Projection screen and projection system
A technology of projection screen and microlens, which is applied in the field of projection display, can solve the problems of uneven image intensity and uneven distribution of light intensity displayed on the projection screen, and achieve the effect of improving the uniform effect of display brightness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
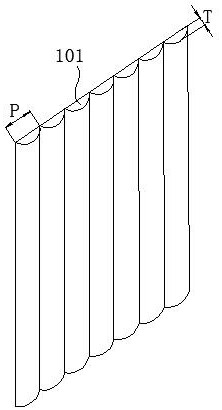
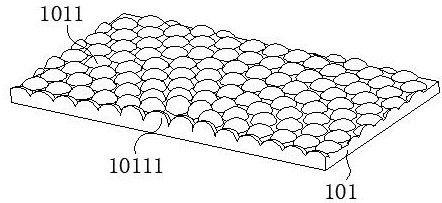
[0045] such as Figure 2 Shown is the schematic diagram of the projection screen structure. such as Figure 2 A shows the bottom view of the projection screen, as shown in Figure 2 B shows the front view of the projection screen, as shown in Figure 2 C shows the left view of the projection screen. The projection screen includes a diffusion layer 101, a first substrate layer 102 and a reflective microstructure layer 103 arranged along the thickness direction of the projection screen, and the diffusion layer 101 is arranged on one side of the first substrate layer 102. The diffusion layer 101 comprises at least one microlens layer, and the microlens layer comprises a plurality of microlenses 1011, wherein at least one of the microlenses 1011 is a central microlens 1011, and other microlenses 1011 are arranged around the center of the central microlens 10111. In the figure, the height of the microlens 1011 is T, the width of the microlens 1011 is P, and the aspect ratio of the microlen...
Embodiment 2
[0064] On the basis of the first embodiment, for example Figure 7 As shown, diffusion particles and / or light absorbing materials are arranged on the diffusion layer.
[0065] such as Figure 7 As shown in Figure A, the diffusion layer includes a microlens layer, which includes several microlenses 1011, and diffusion particles 1034 are arranged in the microlenses 1011. These diffusion particles 1034 can uniformly scatter the light passing through the microlenses 1011, further making the light intensity distribution more uniform. The diffusion particles 1034 include, but are not limited to, silicon dioxide particles, aluminum oxide particles, titanium oxide particles, cerium oxide particles, zirconium oxide particles, tantalum oxide particles, zinc oxide particles, magnesium fluoride particles, etc., and their particle diameters are preferably 5 nm to 200 nm.
[0066] It should be noted that the microlens mainly depends on the change of the lens structure itself to realize the diffus...
Embodiment 3
[0073] This embodiment differs from the projection screen of the first embodiment in that: refer to Figure 8 As shown in the bottom view of the projection screen, the surface of the diffusion layer 101, which is far away from the first base material layer 102, is a rough surface 1012. The diffusion layer 101 includes a microlens layer, which includes a plurality of microlenses 1011. The rough surface 1012 is formed by roughening the spherical surface of the microlenses 1011. Here, the rough surface 1012 can be formed by sand blasting or mold surface roughening, and then glue with diffusion particles can be transferred or sprayed. The rough surface 1012 can further diffuse light, and play the roles of light equalization, hardening protection and imaging.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com