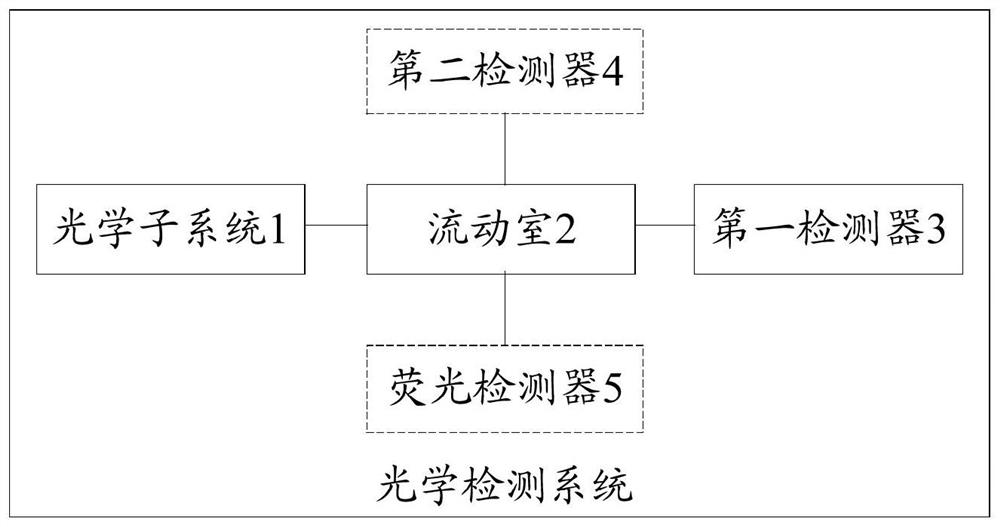
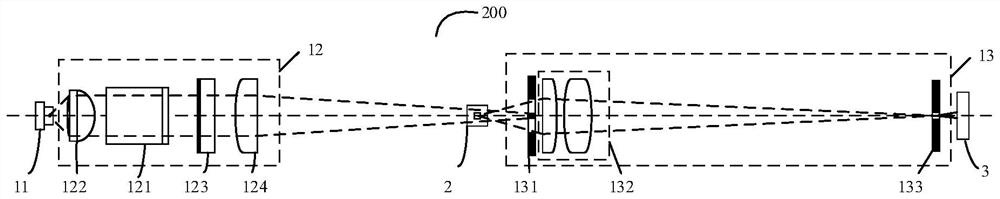
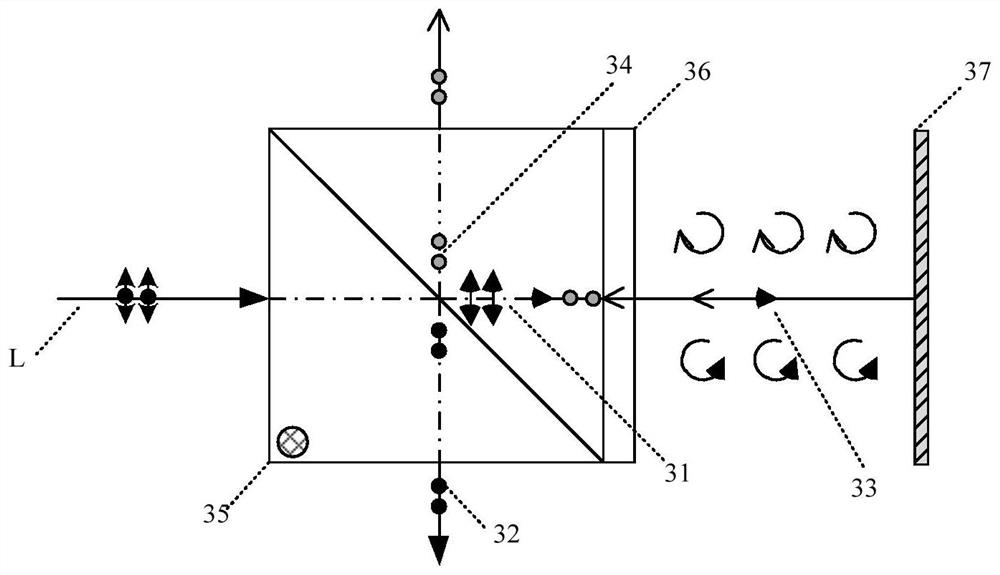
A blood detection method and blood analysis system
A technology for blood testing and blood samples, applied in the field of blood analysis systems and the optical detection of platelets, can solve the problems of inability to distinguish between red blood cell fragments and platelets, and achieve the effect of reducing testing costs and simplifying blood testing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0358] Embodiment 1 Deep hemolysis treatment detects platelets
[0359] Prepare the hemolytic agent of the present invention according to the following formula.
[0360]
[0361] Add 20 microliters of fresh blood samples to 1 mL of the prepared solution above, incubate at 45°C for 60 seconds to prepare the samples to be tested, and then measure them with a flow cytometer (BriCyte E6). Set the gain to 500 for data collection, collect the side scattered light with a measurement angle of 90 degrees to obtain the side scattered light intensity information of the particles in the sample; and collect the forward scattered light signal of 0 degrees. Scatter distribution of platelets and white blood cells Figure 10 shown, from Figure 10 It can be seen that red blood cell fragments, platelets, and white blood cells are highly differentiated, and these three groups of particles can be clearly distinguished, and platelets and white blood cells can be effectively classified and cou...
Embodiment 2
[0363] Example 2 Contrasting the performance of deep hemolysis treatment and conventional hemolysis treatment on platelets
[0364] Prepare the detection reagent of the present invention according to the following formula.
[0365]
[0366] 20 microliters of fresh blood samples were added to 1 mL of the solution prepared according to the above formula, incubated at 45°C for 60 seconds, and then detected by a flow cytometer (BriCyte E6). Set the excitation wavelength to 488nm, the gain to 500, collect the 0° forward scattered light intensity and 90° side scattered light intensity information, and obtain the two-dimensional cell scatter diagram as shown in Figure 11 Shown in A.
[0367] As a comparison, 20 microliters of fresh blood from the same blood sample was added to 1 mL of LD hemolysis agent (which contains conventional hemolysis agent) matched with Mindray blood analyzer BC-6800, incubated at 45°C for 60 seconds, and then analyzed by flow cytometry. (Mindray BriCyt...
Embodiment 3
[0369] Example 3 Deep Hemolysis and Adding Nucleic Acid Dyes Counting Platelets and White Blood Cells by Side Light Scattering and Fluorescent Signals
[0370] Prepare the detection reagent of the present invention according to the following formula.
[0371]
[0372] 20 microliters of fresh blood samples were added to 1 mL of the solution prepared according to the above formula, incubated at 45°C for 60 seconds, and then detected by a flow cytometer (BriCyte E6). Set the excitation wavelength to 488nm, the gain to 500, collect the 90-degree side fluorescence intensity and the 0-degree forward scattered light intensity information, and obtain the two-dimensional cell scatter diagram as shown in Figure 12 As shown in A.
[0373] It can be seen from the figure that in the state of hemolysis, the addition of nucleic acid dyes can effectively distinguish and display platelets and RET in the direction of fluorescence. By dividing the proportion of PLT scattered points, and ac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| reflectance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com