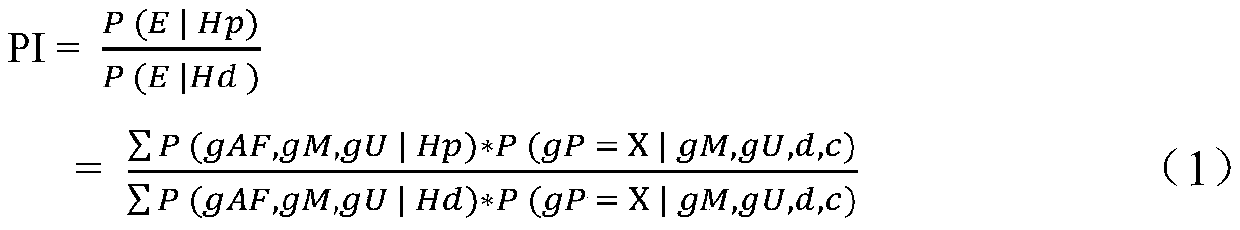Microhaplotype genetic marker combination and method for noninvasive prenatal paternity relationship judgment
A paternity relationship and genetic marker technology, applied in the field of microhaplotype genetic marker combination for non-invasive prenatal paternity determination, can solve the problems of insufficient detection system efficiency, linkage disequilibrium, low SNP polymorphism, etc. Great application prospect, easy operation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] The establishment of a method for non-invasive prenatal parentage determination using micro-haplotype sequencing includes the following steps:
[0043]1. Screening eligible micro-haplotype sites: the present invention attempts to screen out micro-haplotypes that can be used for non-invasive prenatal parental relationship determination in the human genome. The screening criteria are as follows:
[0044] (1) Located on an autosome;
[0045] (2) Conform to Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium law (p<0.001);
[0046] (3) There are ≥ 3 SNPs that make up the micro-haplotype, and the minimum allele frequency of the SNP within the site is > 0.05;
[0047] (4) The number of haplotypes is not less than 4, and at least 3 haplotype frequencies are >0.1;
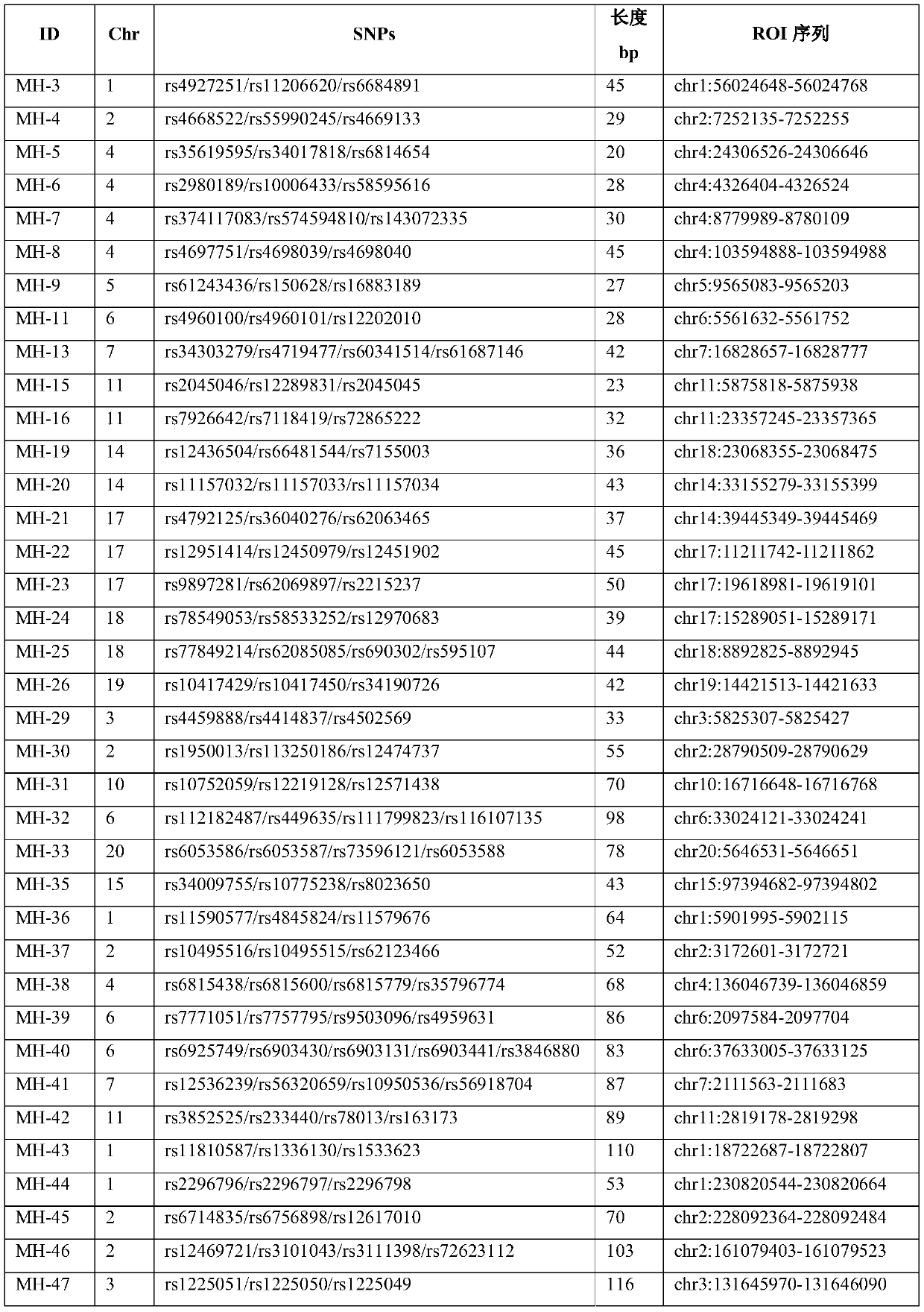
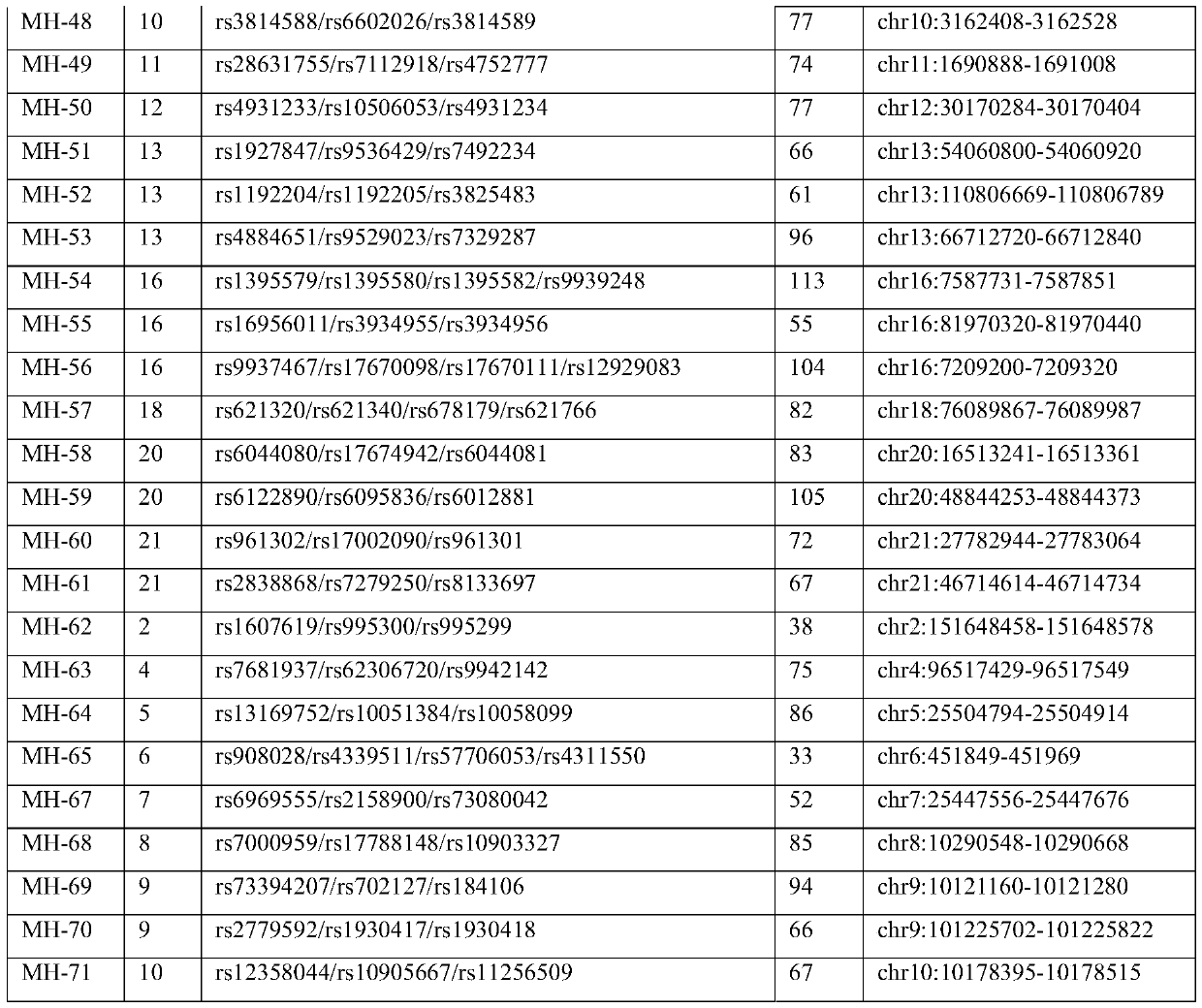
[0048] (5) The length of the target fragment is less than 150bp, which is beneficial to the detection of fragmented cell-free fetal DNA; finally, through creative work, 60 micro-haplotype sites shown in Table 1 were obtained through scree...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com