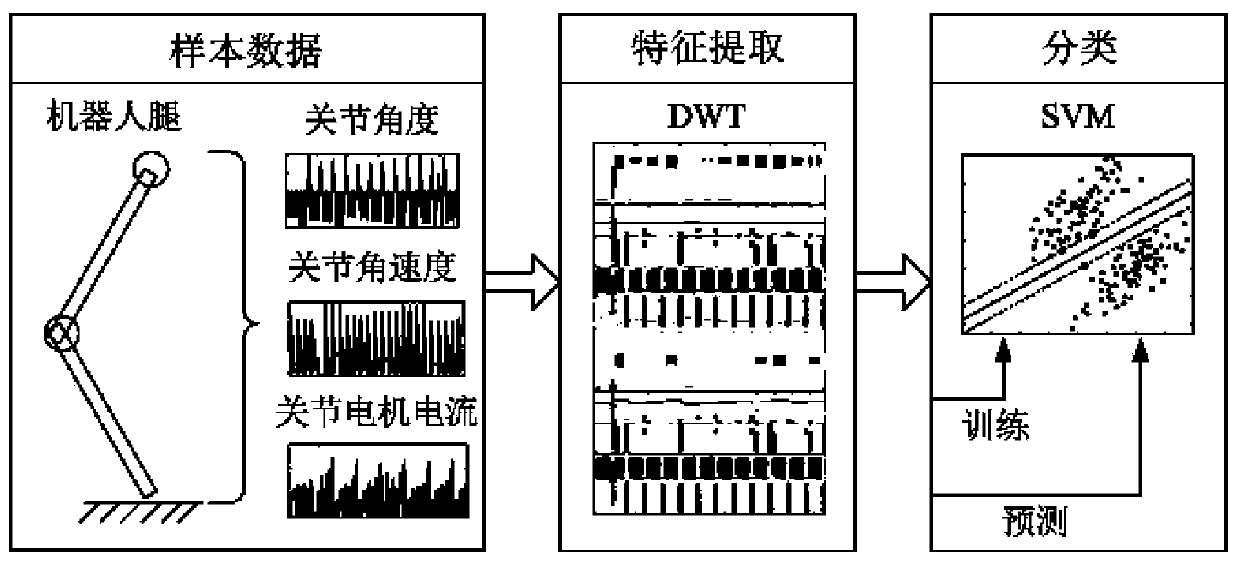
[0041] The modeling of the terrain perception machine learning model is mainly divided into two parts: touchdown detection neural network modeling and soil classification machine learning model modeling
[0042] 1) Touchdown detection neural network modeling
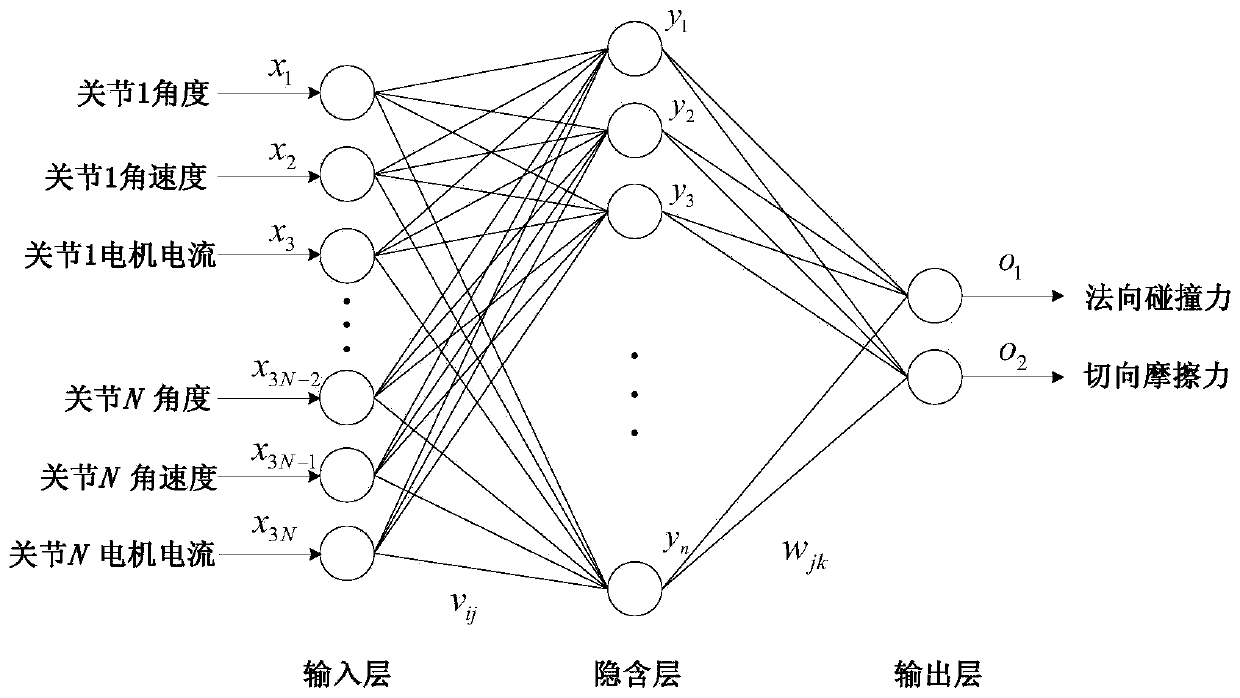
[0043]A neural network learning algorithm considering derivative information is established to establish a neural network model for the ground contact detection of a legged robot to achieve ground contact detection. The neural network model of touchdown detection includes three layers: input layer, hidden layer and output layer, and each layer is connected by function operation relation. The input signal of the input layer is the joint angle, joint angular velocity and joint motor current of each joint of a single leg. If the number of leg joints is N, the input layer of the touchdown detection neural network model contains 3N nodes. The output signal ...
Embodiment 2
[0091] A method for terrain perception using virtual sensors for legged robots, which mainly includes four components: (1) sample data collection; (2) terrain perception machine learning model modeling; (3) machine learning model algorithm; (4) Virtual Sensor Terrain Awareness System. The composition of each part is described in detail below.
[0092] (1) Sample data collection
[0093] In order to verify the effectiveness of this method, a hexapod robot's single-leg ground-touching experiment is designed. The schematic diagram of the experimental scheme is as Figure 5 As shown, a one-dimensional force sensor is installed on the sole of one leg of the robot, and the sampling frequency is 1000 Hz. In the experiment, the robot touched the ground with different centroid heights, different walking speeds, and different materials. Among them, the single walking cycle is taken as: 3s, 4s, 5s, 6s, 7s, 8s, 9s, 10s; the height of the centroid: 0.36m, 0.42m; the ground material: al...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com