A Transformer Winding Arrangement Method and Its Displacement Current Numerical Analysis Method
A transformer winding and displacement current technology, applied in the field of transformers, to eliminate common mode noise, simplify the difficulty of noise elimination, and improve EMI performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
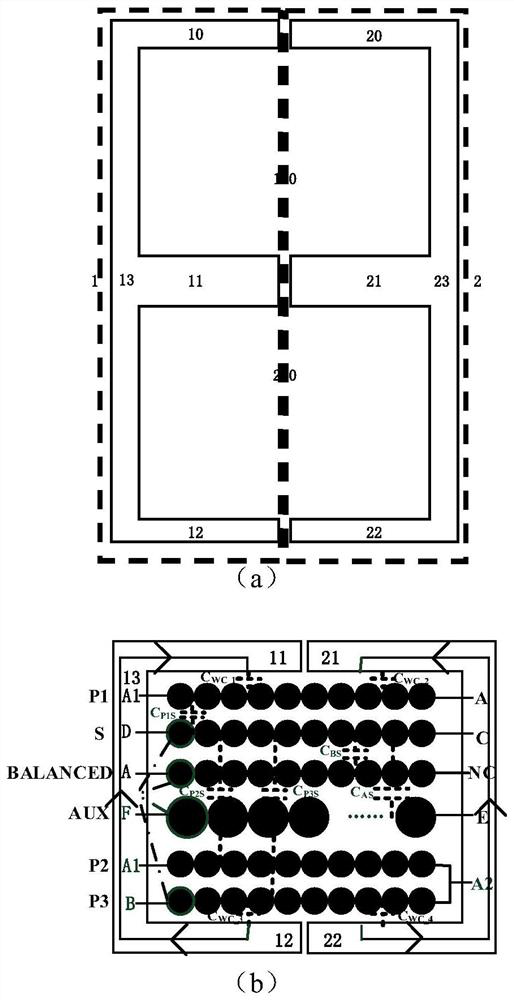
[0030] Example 1. In a transformer winding arrangement method and its displacement current numerical analysis method proposed by the present invention, the transformer winding arrangement is as follows figure 1 shown, figure 1 (a) is a schematic diagram of the magnetic core structure of the transformer. The magnetic core structure includes: a left magnetic core 1 and a right magnetic core 2 . The left magnetic core 1 and the right magnetic core 2 are both E-type magnetic cores. The left magnetic core 1 includes: the left magnetic core upper column 10, the left magnetic core center column 11, the left magnetic core lower column 12, the left magnetic core column 13; the right magnetic core 2 includes: the right magnetic core upper The column 20 , the center column 21 of the right magnetic core, the lower column 22 of the right magnetic core, and the upright column 23 of the right magnetic core. The left magnetic core 1 and the right magnetic core 2 constitute the upper magnet...
Embodiment 2
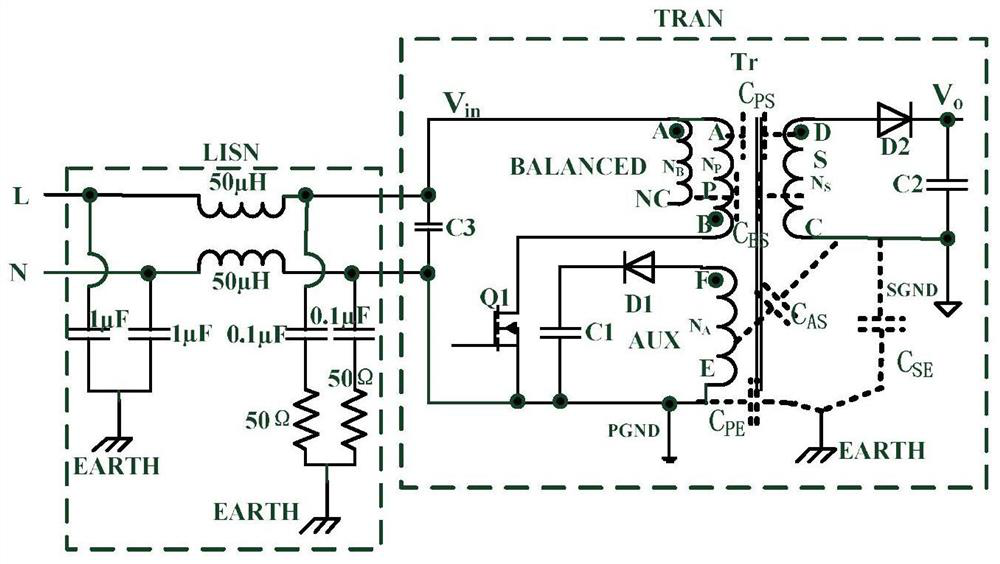
[0040] Example 2. In a preferred embodiment, the transformer structure proposed by the present invention is applied to a flyback converter, and the topology of the flyback converter used is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0041] The topology of the flyback converter includes: a linear impedance stabilization network part LISN and a converter part TRAN.
[0042] The converter part TRAN includes: Transformer T r , the primary side main power tube Q1, the first diode D1, the second diode D2, the first output filter capacitor C1, the second output filter capacitor C2, and the third capacitor C3. Among them, the transformer Tr includes: the primary winding P, the secondary winding S, the balance winding BALANCED, and the auxiliary winding AUX.
[0043] The L end of the linear impedance stabilization network LISN is connected to one end of the third capacitor C3, and the N end is connected to the other end of the third capacitor C3.
[0044] The A end of the primary winding P of t...
Embodiment 3
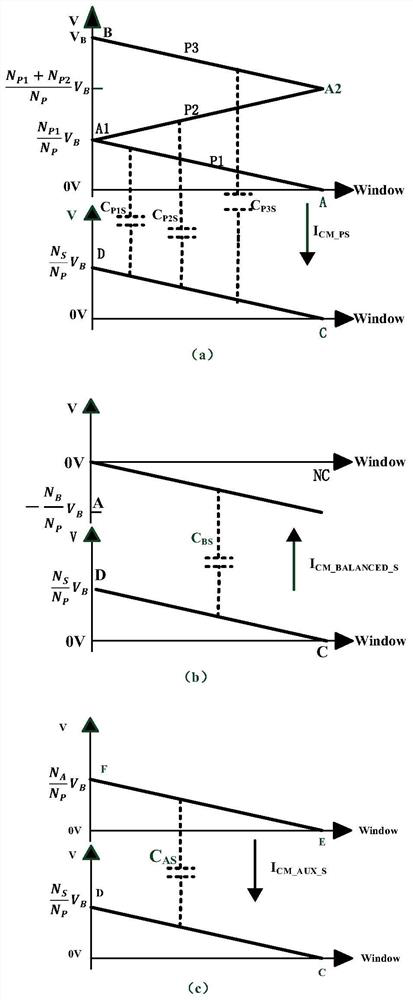
[0048] Example 3. When the flyback converter is working, under the arrangement of the transformer windings proposed by the present invention, the potential change and the displacement current distribution between each winding located at the primary position and the secondary winding S are as follows: image 3 shown. exist image 3 , the abscissas of each potential change and displacement current distribution diagram represent the first primary winding P1, the second primary winding P2, the third primary winding P3, the secondary winding S, the auxiliary winding AUX and the balance on the same layer. The distance between each turn of the winding BALANCED and the left magnetic core column 13, where the starting point of the abscissa represents the closest turn of each winding to the left magnetic core column 13, so the starting point of the abscissa is defined as the leftmost side of the magnetic core window; The coordinates take 0V as the starting point, indicating the magnit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com