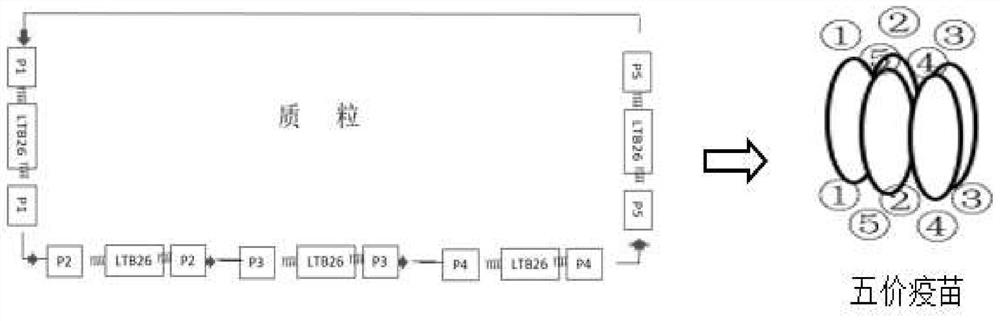
Construction method of multivalent epitope and subunit vaccine
A subunit vaccine and subunit technology, applied in the field of vaccines, to achieve the effect of a large number of immunogens and a rich variety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
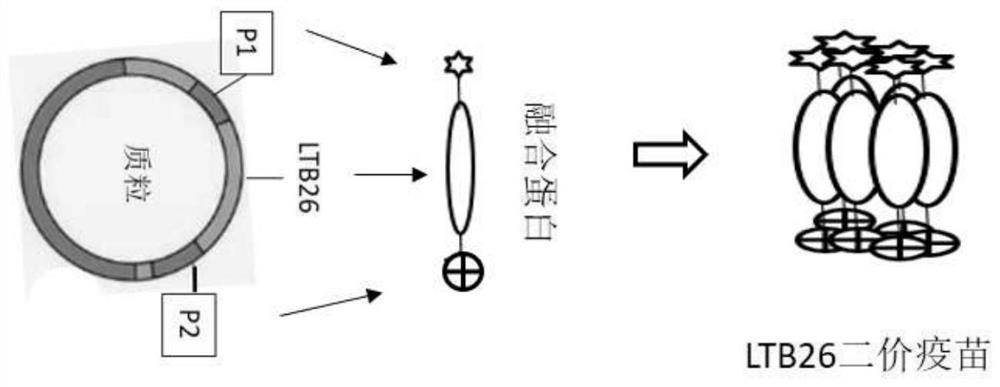
[0033] Example 1 Preparation of EP1-LTB26-EP2 fusion protein (bivalent vaccine):
[0034] 1. Recombinant expression
[0035] 1.1 Cloning and expression of pET32-RBD EP1-LTB26-RBD EP2 gene
[0036] a. Synthetic recombinant target gene:
[0037]Insert LTB26 gene (SEQ ID NO.1) between SacI (GAGCTC) and SalI (GTCGAC) restriction sites of the DNA sequence (SEQ ID NO.1) of the receptor binding domain (RBD) of the novel coronavirus (SARS CoV-2) ID NO.2), which is equivalent to connecting the epitopes EP1 (SEQ ID NO.3) and EP2 (SEQ ID NO.4) of the novel coronavirus at both ends of LTB26 to form an EP1-LTB26-EP2 fusion gene. Then, the EP1-LTB26-EP2 fusion gene was constructed on an ordinary Escherichia coli expression vector (such as pET32a).
[0038] The sequence involved is as follows:
[0039] DNA sequence encoding RBD (SEQ ID NO.1):
[0040]
[0041]
[0042] In SEQ ID NO.1, the underlined part indicates the enzyme cutting sites SacI (GAGCTC) and SalI (GTCGAC).
[0043]...
experiment example 2
[0065] Experimental example 2 Safety detection of EP1-LTB26-EP2 bivalent vaccine polypeptide of the present invention
[0066] 1. Experimental method
[0067] Taking male rats as an animal model, the EP1-LTB26-EP2 prepared in Example 1 of the present invention was injected intraperitoneally into the rats to detect its safety:
[0068] a) Six healthy male rats with a body weight of 3-4 weeks were obtained from the Experimental Animal Center of Chongqing Medical University.
[0069] b) Dissolving the EP1-LTB26-EP2 with immune adjuvant activity prepared in Example 1 with PBS buffer.
[0070] c) Add 0.50ml of EP1-LTB26-EP2 (without Exogenous endotoxin detection and treatment) were intraperitoneally injected into the rats described in a) above, and the differences in signs between the experimental rabbit and the control group were observed within 3 days (such as activity ability, feeding ability, whether there was tremor, vertical hair, loose stool, etc.), and the survival situa...
Embodiment 3
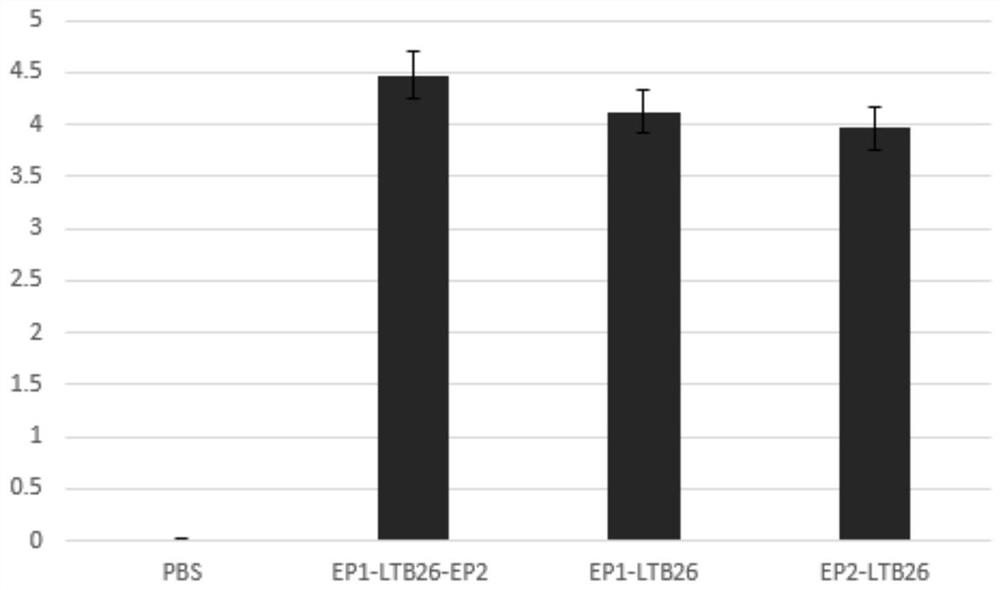
[0076] Embodiment 3 Effectiveness detection of EP1-LTB26-EP2 bivalent vaccine of the present invention
[0077] 1. Experimental method
[0078] The EP1-LTB26-EP2 fusion protein with immune adjuvant activity prepared in Example 1 was dissolved with PBS buffer. Follow the steps below to check the effectiveness:
[0079] a) 18 rats (male) were purchased from the Animal Experiment Center of Chongqing Medical University and randomly divided into 4 groups with 6 rats in each group.
[0080] b) The EP1-LTB26-EP2 fusion protein prepared in Example 1 (6.0 μg / rat) was immunized by nasal drops to 4% chloral hydrate anesthetized rats (1.0 ml / 100 g); PBS nasal drops were used as a control.
[0081] c) On the 7th day after the initial immunization, carry out the second booster immunization with the same dose as in b) above, and perform the third booster immunization on the 14th day. Before each booster immunization, blood samples should be collected and stored at -80°C for future use. On...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com