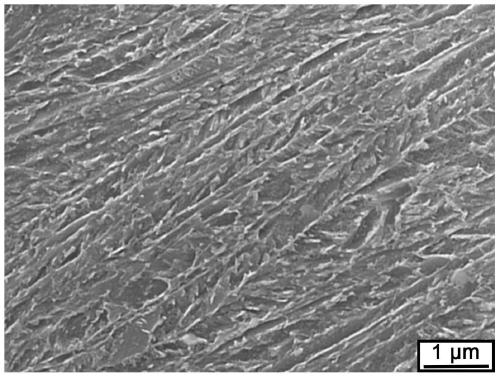
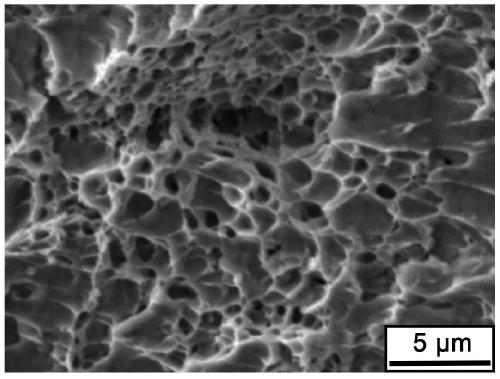
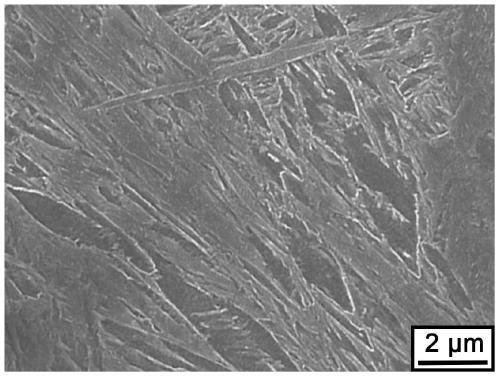
Low-alloy martensite steel high-toughness treatment method and martensite steel
A technology of martensitic steel and processing method, which is applied in the direction of metal processing equipment, etc., can solve problems such as poor forging effect, and achieve the effects of avoiding too low final forging temperature, refining austenite grains, and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] A method for strengthening and toughening low-alloy martensitic steel. The smelted steel ingot is about 15Kg, which contains the following components in mass percentages: 0.27%C, 1.2%Cr, 1.1%Mn, 1.3%Si, 0.5%Mo, and the rest is Fe , the A3 temperature (austenite transformation temperature) of the alloy is about 830°C, and the A1 temperature (eutectoid transformation temperature) is about 750°C. The strengthening and toughening treatment method includes:
[0036] (S1) Pretreatment: heating the steel ingot with the above composition to 1150°C in an inert atmosphere (such as nitrogen) protection furnace, and holding it for 30 minutes for high-temperature homogenization treatment to obtain a uniform single-phase austenite structure;
[0037] (S2) High-temperature forging: take the steel ingot out of the atmosphere protection furnace, and immediately perform high-temperature forging. The forging ratio is about 70%. The final forging temperature is 70°C higher than the A3 tempe...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A low-alloy martensitic steel strengthening and toughening treatment process, the smelted steel ingot is about 10Kg, which contains the following components in mass percentages: 0.4%C, 2.0%Cr, 1.5%Mn, 1.5%Si, 0.5%Mo, and the rest is Fe , the A3 temperature of the alloy is about 810°C, and the A1 temperature is about 745°C. The strengthening and toughening treatment method includes:
[0045] (S1) Pretreatment: heating the steel ingot with the above composition to 1200°C in an inert atmosphere protection furnace, holding it for 45 minutes for high-temperature homogenization treatment, to obtain a uniform single-phase austenite structure;
[0046] (S2) High-temperature forging: take the steel ingot out of the atmosphere protection furnace, and immediately perform high-temperature forging. The forging ratio is about 80%. The final forging temperature is 50°C higher than the A3 temperature, specifically 860°C. Immediately after the final forging, it is immersed in about 60°C....
Embodiment 3
[0051] A low-alloy martensitic steel strengthening and toughening treatment process, the smelted steel ingot is about 12Kg, which contains the following components in mass percentages: 0.3%C, 2.2%Cr, 0.8%Mn, 1.2%Si, 0.5%Mo, 0.3%Ni , and the rest is Fe. The A3 temperature of the alloy is about 820°C, and the A1 temperature is about 750°C. The strengthening and toughening treatment method includes:
[0052] (S1) Pretreatment: heating the steel ingot with the above composition to 1250°C in an inert atmosphere protection furnace, holding it for 30 minutes for high-temperature homogenization treatment, to obtain a uniform single-phase austenite structure;
[0053] (S2) High-temperature forging: take the steel ingot out of the atmosphere protection furnace, and immediately carry out high-temperature forging, the forging ratio is about 70%, and the final forging temperature is 100°C higher than the A3 temperature, specifically 920°C. Immediately after final forging, immerse in quench...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com