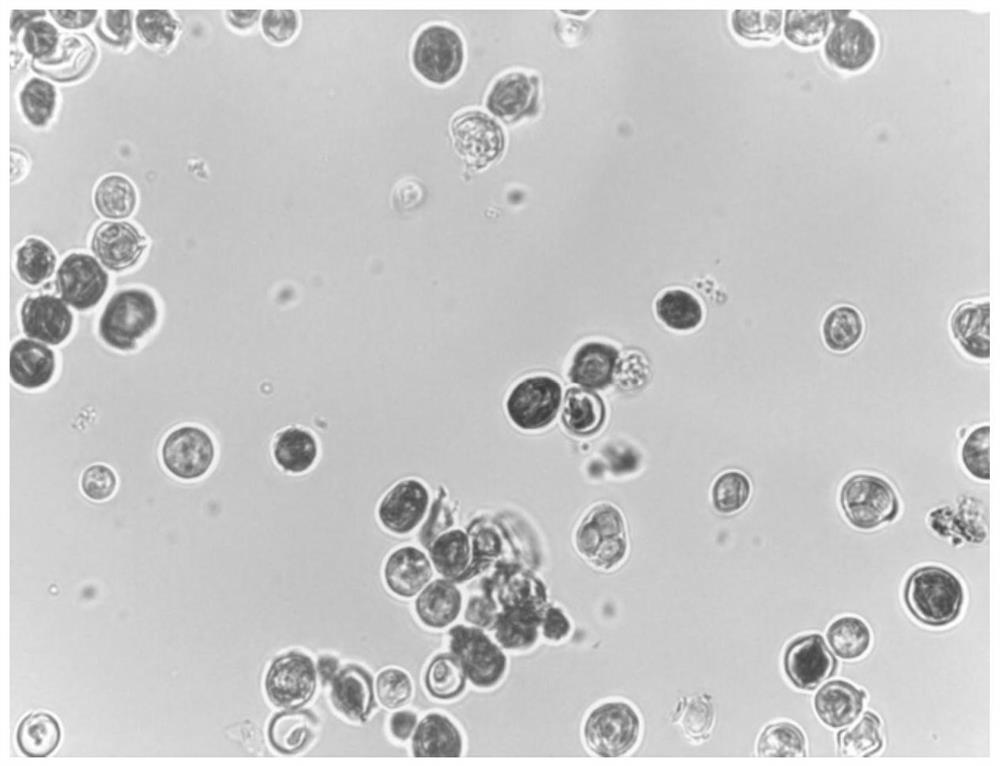
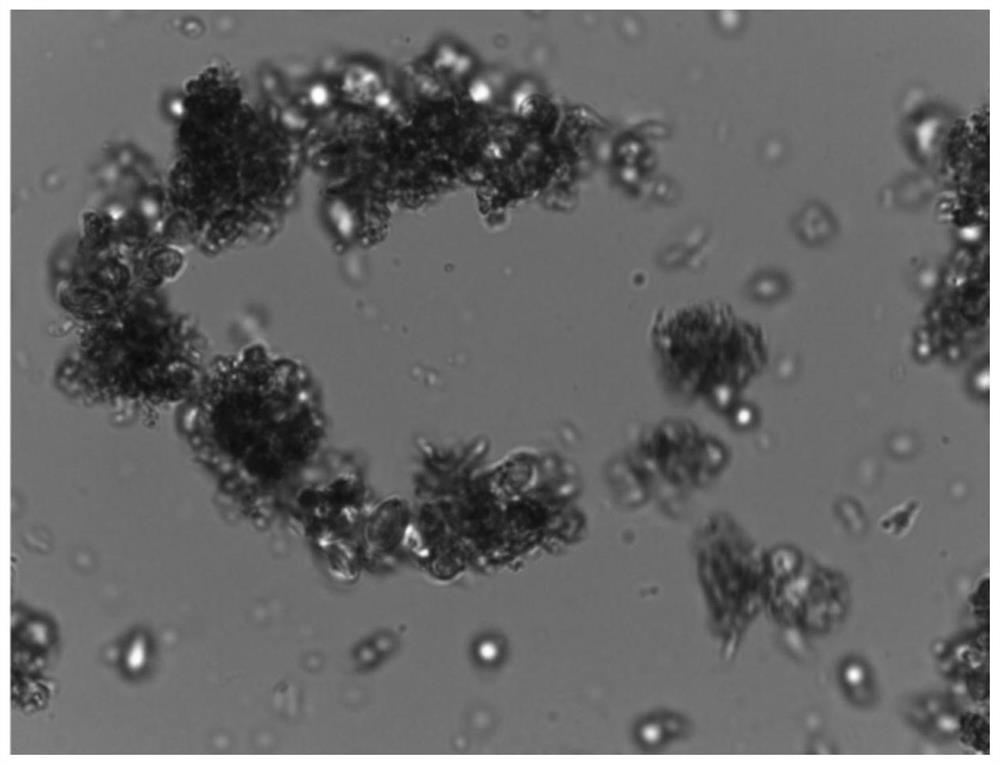
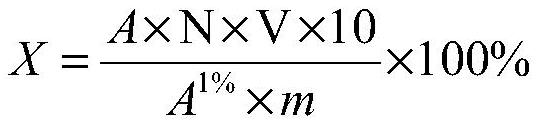Extraction method of biologically fermented carotenoid
A technology of carotenoids and extraction methods, applied in chemical instruments and methods, hydrocarbons, extraction purification/separation, etc., can solve the problems of reducing purity, increasing the difficulty of carotenoid extraction process, limiting extraction yield, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0084] A method for extracting biologically fermented carotenoids, using Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermented liquid expressing lycopene as a raw material for extraction, specifically:
[0085] (1) Spray-dry the 20L lycopene fermented liquid after fermentation and putting it into the tank, set the inlet air temperature to 190°C, and the outlet air temperature to 90°C, spray dry to obtain 1kg of dry yeast powder;
[0086] (2) The dry yeast powder is humidified with purified water and adjusted to a water content of 10%, and then the wall is broken by a low-temperature shearing machine for 30 minutes. The cooling form is closed circulating water cooling, and the temperature is 8°C. The wall-broken bacteria powder is collected, and the wall-breaking rate is greater than 98% after testing, and the loss of lycopene content is less than 2%;
[0087] (3) Add 10 L of ethanol solution with a sodium hydroxide content of 1% to the dried bacterial powder after the wall breaking for saponific...
Embodiment 2
[0093] A method for extracting biologically fermented carotenoids, using Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermented liquid expressing β-carotene as a raw material for extraction, specifically:
[0094] (1) Spray-dry the 22L beta-carotene fermented liquid after fermentation and putting into the tank, set the air inlet temperature to 180°C, and the air outlet temperature to 80°C, spray dry to obtain 1.32kg of dry yeast powder;
[0095](2) The dry yeast powder is humidified with purified water and adjusted to a water content of 10%, and then the wall is broken by a low-temperature shearing breaker for 45 minutes. The cooling form is closed circulating water cooling, and the temperature is 4°C. Collect the broken wall bacteria powder, the broken wall rate is more than 99% after testing, and the loss of β-carotene content is less than 1.5%;
[0096] (3) Add 6.6L of ethanol solution with a sodium hydroxide content of 2% to the dried bacteria powder after the wall breaking for saponification...
Embodiment 3
[0102] A method for extracting biologically fermented carotenoids, using astaxanthin-expressing Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation broth as raw material for extraction, specifically:
[0103] (1) Spray-dry the 25L astaxanthin fermented liquid after fermentation and putting it into the tank, set the air inlet temperature to 190°C, and the air outlet temperature to 90°C, and spray dry to obtain 1.4kg of dry yeast powder;
[0104] (2) The dry yeast powder is humidified with purified water and adjusted to a water content of 9%, and then the wall is broken by a low-temperature shearing breaker for 60 minutes. The cooling form is closed circulating water cooling, and the temperature is 0°C. The wall-broken bacteria powder is collected, and the wall-breaking rate is greater than 99% after testing, and the loss of astaxanthin content is less than 2.5%;
[0105] (3) Add 8.4L of ethanol solution with a sodium hydroxide content of 3% to the dried bacteria powder after the wall breakin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| water content | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| extraction efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com