A pollution-free integrated method and device for recycling extracellular polymers with high added value
An extracellular polymer, high value-added technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, plastic recycling, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in improving EPS extraction rate, secondary pollution, and difficult application, and achieve enhanced EPS extraction rate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
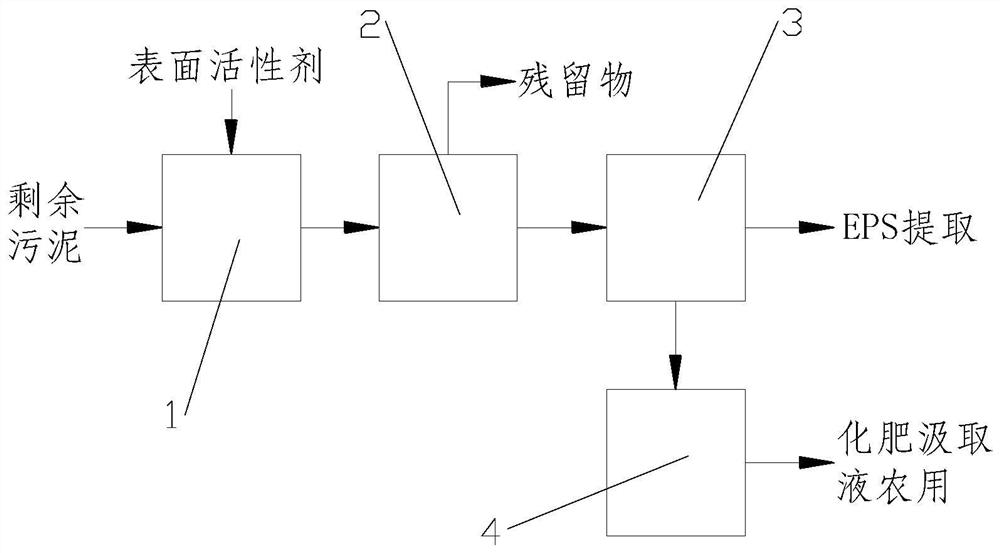
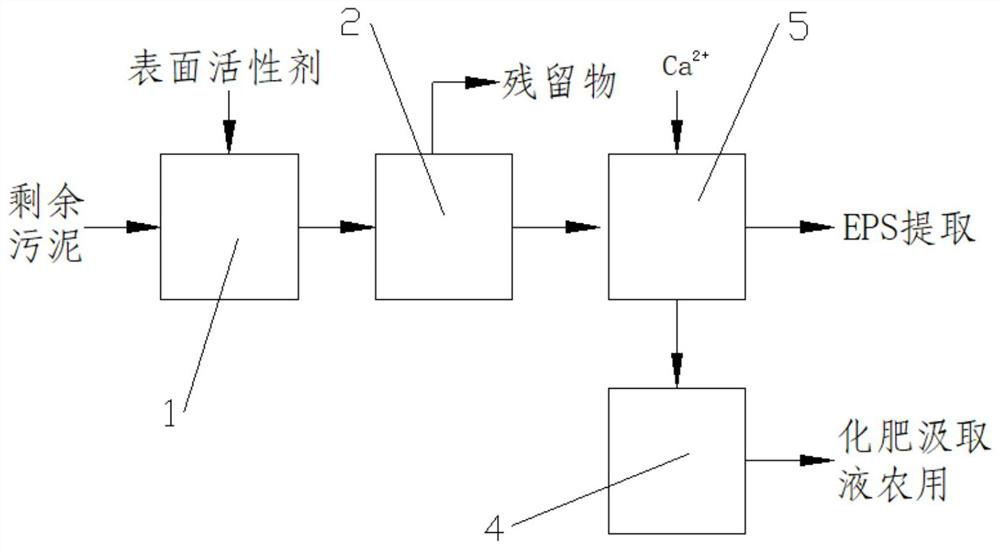
[0035] As shown in the figure Figures 1 through 2 Shown: a high value-added extracellular polymer provided for an embodiment of the present invention Recovery of a pollution-free integrated method, comprising the following steps:
[0036] Step S1: The remaining sludge is transported to the cation exchange resin reactor 1, and the extracellular polymer is optimized by the surfactant-enhanced cation exchange resin method, so that a large number of extracellular polymers are dissolved in water;
[0037] Step S2: The sludge obtained in step S1 containing a large amount of dissolved extracellular polymer enters the microfiltration membrane module 2 for separation treatment, and the separated suspended solids are discharged to obtain an extracellular polymer filtrate containing a dissolved state;
[0038] Step S3: The extracellular polymer solution obtaine...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com