A kind of preparation technology of moisture-wicking fabric
A preparation process, a technology for moisture absorption and perspiration, which is applied in rayon manufacturing, knitting, textile and other directions to save production costs, improve antibacterial ability, and achieve the effect of targeted modification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0086] The invention discloses a preparation process of a moisture-absorbing and sweat-wicking fabric, which specifically includes the following process steps:
[0087] S1: Spinning, using the electrospinning method, spinning fiber A into a first yarn, and spinning fiber B into a second yarn.
[0088]S2: weaving, using the first yarn obtained in step S1 as the warp and weft of the inner layer cloth, and using the second yarn obtained in the step S1 as the warp and weft of the outer layer cloth, weaving to obtain a double-layer gray fabric.
[0089] S3: Dyeing and finishing, specifically including alkali reduction, dyeing, soaping and setting, to obtain finished fabrics. Due to alkali reduction, staining. Soaping and styling etc. are conventional processes, so no more details are given.
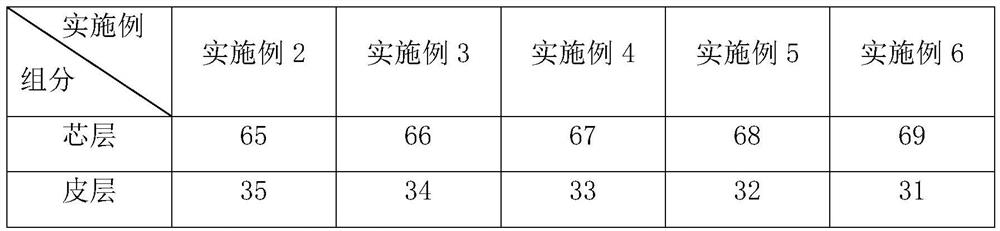
[0090] Wherein, fiber A is a hydrophilic fiber, and includes the following components by weight percentage:
[0091] Core layer 70%;
[0092] Cortex 30%.
[0093] The core layer comprises...
Embodiment 11
[0128] The difference between Example 11 and Example 1 is that the mixed solvent is a mixed solvent with a mass ratio of paraformaldehyde:DMSO=0.9:1.
[0129] The difference between embodiment 12-15 and embodiment 1 is that the percentage by weight of each component in the cortex is calculated as the following table:
[0130]
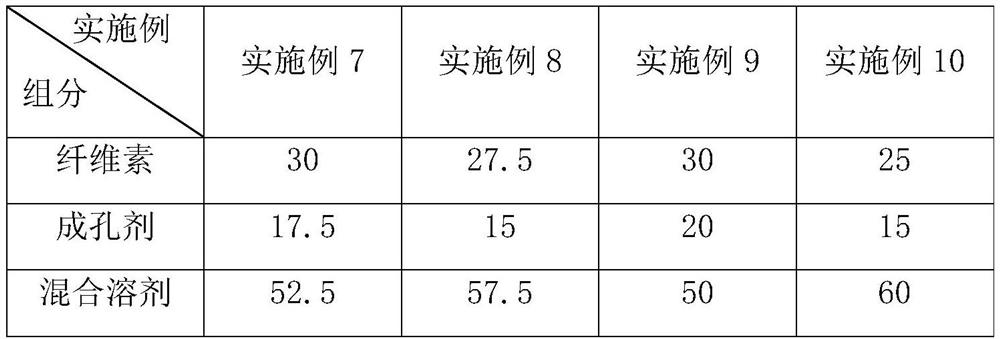
[0131] The difference between embodiments 16-19 and embodiment 1 is that the weight ratio of each component in the pore-forming agent is calculated as the following table:
[0132]
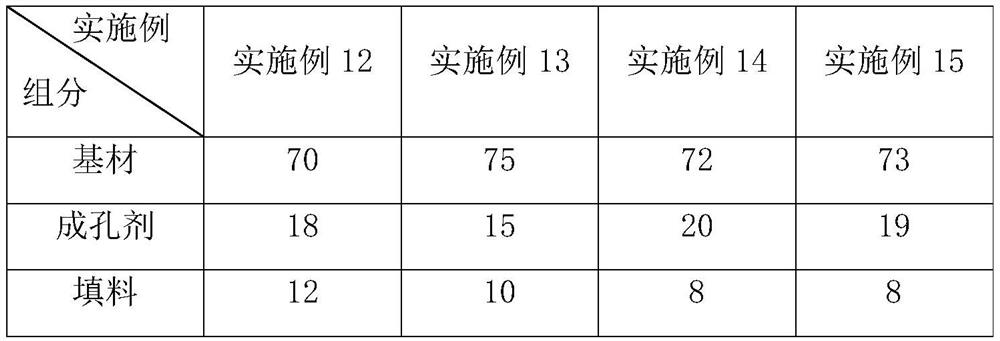
[0133] The difference between embodiment 20-24 and embodiment 1 is that the percentage by weight of each component in the base material of the cortex is calculated as the following table:
[0134]
[0135] The difference between embodiment 25-26 and embodiment 1 is that the percentage by weight of each component in the chitosan solution is calculated as the following table:
[0136]
[0137] The difference between embodiment 27-31 and embodiment 1 is that the w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com