Spine minimally invasive symmetrical porous light-transmitting positioning and guiding device and using method thereof
A positioning-oriented, symmetrical technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems affecting the service life of positioning guide pins, bending of guide pins, physical damage, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing search time, improving accuracy, and protecting from damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Spinal minimally invasive symmetrical porous light-transmitting positioning and guiding device
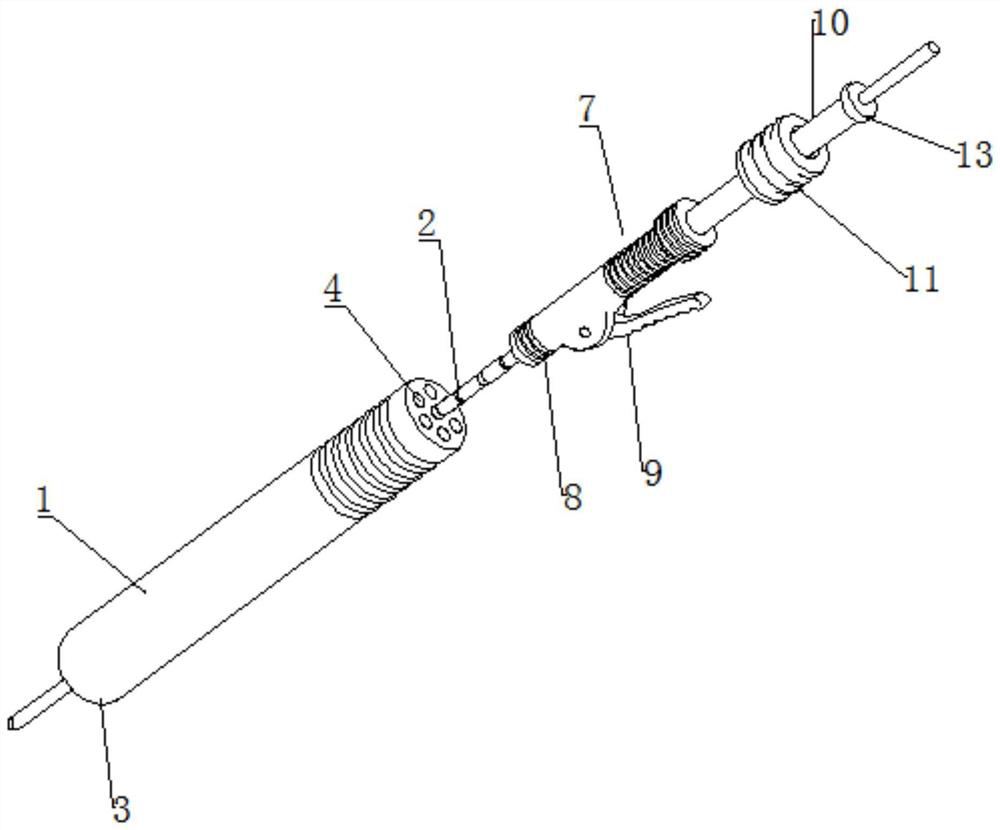
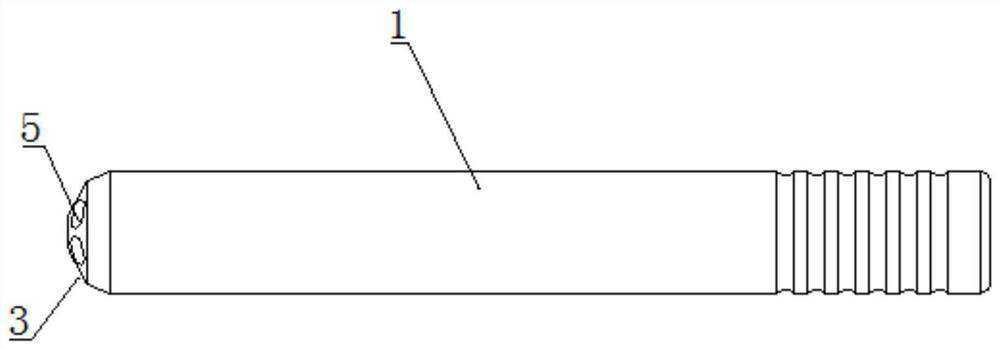
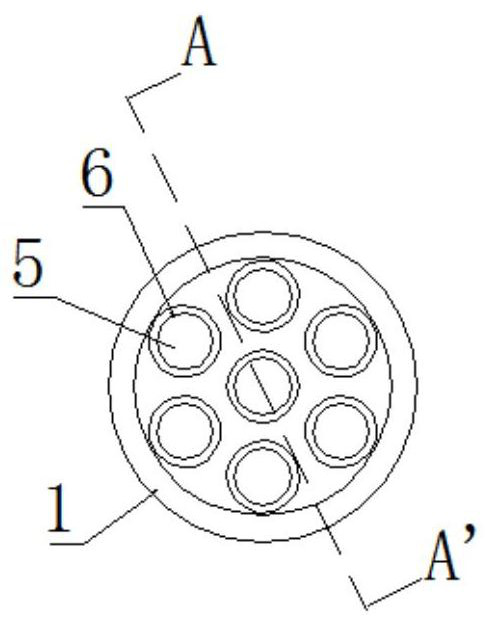
[0035] Such as Figure 1-7In the shown embodiment, a minimally invasive symmetrical porous light-transmitting positioning and guiding device for the spine includes a positioning and guiding body 1 and a positioning guide pin 2. The positioning and guiding body 1 is in a columnar structure, and one end of the positioning and guiding body 1 is provided with a convenient The conical arc 3 that fits the surface of the pedicle, the positioning guide body 1 is provided with a plurality of first guide pin perforations 4 along the length direction, one of the first guide pin perforations 4 is set along the central axis of the positioning guide body 1, and the other first guide pin perforations 4 A guide pin perforation 4 is arranged symmetrically along the central axis of the positioning guide body 1, and one end of the first guide pin perforation 4 close to the conical ar...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2 The method of using the spinal minimally invasive symmetrical porous light-transmitting positioning and guiding device
[0044] A method for using a spinal minimally invasive symmetrical porous light-transmitting positioning and guiding device, comprising the following steps:
[0045] S1: Use an X-ray machine to determine the general location of bone lesions, make a skin incision, put the positioning guide body 1 into the skin incision, observe the bone condition in each local area of the development ring through the development ring 6 under X-ray fluoroscopy, and manually Rotate and fine-tune the positioning guide body 1 to narrow down the target range for finding the bone lesion until the bone lesion is basically determined;
[0046] S2: When the position of the bone lesion is basically determined, the positioning guide pin 2 is penetrated along the corresponding first guide pin perforation 4, and the positioning guide body 1 is rotated with the positionin...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3 The method of using the spinal minimally invasive symmetrical porous light-transmitting positioning and guiding device
[0051] A method for using a spinal minimally invasive symmetrical porous light-transmitting positioning and guiding device, comprising the following steps:
[0052] P1: Use an X-ray machine to determine the general location of bone lesions, make a skin incision, put the positioning guide body 1 into the skin incision, observe the bone conditions in multiple local areas through the development ring 6 under X-ray fluoroscopy, and then place the positioning guide body 1 into the skin incision. The guide pin 2 penetrates into the positioning guide body 1 along one of the first guide pin perforations 4, and with the positioning guide pin 2 as the center of the circle, manually rotate and fine-tune the positioning guide body 1 to narrow the target range for finding the bone lesion until the exact location of the lesion is determined ;
[0053] P2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com