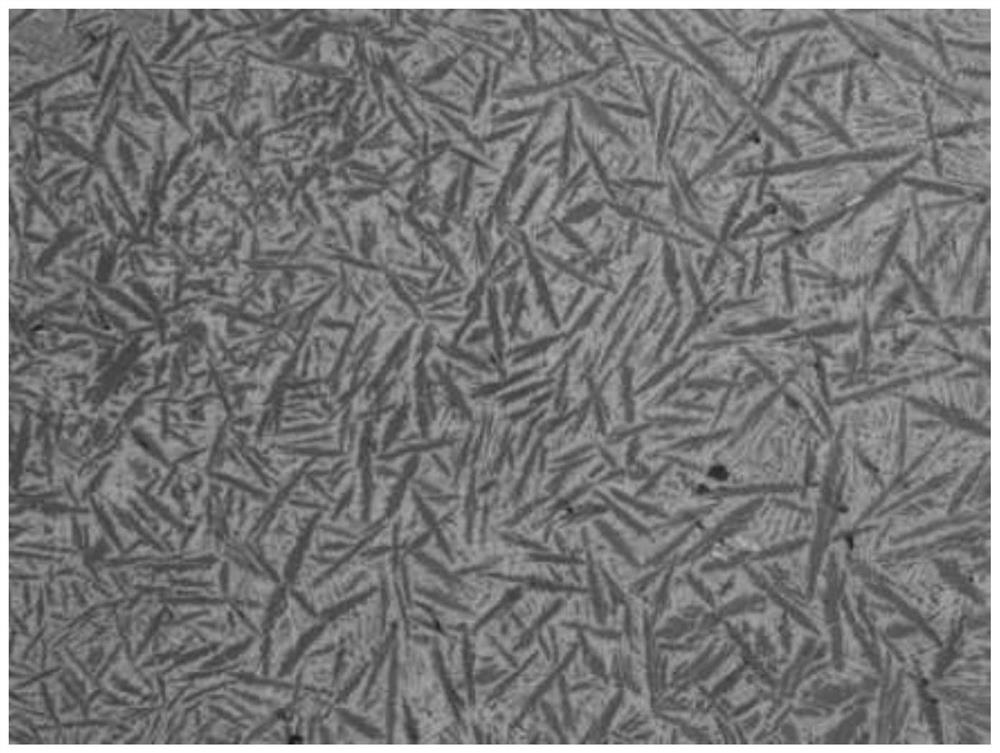
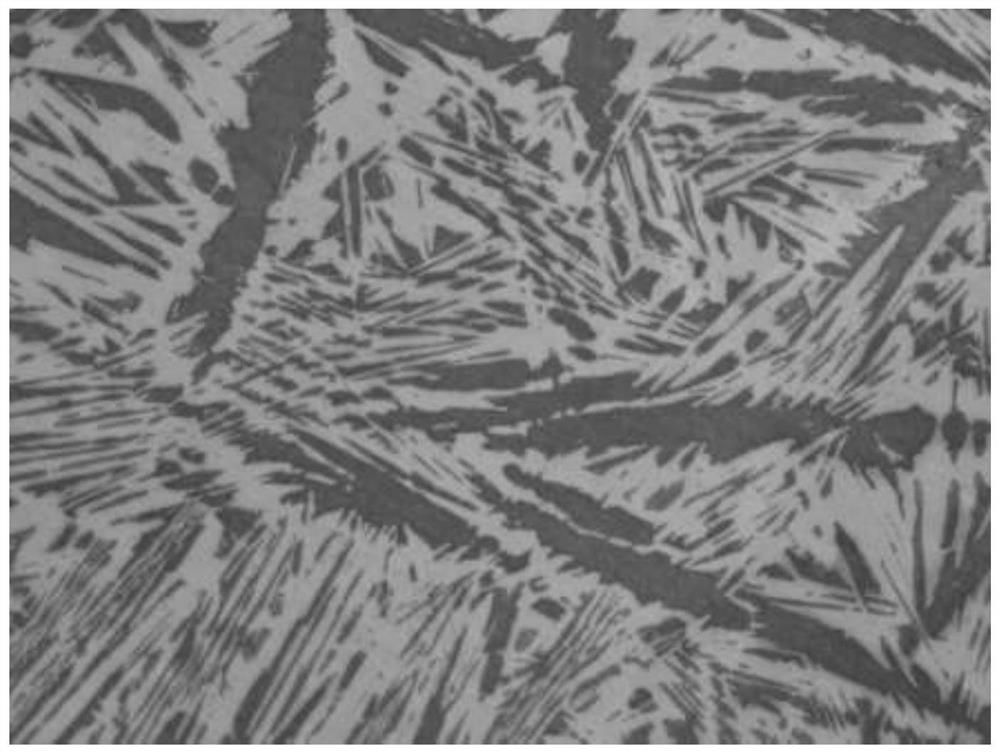
Method for preparing copper-titanium 50 intermediate alloy through magnetic suspension melting process
A magnetic levitation smelting and intermediate alloy technology, applied in the field of copper alloy preparation, can solve the problems of difficult mixing, volatilization loss of metal elements, deviation of alloy Ti content, etc., and achieve the effect of low gas content, good uniformity and high uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
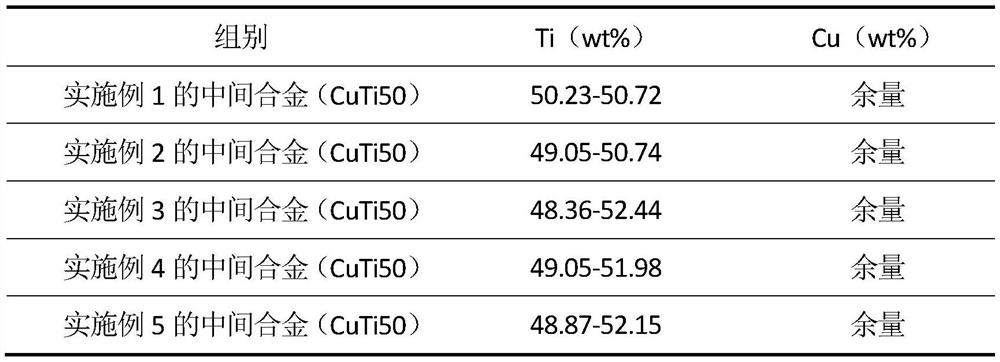
Embodiment 1
[0027] A method for preparing a copper-titanium 50 master alloy using a magnetic levitation smelting process, comprising the following steps:
[0028] (1) Ingredients: Proportion the copper alloy elements according to the weight percentage of 50.5% Ti and Cu as the balance, select and weigh the corresponding raw materials; Ti adopts 0-grade sponge titanium with a purity≧99.7%, and Cu adopts Electrolytic copper plate with purity ≥99.99%;
[0029](2) Alloy smelting pretreatment: The Ti raw material and the Cu raw material are respectively powdered by an electrode induction melting gas atomization system (EIGA method) to obtain Ti powder and Cu powder with a particle size of 150 μm, and the Ti powder and Cu powder After mixing evenly, put it into the crushing chamber of the jet mill, fill in the inert gas to completely isolate the Ti powder and Cu powder from the air, and increase the flow rate of the inert gas to pressurize the Ti powder and Cu powder from two opposite nozzles. ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] A method for preparing a copper-titanium 50 master alloy using a magnetic levitation smelting process, comprising the following steps:
[0036] (1) Batching: according to Ti being 31%-55%, Cu is the weight percent content of surplus to carry out proportioning to copper alloy element, selects and takes by weighing corresponding raw material;
[0037] (2) Magnetic levitation smelting: put the deposited block into the cold crucible of the vacuum magnetic levitation furnace, power on, and vacuumize for about 22min until the vacuum degree reaches 10 -3 Pa, and then rush into argon protection to make the pressure in the furnace reach 0.03MPa. First, increase the power to 110KW at 12KW / min to make the temperature in the furnace reach 1800°C, and heat for 7 minutes until the metal ingot is completely melted and semi-suspended. Under the action of continuous Loren magnetic force, the melt is completely suspended and electromagnetically stirred. , the formed alloy is kept in the...
Embodiment 3
[0042] This example is basically the same as Example 1, except that in step (2) of this example, the Ti raw material and the Cu raw material are respectively powdered by the EIGA method to obtain Ti powder and Cu powder with a particle size of 150 μm. The two metal powders are filled into the product mold for molding, and then the molded compact is sintered in stages. The staged sintering process is first treated at 1380°C for 1 hour, then heated to 1680°C for 1 hour, and sintered copper is obtained after cooling. titanium alloy. Then, the copper-titanium alloy is smelted by magnetic levitation in step (3), and the conditions of other steps are the same as those in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com