Preservation method of anaerobic dehalogenated microorganisms and application of preservation method
A preservation method and microbial technology, which is applied in the field of water pollution control, can solve the problems of reduced activity of dehalogenated microorganisms, reduced efficiency of in-situ bioremediation, and difficulty in maintaining anaerobic conditions, so as to solve the problem of reduced dehalogenated microbial activity and reduced The effects of transportation cost and oxygen tolerance enhancement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Dehalococcoides mccartyi type strain 195 (species preservation number ATCC BAA-2266 T ) (hereinafter referred to as Dhc 195) as an example for immobilization.
[0046] S1. Cultivation of Dehalogenococcus: Inoculate Dhc 195 with 3% inoculum into a 160mL airtight serum bottle containing 100mL inorganic salt medium for culture, and the headspace is N 2 / CO 2 (80 / 20, v / v), and adding 5 mM sodium acetate as a carbon source and 10 mL hydrogen as an electron donor to the inorganic salt medium, and cultured at 30° C. in the dark.
[0047] The composition of the inorganic salt medium is: NaCl 1.0g / L, MgCl 2 ·6H 2 O 0.5g / L, KH 2 PO 4 0.2g / L, NH 4 Cl0.3g / L, KCl0.3g / L, CaCl 2 2H 2 O 0.015g / L, FeCl 2 4H 2 O 1.5mg / L, CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O 190μg / L, MnCl 2 4H 2 O 100μg / L, ZnCl 2 70μg / L, H 3 BO 3 6μg / L, Na 2 MoO 4 2H 2 O 36μg / L, NiCl 2 ·6H 2 O 24μg / L, CuCl 2 2H 2 O 2μg / L, Na 2 SeO 3 ·5H 2 O 6 μg / L, Na 2 WO 4 2H 2 O 8μg / L, resazurin indicator 0.025% (w / v), L-cys...
Embodiment 2
[0066] The method in Example 1 was used to immobilize the Dhc 195 bacteria, except that in step S3, no activated carbon was added, so as to realize the corresponding immobilization of the Dhc 195 bacteria.
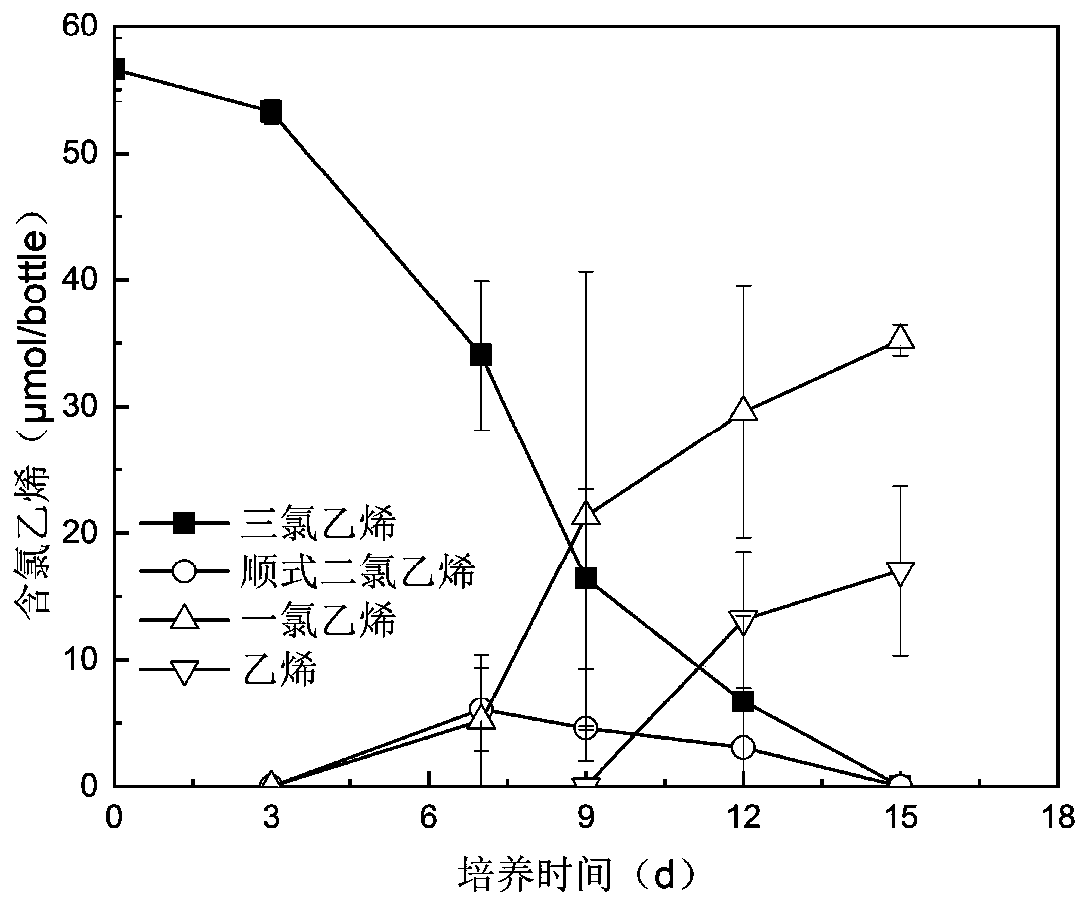
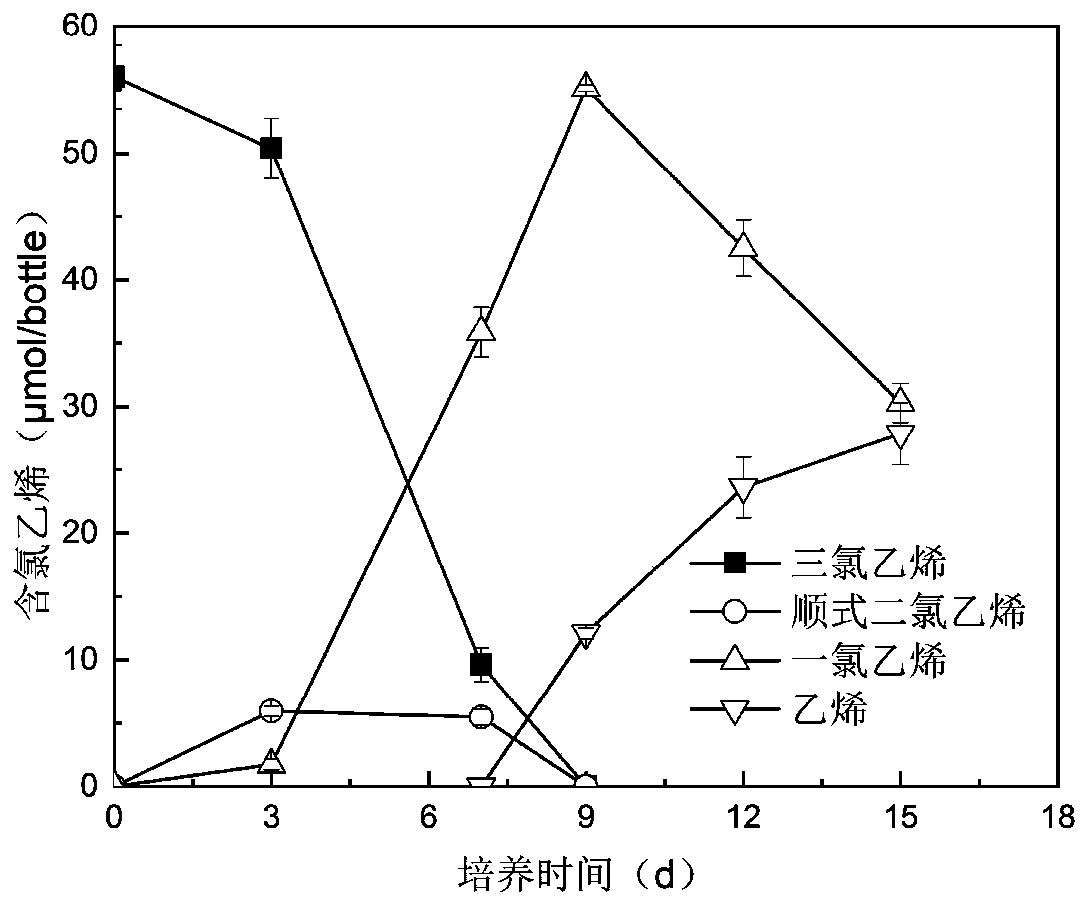
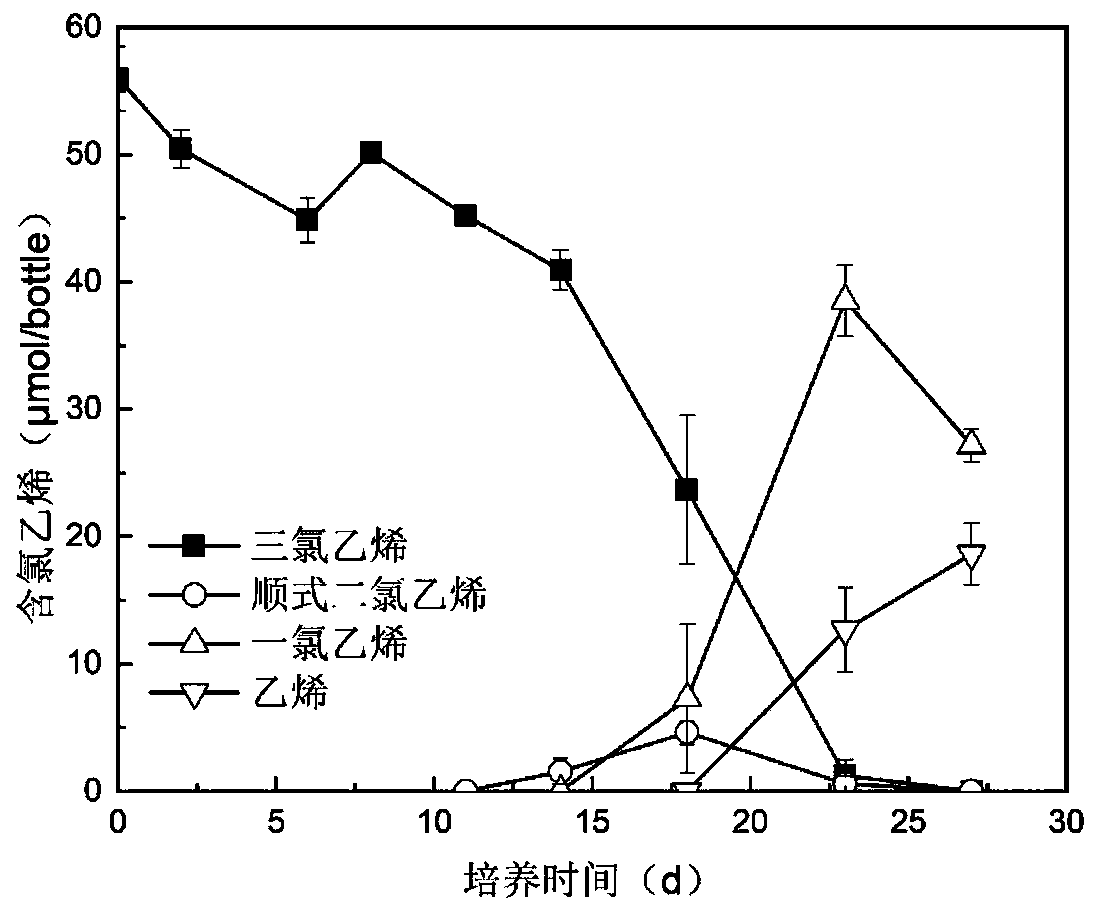
[0067] The immobilized microspheres without activated carbon obtained in this example and the immobilized microspheres of Dhc 195 bacteria obtained in Example 1 were used for the degradation of trichlorethylene. The culture conditions, detection of degradation products and calculation of degradation rate were the same as in Example 1.
[0068] After testing, the degradation rates of trichlorethylene for immobilized microspheres without activated carbon and immobilized microspheres added with activated carbon were 95.3 μM d -1 and 129.9 μM d -1 , adding activated carbon can increase the degradation rate by 36.3%. It can be seen that due to the adsorption of activated carbon to microorganisms, the toxic effect of boric acid on microorganisms during the crosslinking process ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com