Aspheric deformable mirror with high thermal disturbance resistance, and development method thereof
A technology of deformable mirrors and aspheric surfaces, applied in optical components, instruments, optics, etc., can solve the problems of low heat capacity of mirrors, low support stiffness, and high construction costs, and achieve compact overall structure, high axial stiffness, and high resonance frequency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
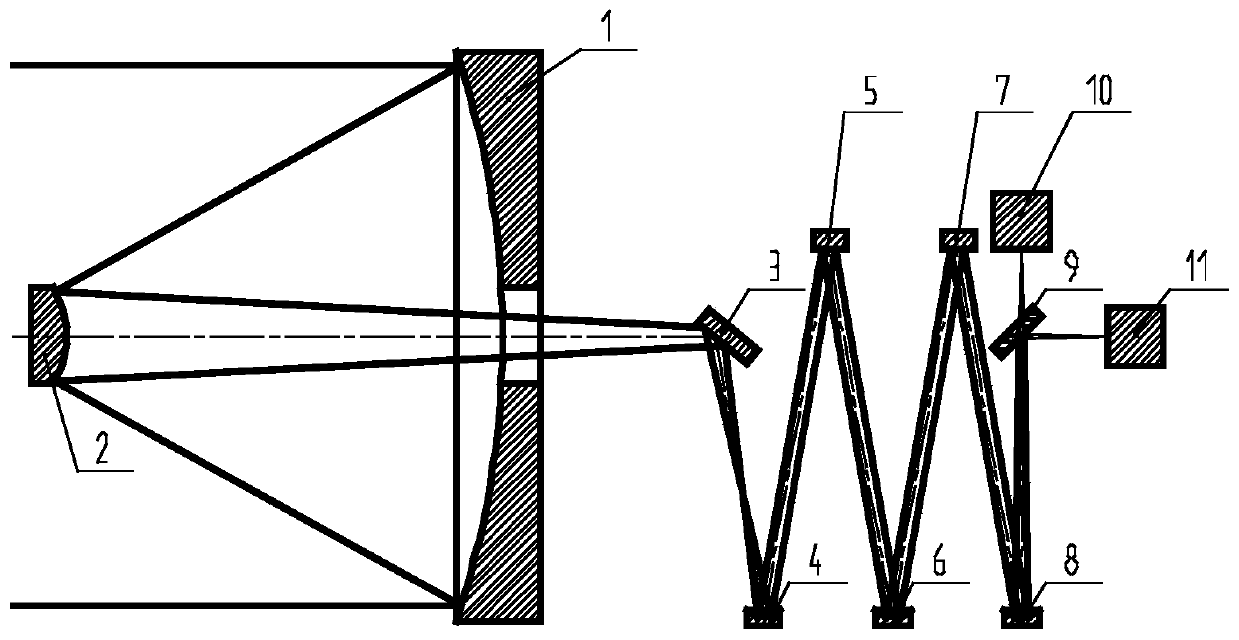
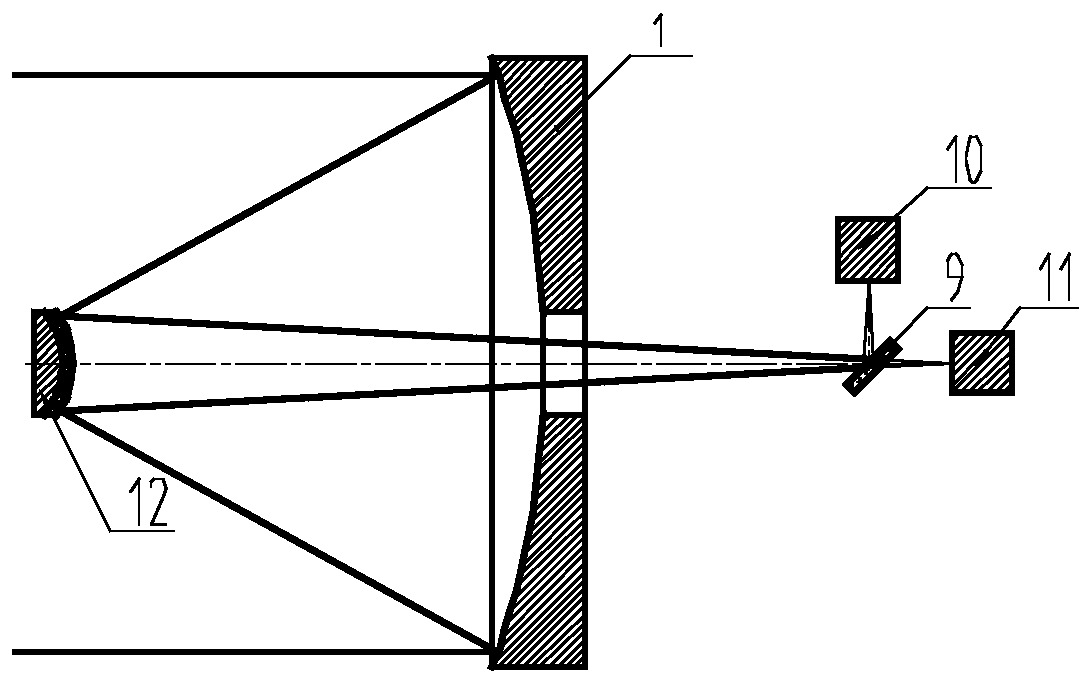
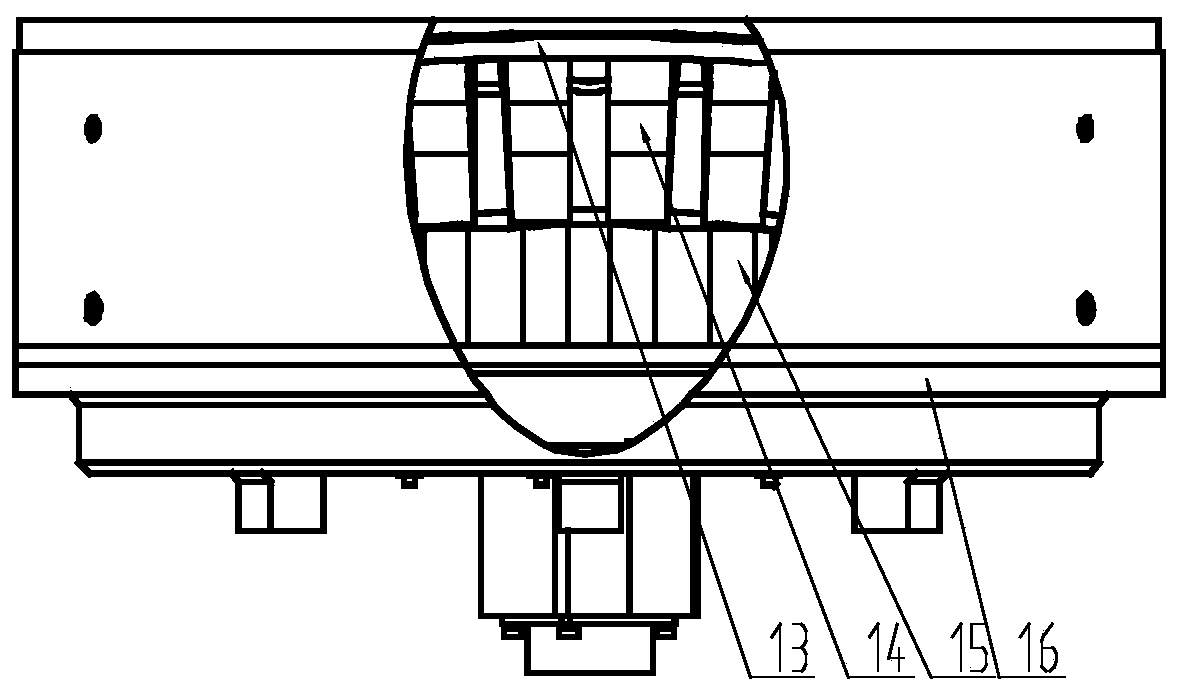
[0033] Such as image 3 As shown, the aspherical deformable reflector of the present invention is assembled by a mirror surface 13, an array of drivers 14, a base, a heat sink 15, and a housing 16, and the housing 16 is used as a connecting mechanism, and the base and the heat sink 15 are used as a displacement reference. The driver 14 is a driving mechanism, and the mirror 13 is a wavefront corrector that is a reflection surface.
[0034] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the mirror surface 13 is a spherical shell structure, the front surface 17 of the mirror surface is an aspheric surface, the back surface 18 of the mirror surface is a spherical surface, and the pole head 19 and the mirror surface are an integral structure. Wherein, the front side of the mirror 17 is simultaneously used as the secondary mirror of the telescope and the reflecting ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com