Nepetalactol oxidoreductases, nepetalactol synthases, and microbes capable of producing nepetalactone
A technology of nepetalactone and lactone, which is applied in the directions of oxidoreductase, biochemical equipment and methods, enzymes, etc., and can solve the problems such as the effective chemical enzymatic method and overview of nepetalactone that are not recorded.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0471]Example 2 and the Sequence Listing submitted herein provide an exemplary set of nucleotide sequences encoding these enzymes. These polynucleotides comprising these sequences or variants thereof can be used to reconstitute the nepetalactone pathway in microorganisms. Due to the degeneracy of the genetic code, one or more nucleotide bases can be substituted without changing the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein. Variants of these polynucleotides include, for example, those having sequences codon optimized for expression in a particular host cell. In various embodiments, variants of these polynucleotides include those having at least 60, 65, 70, 75, 80, Sequences with 85, 90, 95, 96, 97, 98 or 99% sequence identity.
[0472] Novel polynucleotide encoding nepetalactone oxidoreductase
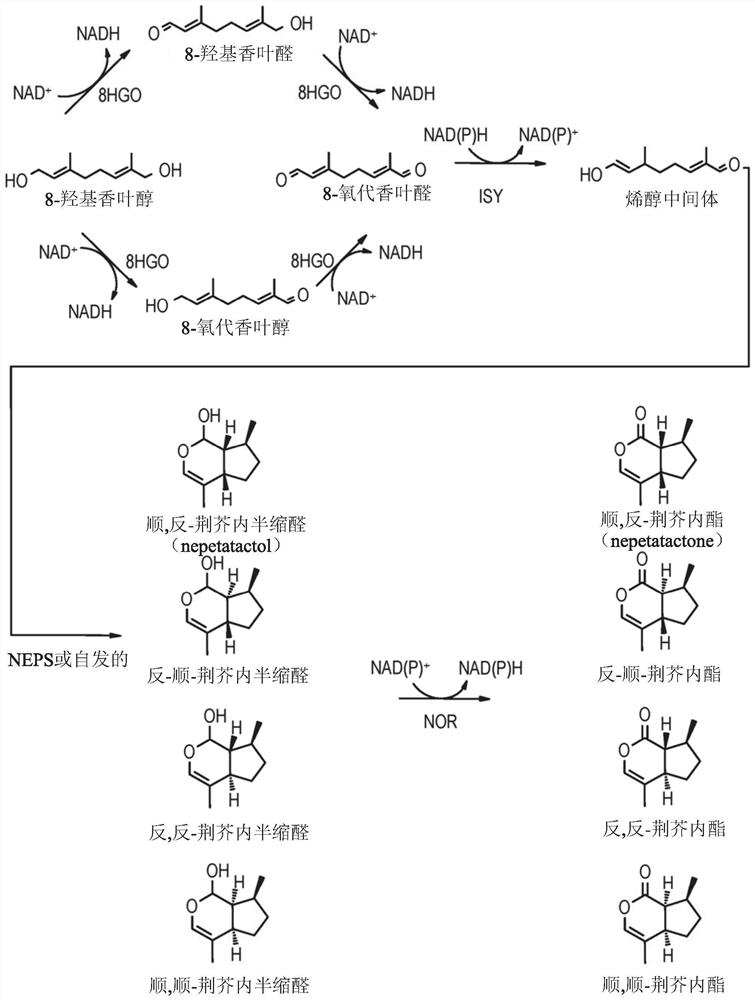
[0473] Examples 1 and 6 describe the identification and isolation of a polynucleotide comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding an active Nepeta lactal oxidoreductase (NOR). Nuc...
Embodiment 4
[0480] Example 4 describes the identification and isolation of a polynucleotide comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding an active nepetalactal synthase (NEPS). Nucleotide sequences encoding tested and / or putative NEPS are described in the accompanying Sequence Listing, eg, SEQ ID NO: 1506-1562.
[0481] These polynucleotides or variants thereof can be used to generate NEPS. Due to the degeneracy of the genetic code, one or more nucleotide bases can be substituted without changing the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein. Variants of NEPS polynucleotide sequences include, for example, those having sequences codon optimized for expression in a particular host cell. In various embodiments, variants of NEPS polynucleotides have at least 60, 65, 70, 75 , 80, 85, 90, 95, 96, 97, 98 or 99% sequence identity.
[0482] New Nepeta Lactal Synthase Polypeptides
[0483] The deduced amino acid sequences of these NEPS are also provided in the Sequence Listing (SEQ ID NO: 718-7...
Embodiment 1
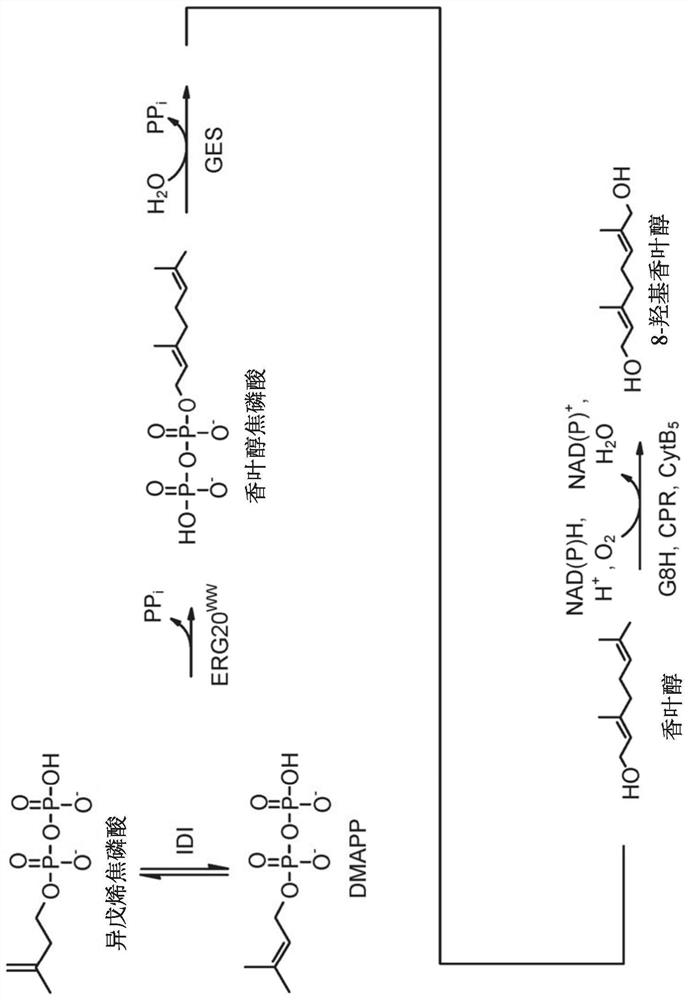
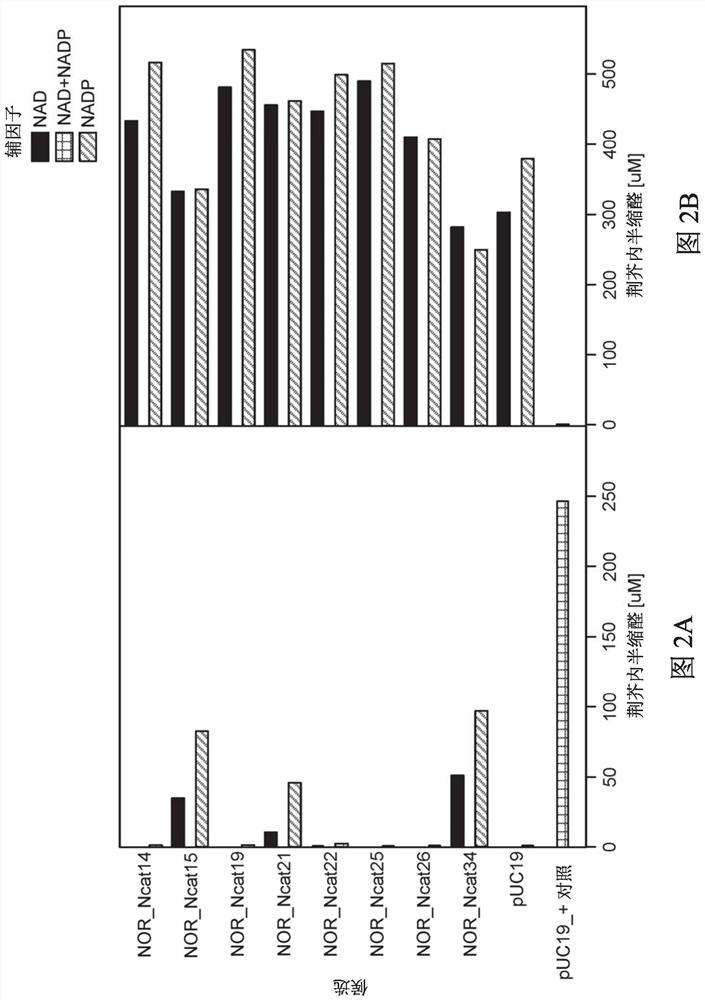
[0561] Example 1 - Nepetalactone redox in Escherichia coli capable of converting nepetalactone to nepetalactone Cloning and expression of the proenzyme
[0562] Identify NOR candidates
[0563] Publicly available next-generation RNA sequencing data from Nepeta cataria (SRR5150709) were obtained from NCBI. Reads are extracted and composed into transcriptomes. Using the protein sequence of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase (HLADH) as a BLAST query, alcohol dehydrogenase candidates from Nepeta sativa that might catalyze the conversion of nepetalactin to nepetalactone were identified.
[0564] Thirty-nine candidates were identified and the coding sequences were codon optimized for expression in E. coli. The codon-optimized nucleotide sequence was synthesized by Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT) using the upstream T7 promoter and ribosome binding site (RBS) and downstream T7 terminator sequence. Synthetic DNA was recovered as a plasmid (provided by IDT) containing the expr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| optical density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| optical density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com