Ceramic-polymer composites obtained by a cold sintering process
A composite material and polymer technology, which is applied in the field of ceramic-polymer composite materials obtained by cold sintering, can solve the problems of warpage, uniform powder wetting and complex, uneven density, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1A
[0086] Example 1A: Cold-sintered ceramic polymer composite
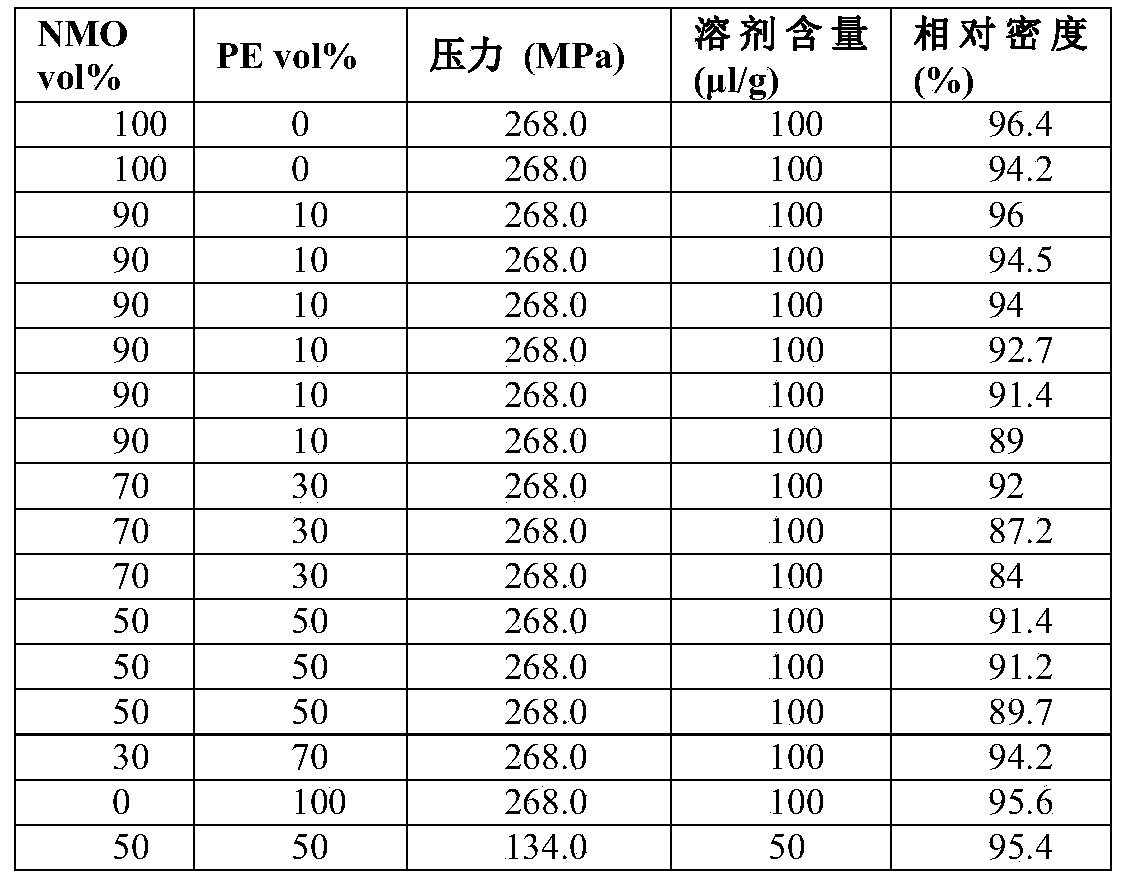
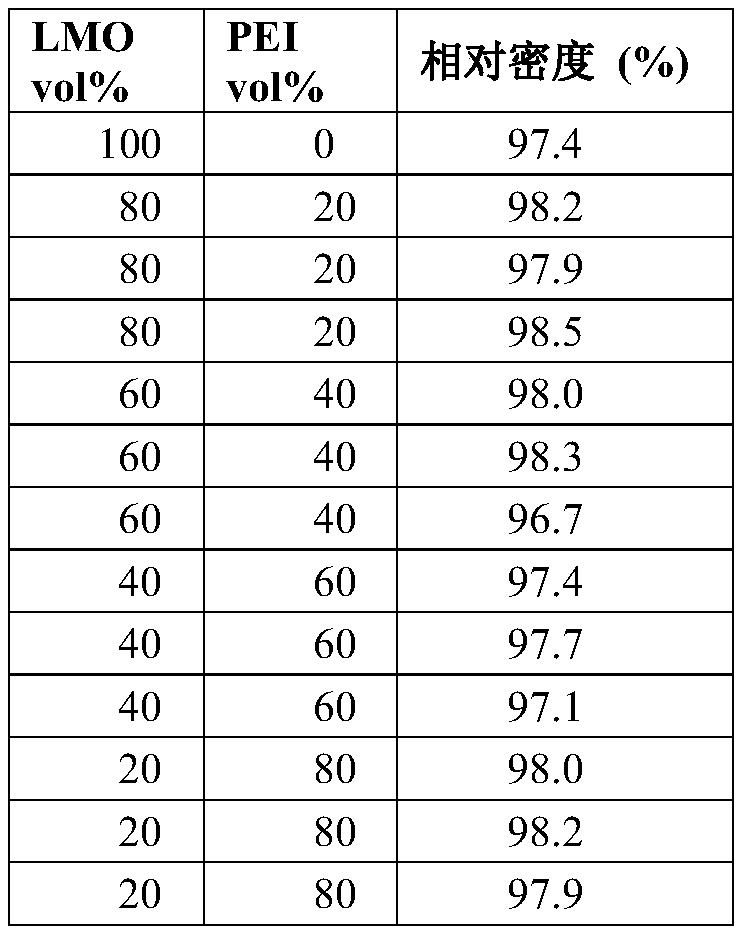
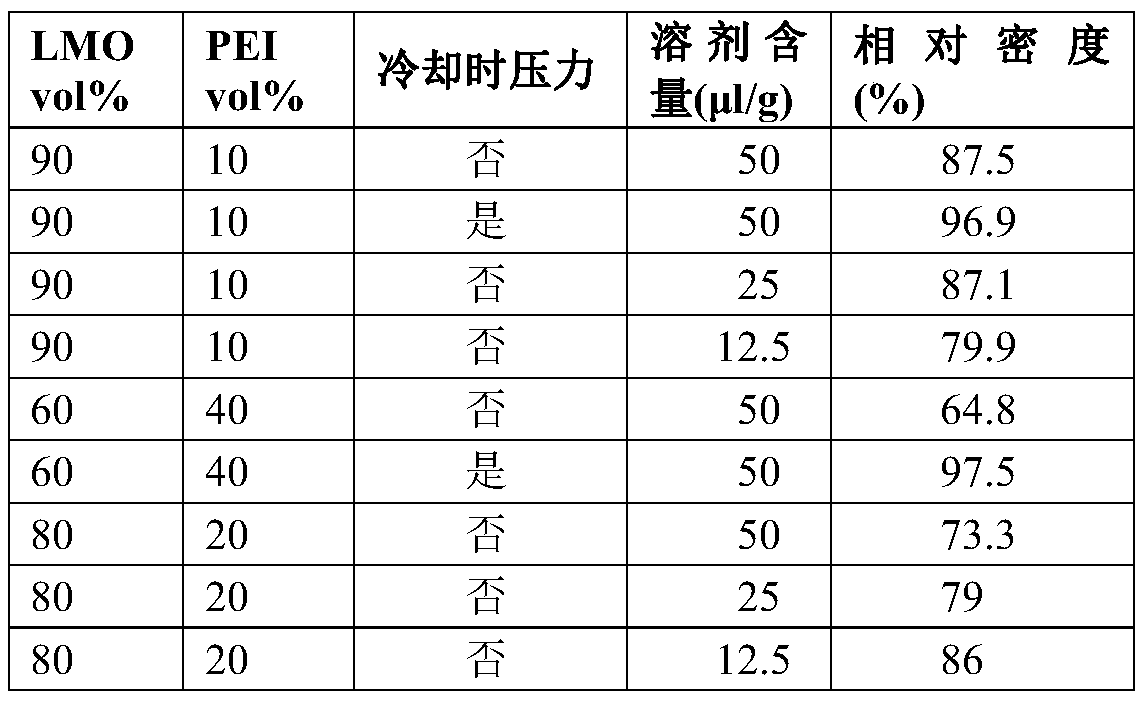
[0087] Cold-sintered ceramic polymer composites are made using different types of ceramics and polymers. Powders of inorganic compound starting materials and polymers are mixed with a small amount of liquid using a mortar and pestle. Then, the resulting mixture is put into cylindrical molds and hot pressed. Compression is performed at various temperatures, hold times and pressures. Densification of cold sintered ceramic polymer composites was analyzed by measuring bulk density (eg, Archimedes method) and by observing the microstructure using SEM / TEM.
Embodiment 2A
[0088] Example 2A: Cold sintered ceramic polymer metal composite
[0089]Cold sintered cerpolymer metal composites are made using different types of inorganic compound starting materials, metals and polymers. Powders of one or more inorganic compounds, polymers and metals are mixed together with a small amount of liquid using a mortar and pestle. Then, the resulting mixture is put into cylindrical molds and hot pressed. Compression is performed at various temperatures, hold times and pressures. The densification of ceramic-polymer-metal composites was analyzed by measuring the bulk density and by observing the microstructure using SEM / TEM.
Embodiment 3A
[0090] Example 3A: Cold-sintered ceramic polymer composite with electronic conductivity
[0091] Ceramics are traditionally known for their electrical insulating properties. Adding conductive fillers to the sintered ceramic body can increase its conductivity. Examples of different conductive fillers include conductive polymers, which are incorporated into the ceramic matrix to improve its conductivity. Conductive polymers (also known as intrinsically conductive polymers (ICPs)) are a group of polymers that conduct electricity. Conductive polymers consist of linear backbones such as polyacetylene, polypyrrole, and polyaniline and their copolymers. Poly(p-phenylene vinylene) (PPV) and its soluble derivatives are useful as electroluminescent semiconducting polymers. Poly(3-alkylthiophenes) are prototype materials for solar cells and transistors.
[0092] Metals and graphite are well known conductors of electricity. Incorporation of these materials showed improvements in elec...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com