Inhibitor for improving genome site-specific integration efficiency, and application thereof
A genome-targeted and inhibitor technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problem of low genome-targeted integration efficiency, and achieve the effects of improving the site-targeted integration efficiency, efficiency, and probability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Construction of CRISPR / Cas9 system and EGFP reporter vector
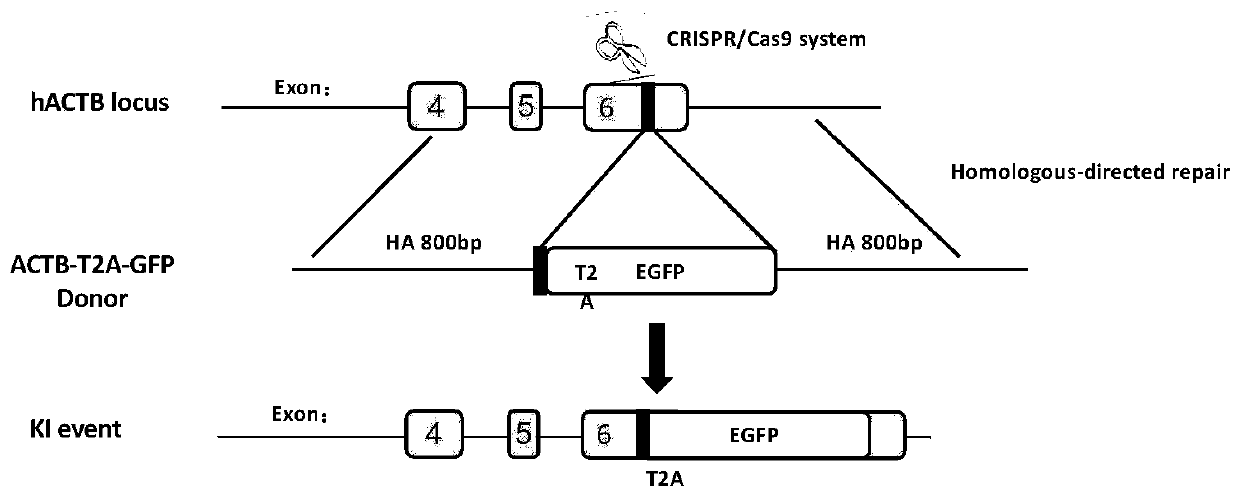
[0034] EGFP reporter carrier: Two kinds of ACTB-T were constructed separately 2 A-GFP (nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 3) and GAPDH-T 2 A-GFP (nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 4) reporter carrier, these two kinds of reporter carriers are all synthesized by Nanjing GenScript Biotechnology Co., Ltd., and its working principle is as follows figure 1 Shown: CRISPR / Cas9 system cuts ACTB gene (NC_000007.14) or GAPDH gene (NC_000012.12). After DNA double-strand breaks, cells undergo homologous directional integration, EGFP is integrated into ACTB or GAPDH genes, and cells can produce green fluorescence. The green fluorescent signal can be detected by flow cytometry. Thus, the efficiency of genome-specific integration can be assessed by detecting the number of cells expressing green fluorescence.
[0035]CRISPR / Cas9 system construction: Design the CRISPR / Cas9 guide sequence sgRNA of ACTB...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment two: the culture of human kidney epithelial cell (293T)
[0041] Adjust the temperature of the water bath to 37°C in advance, take out the frozen cells from the liquid nitrogen, immediately put them into the water bath and shake them quickly to completely dissolve the cell solution within 1-2 minutes. Then add 1ml of cell solution into 8ml of complete medium and mix well, then transfer to 10cm culture dish, and return to 37°C, 5% CO 2 and cultured in an incubator with 95% relative humidity. Subsequent experiments can be carried out when the cells to be cultured grow to 70%-80% confluence.
Embodiment 3
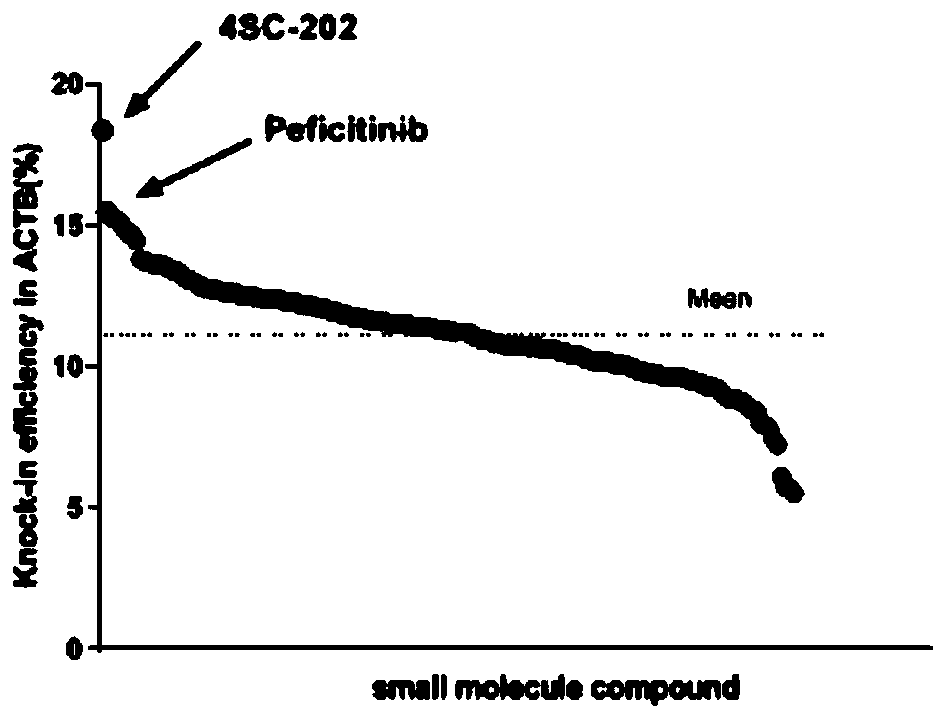
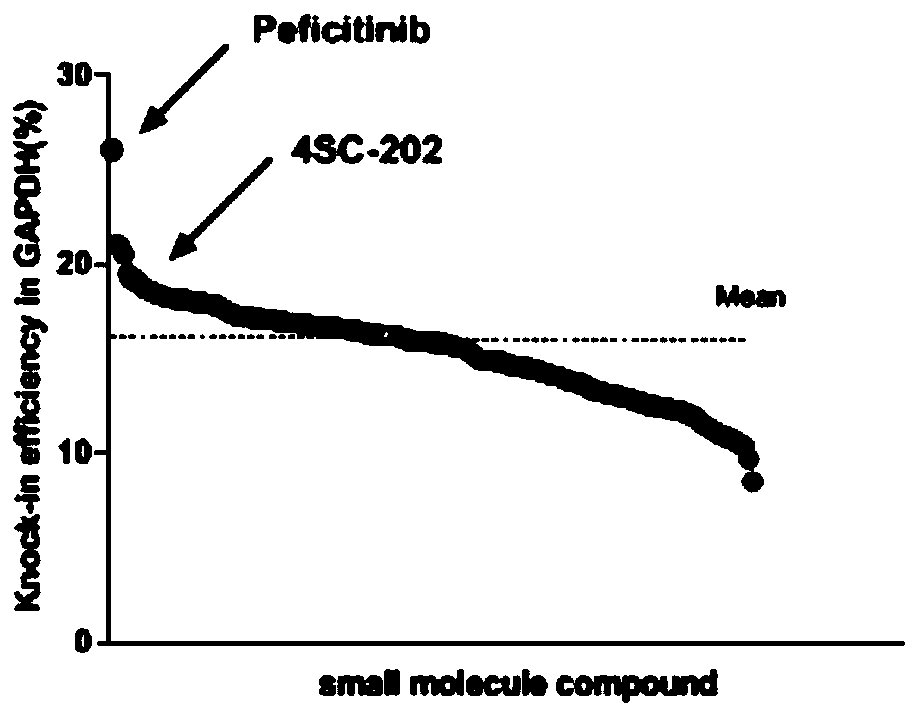
[0042] Example 3: Screening of Small Molecule Compound Library for Appearance Modification to Improve Site-Directed Integration Efficiency
[0043] Small molecule compound library Epigenetics Compound Library was purchased from MCE Company. Use ACTB-T2A-GFP and GAPDH-T2A-GFP reporter vectors to screen whether the 182 compounds in the library can significantly improve the efficiency of genome-specific integration. The specific screening method is as follows: 293T cells are grown to confluence in a 10cm cell culture dish At 70%-80%, transfect the CRISPR / Cas9 vector and EGFP reporter vector according to the instructions of Lipofectamine3000 transfection reagent, and then spread the cells evenly in a 24-well plate. After 12 hours, the old medium was sucked off, and each well was added with 1 μl of small molecule compound (one of 182 compounds in the library) in 1 ml of cell culture medium; control group used 1 μl of DMSO. The cells were then incubated in a 37°C incubator for 48 h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com