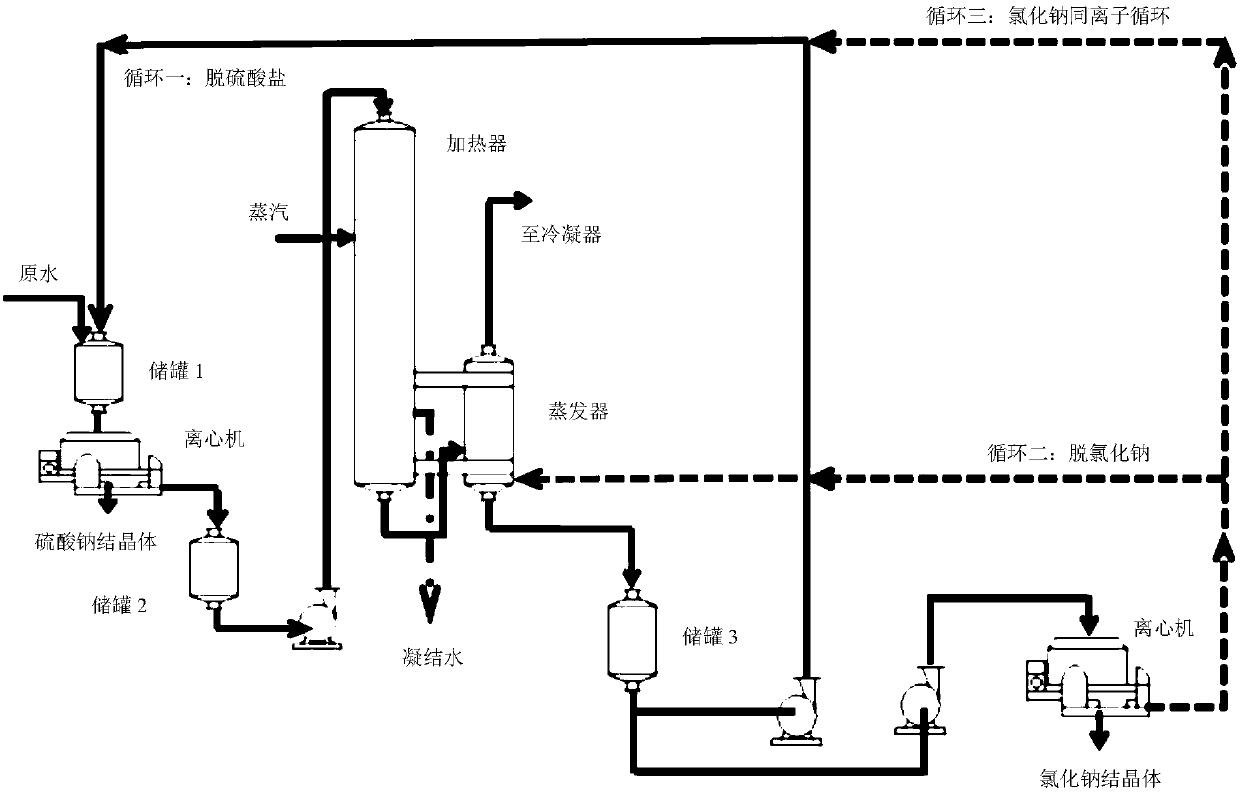
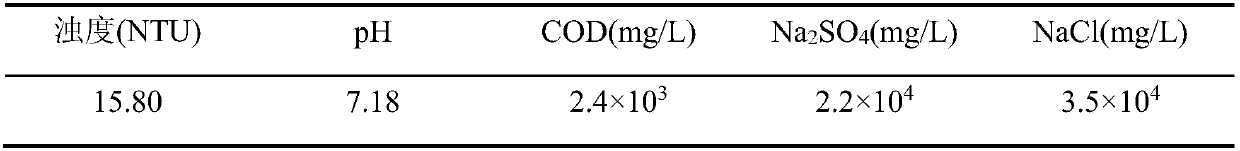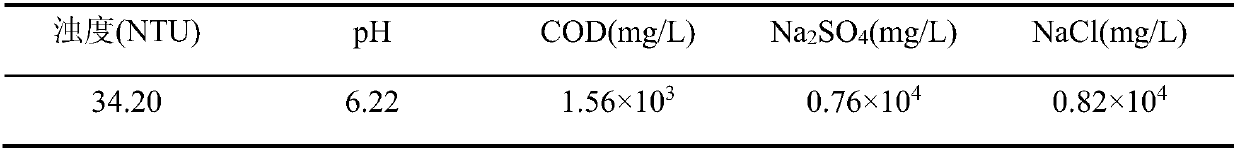Method for synchronously removing sodium sulfate and sodium chloride in wastewater through three cycles
A technology of sodium chloride and sodium sulfate, applied in chemical instruments and methods, alkali metal chlorides, alkali metal sulfites/sulfites, etc., can solve the problems of poor stability, complicated process flow, low product purity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] The water quality index of an industrial high-salt wastewater (No. 1) is shown in the table below:
[0044] Table 1 Water quality index of an industrial high-salt wastewater (No. 1)
[0045]
[0046] Using a method and device for synchronously removing sodium sulfate and sodium chloride in water with three cycles to treat industrial high-salt wastewater, the experimental results: 12m 3 After 24 hours of mixed wastewater operation, the zero discharge rate of wastewater was 99.9%, the average removal rate of COD was 87.2%, the removal rate of sodium sulfate was as high as 97.0%, and the removal rate of sodium chloride was as high as 98.1%. A total of 0.256×10 3 kg sodium sulfate crystals, 0.412×10 3 kg of sodium chloride crystals, the equipment operates stably.
Embodiment 2
[0048] The water quality index of an industrial high-salt wastewater (No. 2) is shown in the table below:
[0049] Table 1 Water quality index of an industrial high-salt wastewater (No. 2)
[0050]
[0051] Using a method and device for synchronously removing sodium sulfate and sodium chloride in water with three cycles to treat industrial high-salt wastewater, the experimental results: 12m 3 After 24 hours of mixed wastewater operation, the zero discharge rate of wastewater was 99.9%, the average removal rate of COD was 92.3%, the removal rate of sodium sulfate was as high as 94.2%, and the removal rate of sodium chloride was as high as 92.0%. A total of 0.086×10 3 kg sodium sulfate crystals, 0.091×10 3 kg of sodium chloride crystals, the equipment operates stably.
Embodiment 3
[0053] The water quality index of an industrial high-salt wastewater (No. 3) is shown in the table below:
[0054] Table 1 Water quality index of an industrial high-salt wastewater (No. 3)
[0055]
[0056] Using a method and device for synchronously removing sodium sulfate and sodium chloride in water with three cycles to treat industrial high-salt wastewater, the experimental results: 12m 3 After 24 hours of mixed wastewater operation, the zero discharge rate of wastewater was 99.9%, the average removal rate of COD was 77.4%, the removal rate of sodium sulfate was as high as 94.3%, and the removal rate of sodium chloride was as high as 96.1%. A total of 0.204×10 3 kg sodium sulfate crystals, 0.242×10 3 kg of sodium chloride crystals, the equipment operates stably.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com