Axl-specific antibodies and uses thereof
A specificity, antibody technology, applied in the direction of antibodies, antibody mimics/scaffolds, preparations for in vivo tests, etc., can solve problems such as lack of sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0137] Embodiment 1: Preparation of anti-AXL antibody
[0138] Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against AXL were generated by immunizing mice with the extracellular domain of recombinant human AXL protein (rhAXL-ECD; SEQ ID NO:58) and by genetic immunization.
[0139] Preparation of rhAXL-ECD: The pTT5 construct containing a synthetic recombinant fragment of the C-terminal His8-tagged recombinant human (rh)AXL extracellular domain (ECD; SEQ ID NO:71) was expressed in CHO cells by Ni-agarose Purified and verified by SDS-PAGE (data not shown).
[0140] Immunization: Mouse mAbs were generated by genetic immunization. For genetic immunization, mice were bled (pre-immune serum) and immunized on days 0 and 42 with 100 μg of pTT40 expression plasmid for expression of soluble rhAXL-ECD by hydrodynamic tail vein delivery (HTV). After 7-10 days, mice were bled, and serum titers were measured by ELISA. After 4-5 months, a booster injection with 100 μg pTT40-AXL-H8G was done by HTV 3-4 d...
Embodiment 2
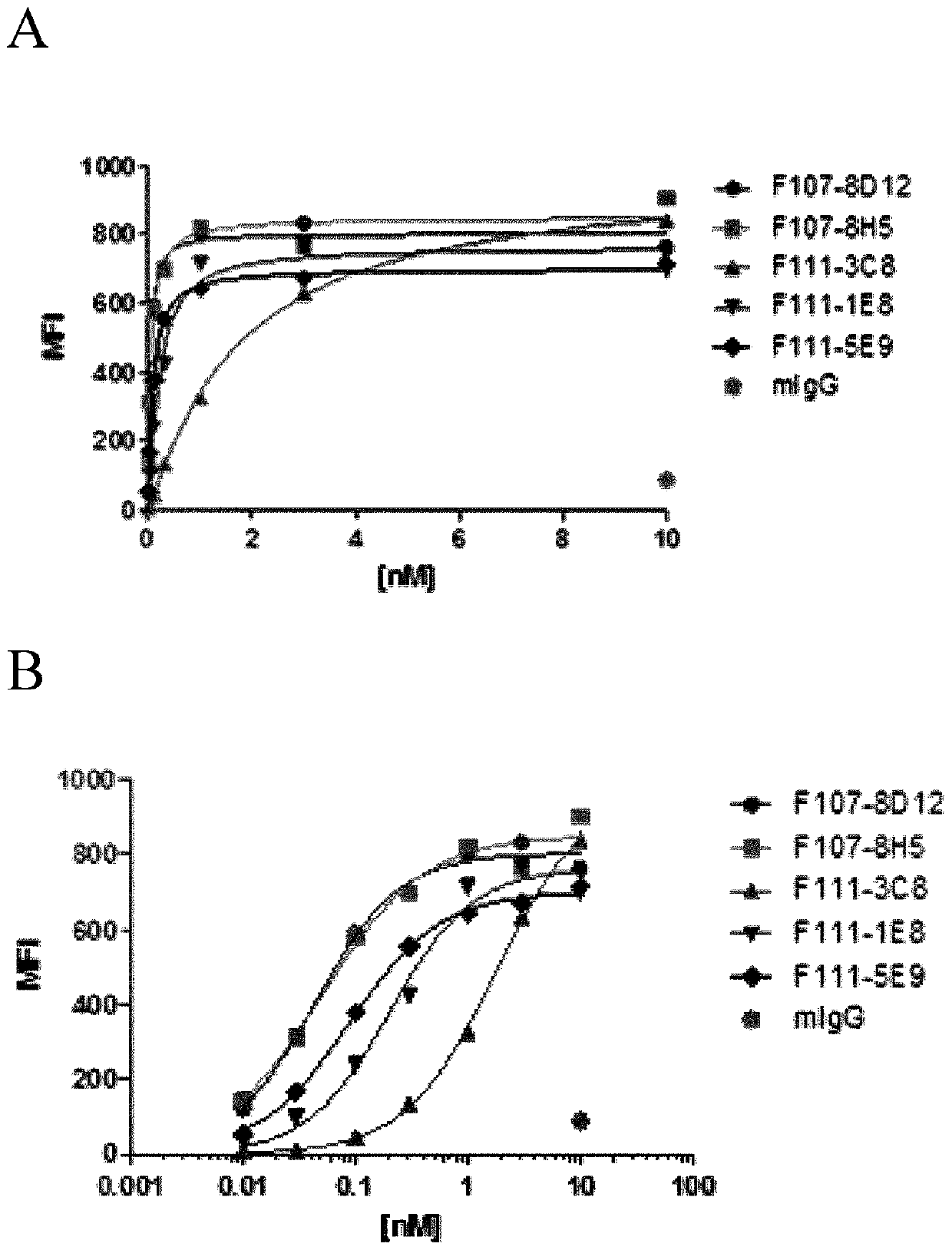
[0144] Example 2: Evaluation of cross-reactivity of anti-AXL mAbs
[0145] The anti-hAXL monoclonal antibodies purified in Example 1 were evaluated for their cross-reactive binding properties to the recombinant AXL extracellular domain.
[0146] To evaluate the cross-reactivity of mAbs with other members of the TAM receptor tyrosine kinase subfamily, the binding of the mAbs to rhAXL-ECD, rhMER-ECD, rhTyro-3 and BSA (negative control) was measured by ELISA. 96-well half-area plates (Costar) were coated with 25 μl of 5 μg / ml rhAXL-ECD, rhMER-ECD, rhTyro-3 or BSA in PBS and incubated overnight at 4°C. Microplates were washed 3 times with PBS, blocked with PBS-BSA 1%, added 25 μl of 10 μg / ml diluted in PBS-BSA 1%, and incubated at 37 °C, 5% CO 2 Incubate for 2 hours. with PBS-TWEEN TM 20 Wash plates 4 times at 0.05% at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Incubate for 1 hour with 25 μl of secondary antibody alkaline phosphatase-conjugated F(ab)'2 goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) (Jackson Immunoresearch)...
Embodiment 3
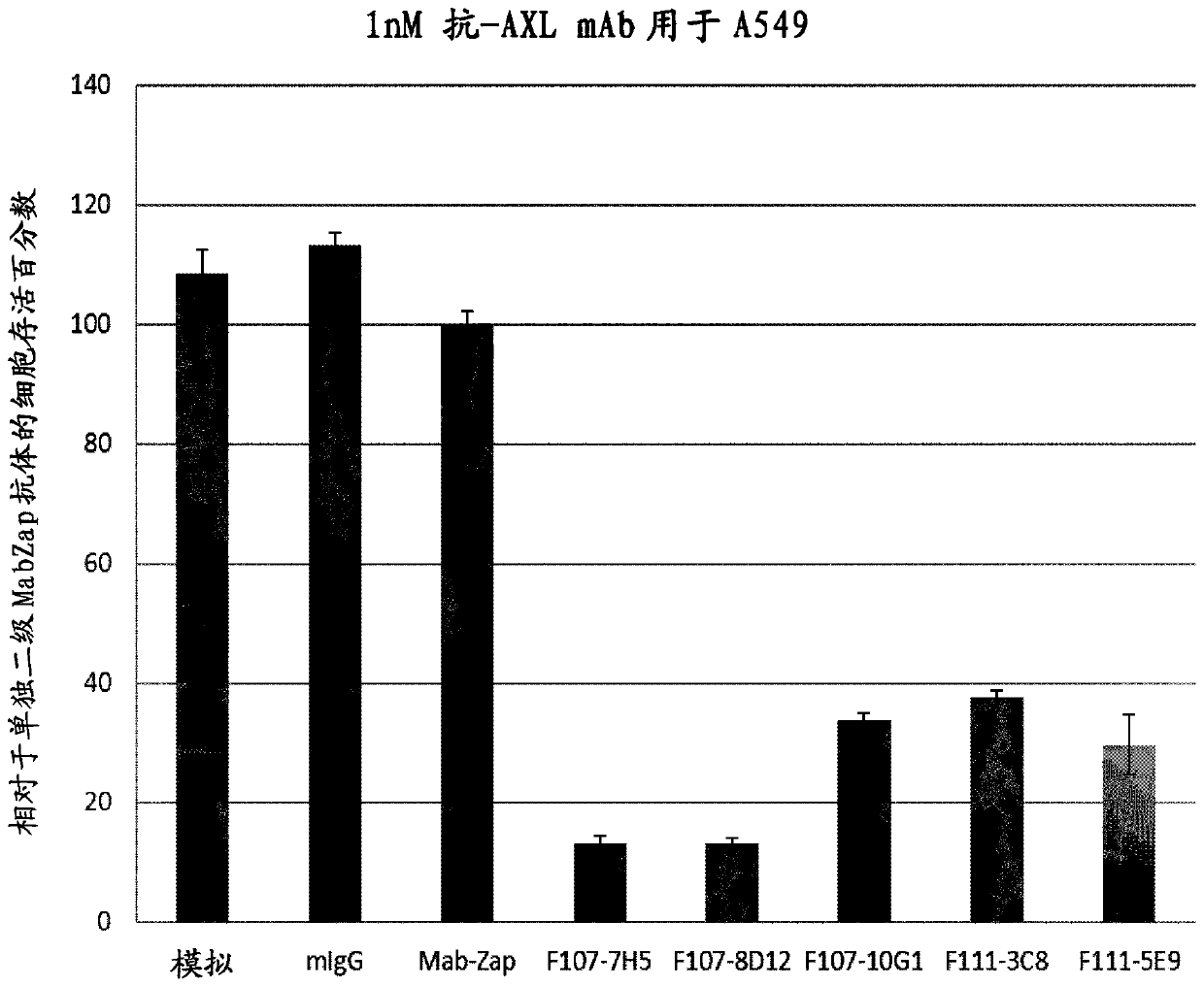
[0150] Example 3: Functional characterization of ADC potential
[0151] The anti-hAXL-ECD monoclonal antibody purified in Example 1 was evaluated for its internalization ability and antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) potential in an ADC surrogate screening assay. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) A549 cells, breast cancer MDA-MB231 cells or glioblastoma U87MG cells, all expressing moderate to high levels of AXL, were used. Selection showed low or sub nM (IC 50 ) efficacy of mAbs.
[0152] cell culture. The following cell lines were obtained from ATCC and cultured according to the supplier's recommendations: A549 human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), MDA-MB-231 triple-negative (ER- / PR- / HER2 low) breast cancer (TNBC) and U87MG Glioblastoma cell line. Typically, cells were passaged once or twice a week and used within 4-6 weeks for all experiments.
[0153] Evaluation of antibody-mediated cytotoxicity as antibody-drug conjugates. Primary mouse antibody (typically 1 nM con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com