Patents
Literature
363results about How to "Improve terrain adaptability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
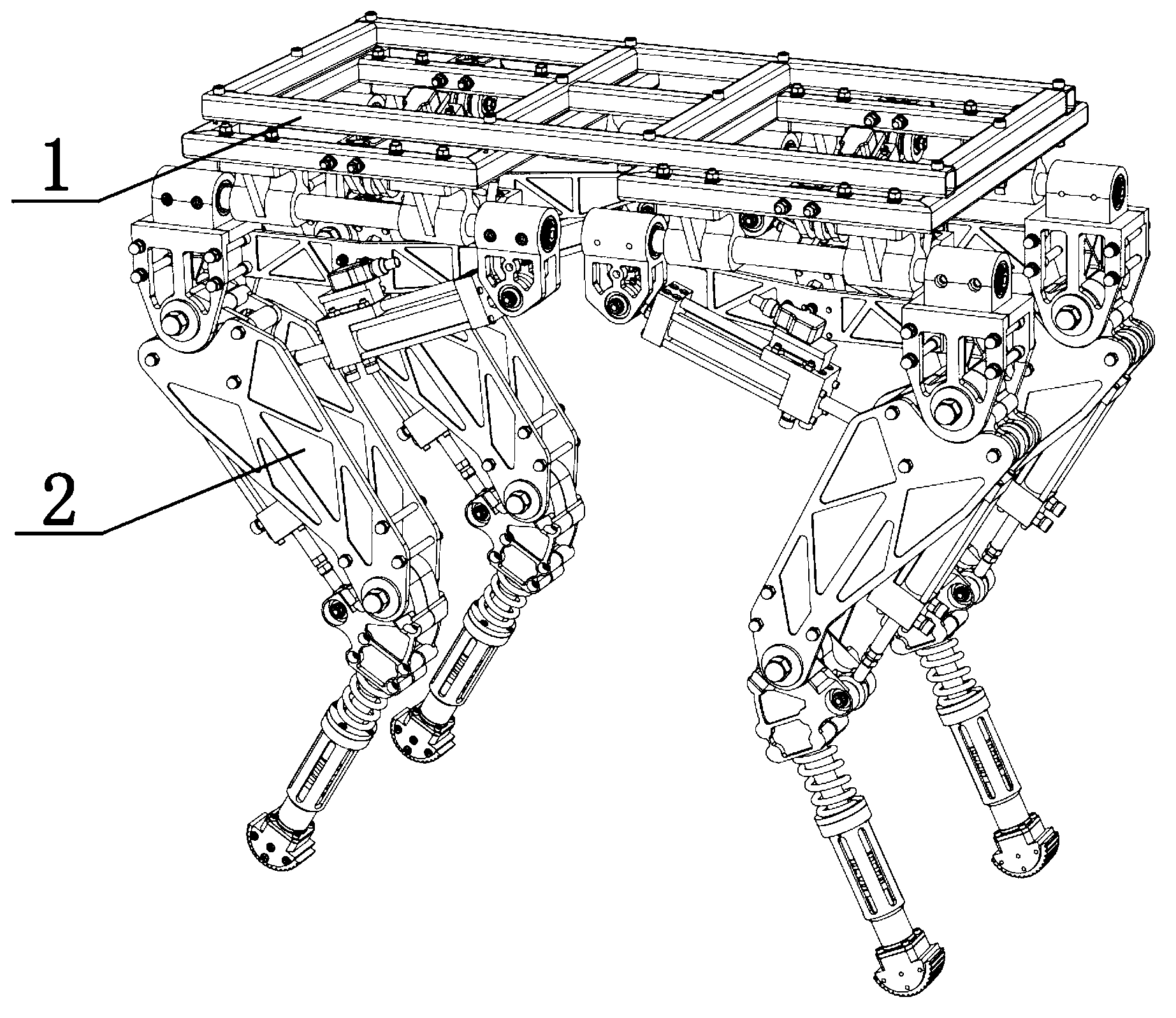
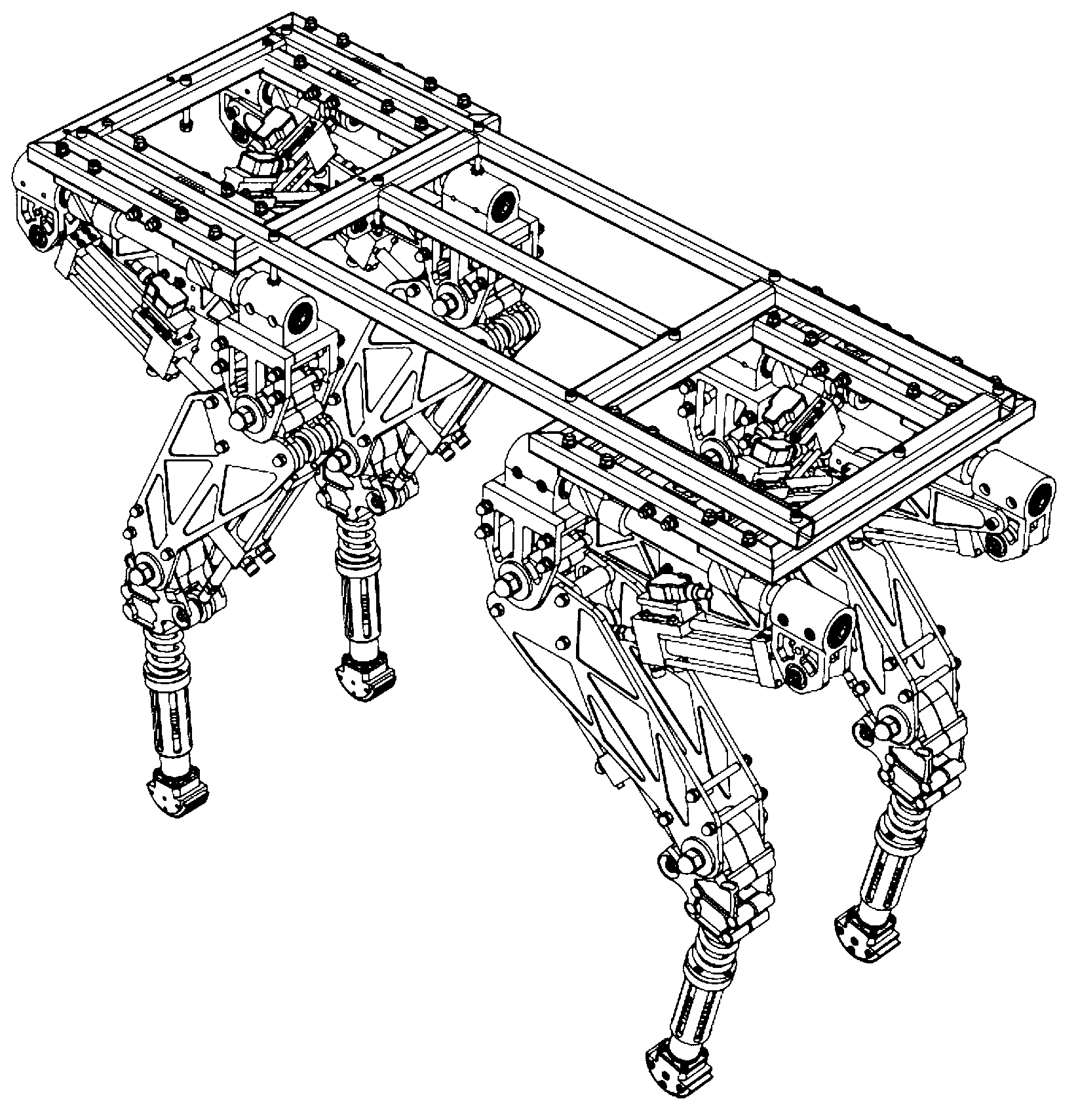
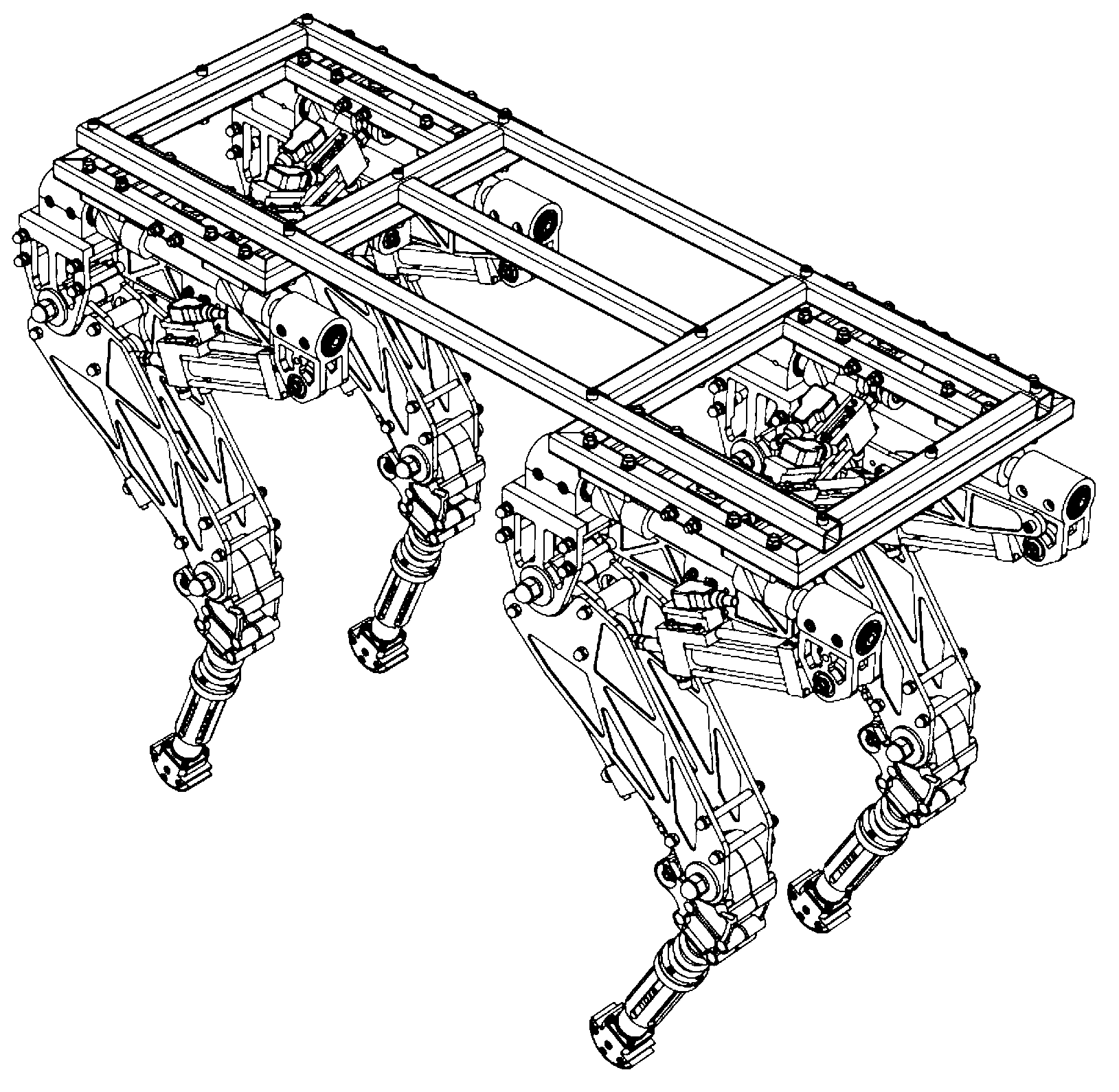
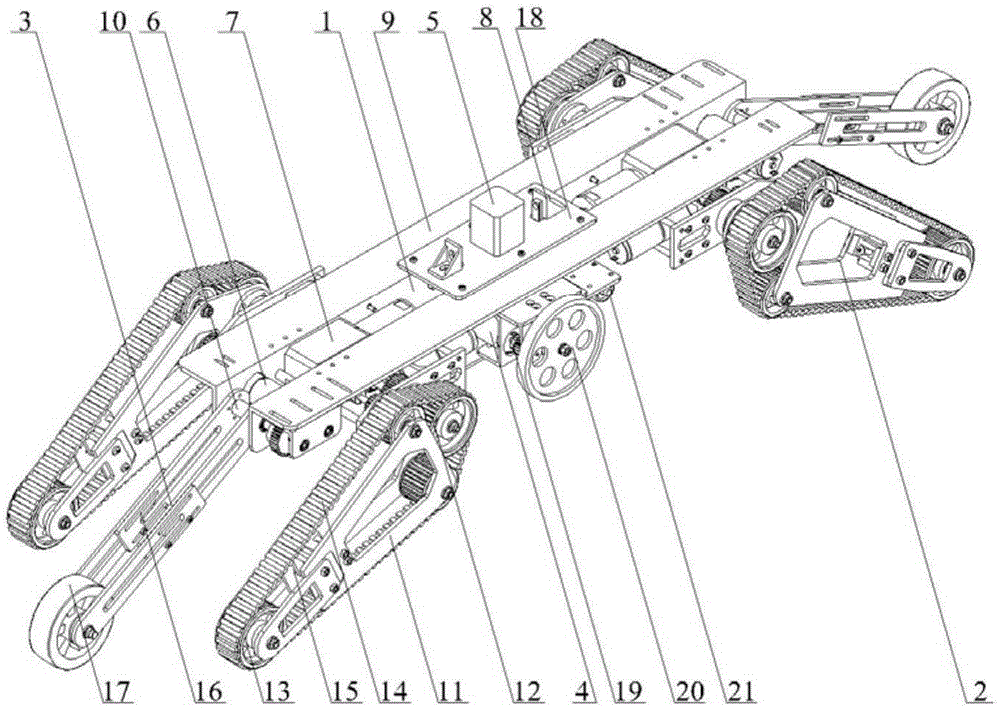
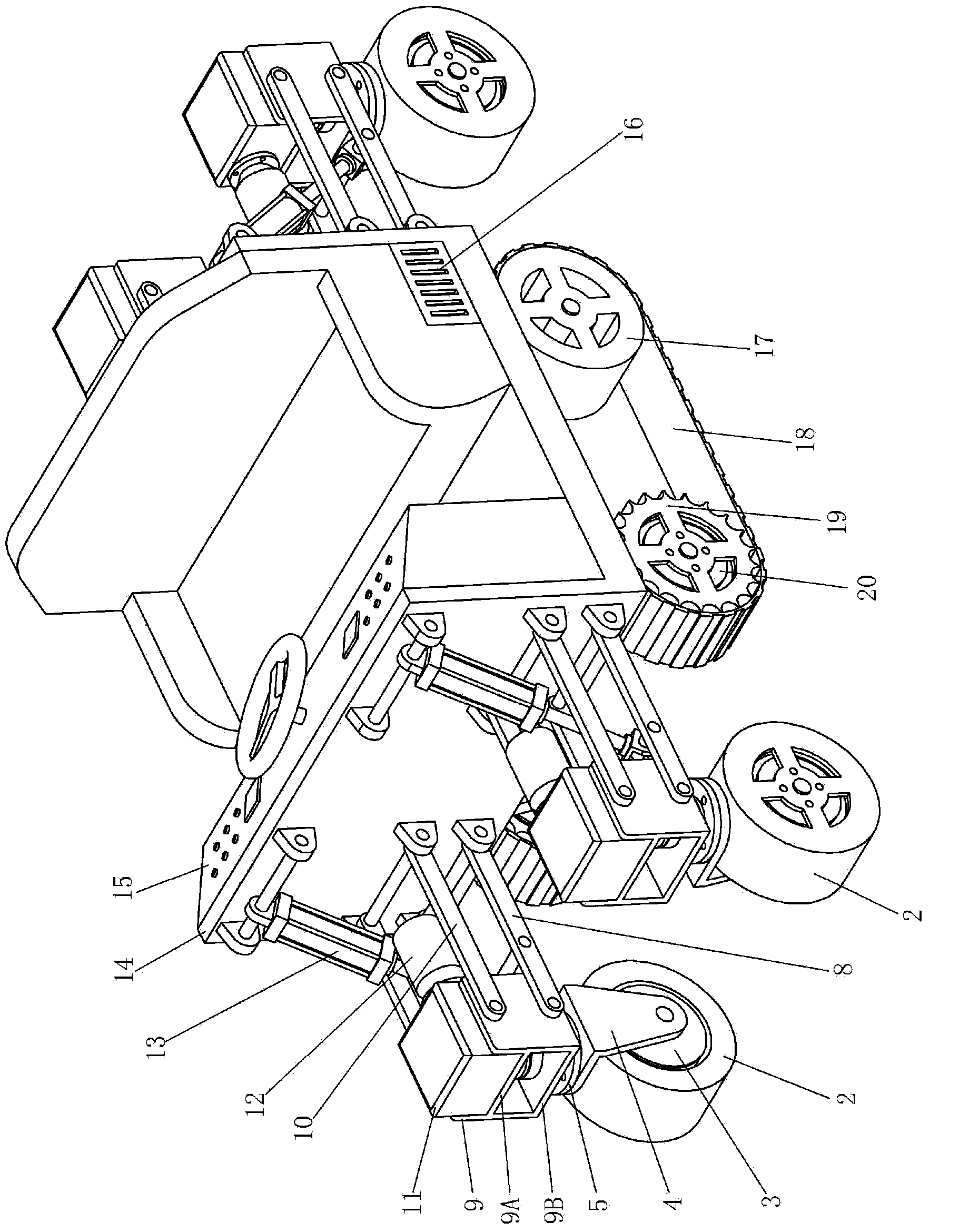
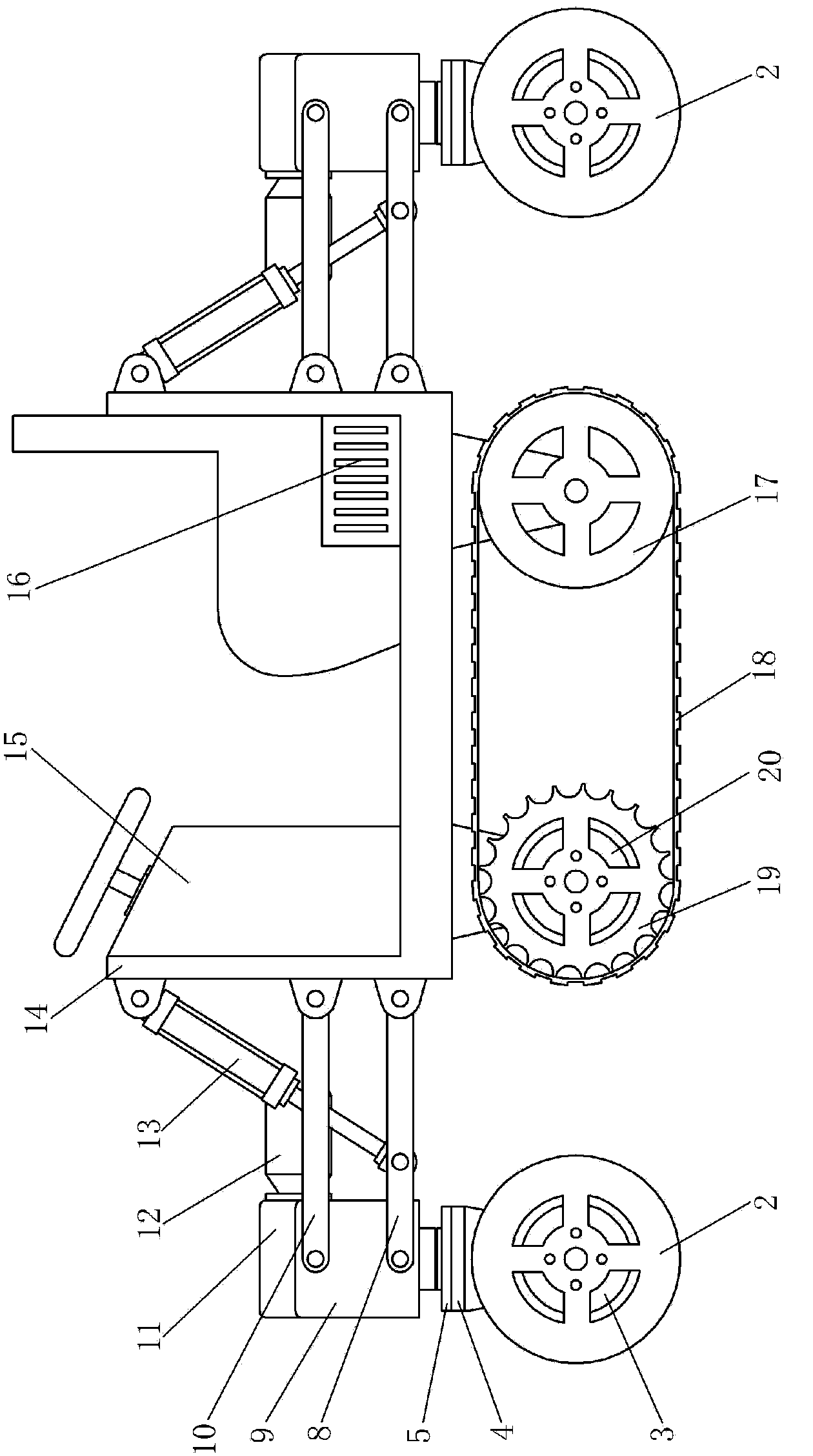
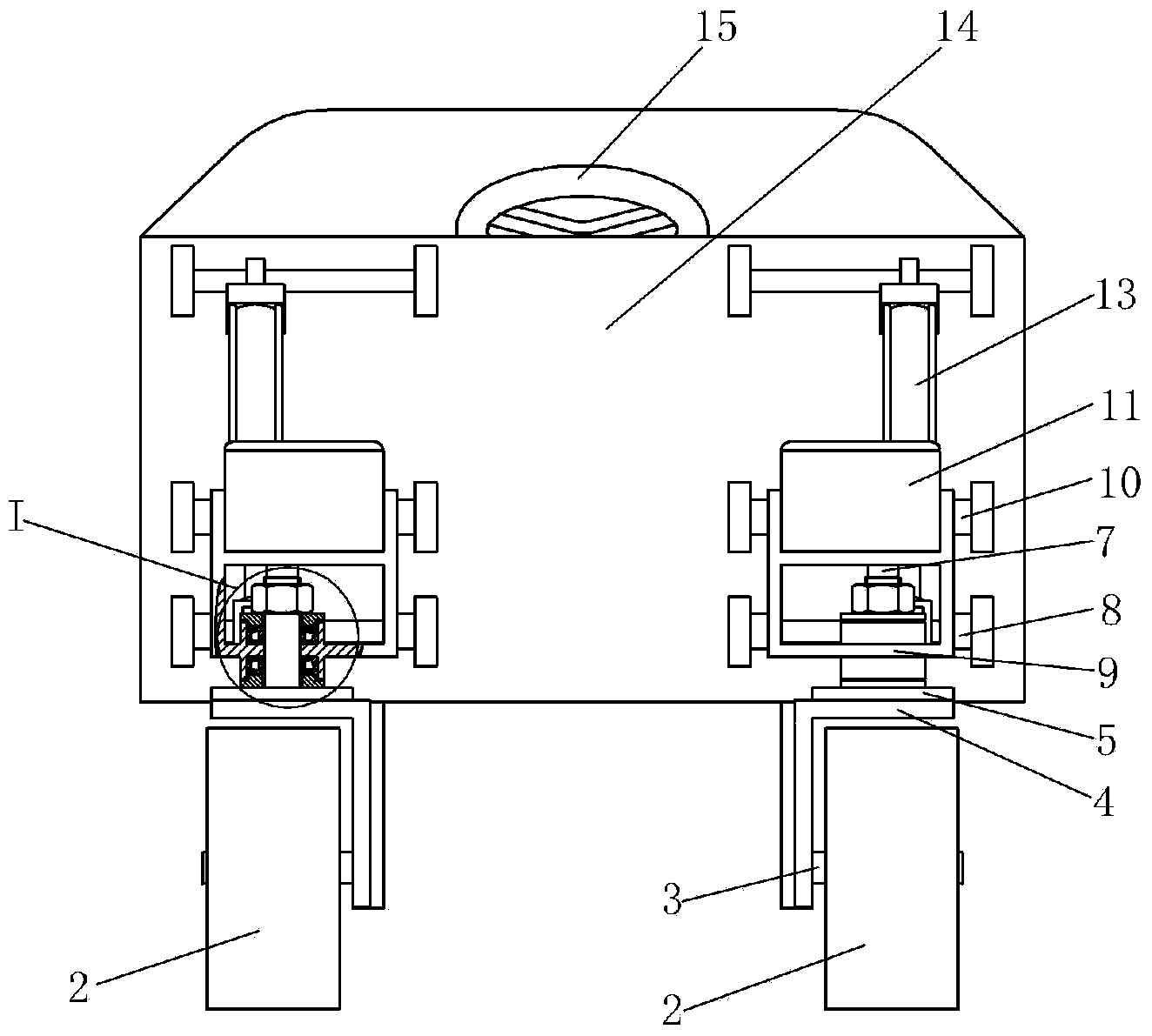
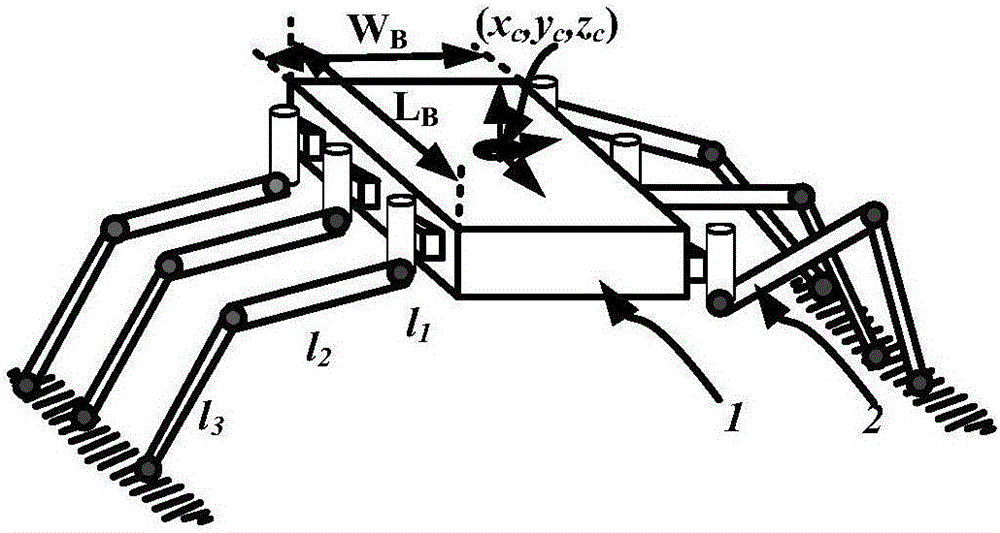
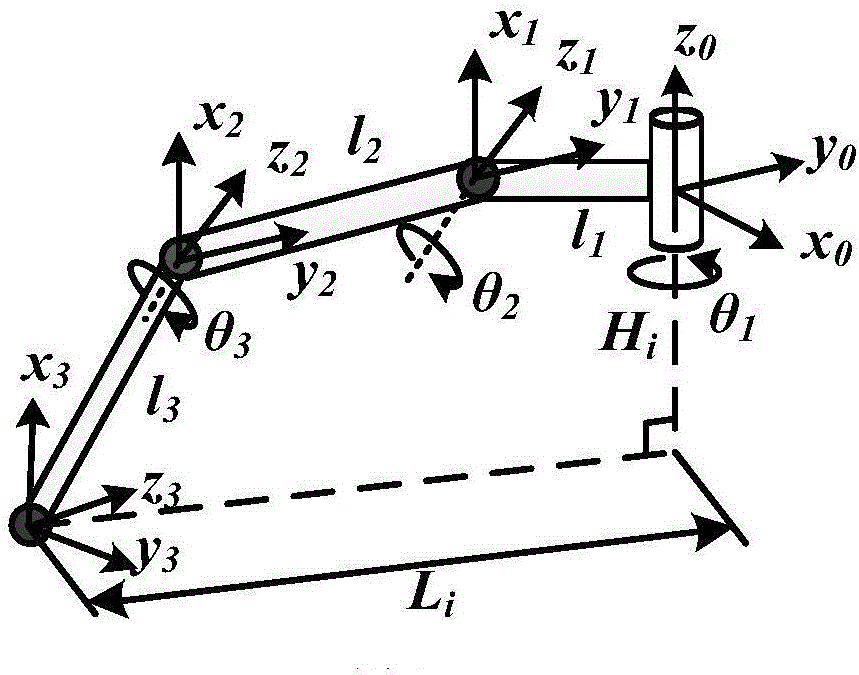
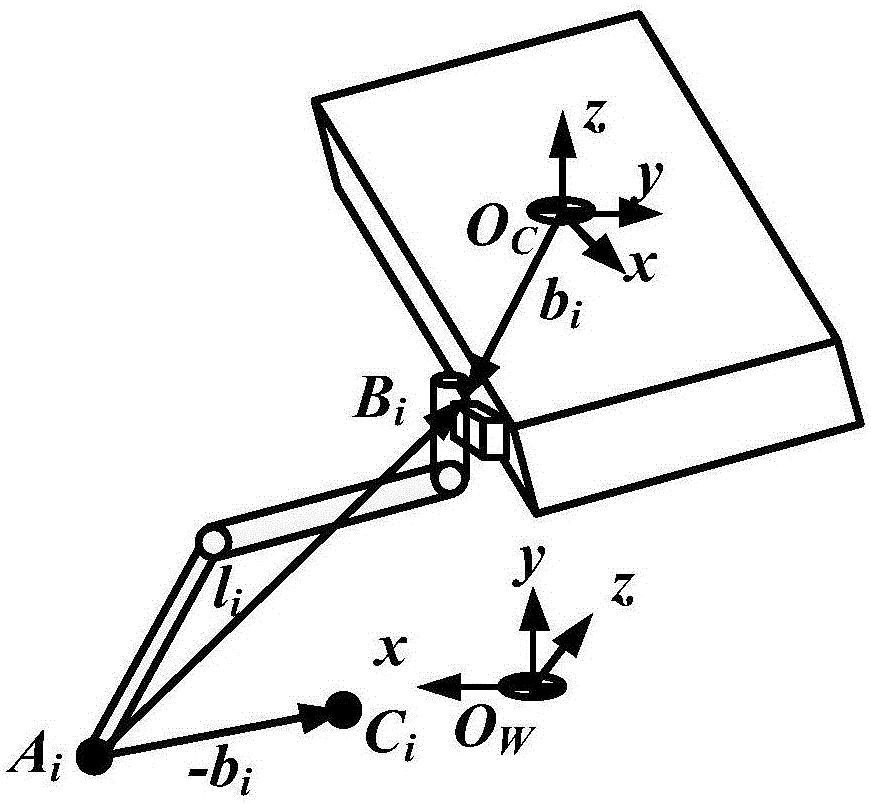
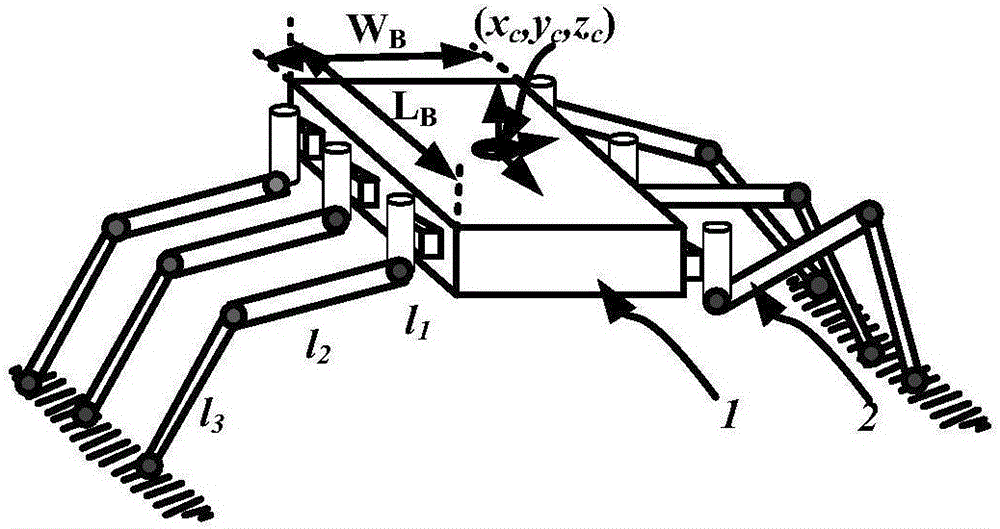
Modular hydraulic-drive four-leg robot with variable leg shape structures
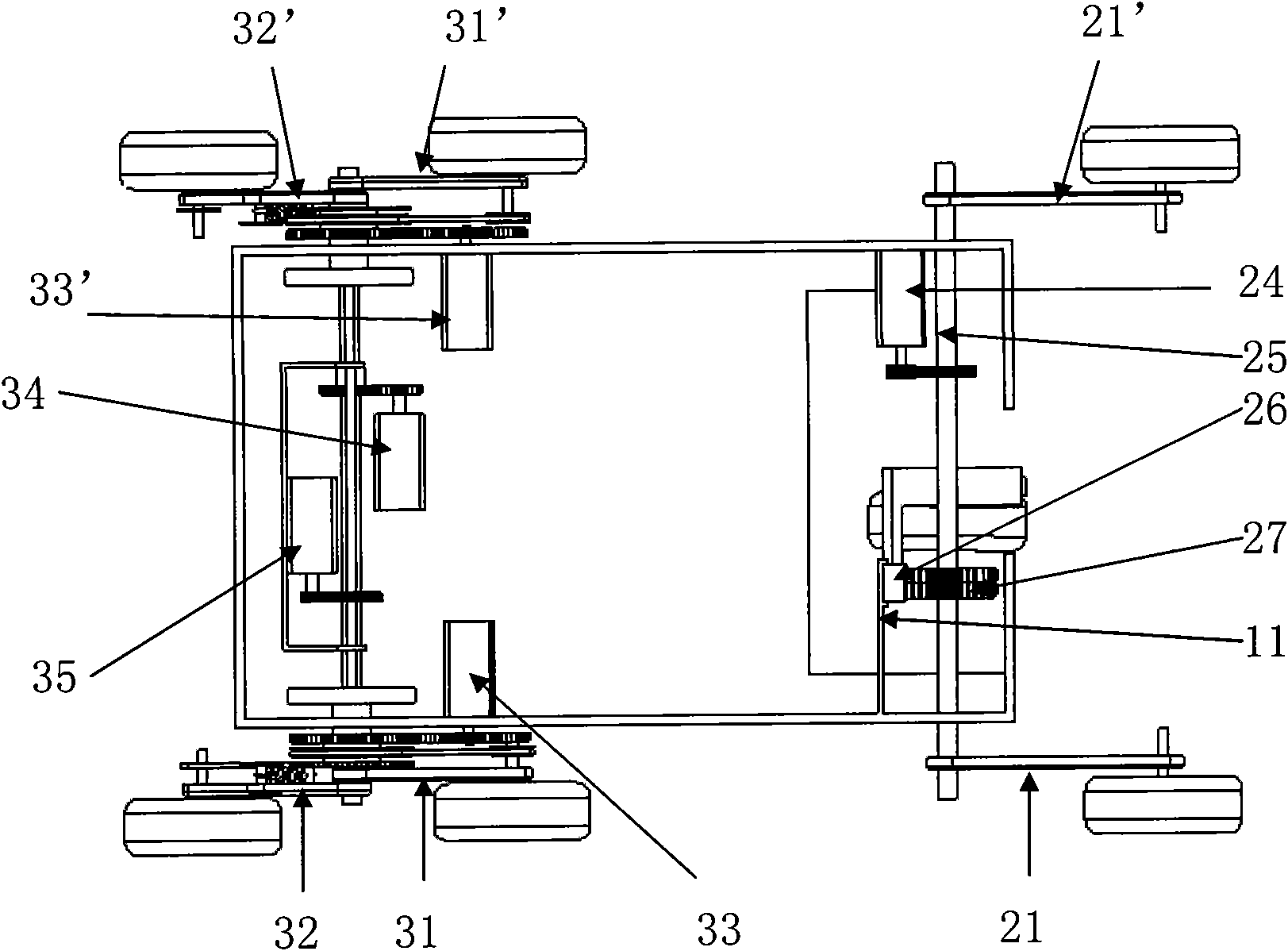
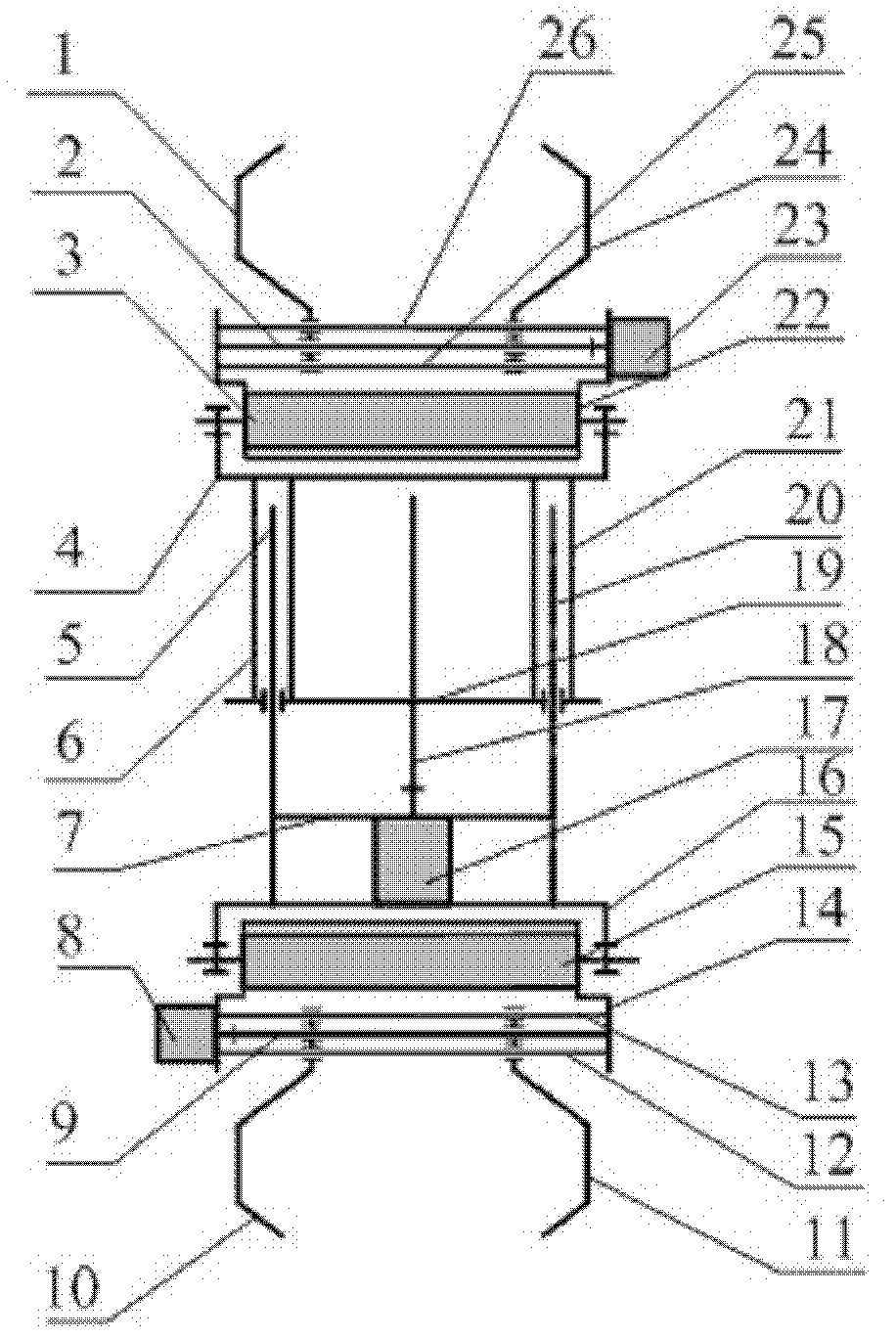
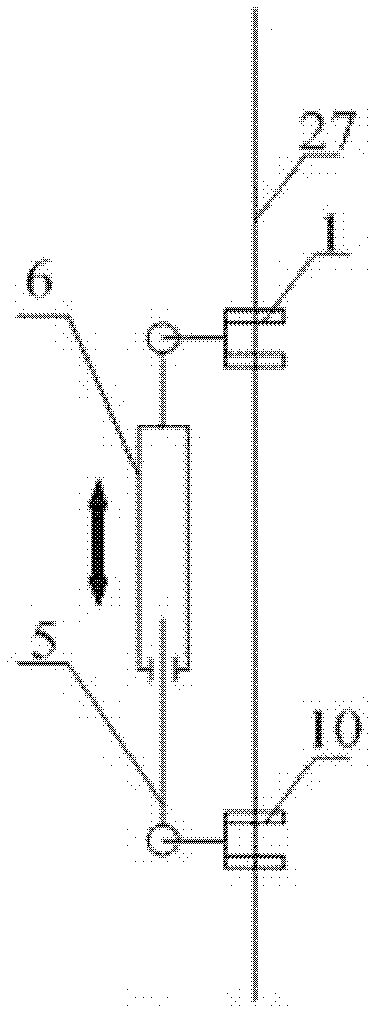
InactiveCN103318289ASolve the lack of spaceImprove terrain adaptabilityVehiclesDynamic balanceKnee Joint
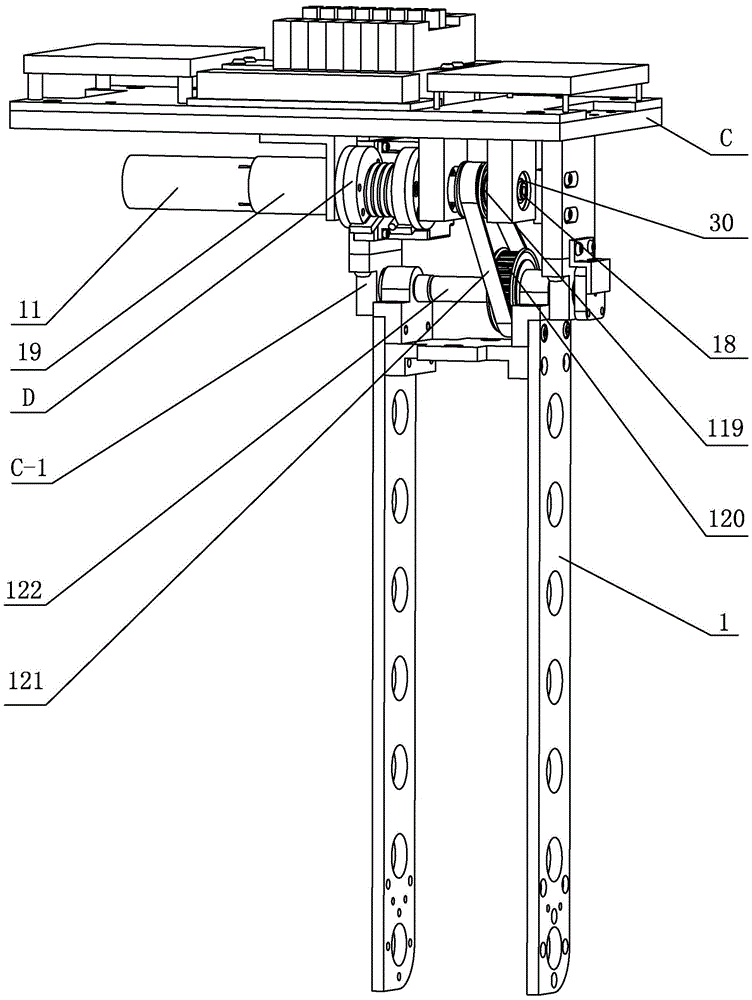
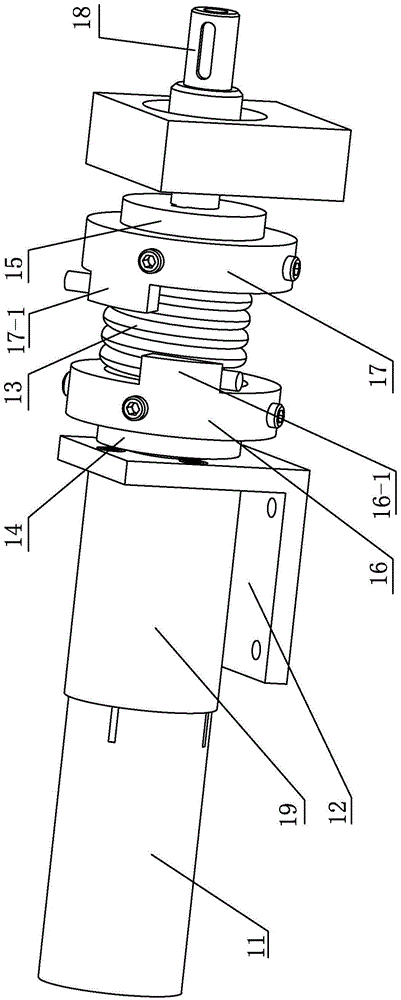
The invention discloses a hydraulic-drive four-leg robot. The modular hydraulic-drive four-leg robot has the advantages that the hydraulic-drive four-leg robot is good in dynamic balance and high in topographical adaptability, loading capacity and cost performance, and is in a modular and bionic structural design, four leg shapes can be switched over by means of quickly assembling and disassembling subassemblies, the modular hydraulic-drive four-leg robot is multipurpose, and merits and shortcomings of various leg shapes are verified by experiments at a physical prototype stage; each single leg is provided with two leg sections, has three degrees of freedom and comprises a hip joint and thigh assembly, a knee joint and shank assembly and a side sway assembly; a side sway and connecting block combining form is adopted for each thigh portion according to a bionic principle, so that sufficient rigidity and strength are guaranteed, the hydraulic-drive four-leg robot can bear a load stably while the weight of the robot is reduced to the greatest extent, and sufficient activity space for hydraulic cylinders is guaranteed; shank portions comprise foot-end rubber pads and passive retractable bidirectional spring shock absorption mechanisms, and instant impact force generated when the robot is in contact with the ground can be effectively buffered and absorbed under multiple shock absorption actions; problems of limited service lives of components and vulnerability of electronic elements such as foot-end force sensors due to the fact that impact force disappears and springs are rebounded quickly when an existing robot leaves the ground can be solved by the aid of the bidirectional spring mechanisms.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
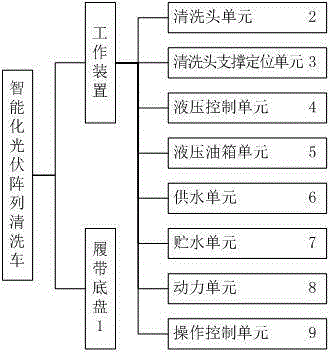
Intelligent photovoltaic array washing car
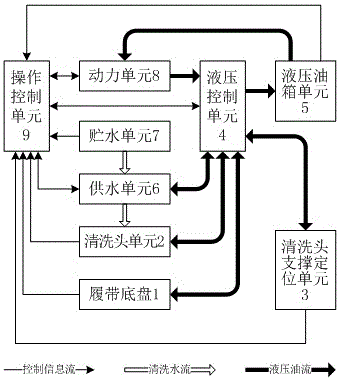
ActiveCN105107772AFunction increaseRegular shapeCleaning using toolsCleaning using liquidsWater storageHydraulic control unit
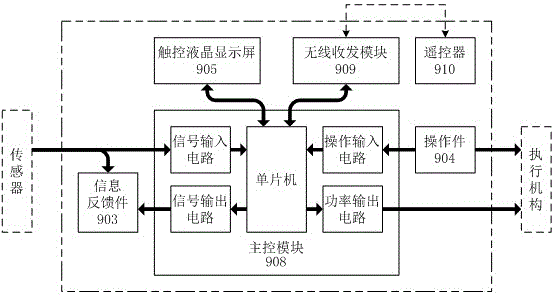
The invention provides an intelligent photovoltaic array washing car used for washing photovoltaic arrays of a large-scale ground photovoltaic power station. A washing head supporting and locating unit and a power unit are arranged on the head portion and the tail portion of a crawler base respectively, a water storage unit is arranged adjacent to the power unit, and a washing head unit is provided with range finder sensors used for measuring the distance between the washing head unit and solar cell panels; the washing head supporting and locating unit comprises a movable base capable of rotating and transversely moving and a working arm set provided with a main arm and an end arm, wherein the main arm and the end arm can pitch respectively; a water pump of a water supply unit is driven by a hydraulic motor; a computer is used as a control kernel of a main control module of an operation control unit; a pair of proportional directional valves of the hydraulic control unit controls two base crawler traveling motors, and other directional valves are electromagnetic directional valves controlled by the main control module. According to the intelligent photovoltaic array washing car, the position and the posture of the washing head unit relative to photovoltaic array panels and the position and the posture of a car body relative to the photovoltaic arrays can be automatically controlled, and the intelligent photovoltaic array washing car is intelligent, efficient, flexible in operation, high in adaptability, easy and convenient to operate, concise in structure and good in washing effect.
Owner:CSIC HAIWEI ZHENGZHOU HIGH TECH CO LTD
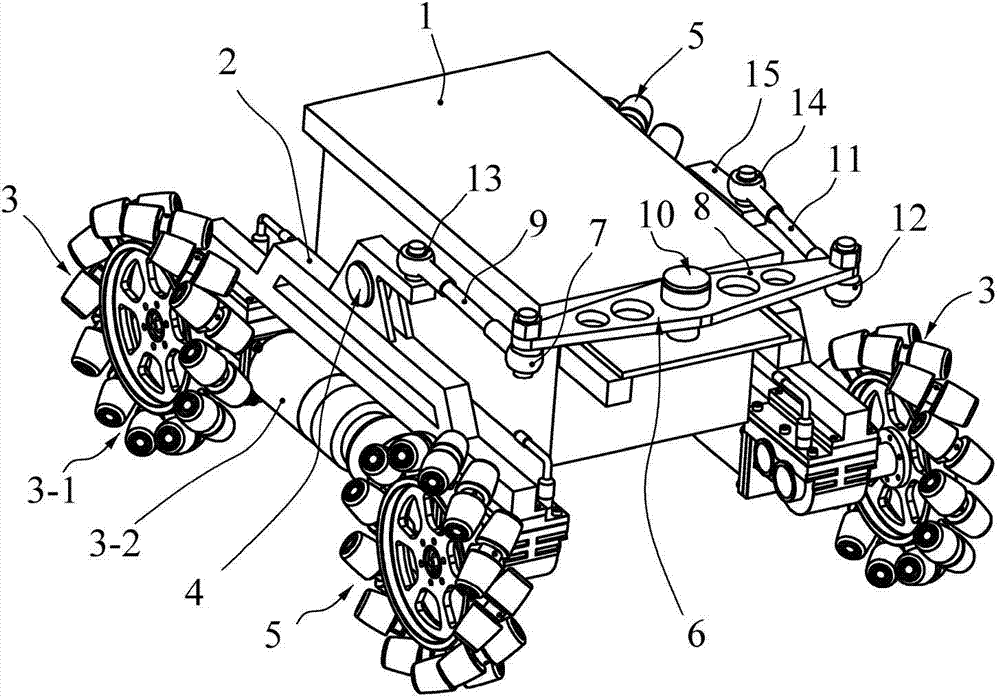
Mecanum wheel-based rocker omnidirectional mobile platform
ActiveCN104494721AImprove terrain adaptabilityEasy to controlInterconnection systemsVehiclesTerrainEngineering
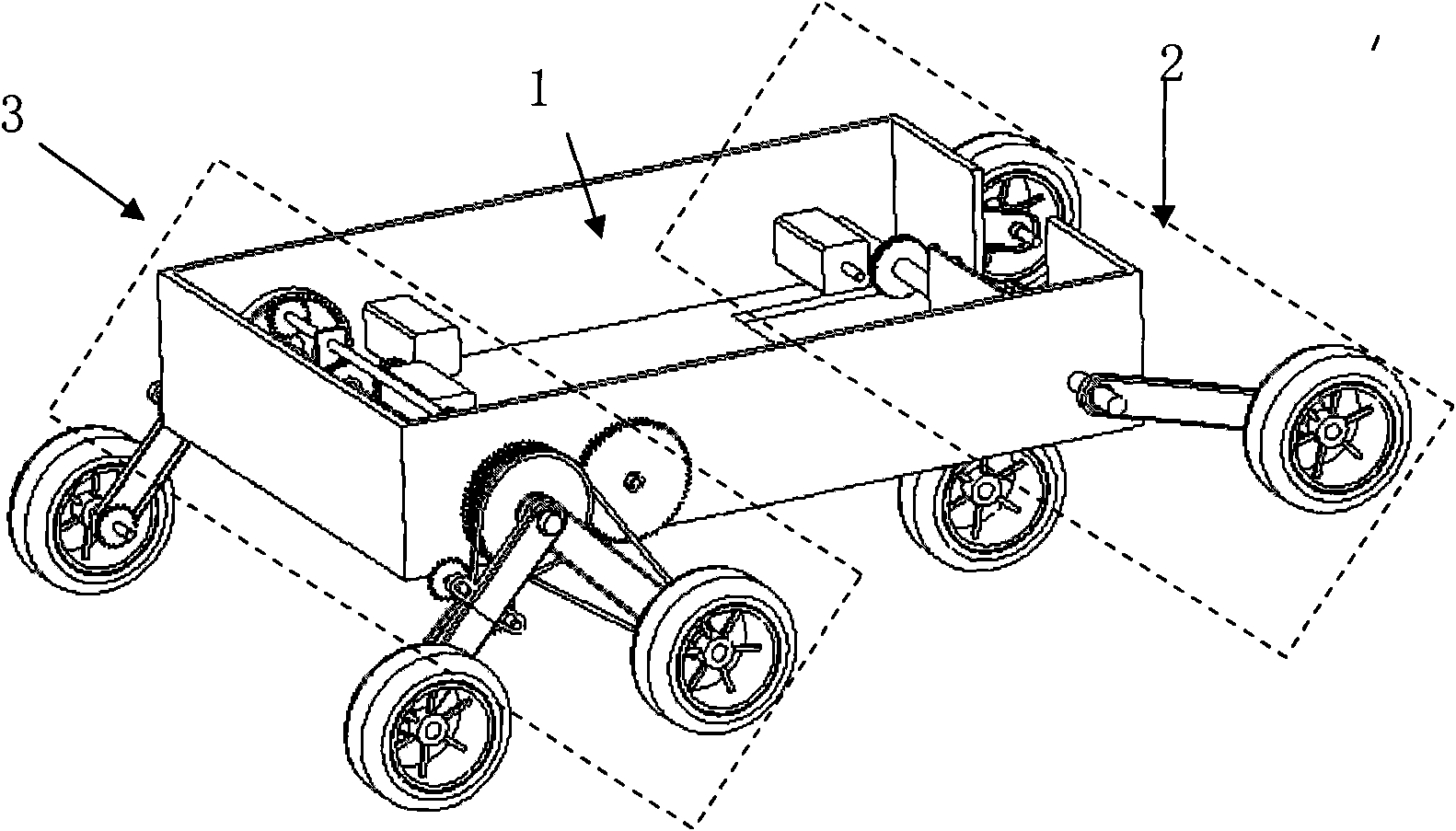
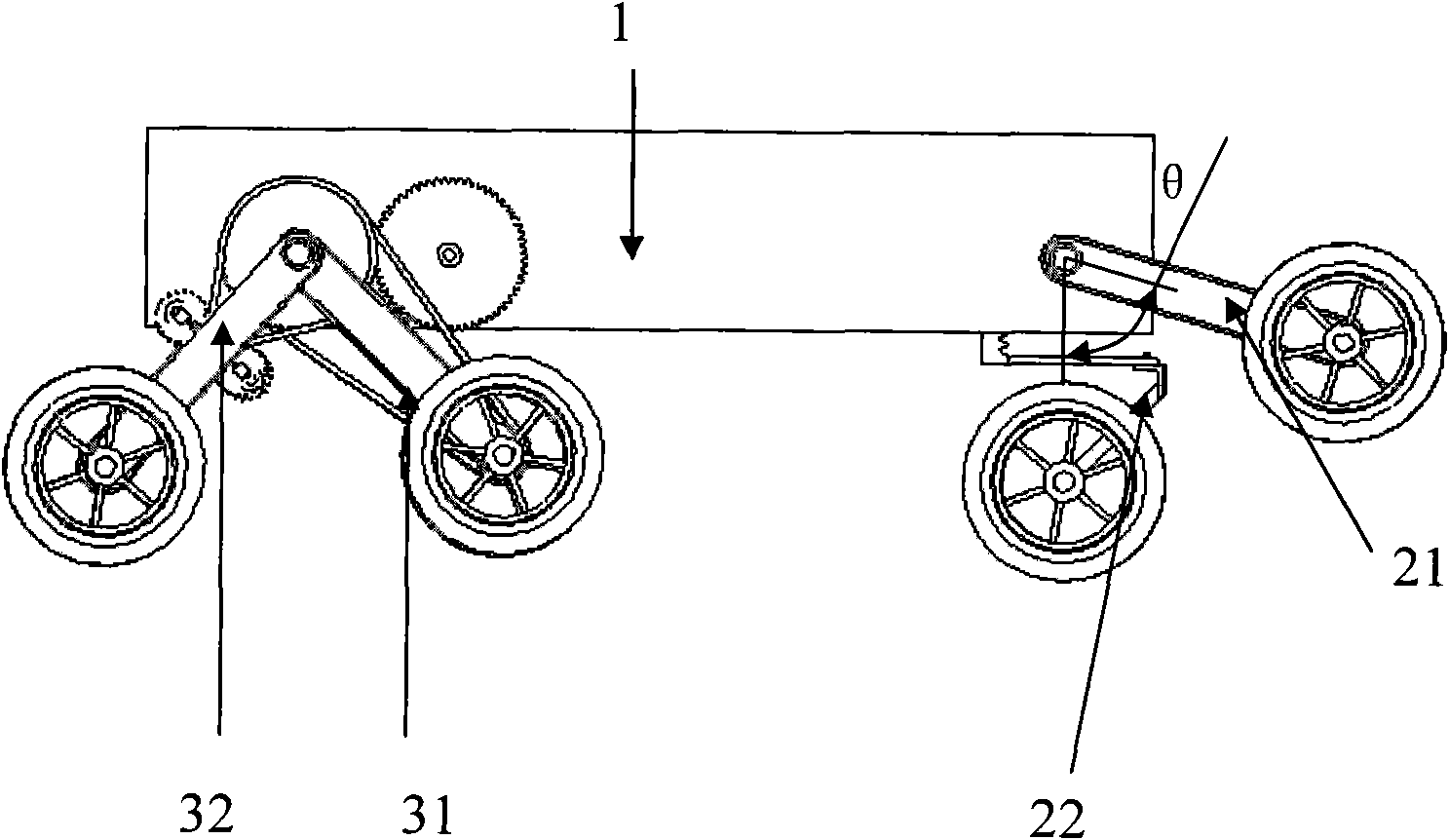
A Mecanum wheel-based rocker omnidirectional mobile platform comprises a main body (1), leftwards-rotating Mecanum wheel assemblies (3), rightwards-rotating Mecanum wheel assemblies (5), a rocker suspension I (2), a rocker suspension II (15) and a balancing mechanism (6); the middle parts of the rocker suspension I and the rocker suspension II are hinged to the left and right sides of the main body through revolute joints symmetrically; the middle part of a transverse rocker (8) of the balancing mechanism and one end of the main body are hinged by a revolute joint (10); one end of a side connecting rod I (9) and one end of a side connecting rod II (11) of the balancing mechanism are hinged to the left and right ends of the transverse rocker by spherical joints, and the other end of the side connecting rod I (9) and the other end of the side connecting rod II (11) of the balancing mechanism are hinged to the rocker suspension I and the rocker suspension II by spherical joints; two Mecanum wheel assemblies with different rotation directions are fixed to the two ends of each rocker suspension, and the Mecanum wheel assemblies at the same ends of the rocker suspension I and the rocker suspension II are opposite in rotation directions. According to the invention, wheels are always in contact with the ground and the load is shared, so that the Mecanum wheel-based rocker omnidirectional mobile platform has better motion controllability and terrain trafficability.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
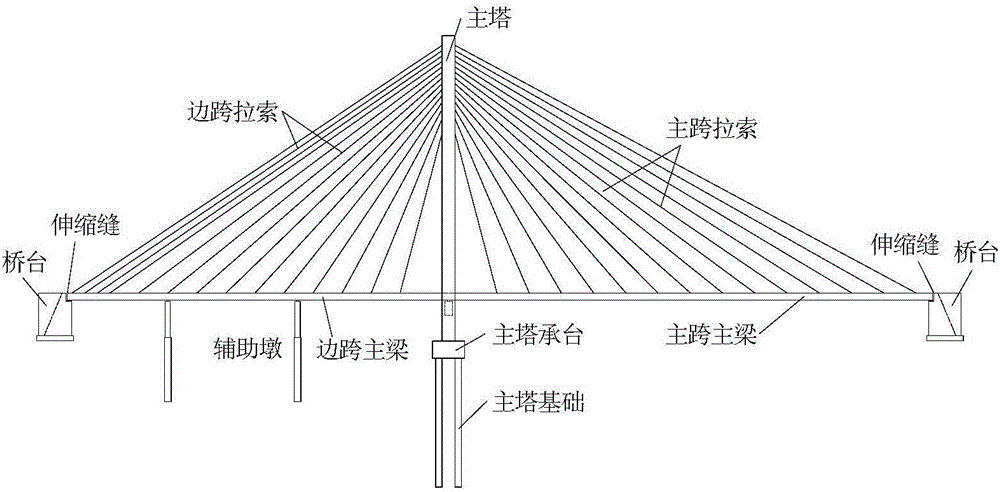
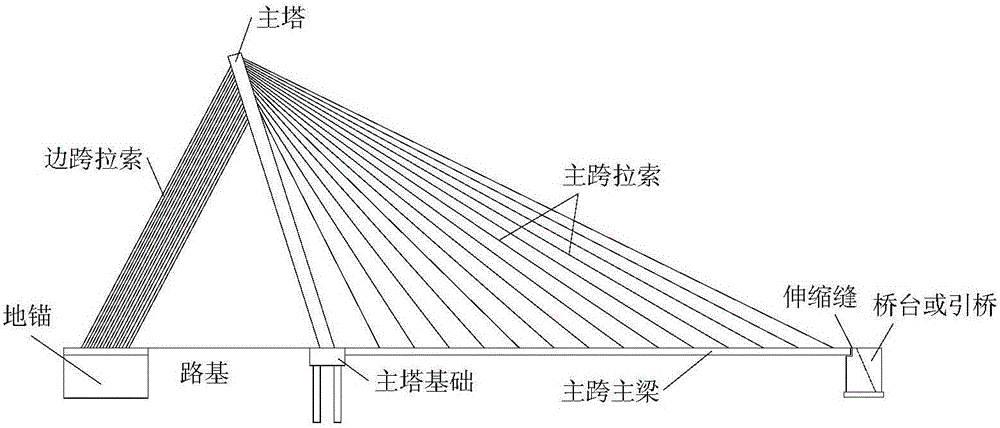
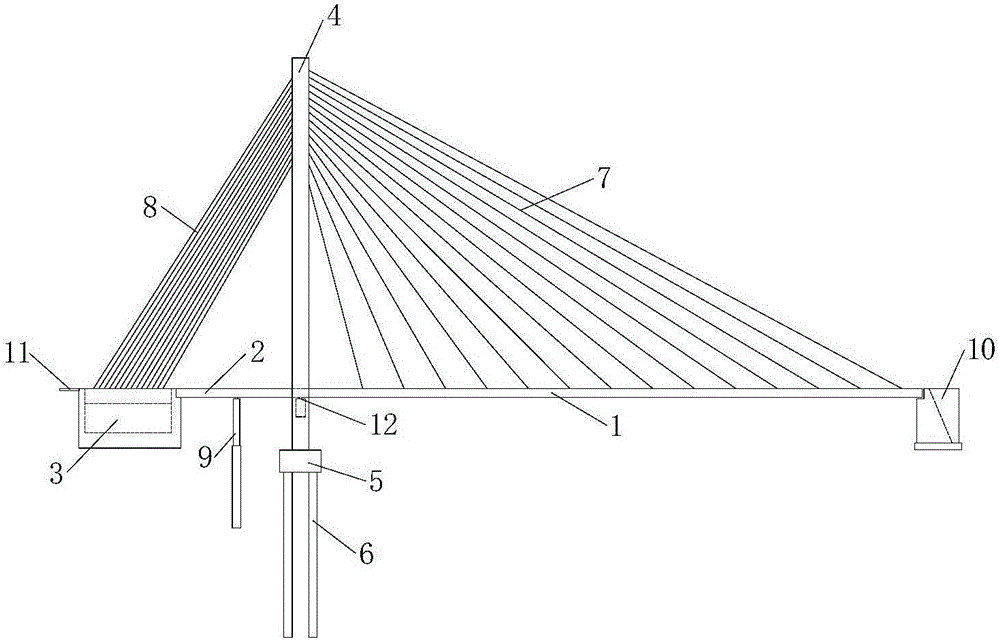
All-ground-anchor type single-tower double-span cable-stayed bridge structure and construction method thereof
InactiveCN106012797AAdaptableStrong terrain adaptabilityCable-stayed bridgeBridge erection/assemblyStructural systemCable stayed
An all-ground-anchor type single-tower double-span cable-stayed bridge system comprises a main beam, a stay cable, a main tower and an anchor. The main beam is composed of a side span main beam body and a main span main beam body. The length of the side span main beam body is far smaller than that of the main span main beam body, and the side span main beam body and the main span main beam body are asymmetrically distributed. The side span main beam body is supported by a support arranged on a side span buttress main tower lower beam and fixedly connected with the main span main beam body and the anchor. The stay cable comprises a main span stay cable body and a side span stay cable body. The main span stay cable body supports the main span main beam body. The upper end of the side span stay cable body is anchored to the main tower and corresponds to the main span stay cable body in position. The lower end of the side span stay cable body is anchored to the anchor. The main tower provides anchorage for the main span stay cable body and the side span stay cable body and meanwhile transmits the vertical force of the side span stay cable body to a foundation through a main tower bearing table and a main tower foundation. The anchor provides anchorage for the whole side span stay cable body and meanwhile balances the horizontal force transmitted by the side span main beam body. The invention further discloses a construction method of the cable-stayed bridge system. The cable-stayed bridge system is high in adaptability, reasonable in structural system, easy and convenient to construct, short in construction period, low in manufacturing cost and small in safety risk in the construction period.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Composite mobile robot with wheel-track legs
The invention provides a composite mobile robot with wheel-track legs. The composite mobile robot comprises a frame, track arms, support legs and a wheeled elevating mechanism, wherein the track arms are connected with the frame through an inner shaft and an outer shaft, the four sets of the track arms are symmetrically distributed at four corners of the frame; the support legs are connected with the frame through a support leg transmission shaft, and the two support legs are symmetrically distributed in front of and behind the frame; the wheeled elevating mechanism is connected with the frame through a connecting plate, and is arranged at the middle part of the frame. According to the composite mobile robot disclosed by the invention, motors are used for driving the track arms, the support legs and the wheeled elevating mechanism to move, so that the robot has different postures, the composite motion manner of wheels, tracks and legs is realized, and the obstacle surmounting capacity is greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
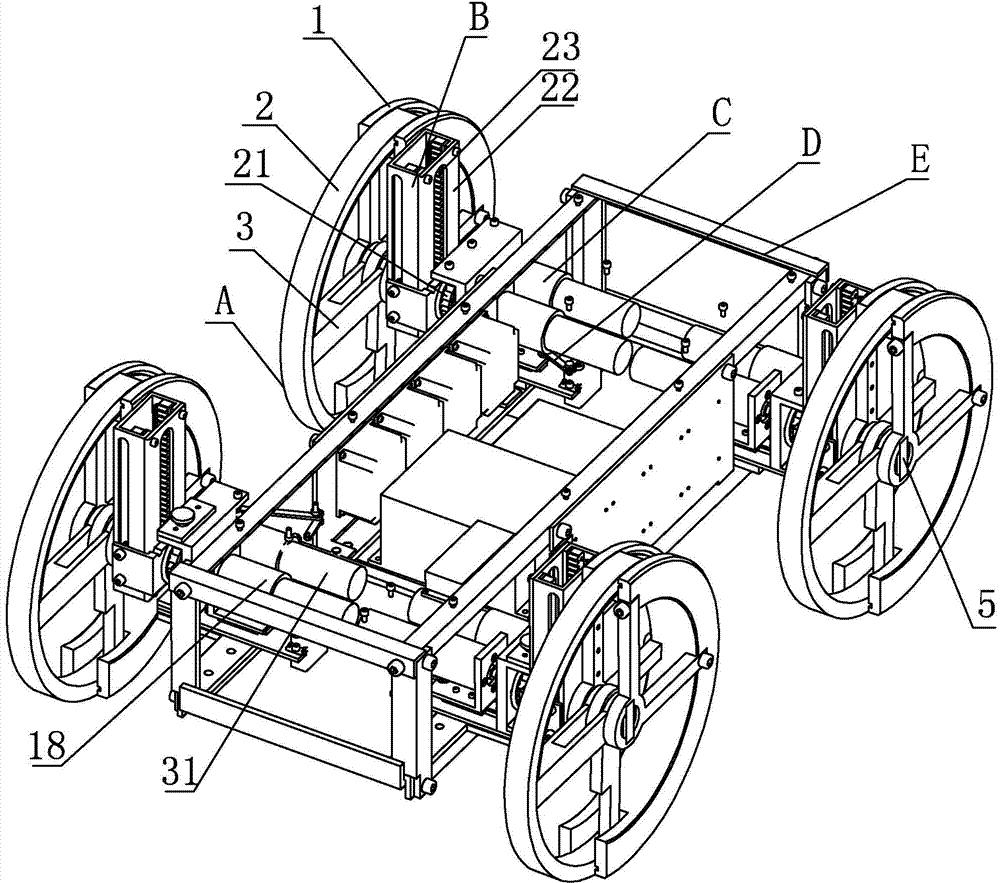
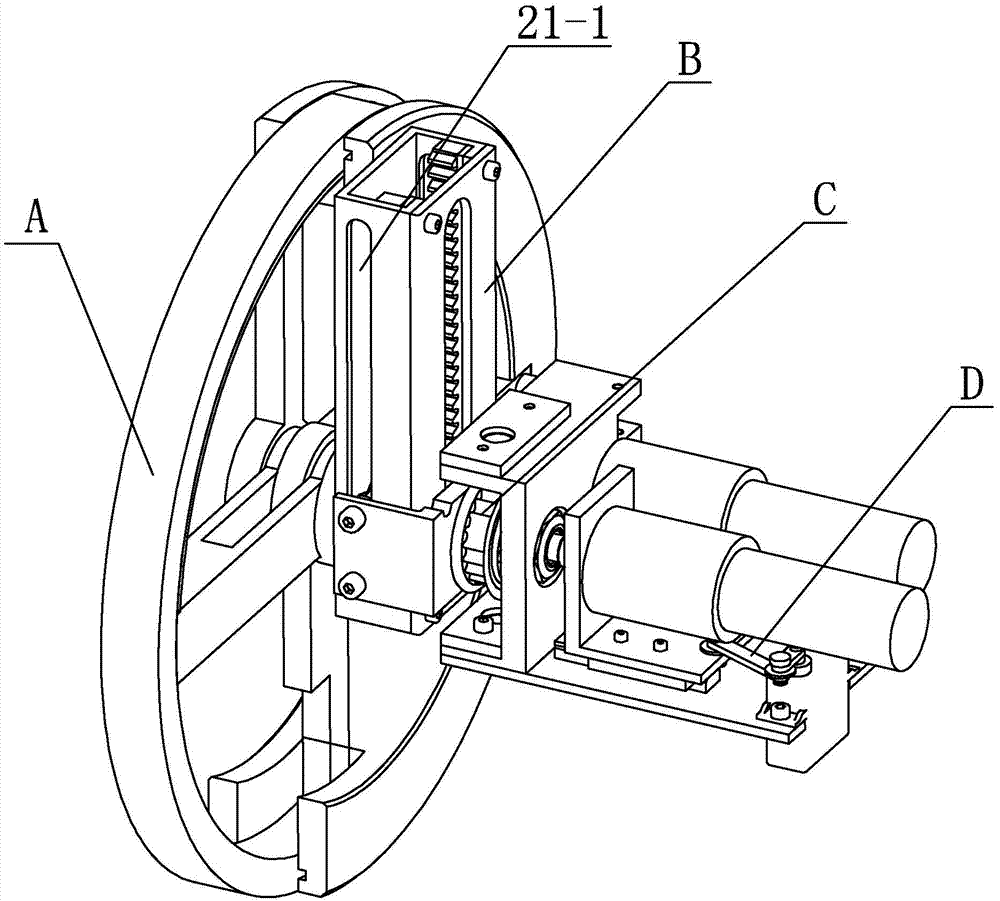
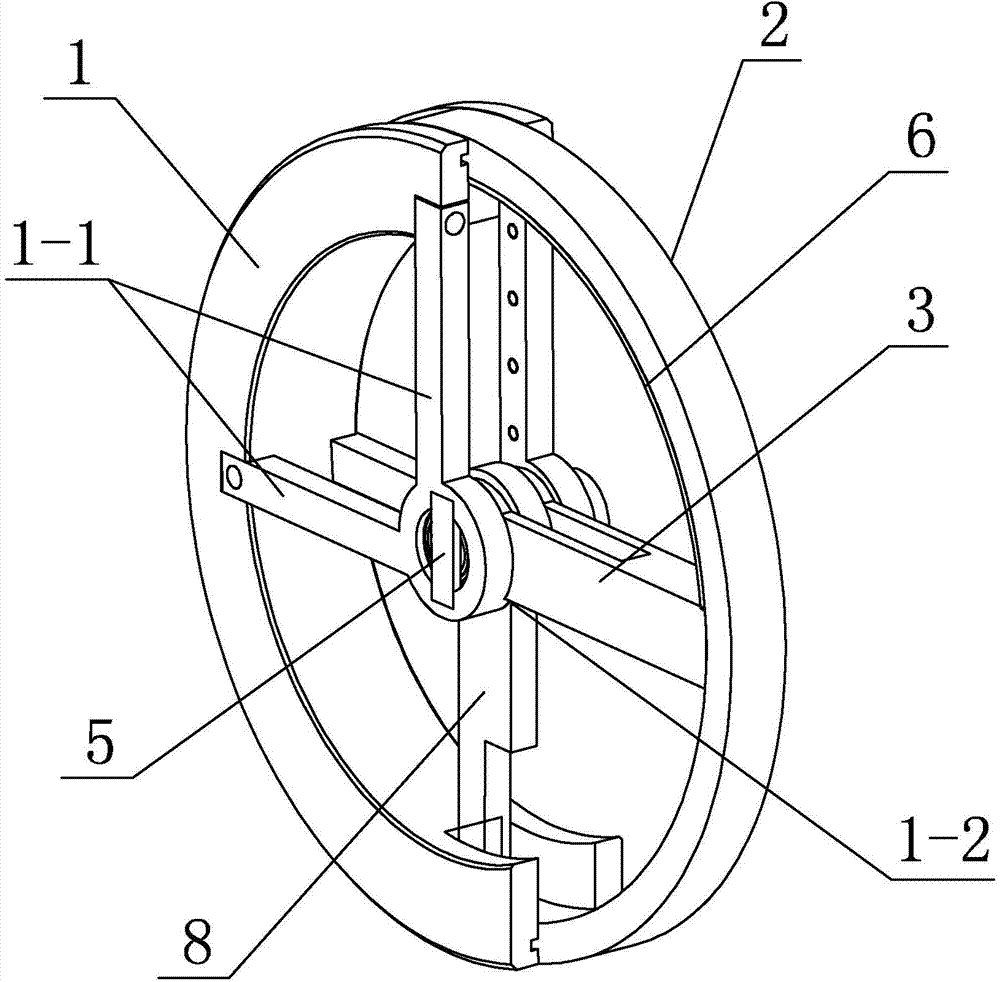
Wheel-foot conversion type mobile robot system
ActiveCN104773226ARealize the combinationImprove terrain adaptabilityVehiclesObstacle avoidanceControl theory
The invention provides a wheel-foot conversion type mobile robot system, relating to mobile robots. The wheel-foot conversion type mobile robot system is used for solving the problems that the obstacle avoidance ability of the existing wheeled robots is poor and the walking speed of the existing footed robots is low. According to the wheel-foot conversion type mobile robot system, one end of each central axle is fixedly connected and is axially locked through a corresponding first limiting block, a shoulder is arranged at the other end of each central axle, a spring sleeves each central axle and is located between a corresponding bearing and the corresponding shoulder, a central blind hole is formed in the other end of each central axle, and a first key groove is formed in each central blind hole; semi-annular grooves are formed in fixed half wheels along the circumferential direction, movable half wheels and the fixed half wheels are in turning connection relatively to the central axles, complete wheels are formed by the fixed half wheels and the movable half wheels during the conversion to a wheeled state, the movable half wheels are turned into the semi-annular grooves of the fixed half wheels during the conversion to a footed state, and single scrolls are mounted on the central axles. The wheel-foot conversion type mobile robot system belongs to the field of the mobile robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Variable structure spherical robot capable of crossing obstacle
The invention relates to a variable structure spherical robot capable of crossing an obstacle. The robot comprises a balancing weight horizontal shifting module, a rolling movement driving module, a flywheel driving module and a flywheel braking module. The two basic movement modes of pure rolling and obstacle crossing can be achieved. In the mode of pure rolling, the variable structure spherical robot is similar to a traditional spherical robot driven by center-of-gravity shift, and the variable structure spherical robot has the advantage of being high in movement efficiency. In the mode of obstacle crossing, the variable structure spherical robot can automatically achieve acceleration energy storage for a flywheel set only by increasing driving torque of a power shaft, and when the rotating speed of flywheels reaches the preset threshold value, claw feet hidden on the two sides of a spherical shell can be triggered to be unfolded. Meanwhile, the movement of the spherical shell is blocked, and the flywheels are braked, so that stored energy instantly breaks out and drives the claw feet to rotate to achieve obstacle crossing, and the movement mode of pure rolling is recovered after the energy is completely released. The variable structure spherical robot has the advantages of being compact in structure, easy to control, high in obstacle crossing ability, reliable in system and the like, and the terrain adaptability and practicability of the spherical robot are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
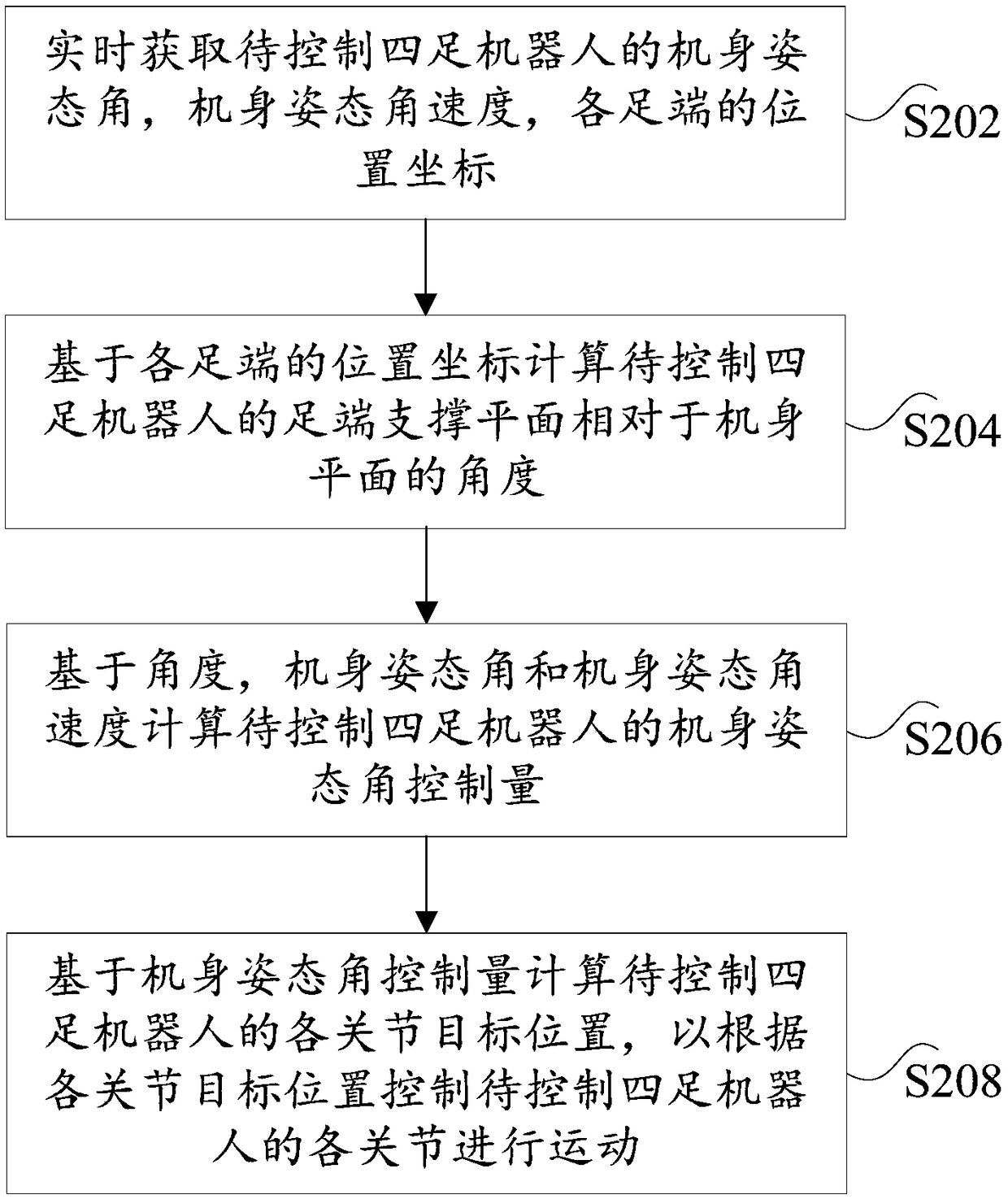
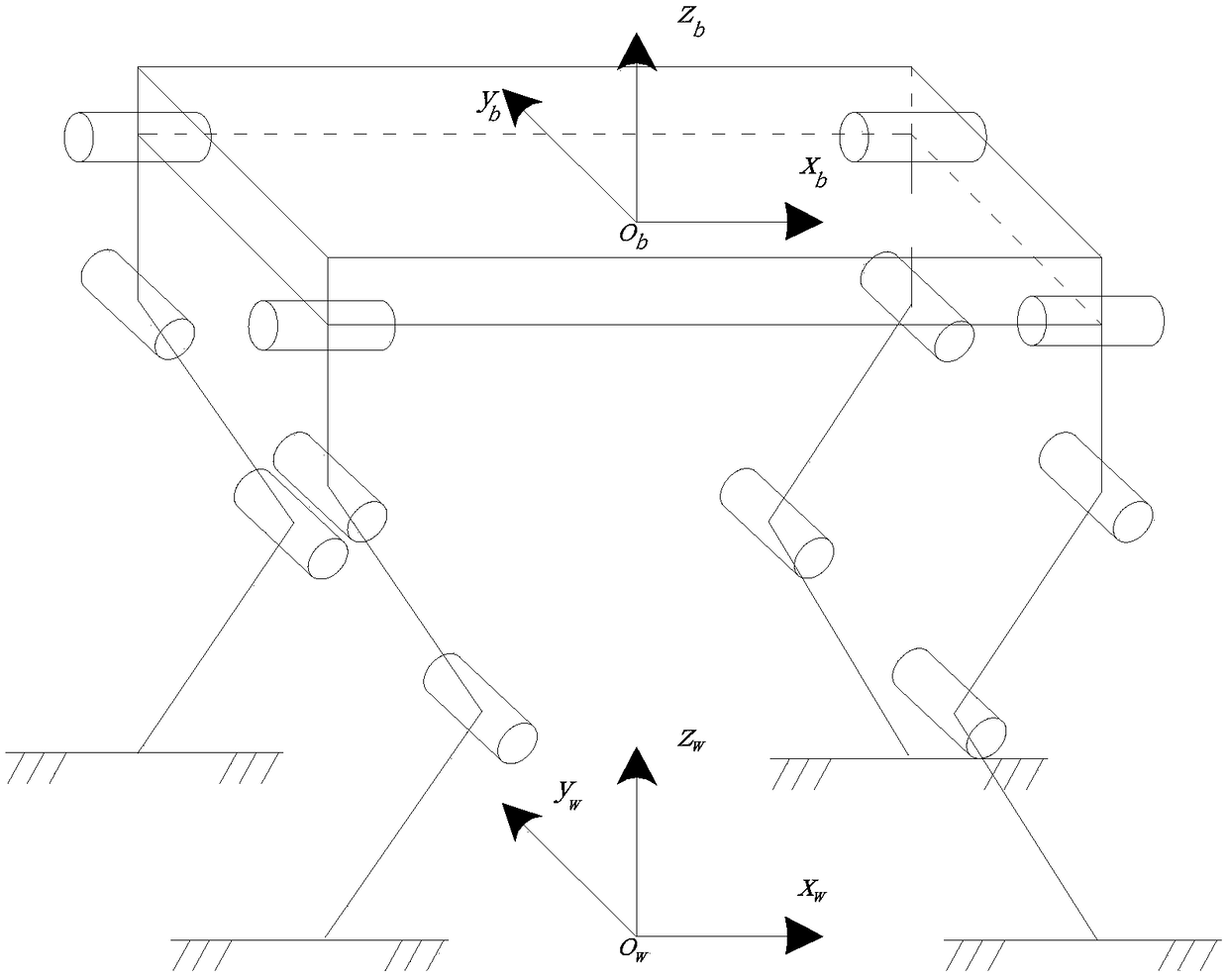
Quadruped robot body posture control method and quadruped robot body posture control device
ActiveCN109093626AImprove motion stabilityImprove terrain adaptabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorTerrainBody posture
The invention provides a quadruped robot body posture control method and a quadruped robot body posture control device. The method includes acquiring robot body posture angle, a robot body posture angular speed and position coordinates of all leg ends of a to-be-controlled quadruped robot in real time; computing an angle of a leg end supporting plane of the to-be-controlled quadruped robot relative to a robot body plane on the basis of the leg end position coordinates; computing a robot body posture angle control quantity of the to-be-controlled quadruped robot on the basis of the angle, the robot body posture angle and the robot body posture angular speed; computing all joint target positions of the to-be-controlled quadruped robot on the basis of the robot body posture angle control quantity, and controlling all joints of the to-be-controlled quadruped robot to move according to all the joint target positions. The quadruped robot body posture control method has the advantages that the method can achieve real-time robot body posture control of the to-be-controlled quadruped robot, and the movement stability and the terrain adaptability of the to-be-controlled quadruped robot are enhanced, so that the technical problem that the movement stability of the quadruped robot is affected severely by the poor real-time performance of an existing posture adjustment mode is relieved.
Owner:SIASUN CO LTD
Electric mountain orchard single-rail transporting machine
InactiveCN102490727AMechanization of transportationHigh degree of automationRack railwaysElectricityAgricultural machinery
The invention relates to an electric mountain orchard single-rail transporting machine, which comprises a traction vehicle and a transporting trailer, wherein the traction vehicle drags the transporting trailer, the traction vehicle and the transporting trailer span on an erected rail, a rack is arranged under the rail, the traction vehicle comprises a main machine frame, an electric motor, a storage battery, a transmission device, a driving device and a control device, the motor, the storage battery, the transmission device and the driving device are arranged on the main machine frame, the driving device comprises an active driving wheel positioned under the rail, the electric motor is controlled by the control device and rotates by using the storage battery for electricity supply, and the active driving wheel is driven to rotate by the electric motor through the transmission device and is in engaged transmission with the rail. The electric mountain orchard single-rail transporting machine has the advantages that the structure is simple, the size is small, the weight is light, the electric starting is adopted, the operation cost is low, and in addition, the vertical and transverse transportation can be realized. The electric mountain orchard single-rail transporting machine belongs to the technical field of transportation machinery in agriculture machinery.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for generating free gaits for four-footed bionic robot
ActiveCN104267720ASufficient marginImprove terrain adaptabilityVehicle position/course/altitude controlPosition/direction controlTerrainFoot supports
The invention relates to a method for generating free gaits for a four-footed bionic robot. All of the free gaits of the four-footed robot are programmed according to moving periods, and each moving period comprises a four-footed supporting stage and a stepping stage; at the four-footed supporting stages, four feet of the robot are all positioned at supporting phases, the center of gravity of the robot moves in the advancing direction and the side directions of the advancing direction, in the advancing direction, the robot moves the largest advancing distance allowed by a current state, and in the side directions, the moving distance of the robot is determined taking account of the stability and the energy consumption of the robot at the same time; at the stepping stages, one foot of the robot is positioned at a swinging phase, and the other three feet of the robot are positioned at the supporting phases; when the swing foot of the robot for a certain moving period comes in contact with the ground, the movement of the robot for the next moving period is programmed. Through the adoption of the method, the adaptability of the four-footed robot to terrain is effectively improved, the stability of the robot can be improved, the continuity of the movement of the robot is ensured, the energy consumption is reduced, and the mean movement speed is accelerated.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Pneumatic-electric combined driving flexible biped robot
The invention relates to a flexible biped robot, in particular to a pneumatic-electric combined driving flexible biped robot. The problems that linkage between joint flexibility and a dynamic response characteristic of existing flexible biped robots is poor, the walking efficiency of the robots is low and the dynamic stability of the robots is poor are solved. The pneumatic-electric combined driving flexible biped robot comprises a left leg, a right leg and a pelvis. The left leg and the right leg each comprise a thigh, a shank, a foot, a hip joint, a knee joint and an ankle joint. Each hip joint comprises a one-way series-connection elastic driver and a hip joint transmission mechanism. Each one-way series-connection elastic driver comprises a motor, a motor seat, a torsion spring, a first hub, a second hub, a first clamping ring, a second clamping ring and a hip joint driving shaft. Each hip joint transmission mechanism comprises a driving belt wheel, a driven belt wheel, a driving belt and a hip joint driven shaft. The driving belt wheels are mounted on the hip joint driving shafts correspondingly. Each knee joint comprises a knee joint driving mechanism and a knee joint transmission mechanism. The pneumatic-electric combined driving flexible biped robot belongs to the field of humanoid robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Wheel-leg combined type mobile robot platform
The invention discloses a wheel-leg combined type mobile robot platform. The robot comprises a machine frame, a front wheel-leg system and a rear wheel-leg system, wherein the front wheel-leg system comprises a front shaft, three front wheel legs, a front motor, a rack and a front transmission system; the rear wheel-leg system consists of two subsystems of a leg swinging system and a driving system and is arranged on the back part of the machine frame; the leg swinging system comprises a shaft frame, a rear shaft, a matched shaft, two same shaft sleeves, four same rear wheel legs, two same first group rear motors and a rear transmission system; the driving system are divided into two parts which are symmetrical left and right and have the same structure, and the two parts are independently driven by two identical second group rear motors respectively; and each part comprises combined wheels, chains, belts, small belt wheels and small chain wheels. The robot platform adopts a wheel-leg combined type structure, so that the robot platform is simple in structure and can be easily controlled; the robot platform can move on the even terrain in a wheel mode, and the energy consumption is lowered; and the robot platform can move on the complex terrain in a wheel-leg combined mode, the efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHAANXI JIULI ROBOT MFG
Clamping type integral shrinking and overturning climbing robot
InactiveCN102632505AFast straight climbImprove terrain adaptabilityGripping headsEngineeringClimbing robots
The invention aims at providing a clamping type integral shrinking and overturning climbing robot comprising two clamping parts, an internal extension tube, an external extension tube, a shrinking motor, an extension tube connecting frame, an overturning frame and an overturning motor, wherein each clamping part comprises a clamping paw, a clamping motor, a clamping motor rack, a guide shaft and a paw lead screw, and the two clamping parts are respectively located on the two ends of a main body of the clamping type integral shrinking and overturning climbing robot and are connected with the corresponding overturning motors through the respective clamping motor racks. According to the invention, a shrinking mechanism is designed according to the helical lead screw transmission principle to enable the robot to quickly and linearly climb in a shrinking manner; the integral shrinking and overturning design mode entitles better terrain adaptability to the robot; and the shrinking part utilizes an internal and external extension tube structure so as not to bear radial force.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Bionic galloping robot based on connecting rod mechanism
InactiveCN101797937AFast energy storageQuick releaseSelf-moving toy figuresVehiclesTerrainControl theory
The invention relates to a bionic galloping robot based on a connecting rod mechanism. The bionic galloping robot is characterized by concretely comprising a robot body (a), a track marching module (b), a galloping mechanism module (c) and a power module (d), wherein the robot body (a) consists of two quadrilateral pierced metal plates with the shape similar to a trapezoid and is used for fixing and installing other parts of the robot; the track marching module (b) mainly comprises two damping pins, a pair of damping springs and three pairs of crawler wheels; the galloping mechanism module (c) mainly comprises thighs, shanks, soles, foot connecting rods and shank connecting rods; and the power module (d) can be divided into two submodules i.e. a unidirectional transmission gear set and an automatic energy storage and release mechanism submodule. The robot can cross a higher obstacle and jump on a higher step on one hand and abandon a pure and complete simulation principle on the other hand. A jumping mode of the robot is combined with a machine track marching mode with convenience, rapidness and strong terrain adaptability, therefore, the bionic robot has the super strong obstacle-surmounting ability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Overturning and climbing robot with two telescopic arms
ActiveCN103273500AIncrease flexibilityIncreased range of mobile workGripping headsArmsControl modeClimbing robots
Provided is an overturning and climbing robot with two telescopic arms on different sides. A body is driven to climb in the modes of grabbing through two hands, stretch outing or drawing back of the arms and spatial overturning. The opening and closing of each hand is realized through horizontal movement of a screw rod along two guiding shafts, wherein the screw rod is driven by a motor and provided with a forward buckle and a reverse buckle in a machined mode. The stretch and contraction of the arms are realized through vertical movement of a single-buckle screw rod along two telescopic pipes, wherein the single-buckle screw rod is also driven by the motor. The spatial overturning is realized through a cross-shaped motor installation structure. A unit formed by the two hands, a unit formed by the arms and a spatial overturning unit are connected in sequence and then fixedly mounted on the body (namely a vehicle body) through a support, and therefore the body is driven in a grabbing type climb mode. The overturning and climbing robot with the two telescopic arms on different sides is simple in structure and high in mobility. Corresponding technology application demands for carrying out field tasks can be met in different control modes by means of carrying different sensors.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Amphibious robot with multiple movement modes
InactiveCN106004281AMove fastReduce energy consumptionAmphibious vehiclesEndless track vehiclesThighEllipse
The invention provides an amphibious robot with multiple movement modes. The amphibious robot with the multiple movement modes comprises a main robot body structure, two elliptical rotating wheels and four sets of walking legs. Each set of walking leg comprises a thigh and a calf. Active revolute pairs parallel to each other are arranged between each thigh and the corresponding calf and each thigh and the corresponding elliptical rotating wheel. The outer edges of all the legs are designed to be of circular-arc-shaped structures. When all the legs are deflected from one another at a certain angle, the robot can overall roll up, form an integral circular-wheel-shaped structure and achieve rolling or pulse thrust in the longitudinal direction of a robot body. When the legs of the robot are deflected from one another to be in the state that four feet stand on the ground, the robot can walk in the longitudinal direction of the robot body. When foreleg bodies and hind leg bodies of the robot shrink, the robot can move through crawler mechanisms of a main robot body. The amphibious robot can further achieve inchworm wriggling through alternate reciprocating swing of a chainlike mechanism formed by the foreleg bodies, the hind leg bodies and the robot body. If the amphibious robot is in the water, when the foreleg bodies and the hind leg bodies are in an extended state, the robot can further move forwards by paddling through unidirectional rotation of the calves.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Four-foot robot static gait planning method based on terrain fuzzy self-adaption
ActiveCN110328670AAvoid Loss of Stability SituationsCausing a loss of stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorVehiclesTerrainGait planning
Disclosed is a four-foot robot static gait planning method based on terrain fuzzy self-adaption. The four-foot robot static gait planning method based on terrain fuzzy self-adaption comprises the following steps of (1) calculating a trunk pitching angle according to foot falling position information of a robot; (2) planning a trunk movement track, and ensuring the stability of the robot in a nextstepping stage; (3) estimating the complexity of walking terrain by using the time of ground touching of two feet of the robot, and automatically adjusting parameters of truck moving track planning onthe basis of a fuzzy algorithm; and (4) completing a complete gait cycle and repeating the whole process. By means of the method, the pitching angle of a trunk can be automatically adjusted accordingto the terrain fluctuation in the walking process of the fur-foot robot, and the height and the terrain adaptability of the four-foot robot swinging feet across an obstacle are effectively increasedand improved respectively; the situation that the robot loses stability due to the fact that the speed or the acceleration is suddenly changed is effectively avoided; the self-adaption of the four-foot robot to the terrain is realized, and the terrain adaptability of the four-foot robot is effectively improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
All-dimensional steering obstacle crossing vehicle based on hub motor
InactiveCN103935410AFlexible steeringEasy to controlMotor depositionEndless track vehiclesTerrainControl system
The invention discloses an all-dimensional steering obstacle crossing vehicle based on a hub motor. The all-dimensional steering obstacle crossing vehicle comprises a central control system, a storage battery pack, an operating table, a hydraulic system and wheels, wherein the storage battery pack is fixed to a vehicle body, and the wheels are arranged on the left front portion, the right front portion, the left rear portion and the right rear portion of the vehicle body respectively. The all-dimensional steering obstacle crossing vehicle is characterized in that the wheels and the vehicle body are connected through a steering lifting mechanism, and crawler wheel mechanisms are arranged on the left side and the right side of the bottom of the vehicle body respectively. The all-dimensional steering obstacle crossing vehicle can realize on-site steering, transverse traveling and wheel lifting obstacle crossing, flexibility, maneuverability and obstacle crossing performance of the all-dimensional steering obstacle crossing vehicle are high, and stability, power performance and the terrain adaptive capacity of the all-dimensional steering obstacle crossing vehicle are high.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
High-maneuverability and high-adaptability ground unmanned platform
ActiveCN105857423AImprove terrain adaptabilityIncrease approach angleEndless track vehiclesTerrainVertical plane
The invention discloses a high-maneuverability and high-adaptability ground unmanned platform. The high-maneuverability and high-adaptability ground unmanned platform is characterized in that the high-maneuverability and high-adaptability ground unmanned platform comprises a vehicle body platform and six sets of independent driving mechanisms. The six sets of independent driving mechanisms are symmetrically disposed on the two sides of the vehicle body platform; each independent driving mechanism comprises a suspension system, a crawler belt traveling mechanism and a half shaft; the crawler belt traveling mechanisms are connected with the vehicle body platform through the suspension systems; the crawler belt traveling mechanisms comprise crawler belt driving mechanisms and crawler belt rotating mechanisms; the crawler belt driving mechanisms comprise driving motors, central driving wheels, wing wheels and crawler belts; the crawler belts which achieve transmission through together engagement of the central driving wheels and the wing wheels on the two sides form a geometrical shape of a parallelogram on the vertical plane; and the relative positions of the wing wheels and the central driving wheels are controlled, so that different moving postures of the independent driving mechanisms are obtained. The high-maneuverability and high-adaptability ground unmanned platform is adaptable to complex terrains and has quite high capacity of obstacle crossing, trench crossing and climbing.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
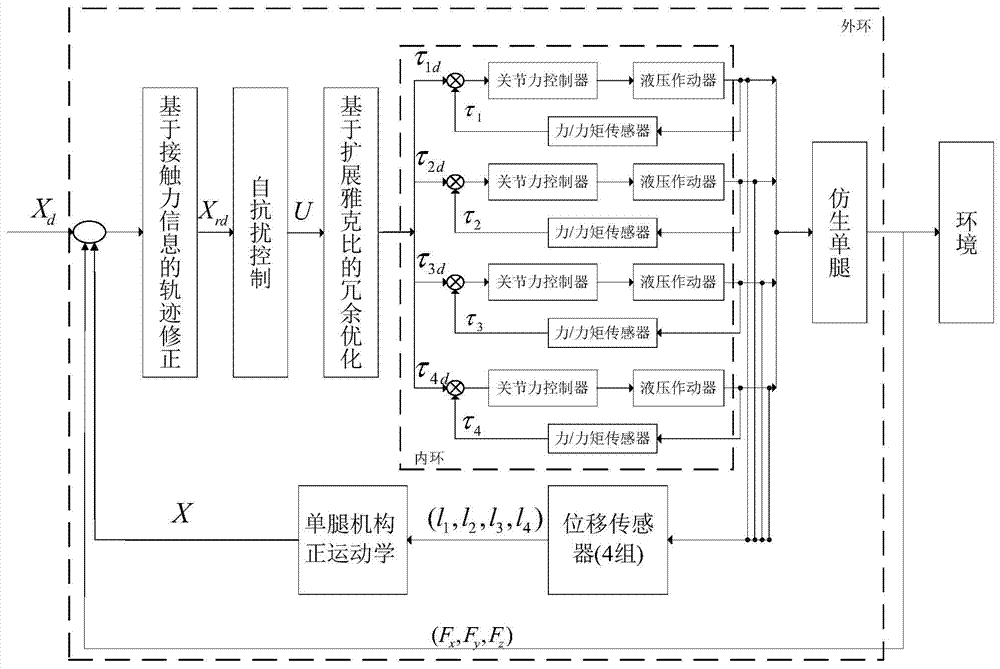
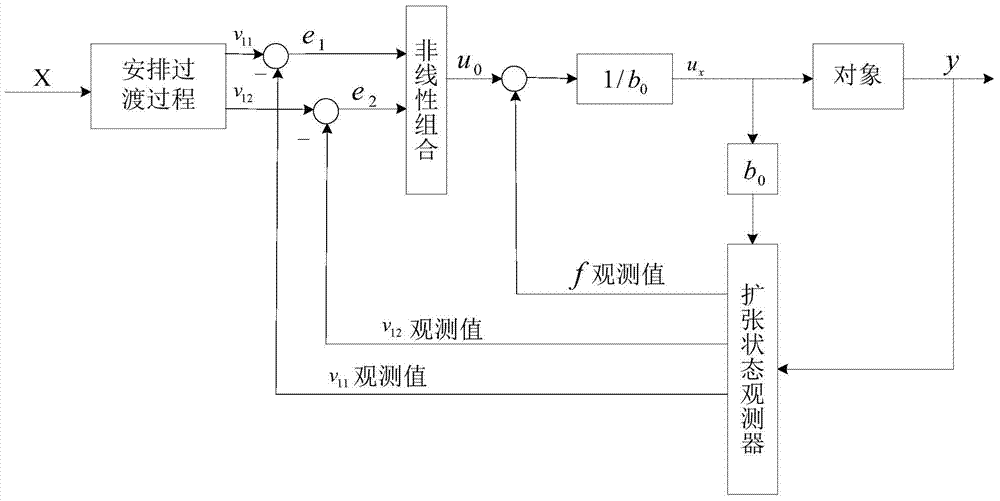
Hydraulically-driven type bionic single-leg double-loop control method
The invention discloses a hydraulically-driven type bionic single-leg double-loop control method. The hydraulically-driven type bionic single-leg double-loop control method is composed of two links including the outer loop force / position control link and the inner loop single-joint force control link. In the outer loop force / position control link, an externally-input original expected foot end position track is received, and replanning, active-disturbance-rejection controlling and redundant optimizing based on the expansion Jacobian are sequentially carried out on the original expected foot end position track to obtain original joint space control amount of joints of a bionic single leg; in the inner loop single-joint force control link, output force information of the joints of the bionic single leg is collected, the original joint space control amount of the joints of the bionic single leg is amended based on the output force information to obtain amended joint space control amount, and motions of hydraulically-driven motion controllers of the joints of the bionic single leg are respectively controlled according to the joint space control amount of the joints of the bionic single leg. The hydraulically-driven type bionic single-leg double-loop control method has the advantages of being good in terrain adaptive capacity, good in supple capacity, high in universality, high in robustness and wide in application scope.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Stretchy snake-shaped robot
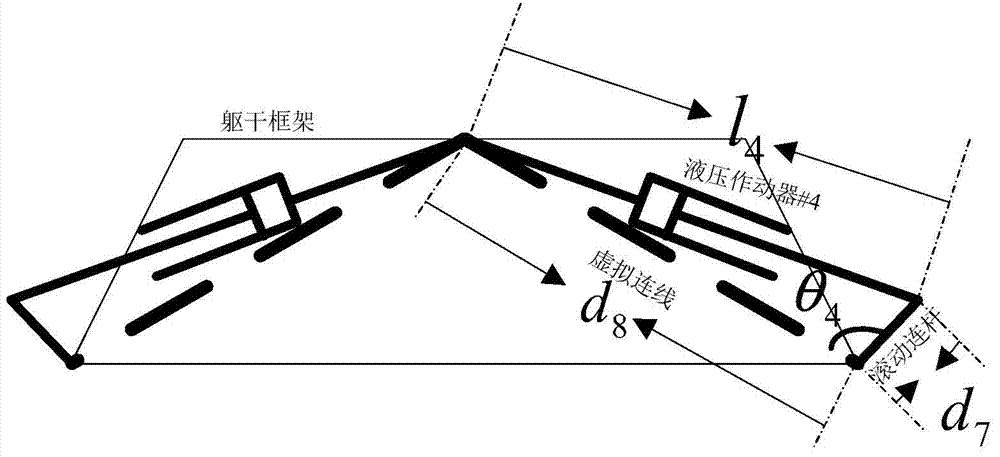
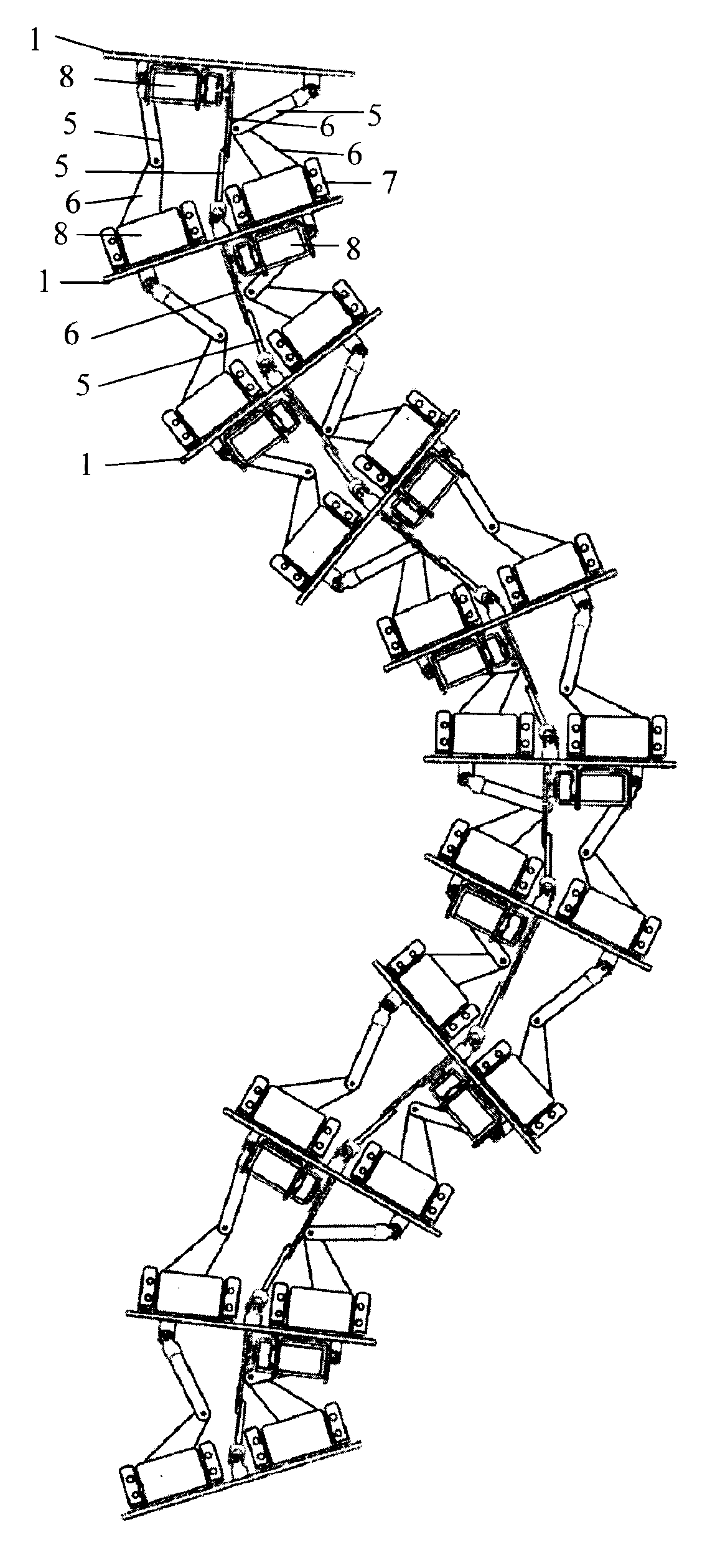
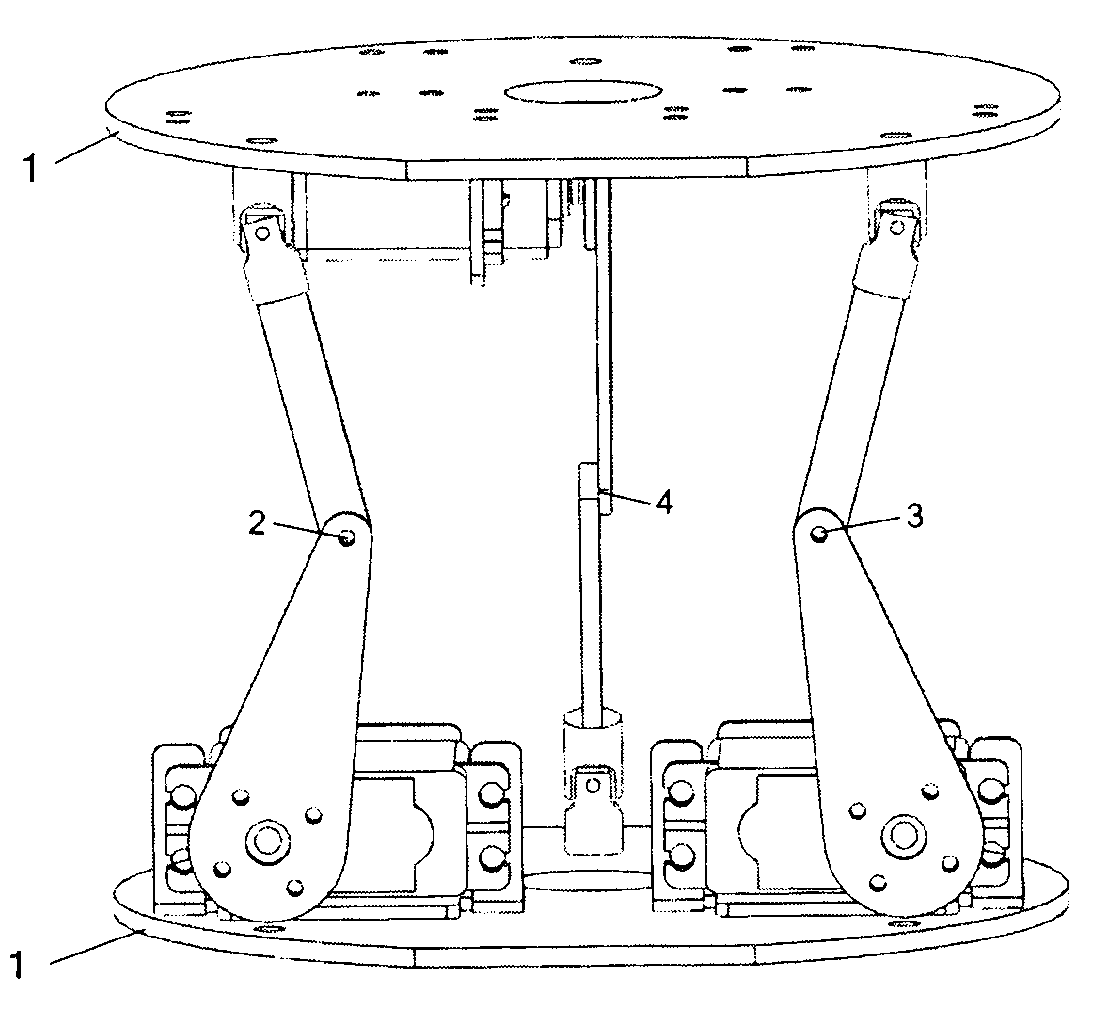
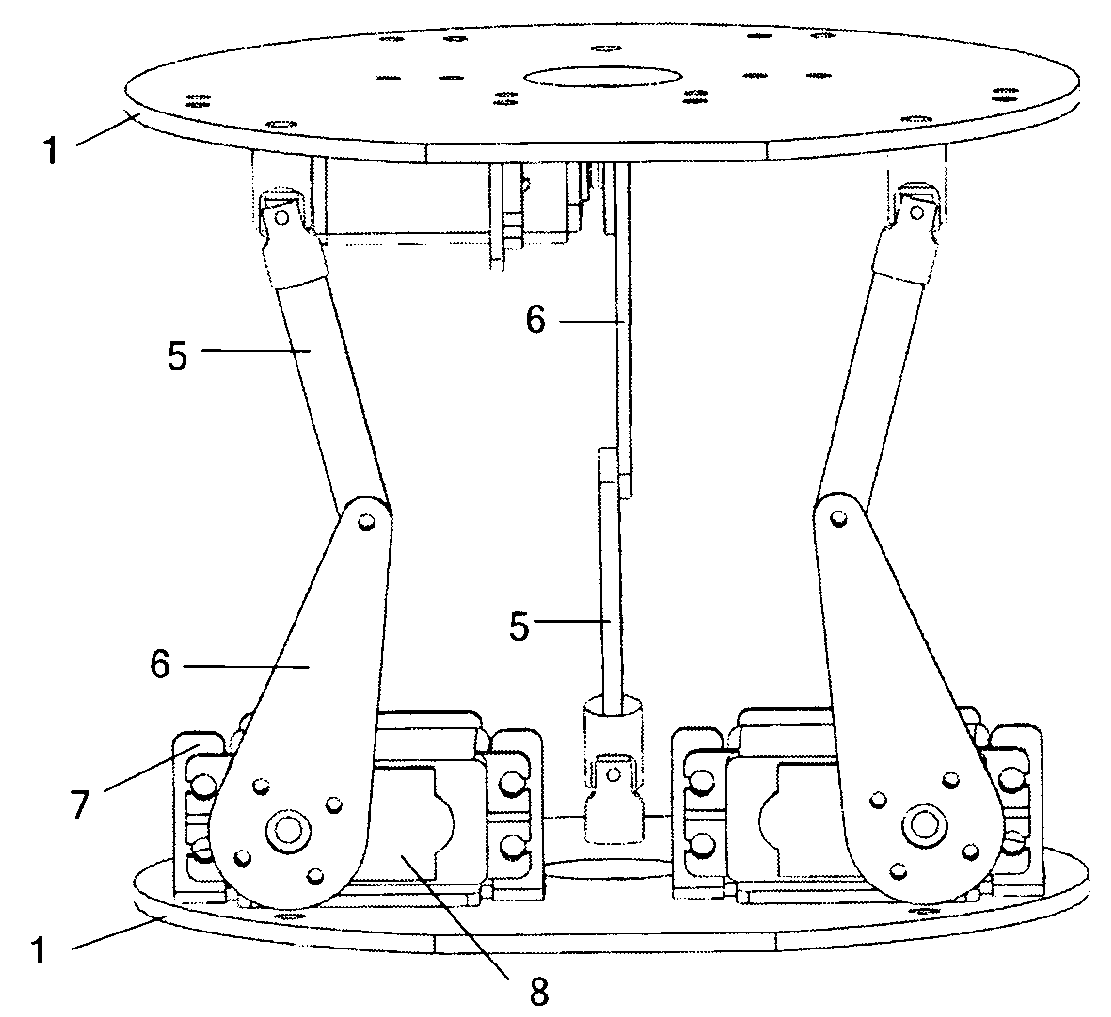
InactiveCN103341855AAchieve tight windingSimple structureProgramme-controlled manipulatorMotor functionElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention discloses a stretchy snake-shaped robot which is composed of 8-15 connection plates of the identical structure and series-connection branches connected with the connection plates. Two adjacent connection plates are connected through three series-connection branches which are of the same structure and are distributed in a triangular mode to form a parallel mechanism unit module, a steering engine of each serial-connection branch is fixedly connected with a steering engine support, the output shafts of the steering engines are fixedly connected with one ends of driving rods, the other ends of the driving rods are connected with one ends of driven rods through rotation pairs, the steering engine supports of the first branches and the steering engine supports of the second branches are fixedly connected with the connection plates, the other ends of the driven rods of the third branches are connected with the connection plates through universal hinges, the other ends of the driven rods of the first branches and the other ends of the driven rods of the second branches are connected with another connection plates through universal hinges, the steering engine supports of the third branches are connected with another connection plates, and the output shafts of the steering engines of the third branches in two adjacent modules are opposite in the arrangement direction. The stretchy snake-shaped robot is simple in structure, has the straight-line stretchy motion function and can flexibly move in the narrow space.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Diaphragm wall joint and manufacturing method of diaphragm wall
InactiveCN102061710AGood terrain adaptabilityNot easy to gushing water and sandArtificial islandsUnderwater structuresJoistWater leakage
The invention discloses a diaphragm wall joint and a manufacturing method of a diaphragm wall. The diaphragm wall joint comprises two sections of first-stage walls in one foundation pit, wherein the sides of the two sections of walls are opposite; the opposite sides of the first-stage walls are respectively and fixedly connected with two joist steel webs; one section of second-stage wall is arranged in a middle foundation pit; and the second-stage wall is connected with the joist steel webs by adopting a sleeve valve tube for grouting. The manufacturing method of the diaphragm wall aims to manufacture the diaphragm wall. For the diaphragm wall joint, the second-stage wall is utilized to transit; the connecting position is fixed by the joist steels and grouted by a sleeve valve tube, thus having good structure adaptability, no water leakage, low possibility of water burst and sand burst, good water-stopping effect, and safety and reliability. In the manufacturing method, substage grouting is carried out on wall sections in the joint, and the fillers of the joist steel webs are washed and then grouted, thus realizing fast forming and firm connection for the joint, and avoiding the water burst and the sand burst.
Owner:GUANGDONG FOUND ENG GRP CO LTD
Combined type obstacle crossing walking system
InactiveCN101181911AGuaranteed to be under tensionGuaranteed tensionEndless track vehiclesBogieDrive wheel
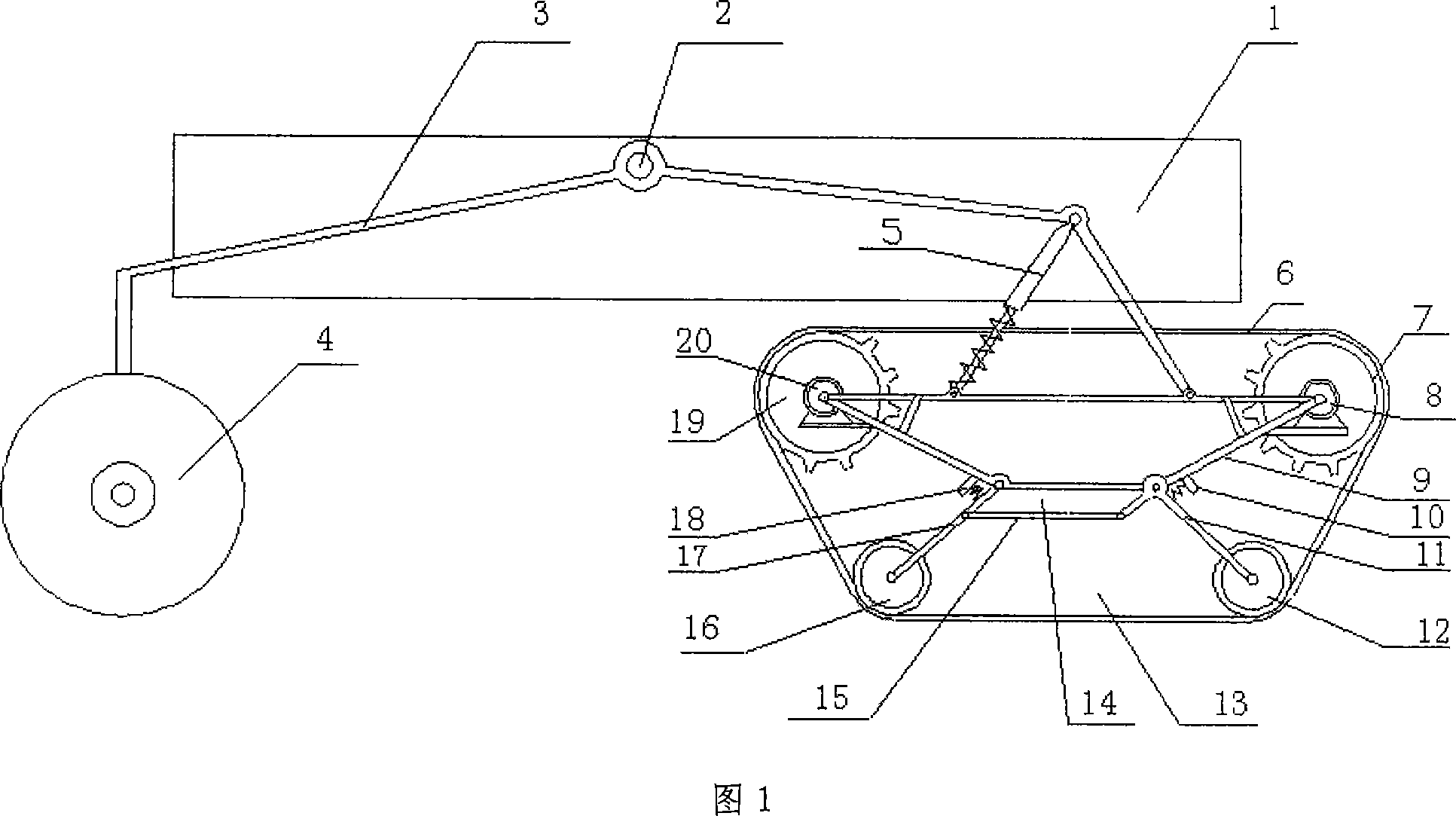
The invention discloses a composite obstacle-surmounting walking system, which belongs to an obstacle-overriding walking mechanism. It is characterized in that it consists of a rocker suspension (3), a differential balance mechanism (2), a rear wheel (4), and a front track wheel (13), wherein the front track wheel (13) and the rocker suspension (3) Hinged and damping spring (5) is installed between the two, front crawler wheel (13) is made of track (6), internal support (9), drive motor (8,20), two driving wheels ( 7, 19), and two load-bearing wheels (12, 16) located below that are connected to the internal bracket (9) through a parallelogram mechanism (14), the side bars on both sides of the parallelogram mechanism (14) are connected to the interior Elastic stoppers (10, 18) are respectively installed between the supports (9). The composite obstacle-crossing walking mechanism has good obstacle-crossing performance, strong ground adaptability, easy control and light weight, and can be used for various special detection vehicles.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Wheel-shoe deformation mechanism, travel device and vehicle
PendingCN109131610AAchieve deformationIncreased load-bearing capacityEndless track vehiclesMechanical engineeringLoad bearing
The invention provides a wheel-shoe deformation mechanism which includes a traveling device of the wheel shoe deformation mechanism and a vehicle provided with the traveling device. The wheel shoe deformation mechanism comprises a gear seat, the transmission gear and two sets of track spreading units which are hinged on the gear base and whose hinge axes are both parallel to the transmission gearaxes. The gear base is connected with a deformation driving unit capable of driving the reciprocating linear movement thereof, and the reciprocating linear movement direction is perpendicular to the axial direction of the transmission gear. The two sets of track spreading units are connected with a limit structure capable of controlling the opening angle thereof, and the transmission gear is positioned between the two sets of track spreading units so as to be meshable with the inner side of the track. The invention can realize the change of the track shape, and the cooperation of a plurality of wheel-shoe deformation mechanisms can make the traveling device have various working modes such as wheel type and track type, and improve the load bearing performance and obstacle overtaking performance. The track spreading unit can cooperate with the transmission gear to induce and support the track and can adjust the tightness of the track.
Owner:INST OF DEEP SEA SCI & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Wheel-legged combined-type robot platform
The invention discloses a wheel-legged combined-type robot platform, which comprises a vehicle body, a front vehicle body, a rear vehicle body, a front wheel-legged system and a rear wheel-legged system, and is characterized in that the front wheel-legged system comprises a steering system and a front leg swinging system; the steering system comprises a steering motor, a steering mechanism and steering wheels; the front leg swinging system comprises a front leg swinging motor, a front wheel-legged supporter and front leg swinging wheels; the two subsystems are installed in a front box body, and the front box body is connected with the vehicle body by utilizing a front stub axle extending out of the rear part of the front box body; the rear wheel-legged system comprises a vehicle body and rear leg swinging system and a driving system, and the two subsystems are installed on the rear vehicle body; the rear vehicle body is connected with the vehicle body by utilizing a rear stub axle extending out of the front part of the rear vehicle body; the vehicle body part mainly comprises an angle-turning motor which is installed inside the vehicle body and has no relative motion with the vehicle body; a gear is connected to a torque output end, and another gear engaged with the gear is rigidly connected with the rear stub axle; and leftward and rightward adjustment and inclination of the vehicle body are realized through the angle-turning motor.
Owner:SHAANXI JIULI ROBOT MFG
Vane wheel type snake-like robot
InactiveCN101695833AStrong ability to overcome obstaclesStrong terrain adaptabilityManipulatorElectric machineryFuselage
The invention discloses a vane wheel type snake-like robot, which comprises vane wheels, machine bodies, a universal joint and motors, wherein two machine bodies are connected with each other through the universal joint; a plurality of the machine bodies are connected in series to form a snake body of the robot; two horizontal sides in each machine body are provided with a motor respectively; two sides of each machine body are provided with a vane wheel respectively; and the motors are in transmission connection with the vane wheels. The vane wheel type snake-like robot has the advantages of strong obstacle passing capacity, strong landform adaptability and simple structure.
Owner:CHONGQING JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Multi-foot robot gait optimization control method based on multidimensional workspace coupling algorithm
ActiveCN106681341AFind out the effective working space quicklyImprove algorithm efficiencyAttitude controlVehiclesInstabilitySacroiliac joint
Disclosed a multi-foot robot gait optimization control method based on the multidimensional workspace coupling algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, solving a virtual constraint radius and parsing robot body swing leg movement constraint K space according to the virtual constraint radius; step 2, solving the swing leg ideal foothold constraint R space and the robot body stability constraint B space, coupling the robot body swing leg movement constraint K space, the swing leg ideal foothold constraint R space and the robot body stability constraint B space, solving the multidimensional robot body workspace W, and then putting forward the robot body 'dead-lock' instability situation and countermeasures; step 3, parsing the mapping relation between the standing leg joint output position and the robot body workspace according to the multidimensional robot body workspace obtained in step 2, and finally, making polynomial interpolation calculation on the joint rotation angle, and finishing a gait plan for the robot in a non-structural environment. The method guarantees the gait stability and gait high-efficiency of the robot in the non-structural environment.
Owner:杭州宇芯机器人科技有限公司
Stepped horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland combined system and application thereof
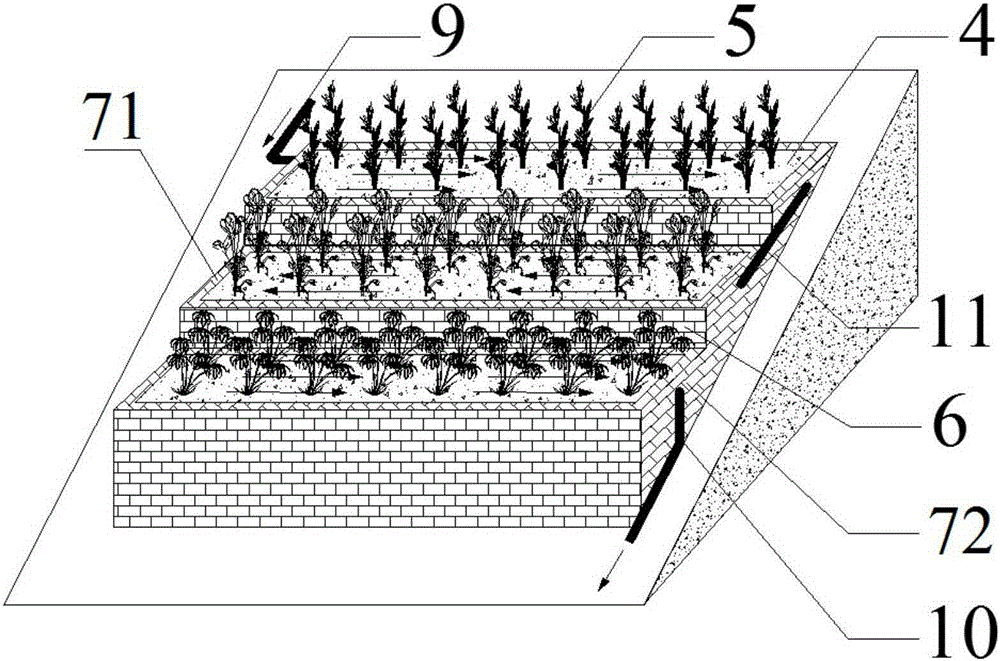
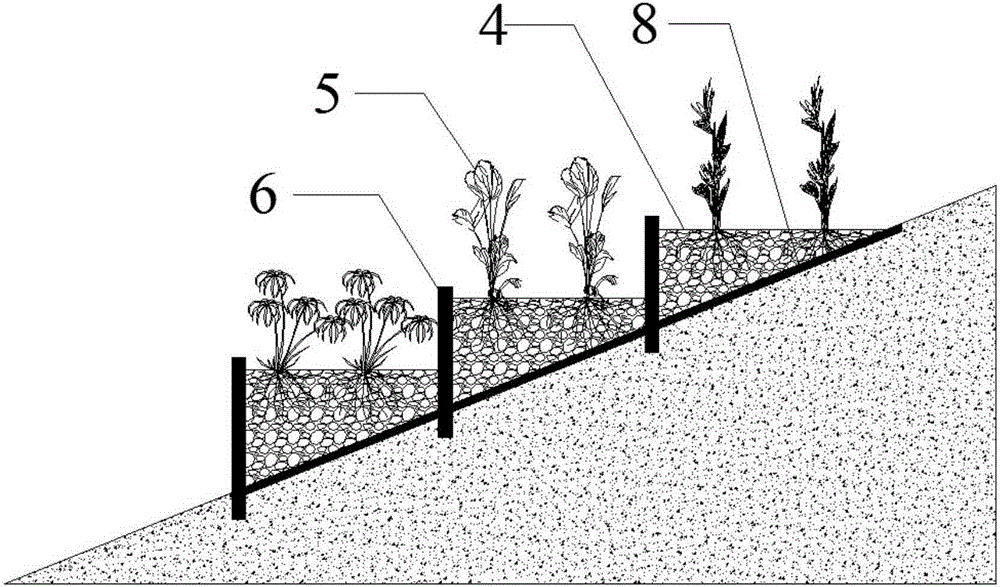
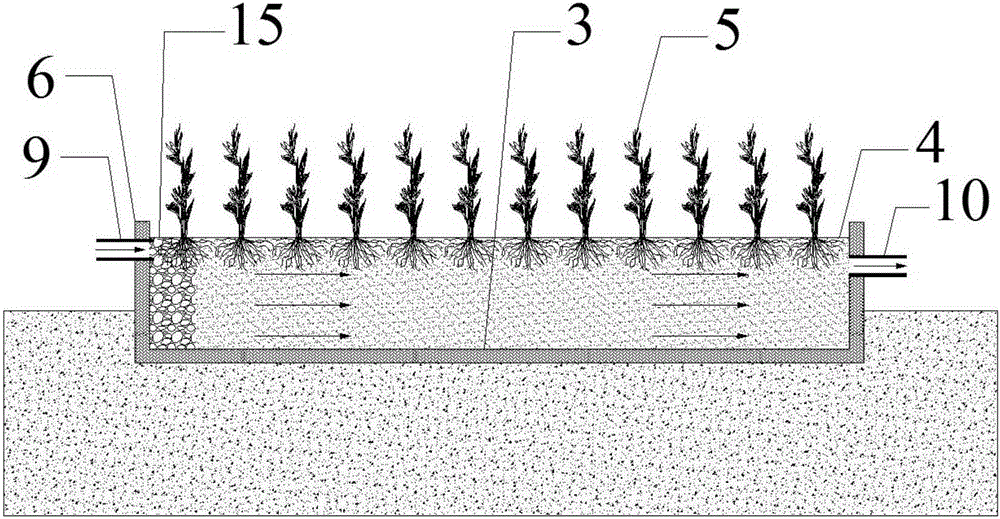
ActiveCN105198085ASimple structureEasy constructionSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentConstructed wetlandTerrain
The invention relates to a stepped horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland combined system and application thereof. The combined system is built along clinoform and comprises multiple stages of stepped horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland units which are distributed in a stepped mode from top to bottom according to the slope gradient, and a pipe network unit through which all the stages of stepped horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland units are communicated. The side face water inlet mode is adopted for the stepped horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland units. Water flow in the stepped horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland units horizontally flows in the length direction of the stepped horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland units. Compared with the prior art, the limitation of terrains on application of constructed wetlands is broken through, slope space can be fully used, the structure is simple, construction is easy and convenient, cost is low, the stepped horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland combined system and application can be widely applied to processing of various types of sewage such as domestic sewage, municipal sewage, industrial wastewater, animal husbandry sewage, agricultural surface resource pollution, surface flow and tail water of sewage treatment plants in slope areas such as mountainous regions, hills and water body banks, and the application range of constructed wetlands is greatly widened.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Robot stable motion control method based on curve fitting modeling and multi-constraint foot point estimation
ActiveCN106826813APrevent dead pixelsImprove stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorDesign optimisation/simulationTerrainEngineering
The invention discloses a robot stable motion control method based on curve fitting modeling and multi-constraint foot point estimation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a local environment of a swing leg foot end is modeled based on a curve fitting algorithm; (2) a reachable area of the swing leg foot end is fitted by combining with working space of the swing leg foot end according to the fitted local environment; (3) according to the reachable area of the swing leg foot end fitted in the step (2), a multi-constraint foot point estimation algorithm is combined to estimate and analyze a plannable foot point in the reachable area of the swing leg foot end; and (4) according to the steps (1) to (3), a multi-gesture conversion algorithm is combined to analyze a robot joint output position, and the polynomial interpolation operation is performed for a joint corner to finish the stable motion control of a robot under non-structural environment. The stable motion control method is high in terrain adaptability and high in efficiency.
Owner:杭州宇芯机器人科技有限公司
Multi-moving-mode bionic moving robot
ActiveCN102849140ASmooth motionThe way of movement is to move quickly and stablyVehiclesVideo monitoringControl system
The invention discloses a multi-moving-mode bionic moving robot, which is characterized by consisting of a machine body platform, six machine legs in the same structures, a video monitoring system based on 3G (3rd generation) network and a double-rocker-rod remote operation and control system based on remote operation, wherein the machine legs comprise four joint parts and one wheel part, each joint part is driven by a large-torque steering engine with the rotating angle being 180 degrees, one steering engine is in charge of driving one joint, the wheel parts are driven by large-toque steering engines with the rotating angle being 360 degrees, and the whole circle rotation can be realized. The two ends of the steering machine rotating center shaft are respectively fixed by bearings, the six machine legs are symmetrically arranged at two sides of the robot machine body platform for forming a bionic mechanism, a connecting rod arranged at the lower end of the machine legs adopts a right-angle reverse L-shaped deign, one end of the connecting rod is connected with the machine body, the other end of the connecting rod is in contact with the ground, the video monitoring system mainly comprises a sending end and a receiving end, and the remote operation and control system carries out operation and control by aiming at the six machine legs, and mainly comprises a sending end and a receiving end.
Owner:彼合彼方机器人(天津)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com