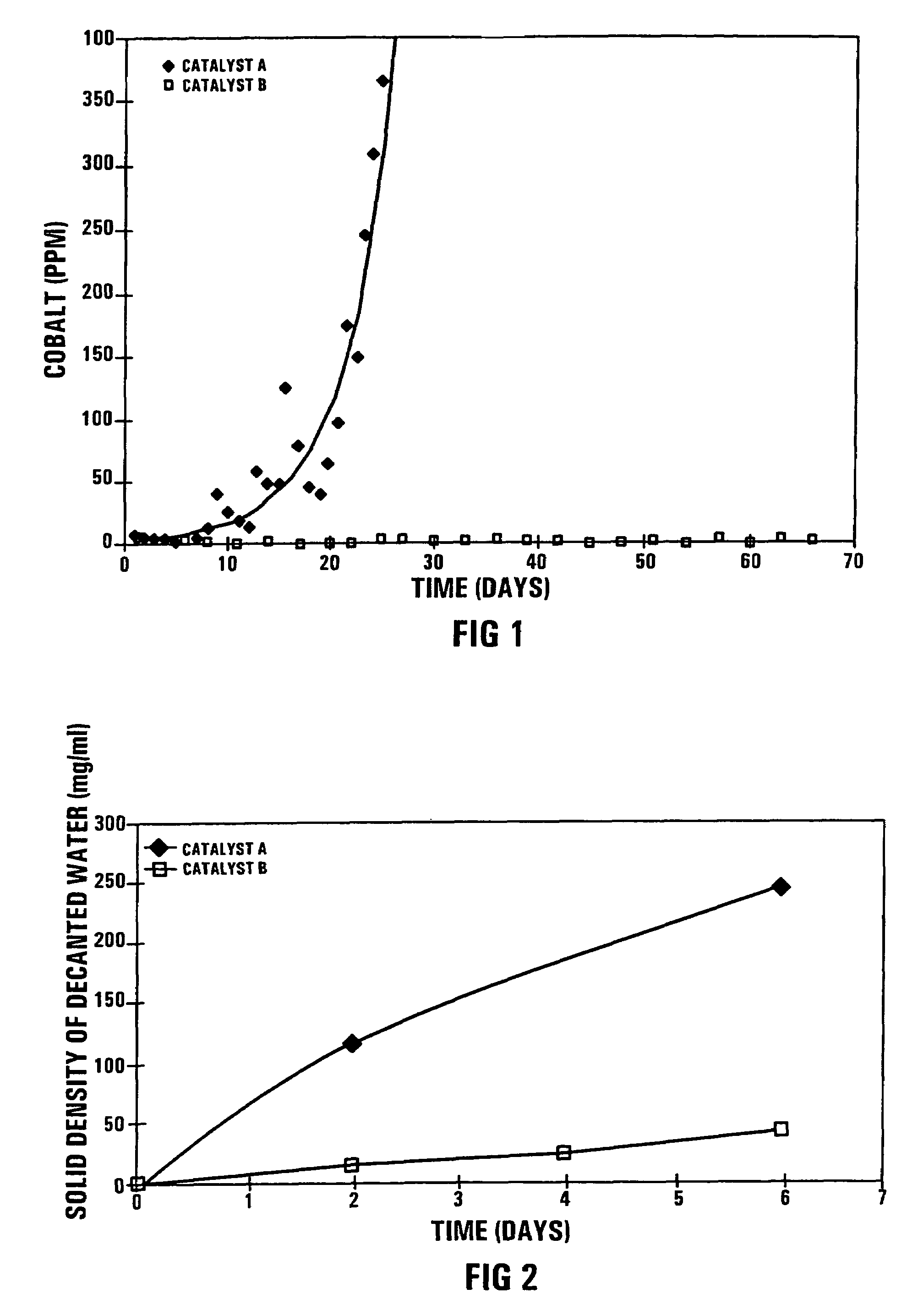
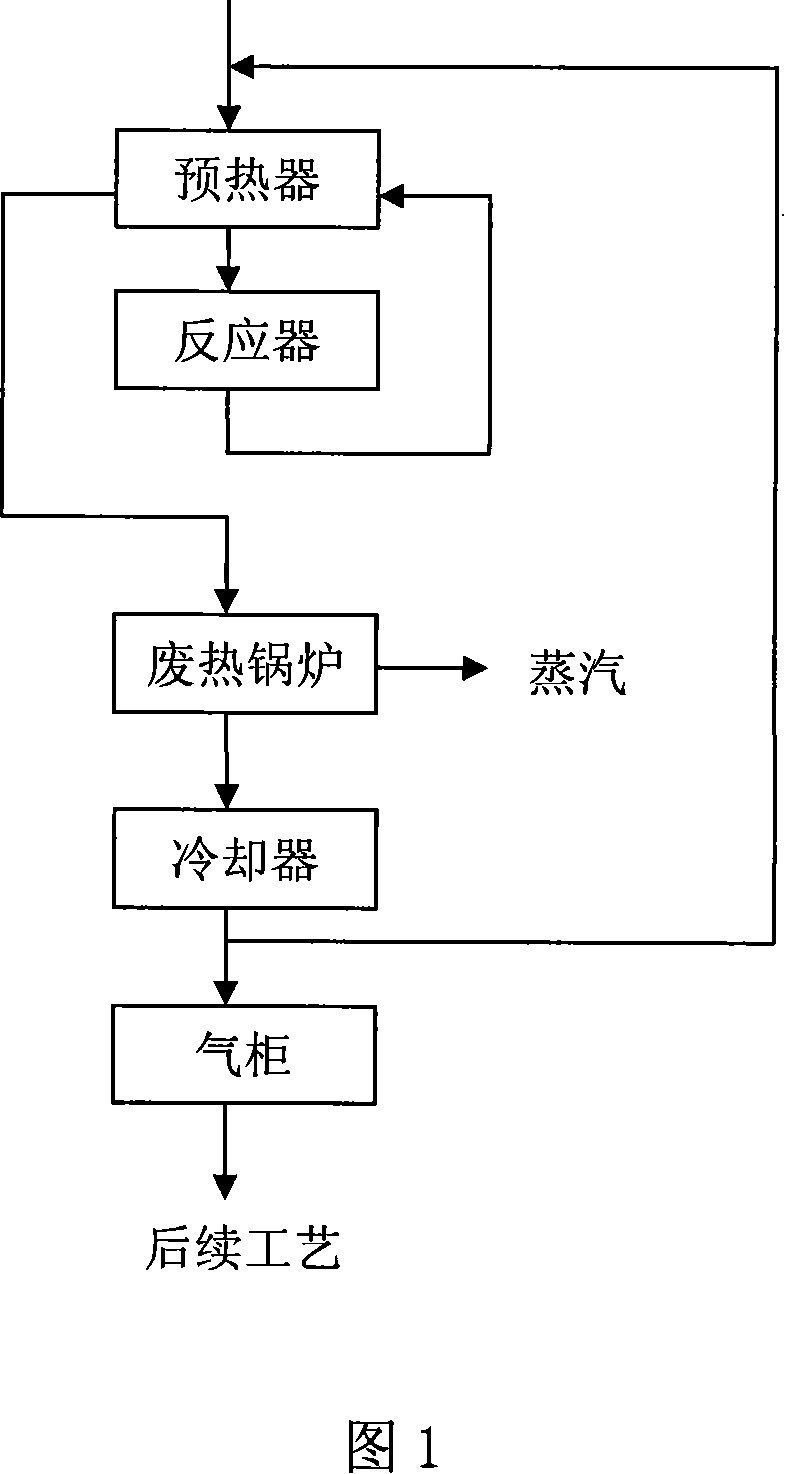
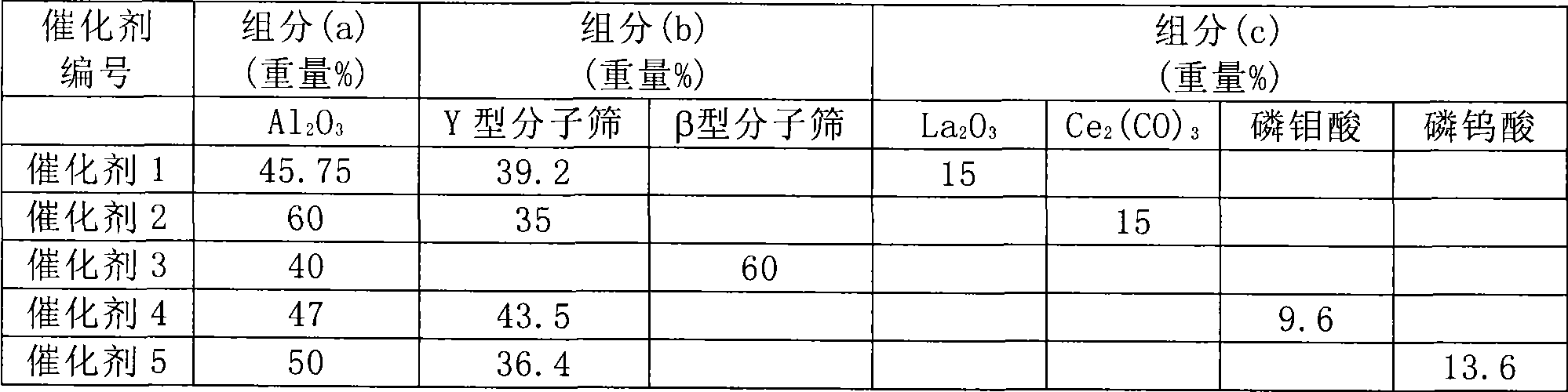
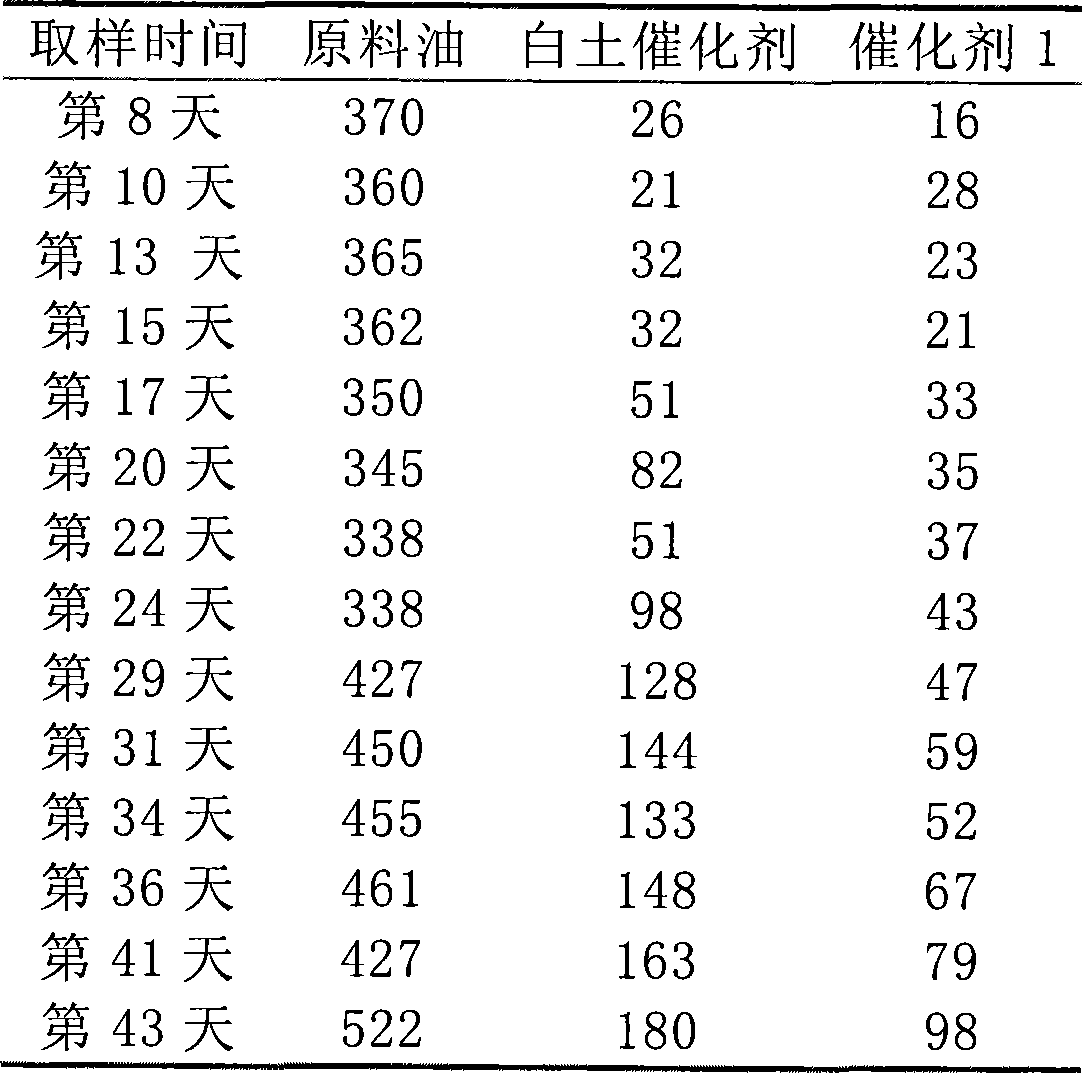
Patents
Literature
777results about "Chemical modification purification/separation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
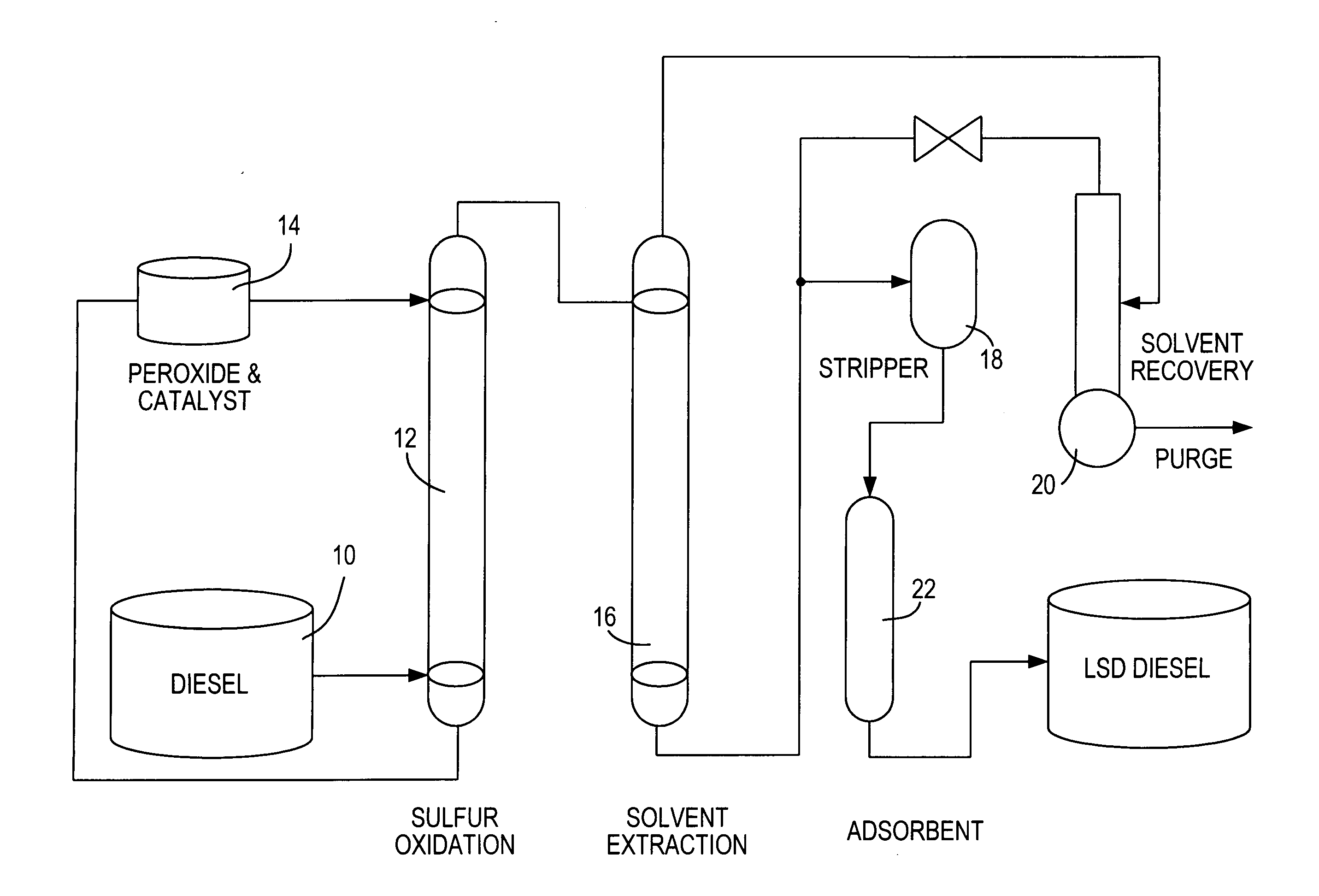
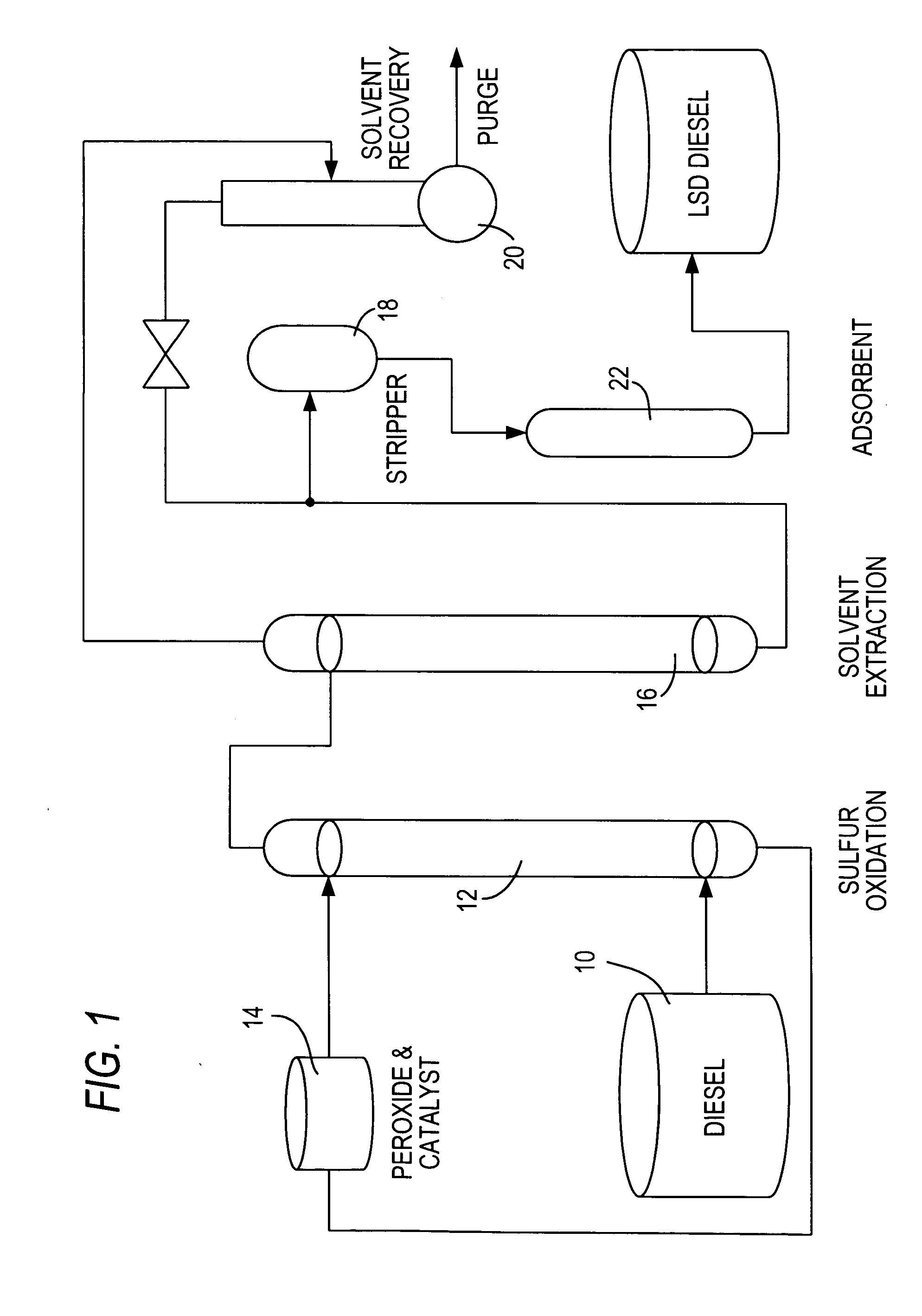
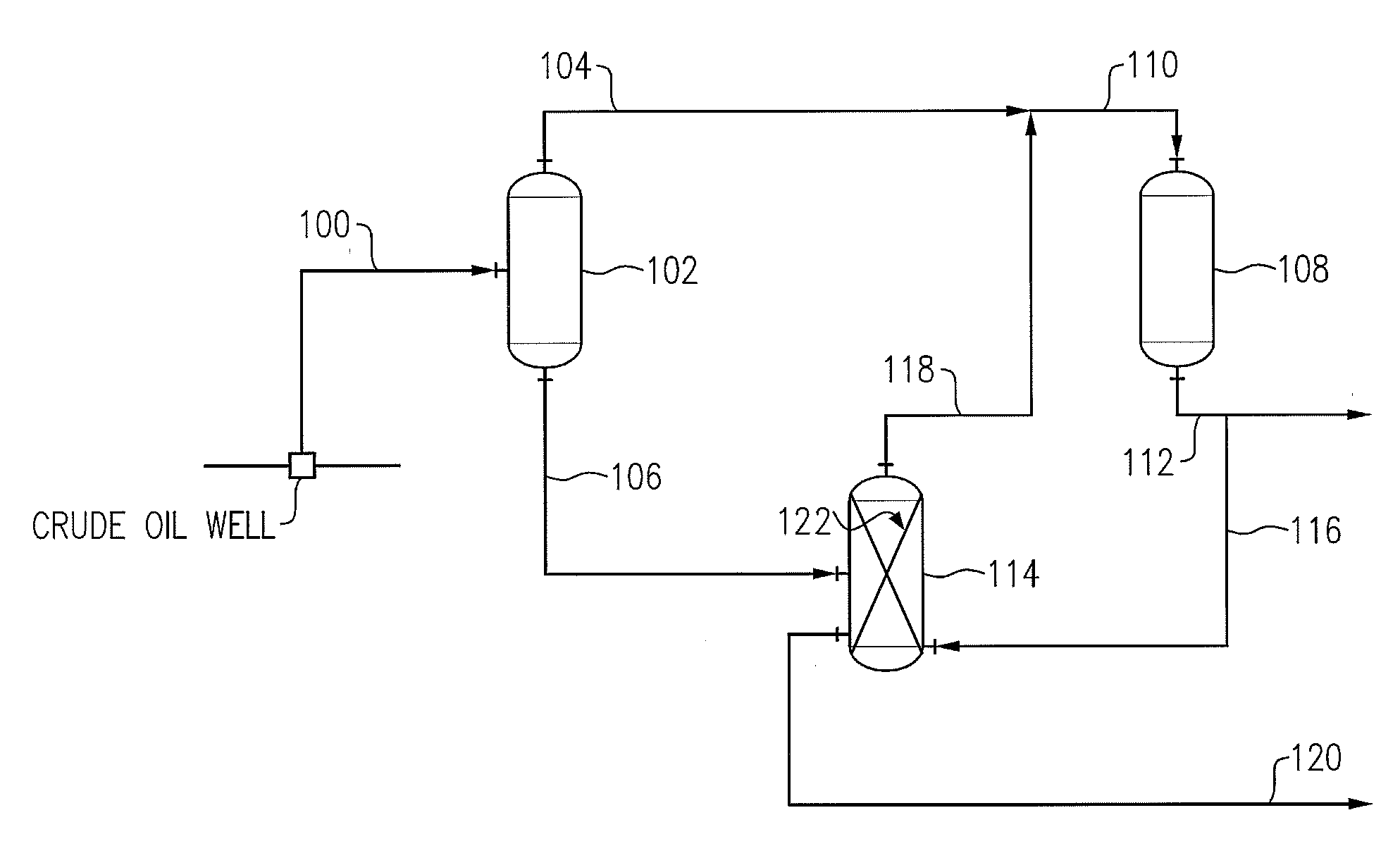
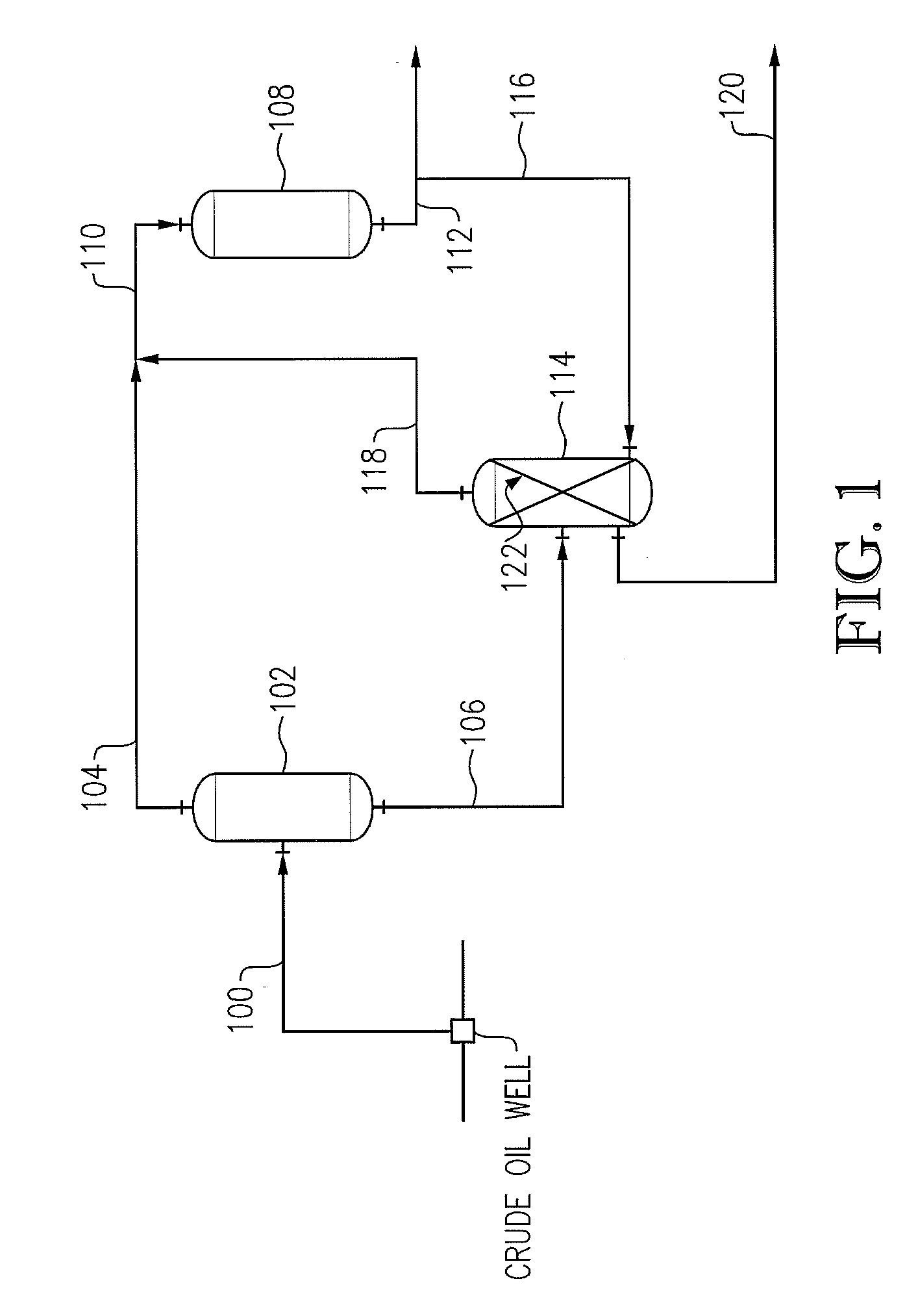
Diesel oil desulfurization by oxidation and extraction
ActiveUS20070051667A1Refining with oxygen compoundsRefining with acid-forming oxidesSulfur containingDiesel fuel
The reduction in the sulfur-containing content of diesel fuel is achieved by oxidation in the presence of a catalyst followed by a liquid-liquid countercurrent extraction.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
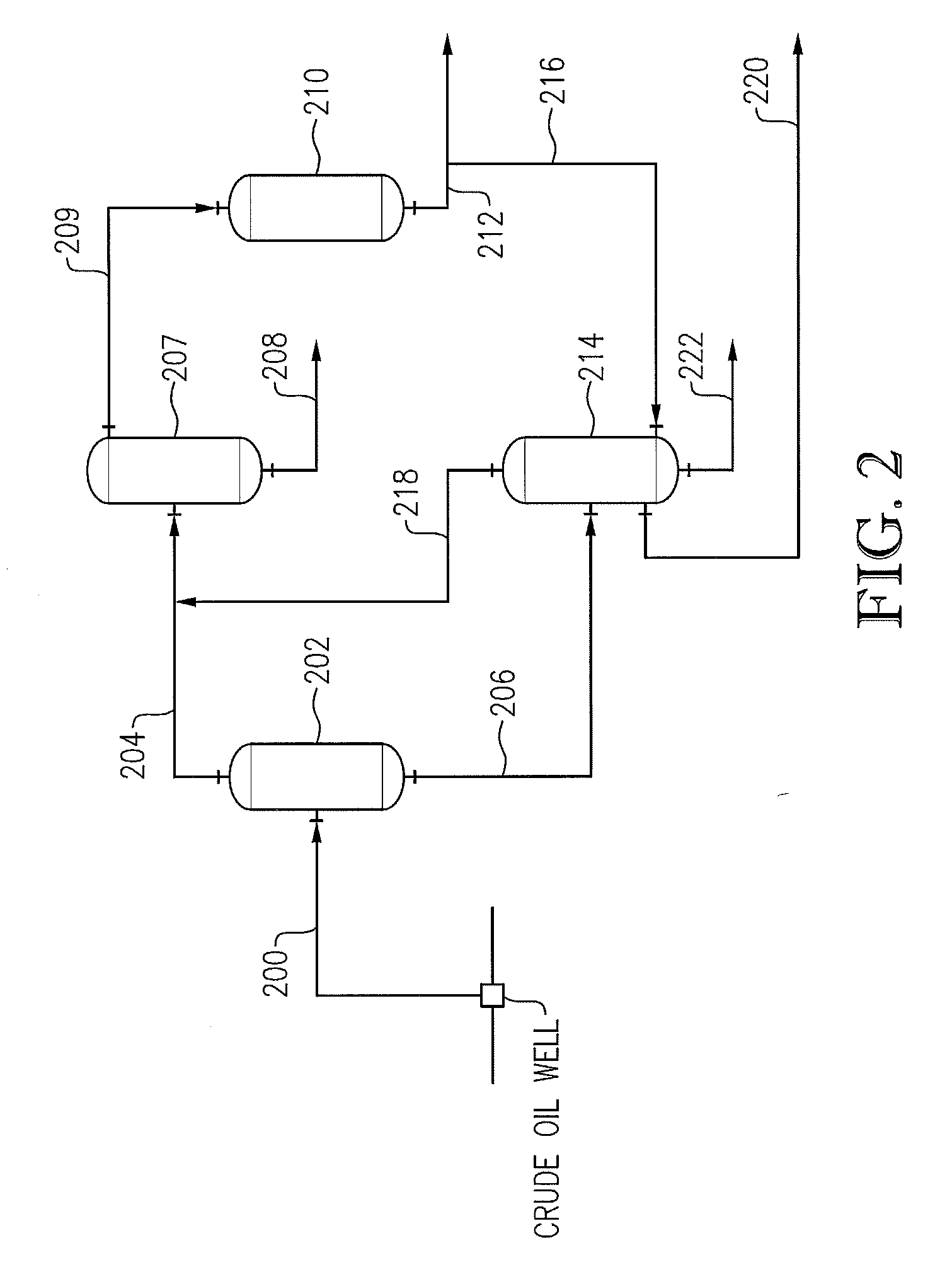
Process for BTX purification
InactiveUS6500996B1Lowering indexEfficient executionOrganic chemistry methodsTreatment with plural serial refining stagesCobaltChromium
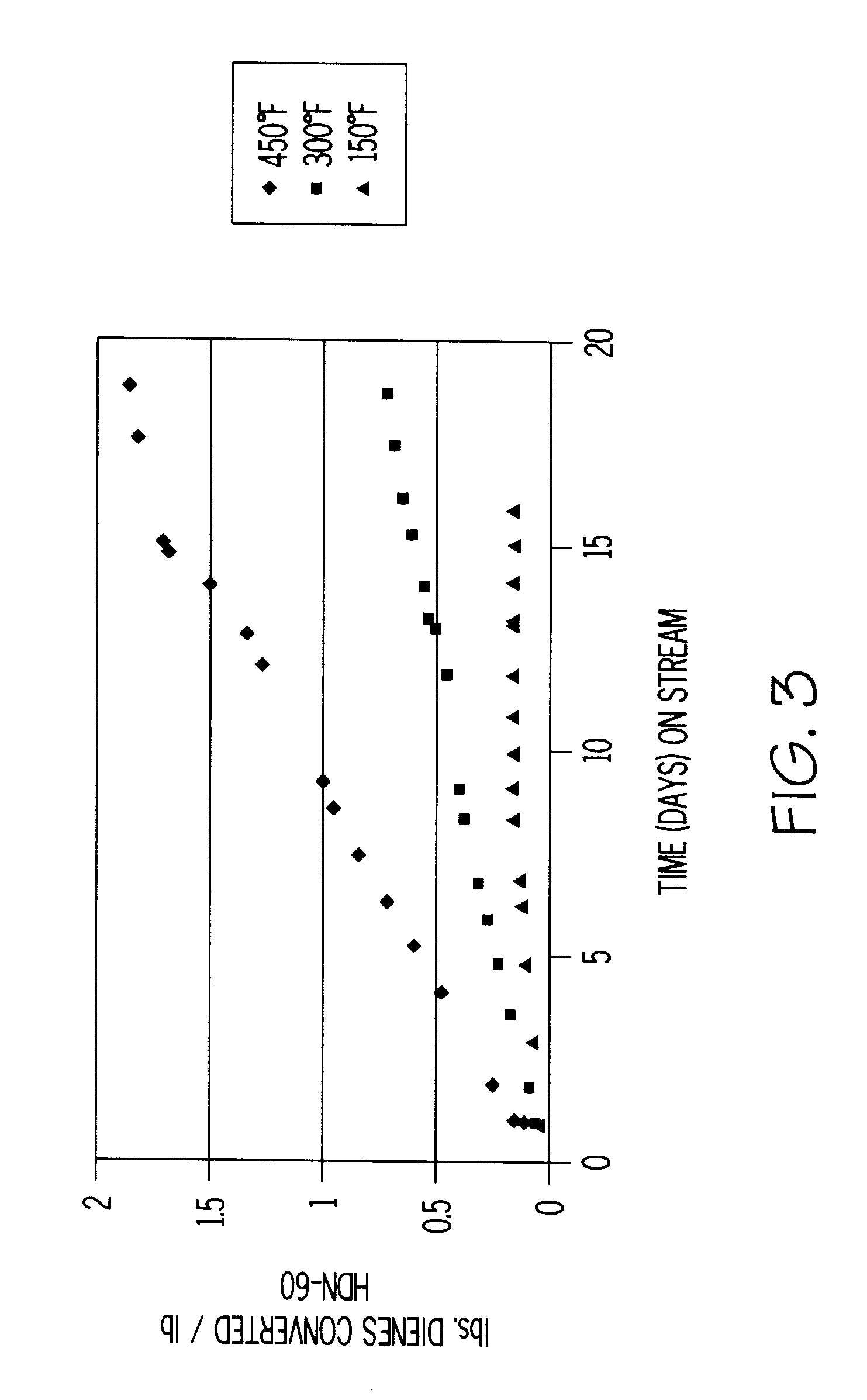
A process for the removal of hydrocarbon contaminants, such as dienes and olefins, from an aromatics reformate by contacting an aromatics reformate stream with a hydrotreating catalyst and / or a molecular sieve. The hydrotreating catalyst substantially converts all dienes to oligomers and partially converts olefins to alkylaromatics. The molecular sieve converts the olefins to alkylaromatics. The process provides an olefin depleted product which can be passed through a clay treater to substantially convert the remaining olefins to alkylaromatics. The hydrotreating catalyst has a metal component of nickel, cobalt, chromium, vanadium, molybdenum, tungsten, nickel-molybdenum, cobalt-nickel-molybdenum, nickel-tungsten, cobalt-molybdenum or nickel-tungsten-titanium, with a nickel molybdenum / alumina catalyst being preferred. The molecular sieve is an intermediate pore size zeolite, preferably MCM-22. The clay treatment can be carried out with any clay suitable for treating hydrocarbons.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CORP (US)
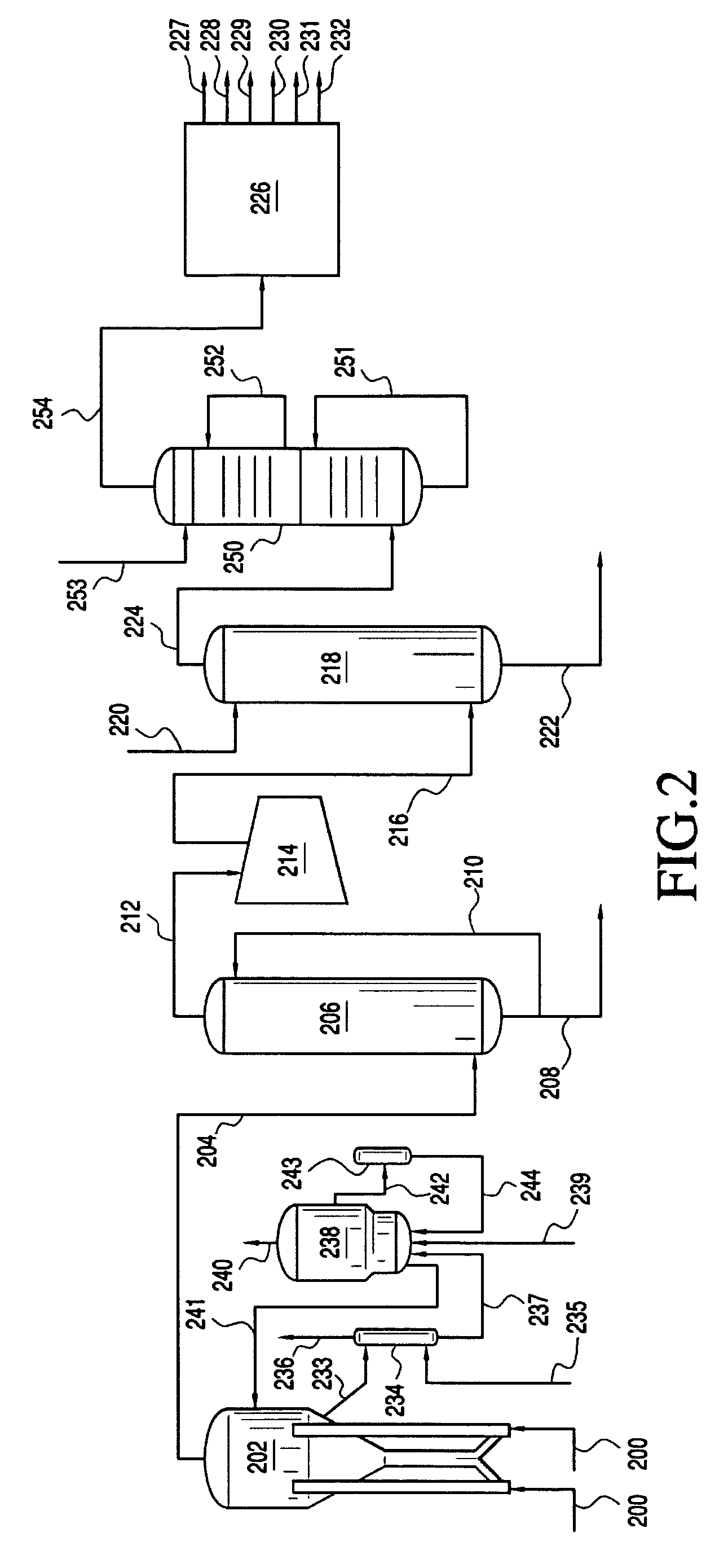
Oxidative desulfurization of sulfur-containing hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20050150819A1Reduce sulfur contentLow sulfurRefining with oxygen compoundsRefining with metal oxidesGas phaseOxygen
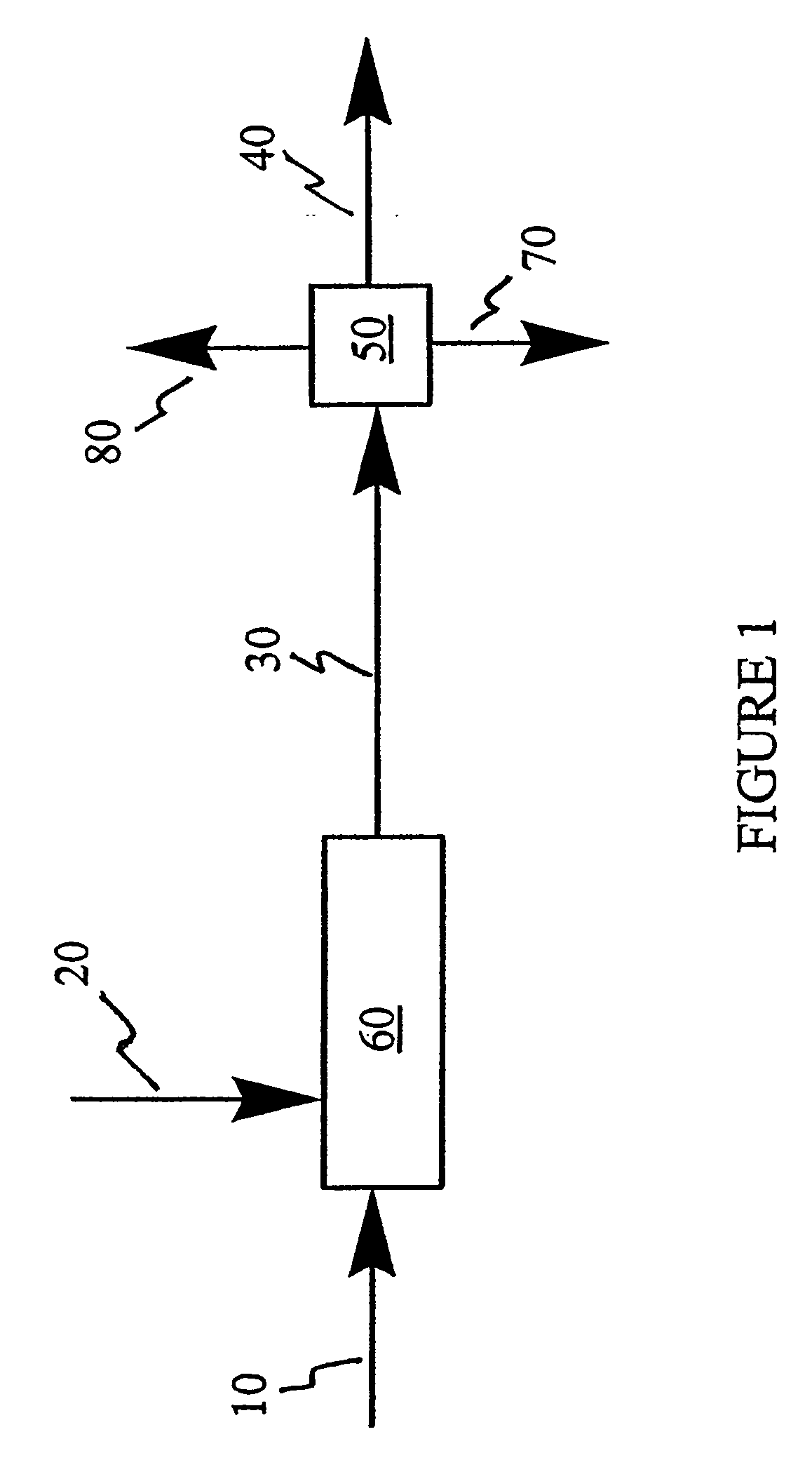
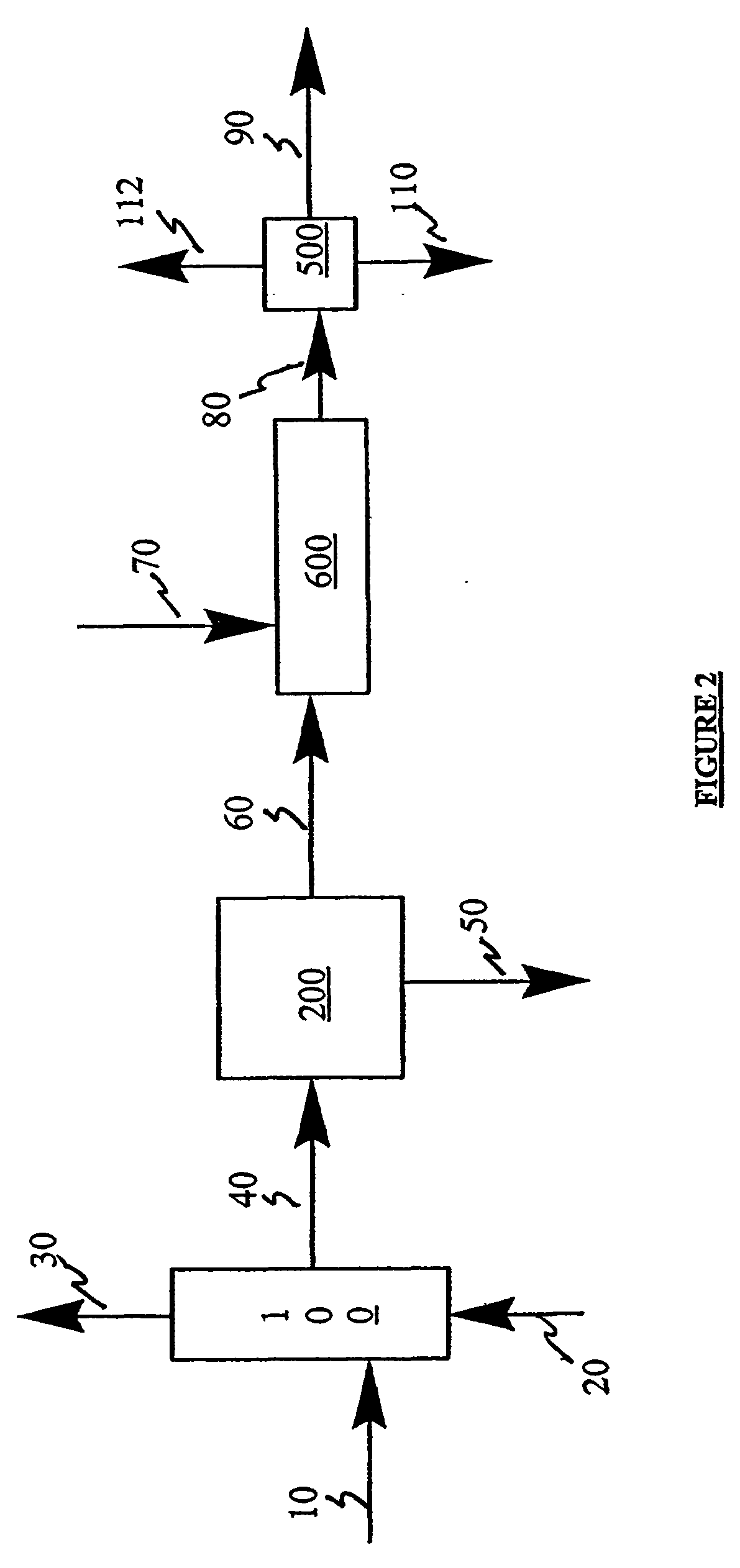
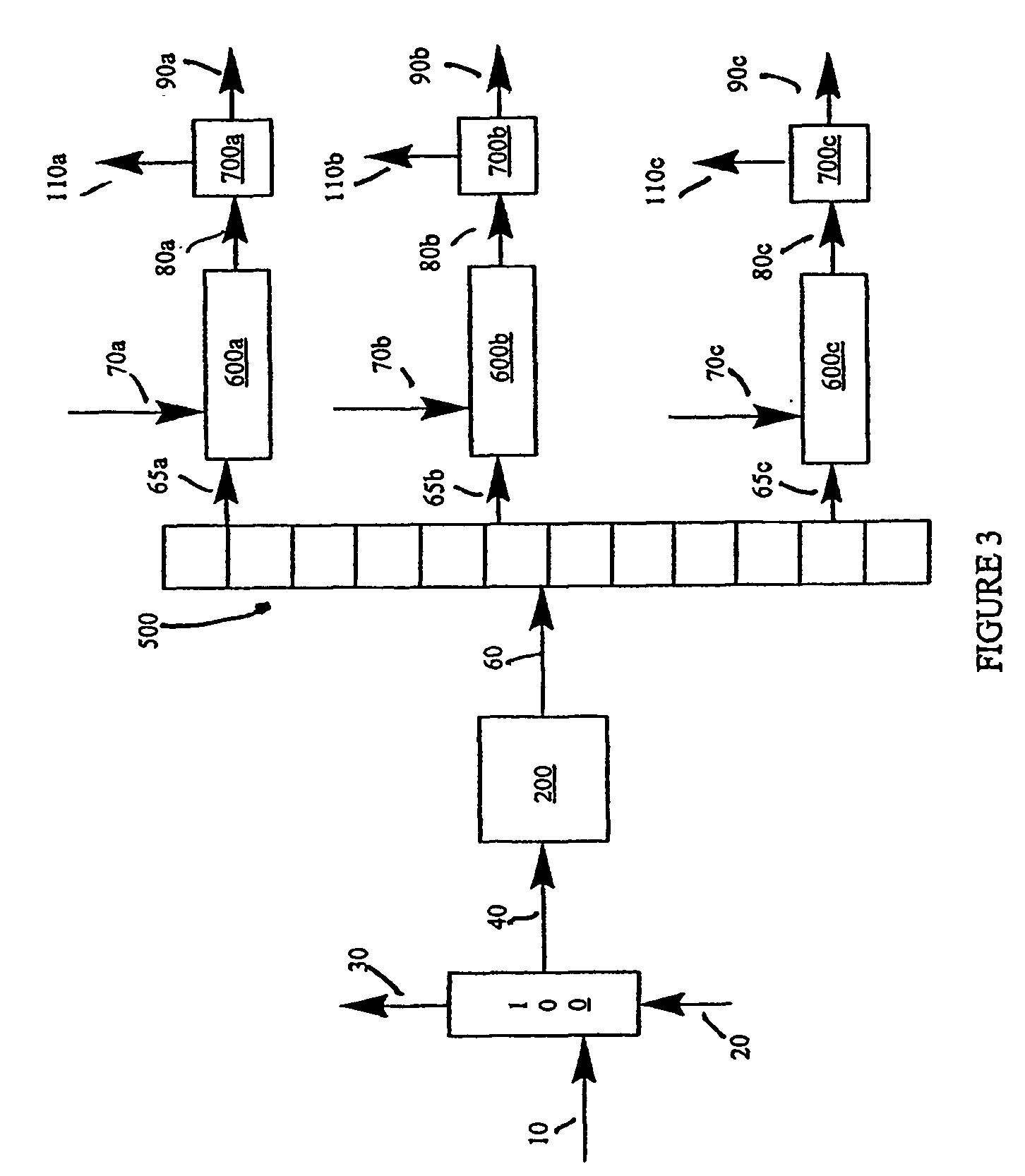
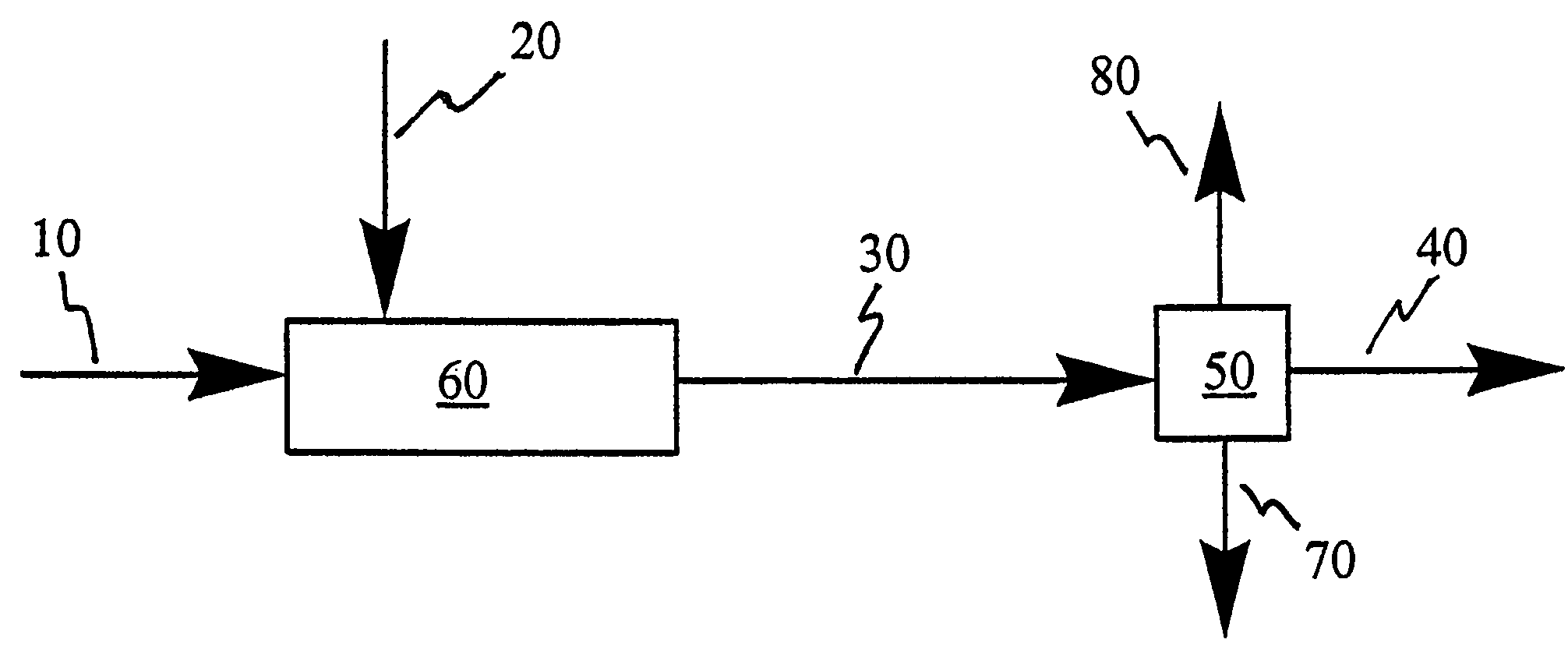
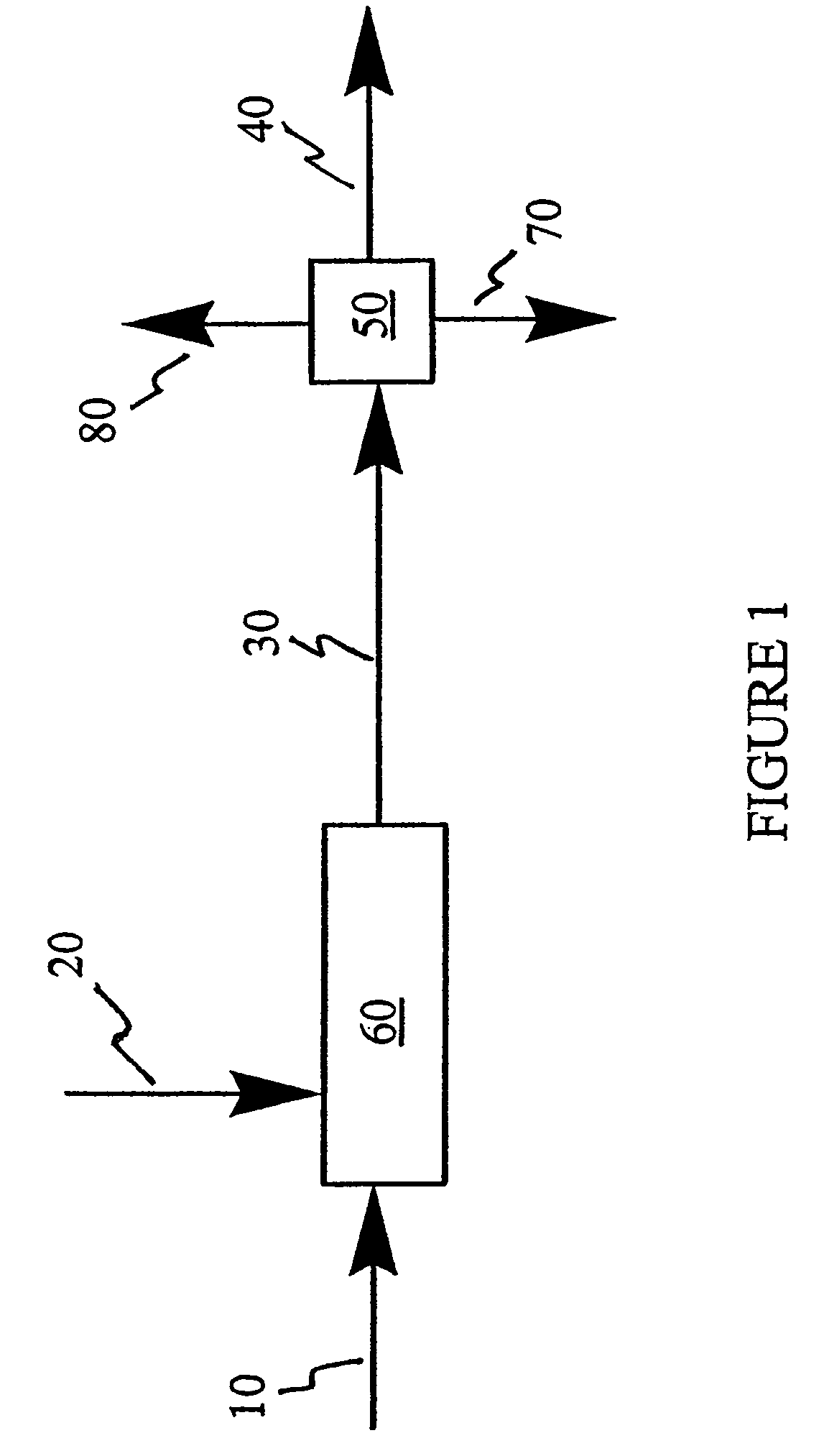
A method for desulfurizing a hydrocarbon stream (10) containing heterocyclic sulfur compounds, which process comprises contacting the heterocyclic sulfur compounds in the gas phase (60) in the presence of oxygen (70) with a supported metal oxide catalyst, or with a bulk metal oxide catalyst (600) to convert at least a portion of the heterocyclic sulfur compounds to oxygenated products as well as sulfur-deficient hydrocarbons and separately recovering the oxygenated products separately from a hydrocarbon stream with substantially reduced sulfur.
Owner:LEHIGH UNIVERSITY
Oxidative desulfurization of sulfur-containing hydrocarbons
A method for desulfurizing a hydrocarbon stream (10) containing heterocyclic sulfur compounds, which process comprises contacting the heterocyclic sulfur compounds in the gas phase (60) in the presence of oxygen (70) with a supported metal oxide catalyst, or with a bulk metal oxide catalyst (600) to convert at least a portion of the heterocyclic sulfur compounds to oxygenated products as well as sulfur-deficient hydrocarbons and separately recovering the oxygenated products separately from a hydrocarbon stream with substantially reduced sulfur.
Owner:LEHIGH UNIVERSITY
Catalysts
ActiveUS7365040B2Facilitates the eventual dislodging and washingReducing the catalyst precursorLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocarbon oils refiningPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
A process for preparing a cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst includes introducing a soluble modifying component precursor of the formula Mc(OR)x, where Mc is a modifying component selected from the group comprising Si, Ti, Cu, Zn, Zr, Mn, Ba, Ni, Na, K, Ca, Sn, Cr, Fe, Li, Tl, Sr, Ga, Sb, V, Hf, Th, Ce, Ge, U, Nb, Ta, W or La, R is an alkyl or acyl group, and x is an integer having a value of from 1 to 5, onto and / or into a cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst precursor, which comprises a porous pre-shaped catalyst support supporting cobalt in an oxidized form. The resultant modified cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst precursor is reduced to obtain a cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst.
Owner:SASOL TEKHNOLODZHI PROPRIEHJTEHRI LTD
Sulfur-resistant catalytic deoxidization process for methane-rich gas
InactiveCN101139239ALow priceSulfur resistanceMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsChemical modification purification/separationReaction temperatureManganese
The present invention discloses a sulfur wearable and catalyzing and oxidizing method for gas abundant of firedamp; the raw material gas abundant of firedamp such as coal bed gas firstly passes through a preheater for preheating, and then enters a oxidizing reaction device; under the condition of 0-0.5MPa of pressure, 500-750 DEG C of reaction temperature, 1000-3000h-1of reaction air speed, the firedamp in the air is reacted with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water in manganese base sulfur wearable and catalyzing and oxidizing bed; at the same time, a small quantity of firedamp is decomposed to produce carbon and hydrogen gas; the carbon and the hydrogen after being decomposed are also reacted with oxygen so as to reach the purpose of getting rid of oxygen in the airs abundant of firedamp effectively. The present invention adopts much newer and more economical new catalyzer, which does not need to desulfurize firstly for the air; the air can directly enter the oxidization reaction device for oxidization. So the present invention can decrease the cost and simplify the technics process.
Owner:HAO HUA CHENGDU TECH
Catalyst for removing trace amounts of olefin hydrocarbon in arene
InactiveCN101433856AMolecular sieve catalystsChemical modification purification/separationMolecular sieveRare earth
The invention discloses a catalyst removing trace olefin in aromatic hydrocarbon. The catalyst comprises the following compositions by weight percentage: 30 to 70 percent of Al2O3, 30 to 70 percent of molecular sieve, and 0 to 40 percent of one or a compound of La-based rare earth, P, W, Nb and Mo. The catalyst is an alkylate catalyst, and can maintain high catalytic activity for a long time.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Process for the separation of olefins from paraffins using membranes
Chitosan membranes chelated with silver or cuprous material may be used to separate olefins from a mixture of olefins and paraffins. The feed stream is humidified, demisted, treated to remove sulfur compounds and passed to a cell having a chitosan membrane containing chelated silver or cuprous compounds. The process has a reasonable flux rate and is operable at reasonable temperatures and pressures. The process could be used in an olefin separation train.
Owner:IMTEX MEMBRANES CORP
Manganese deoxidier and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN1955150AImprove deoxygenation capacityExtended regeneration cycleChemical modification purification/separationAlkali metal oxideManganese
This invention discloses a deoxidizer of manganese system and its preparation and application. The deoxidizer of this invention is using MnO / Mn3O4 as active constituent. Add alkali metal oxide and aluminium oxide that are active accelerators. This invention provides two preparations, which adopt precurosor compound of Mn3O4 or active Mn3O4 that is produced by calcining precurosor compound of Mn3O4 to mix with alkali metal oxide or hydroxide oxide and aluminium, kneading, forming, open-air drying, at last drying or then producing deoxidizer of this invention by calcining after drying. The deoxidizer of this invention can eliminate 1- 2000ppm oxygen which is in the aethylenum or propylene, at the same time it possesses fairly high mechanical strength.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
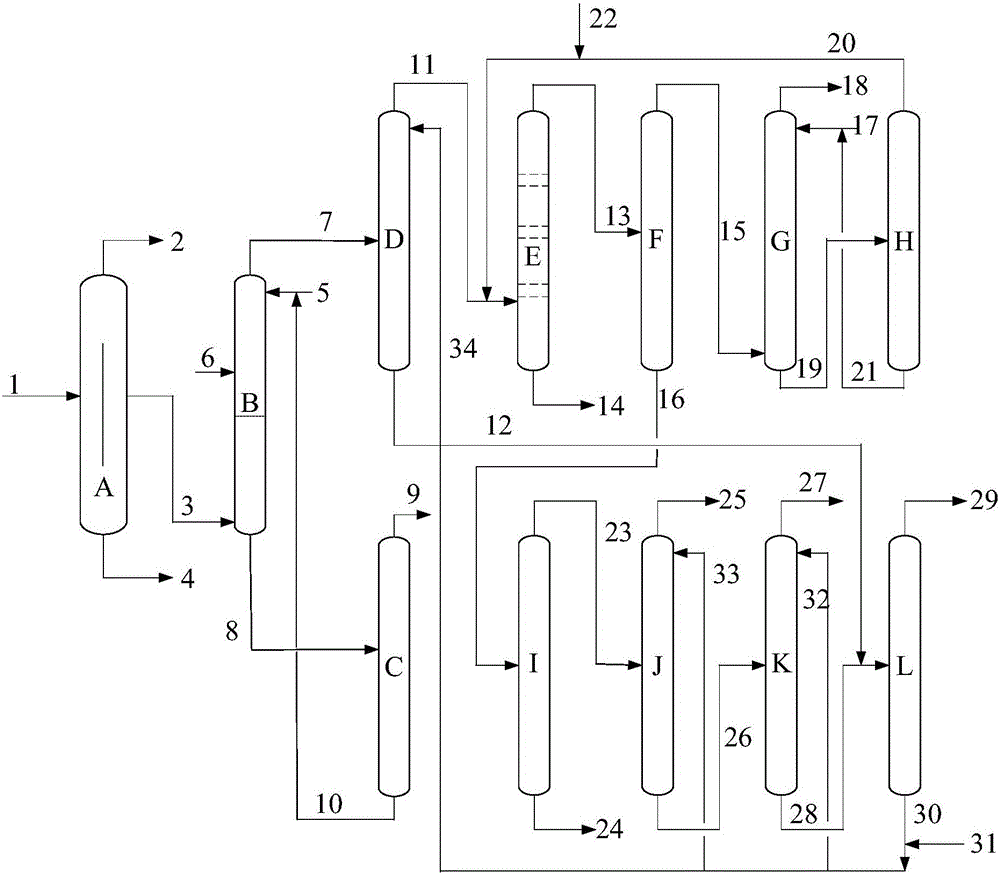
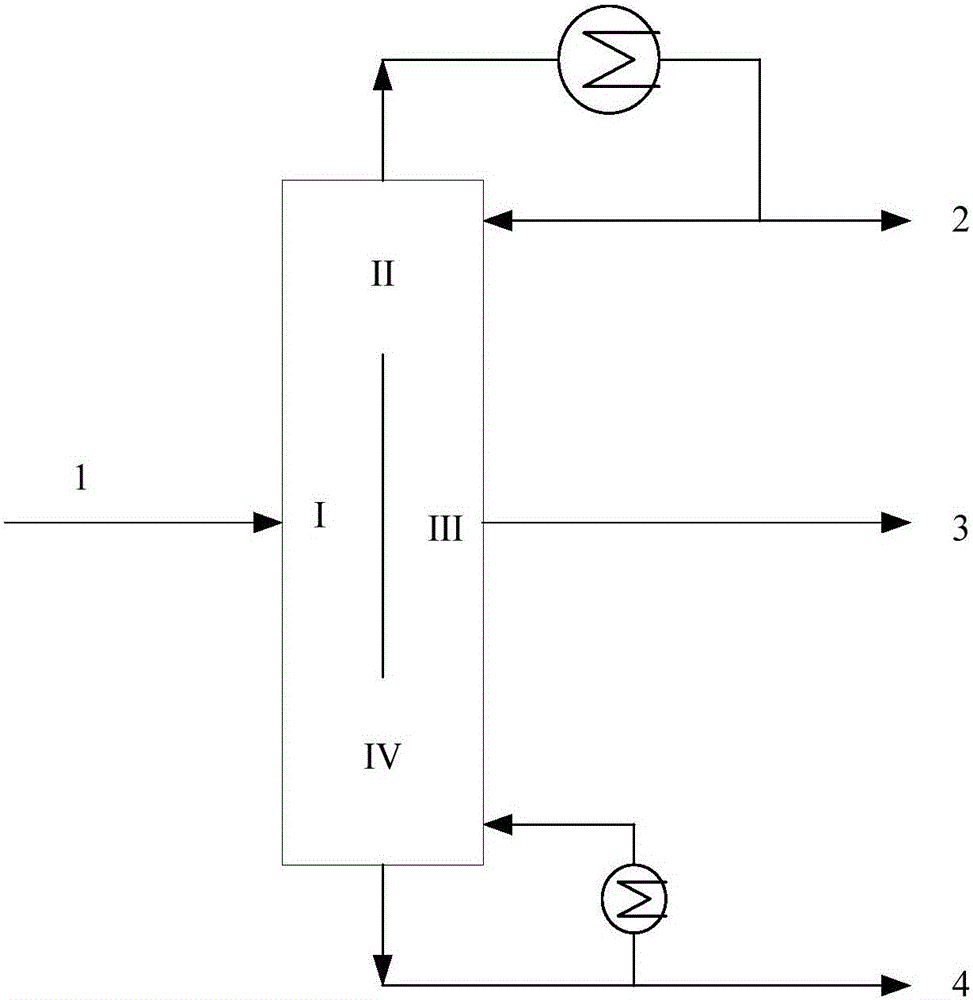
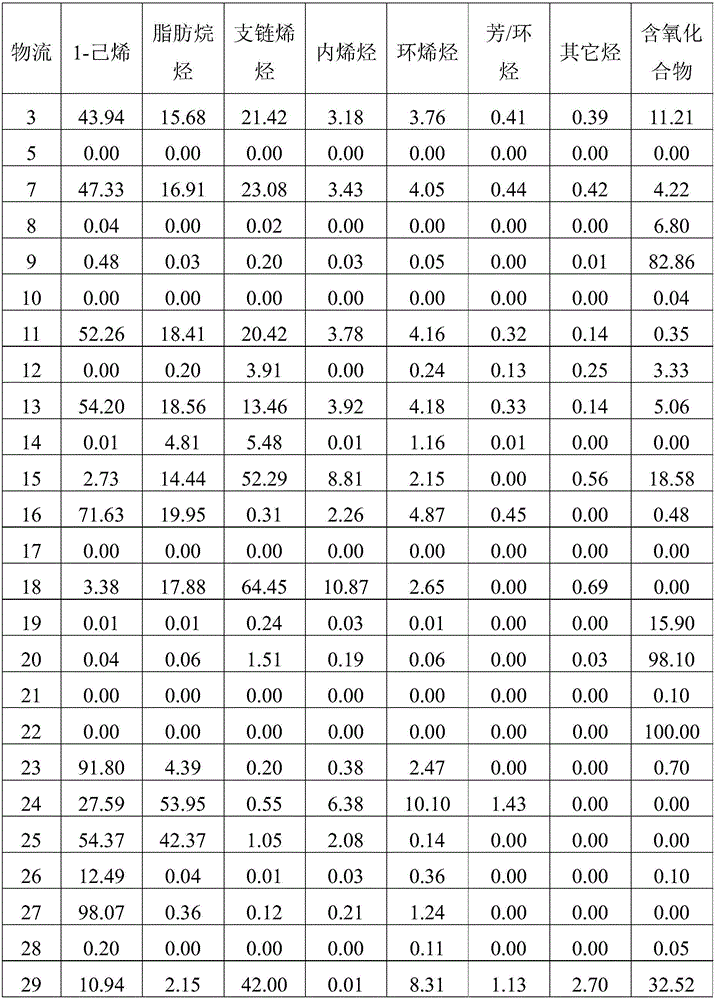
Method for separating oxygenated chemicals and 1-hexene from Fischer-Tropsch synthesis oil product
ActiveCN105777467AIncrease productionExpand product rangeOrganic compound preparationDistillation purification/separationAlkaneAlcohol
The invention relates to a method for separating oxygenated chemicals and 1-hexene from a Fischer-Tropsch synthesis oil product.The method comprises the steps that C6 fraction material flow is obtained through distillation in a predistillation tower by taking the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis oil product as a raw material, and two streams of extraction agents are fed to remove oxygenated chemicals in an extraction tower to obtain material flow rich in the oxygenated chemicals and crude C6 hydrocarbon material flow; the oxygenated chemicals contained in the crude C6 hydrocarbon material flow are further removed through a third extraction agent, tertiary olefins are converted into corresponding ethers through methyl alcohol under the action of an etherification catalyst to be removed, further purification is performed through rectification, and then C6 isoparaffin components and cycloolefin components are removed sequentially through a fourth extraction agent and a fifth extraction agent respectively to obtain 1-hexene product material flow.Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of being simple in technological process, low in cost and the like, and not only is 1-hexene separated and purified from the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis oil, but also the oxygenated chemicals can be separated.
Owner:YANKUANG ENERGY R&D CO LTD
Method for extracting high-purity squalene by taking olive oil as raw material
ActiveCN101597204AIncrease productionImprove qualityDistillation purification/separationAdsorption purification/separationDistillationEvaporation
The invention relates to a method for extracting high-purity squalene by taking olive oil as a raw material. A technological route formed by adopting a secondary molecular distillation and silica gel column chromatography is as follows: an olive oil unsaponifiable substance is taken, squalene is separated and purified by using two stages of molecular distillation, primary molecular distillation is carried out under the conditions of the evaporation surface temperature of 100 to 200 DEG C, the systemic pressure of 0.001 to 0.01mbar and the scraping film rotor speed of 150 to 300rpm, and secondary molecular distillation is carried out to the obtained distillate; the secondary molecular distillation is carried out under the conditions of the evaporation surface temperature of 150 to 300 DEG C, the systemic pressure of 0.001 to 0.01mbar and the scraping film rotor speed of 200 to 350rpm, and the obtained distillate is a squalene crude product; ethyl acetate-normal hexane with different concentrations is used as a mobile phase to carry out gradient elution, the obtained eluent is collected according to time and a solvent is evaporated, the same fractions are merged through chromatographic detection, and the high-purity squalene can be obtained, wherein the content of the raw material olive oil of the squalene is enhanced from 3.6% to about 98%; and especially, by considering the requirement of industrialized production to select an extraction condition especially, the large-scale production of the squalene taking the olive oil as the raw material can be realized.
Owner:JIANGSU ZODIAC MARINE BIOTECH
Removing carbon dioxide from an oxygenate to olefins reaction effluent
The present invention provides processes for removing CO2 from an effluent stream derived from an oxygenate to olefins reaction system. In one embodiment, the invention comprises contacting the effluent stream with a first CO2 removal medium in a first CO2 removal zone under conditions effective to remove a first portion of the CO2 from the effluent stream and form a first CO2 depleted stream. The first CO2 depleted stream is contacted with a second CO2 removal medium in a second CO2 removal zone under conditions effective to remove a second portion of the CO2 from the first CO2 depleted stream and form a second CO2 depleted stream comprising less than about 0.5 vppm CO2.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
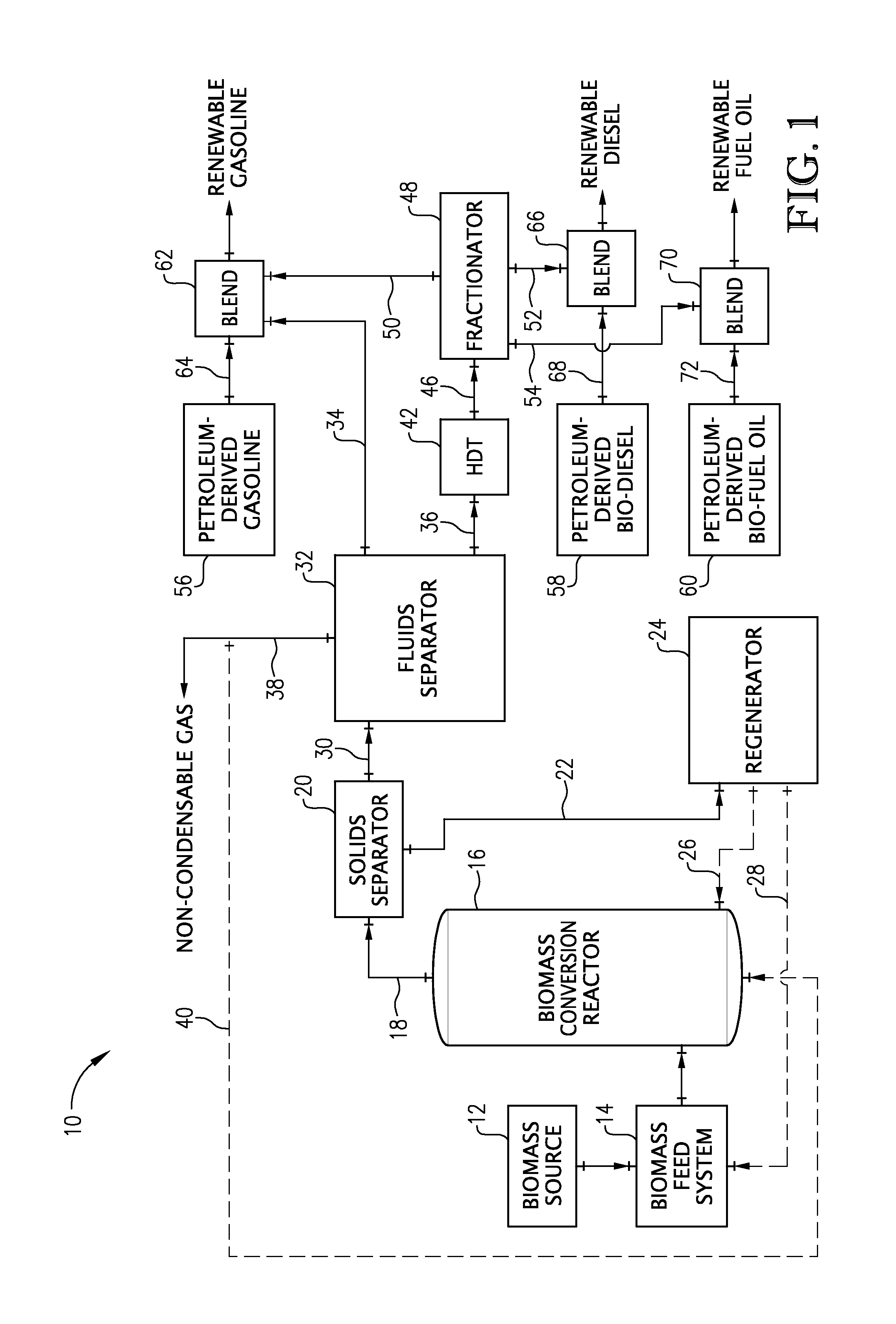
Production of renewable biofuels
A process and system for separating and upgrading bio-oil into renewable fuels is provided. The process comprises separating bio-oil into a light fraction and heavy fraction based on their boiling points. The heavy fraction is then subjected to hydrotreatment, while the light fraction is not subjected to hydrotreatment. At least a portion of the un-hydrotreated light fraction and at least a portion of the hydrotreated heavy fraction are blended with petroleum-derived gasoline to thereby provide a renewable gasoline, and at least a portion of the hydrotreated heavy fraction is blended with petroleum-derived diesel to thereby provide a renewable diesel.
Owner:MARD INC
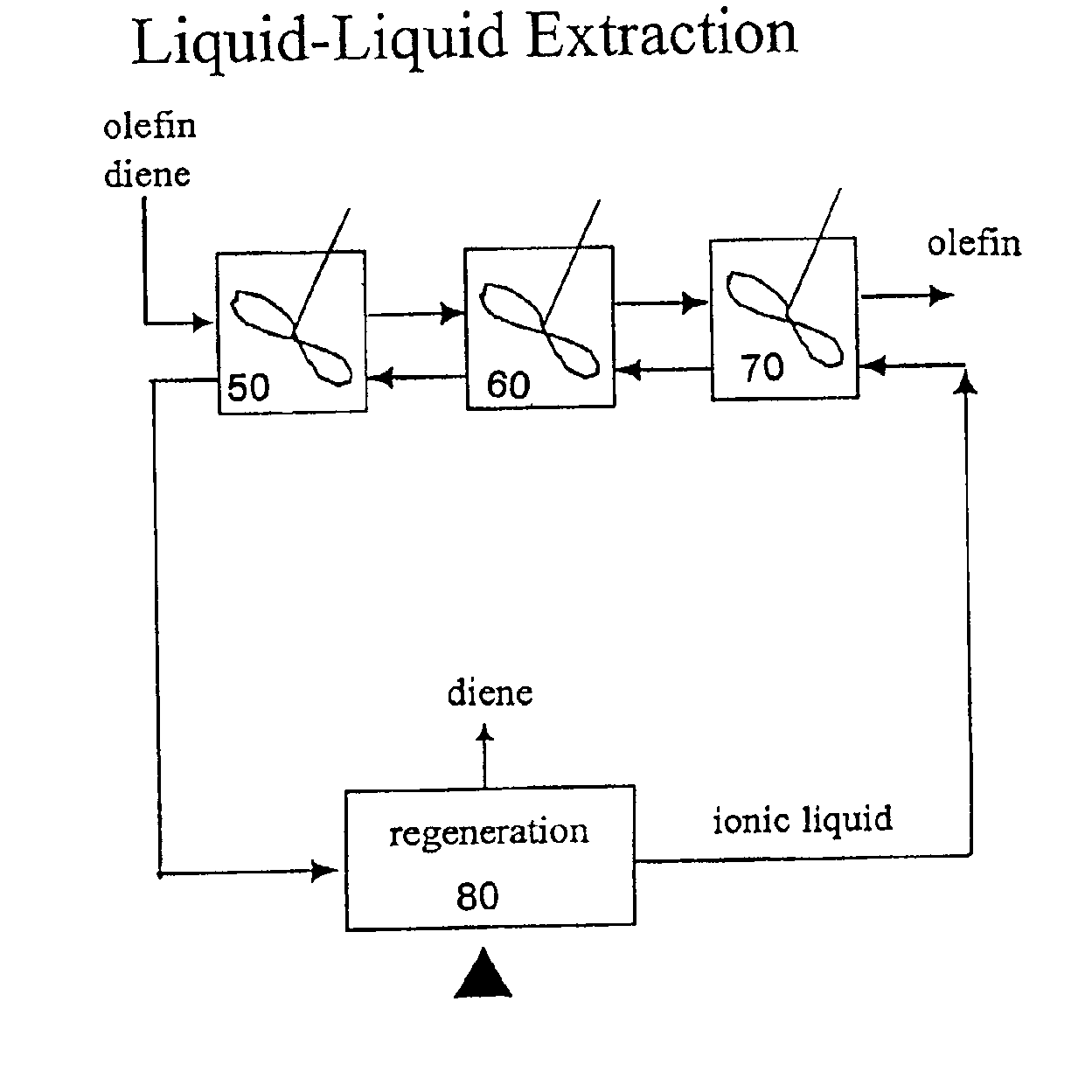
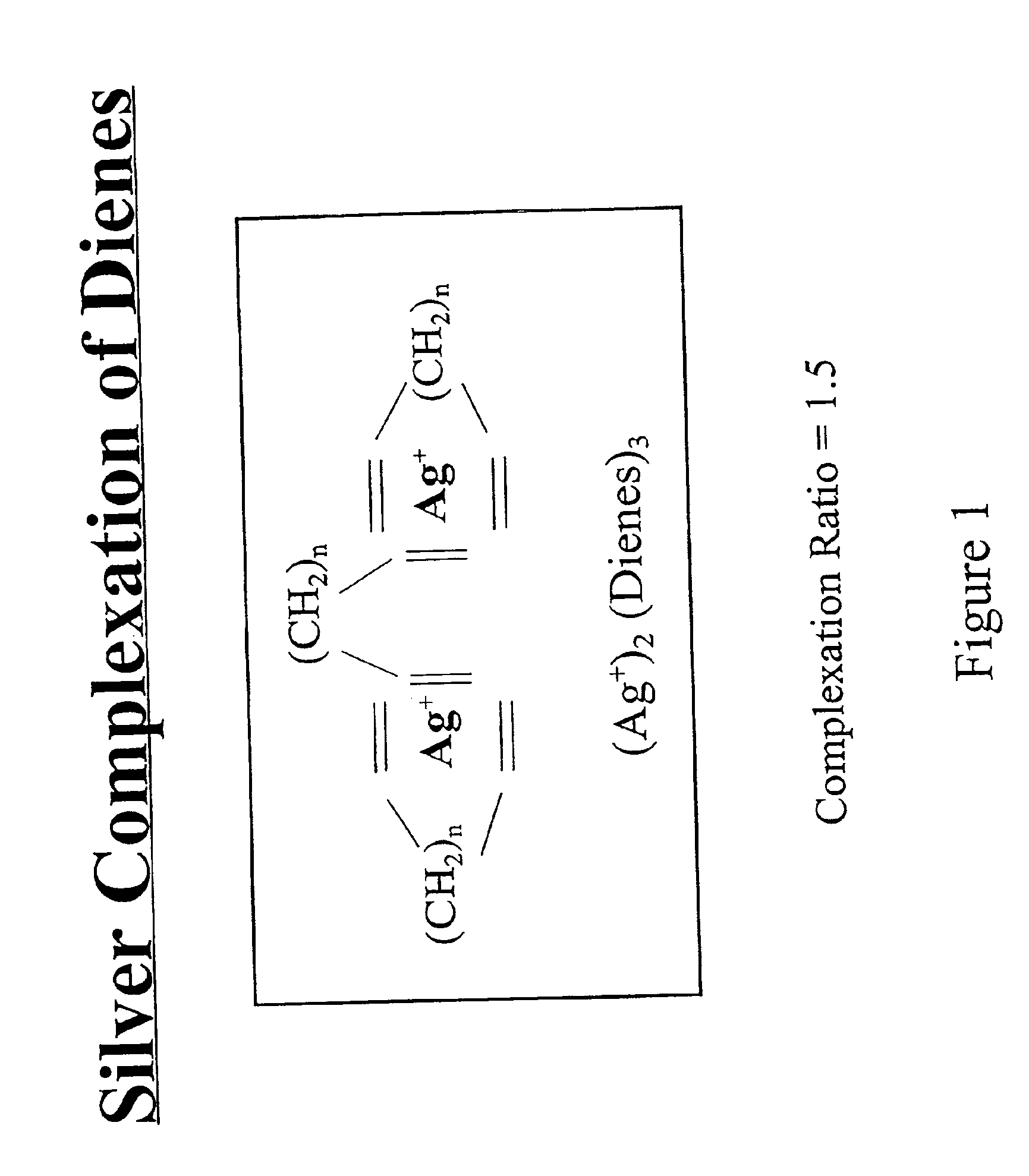
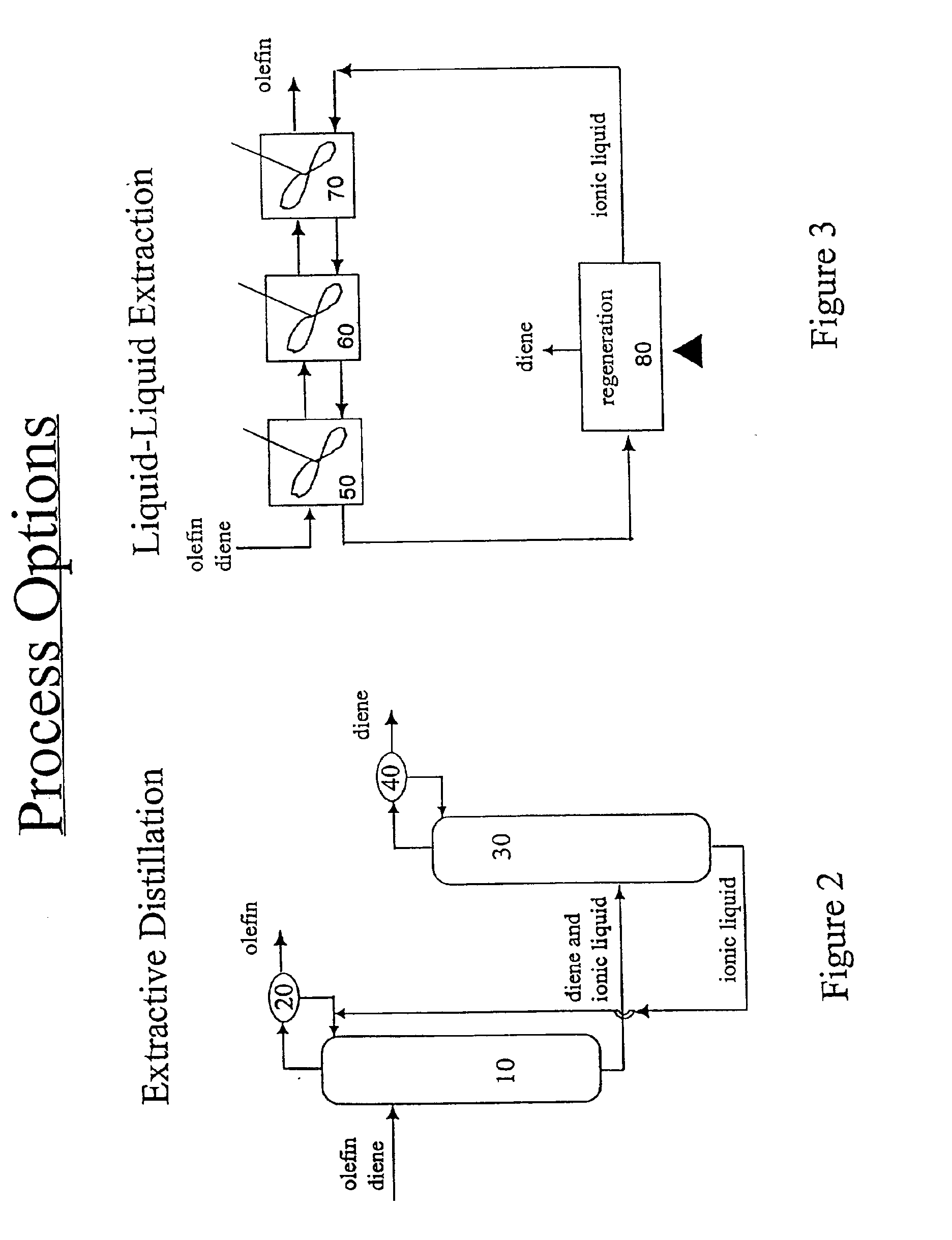
Separation of dienes from olefins using ionic liquids
InactiveUS6849774B2Facilitate desorptionDesorbed more readilyRefining with metal saltsRefining with acid-containing liquidsGas phaseIonic liquid
Methods for separating di-olefins from mono-olefins, and olefins from non-olefins such as paraffins, oxygenates and aromatics; are provided. The methods use metal salts which complex both mono-olefins and di-olefins, but which selectively complex di-olefins in the presence of mono-olefins. The metal salts are dissolved or suspended in ionic liquids, which tend to have virtually no vapor pressure. Preferred salts are Group IB salts, more preferably silver and copper salts. A preferred silver salt is silver tetrafluoroborate. A preferred copper salt is silver CuOTf. Preferred ionic liquids are those which form stable solutions, suspensions or dispersions of the metal salts, which do not dissolve unwanted non-olefins, and which do not isomerize the mono- or di-olefins. The equivalents of the metal salt can be adjusted so that di-olefins are selectively adsorbed from mixtures of mono- and di-olefins. Alternatively, both mono- and di-olefins can be adsorbed, and the mono-olefins selectively desorbed. The latter approach can be preferred when non-olefins are also to be separated. The mono- and di-olefin-containing mixture can be in the gas phase or in the liquid phase. The flow of mono- and di-olefin-containing mixture over / through the ionic liquid can be, for example, co-current, counter-current, or staged in stirred tanks, with countercurrent being preferred.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Process for separating aromatics by extractive distillation and a composite solvent used therein
InactiveUS7078580B2Improve solubilityWide boiling rangeDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsSulfolaneAlkalinity
This application relates to a composite solvent for separating aromatics by extractive distillation, comprising a main solvent, a solutizer and a modifier. Said solutizer is selected from any one or mixtures of any two of C8–C11 aromatics having different number of carbon atoms, the content of which is 3–39 wt %, and the number of carbon atoms of the lowest aromatic in the solutizer should be greater than that of the highest aromatic in the aromatics to be separated. When the solutizer is selected from any one of C8–C11 aromatics, the composite solvent contains 0.01–10.0 wt % of the modifier; when the solutizer is selected from mixtures of any two of C8–C11 aromatics having different number of carbon atoms, the composite solvent contains 0–10.0 wt % of the modifier. Said main solvent and modifier are independently selected from sulfolane derivatives, N-formyl morpholine, and N-methyl pyrrolidone, provided that the acidity and basicity of the modifier are opposite to those of the main solvent. When the composite solvent is used to recover aromatics by extractive distillation, it is possible to moderate the operation conditions of solvent recovery, increase the yield of aromatics, and make the separated aromatics to be neutral.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Bi-component copper-zirconium catalyst for deeply removing CO
InactiveCN101642707AHigh activityImprove stabilityDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsReaction temperatureCopper
The invention discloses a bi-component copper-zirconium catalyst for deeply removing CO, belongs to the technical field of impurity removal, and provides the bi-component copper-zirconium catalyst inorder to solve the problems of insufficient depth for removing the CO, high CO removing temperature, short service life and the like in the prior art. The bi-component copper-zirconium catalyst comprises 0.1 to 99.9 weight percent of main component CuO and 0.1 to 99.9 weight percent of second component ZrO2; the ZrO2 exists in a morphous form; and the XRD analysis shows that the grain diameter ofthe catalyst CuO is between 1 and 30nm and the specific surface is between 1 and 300m<2> / g. The catalyst can deeply remove the micro CO in various materials to below 30ppb at a reaction temperature ofbetween 0 and 150DEG C.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for removing mercury from liquid hydrocarbon
InactiveUS20030075484A1Simple wayEffective contactRefining with metal saltsHydrocarbonsHydrogen atomSulfur
A process for removing mercury of the present invention is characterized in that an ionic mercury-containing liquid hydrocarbon placed in a container equipped with a circulating means is effectively contacted with a sulfur compound represented by the general formula (I): M1-S-M2 (I) wherein M1 and M2 may be the same or different and are each independently a hydrogen atom, an alkali metal or an ammonium group, by introducing the sulfur compound into a suction side and / or a discharge side of the circulating means while circulating the ionic mercury-containing liquid hydrocarbon into the container through the circulating means. By the process for removing mercury of the present invention, the ionic mercury is effectively removed from the liquid hydrocarbon in simple manner.
Owner:IDEMITSU PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Method of desulfurizing a hydrocarbon gas by selective partial oxidation and adsorption
A hydrocarbon gas such as methane and LPG is desulfurized in the presence of oxygen and an oxidation catalyst to convert sulfur compounds in the gas to sulfur oxides. The sulfur oxides are then trapped downstream of the oxidation by an adsorbent. The amount of oxygen added to the hydrocarbon gas to promote oxidation is such that the sulfur compounds are selectively oxidized and the oxidation of the hydrocarbon gas is minimized to reduce hydrogen formation.
Owner:ENGELHARD CORP
Dual zone aromatic alkylation process
ActiveUS20080171900A1High selectivityLow molar ratioMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystAlkyl transferAlkylation
A process for the catalytic alkylation of an aromatic substrate with an alkylating agent is disclosed that comprises contacting the aromatic substrate and the alkylating agent in sequential alkylation zones to obtain an alkylaromatic. The first catalyst comprises UZM-8 zeolite and the second catalyst comprises beta zeolite. The process is particularly well suited for the alkylation of benzene with propylene to produce cumene.
Owner:UOP LLC
Process and Apparatus for para-Xylene Production Using Multiple Adsorptive Separation Units and a Split Fractionating Column
ActiveUS20130158330A1Distillation purification/separationMultistage water/sewage treatmentFractionating columnRaffinate
A process for separating para-xylene from a plurality of xylene isomers, wherein the process introduces at a first feed point a first mixed xylene stream comprising a plurality of xylene isomers into a first adsorptive separation unit to produce a first para-xylene enriched stream and a first raffinate stream, and introduces a second mixed xylene stream comprising a plurality of xylene isomers into a second adsorptive separation unit to produce a second raffinate stream. The process feeds both the first raffinate stream and the second raffinate stream into a raffinate column. The process further introduces an extract stream from the second adsorptive separation unit into a first input of a split extract column comprising an internal partition defining a first distillation zone and a second distillation zone.
Owner:UOP LLC
Mercury removal from crude oil
Methods and apparatus relate to removal of mercury from crude oil. Such removal relies on transferring mercury from a liquid hydrocarbon stream to a natural gas stream upon contacting the liquid hydrocarbon stream with the natural gas stream. Processing of the natural gas stream after used to strip the mercury from the liquid hydrocarbon stream removes the mercury from the natural gas stream.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
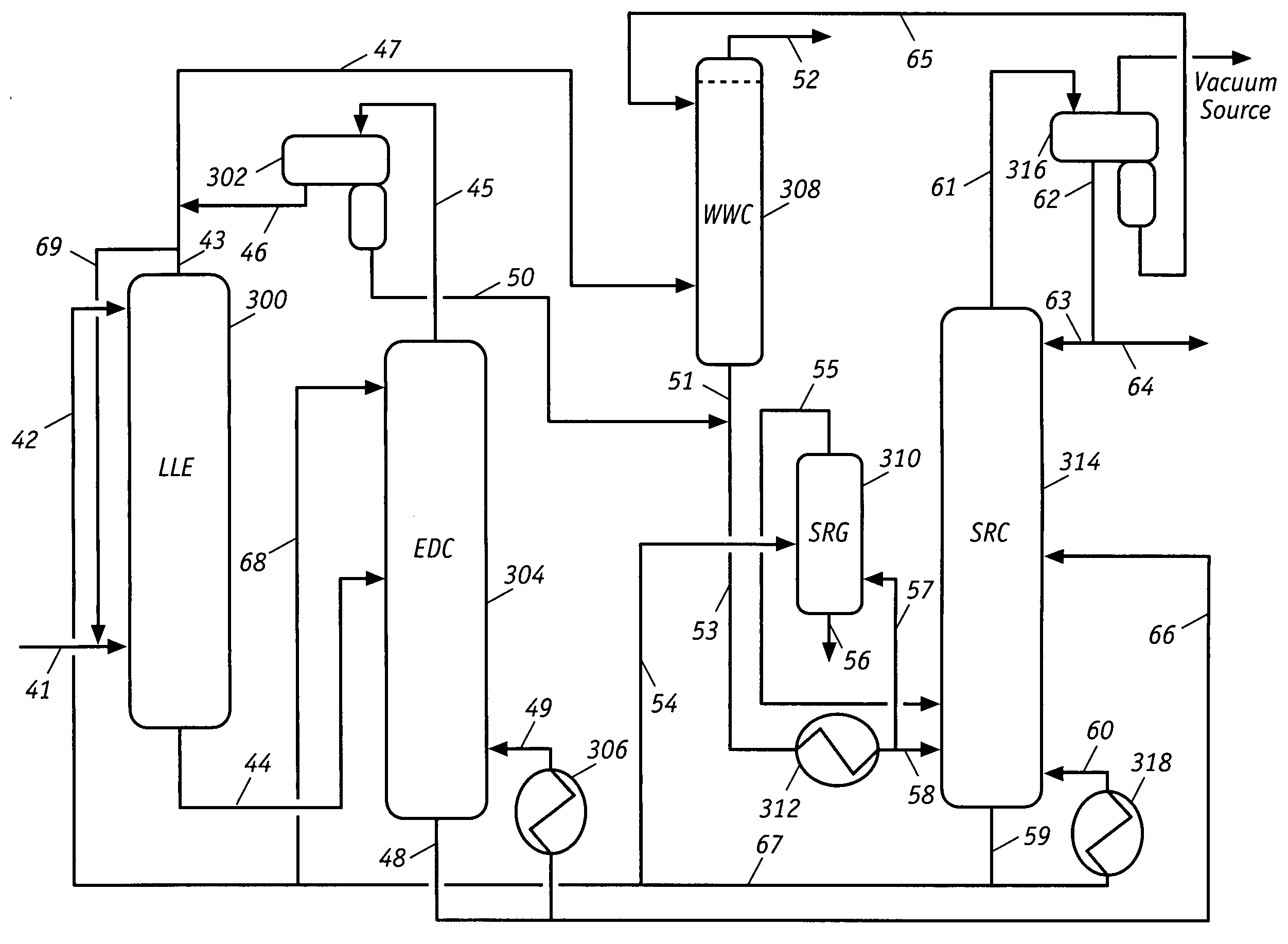
Novel energy efficient and throughput enhancing extractive process for aromatics recovery
InactiveUS20090255853A1Satisfactory aromatic puritySatisfactory recoveryHydrocarbon distillationRefining with acid-containing liquidsSulfolaneExtractive distillation
An energy efficient, high throughput process for aromatics recovery can be readily implemented by revamping existing sulfolane solvent extraction facilities, or constructing new ones, so as to incorporate unique process operations involving liquid-liquid extraction and extractive distillation. Current industrial sulfolane solvent based liquid-liquid extraction processes employ a liquid-liquid extraction column, an extractive stripping column, a solvent recovery column, a raffinate wash column, and a solvent regenerator. The improved process for aromatic hydrocarbon recovery from a mixture of aromatic and non-aromatic hydrocarbons requires transformation of the extractive stripping column into a modified extractive distillation column. The revamping incorporates the unique advantages of liquid-liquid extraction and extractive distillation into one process to significantly reduce energy consumption and increase process throughput. The revamp entails essentially only piping changes and minor equipment adjustments of the original liquid-liquid extraction facility, and is therefore, reversible.
Owner:CPC CORPORATION +1
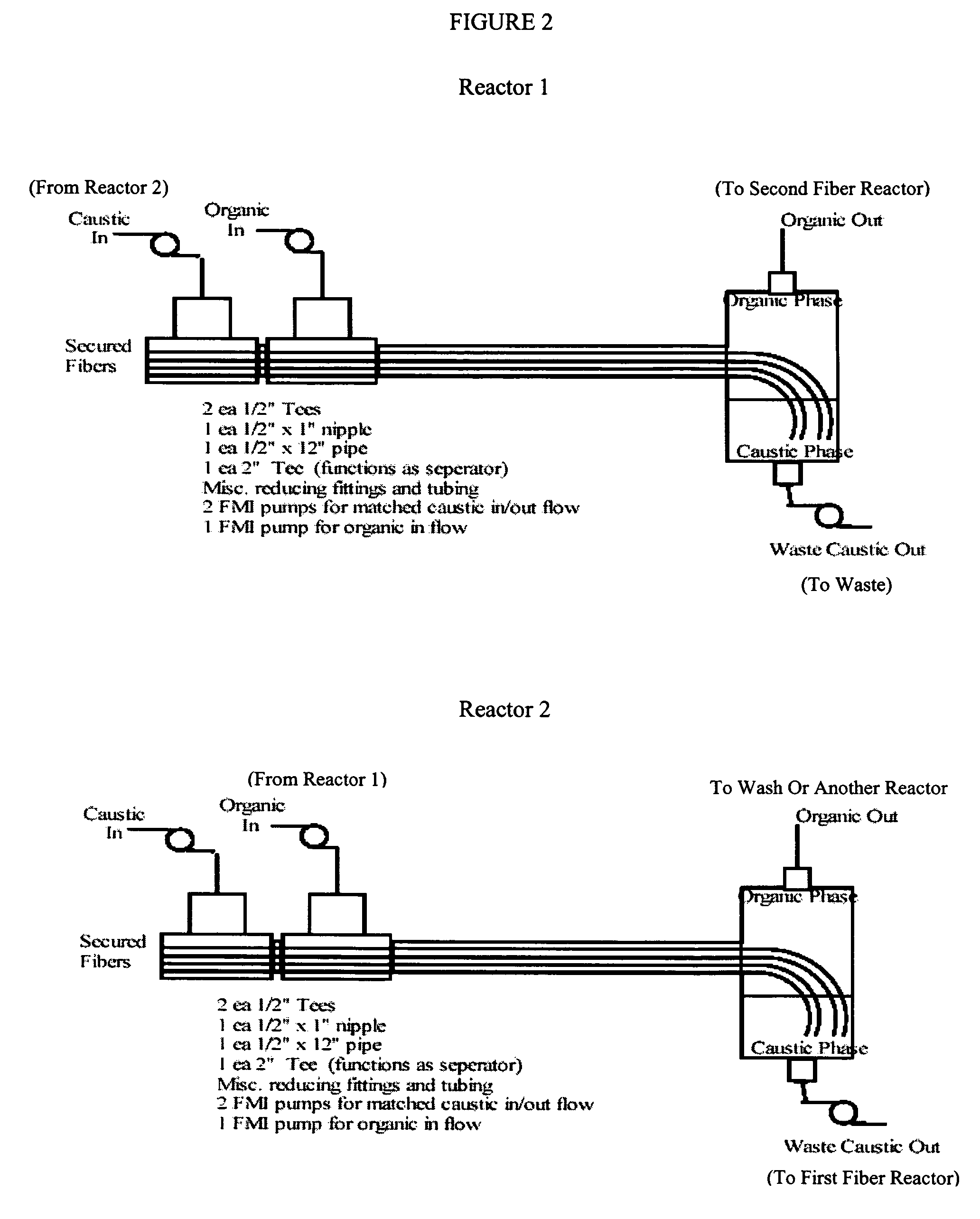
Fiber film reactors to effect separation and reaction between two immiscible reaction components
ActiveUS7618544B2Improve solubilityEnhanced mass transferFatty acid esterificationBiofuelsFiberChemical reaction
A fiber reaction process whereby reactive components contained in immiscible streams are brought into contact to effect chemical reactions and separations. The conduit reactor utilized contains wettable fibers onto which one stream is substantially constrained and a second stream is flowed over to continuously create a new interface there between to efficiently bring about contact of the reactive species and thus promote reactions thereof or extractions thereby. Co-solvents and phase transfer catalysts may be employed to facilitate the process.
Owner:CHEMTOR LP
Method for producing super-low sulfur gas oil blending component or super-low sulfur gas oil composition, and super-low sulfur gas oil composition
InactiveUS7938955B2Reduce sulfur contentLow aromatic contentRefining with metalsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsAdverse effectFuel injection
Provided are a method for producing a super-low sulfur gas oil blending component or a super-low sulfur gas oil composition having a sulfur content of less than 5 mass ppm, under relatively mild conditions, without greatly increasing the hydrogen consumption and without remarkably decreasing the aromatic content; and a super-low sulfur gas oil composition having a sulfur content of less than 5 mass ppm which exhibits a high heating value, is excellent in fuel economy and output power, and is free from an adverse effect on a sealing rubber member or the like used in the fuel injection system and thus does not cause the leakage of a fuel. A method for producing a super-low sulfur gas oil blending component or a super-low sulfur gas oil composition having a sulfur content of less than 5 mass ppm is also disclosed.
Owner:JAPAN ENERGY CORP
Process for upgrading of Fischer-Tropsch products
A process for treating nitrogen-containing, substantially paraffinic product derived from a Fischer-Tropsch process. The substantially paraffinic product is purified in a purification process to lower the concentration of oxygen, nitrogen, and other impurities. The nitrogen content of the purified product is monitored, and the conditions of the purification step are adjusted to increase nitrogen removal if the nitrogen content of the purified product exceeds a preselected value.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Process for producing hydrocarbons
ActiveUS9752080B2Reduces the potential for i.aReduce device sizeHydrogenHydrocarbon by hydrogenationLiquid hydrocarbonsChemistry
Owner:TOPSOE AS
Process and apparatus for para-xylene production
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
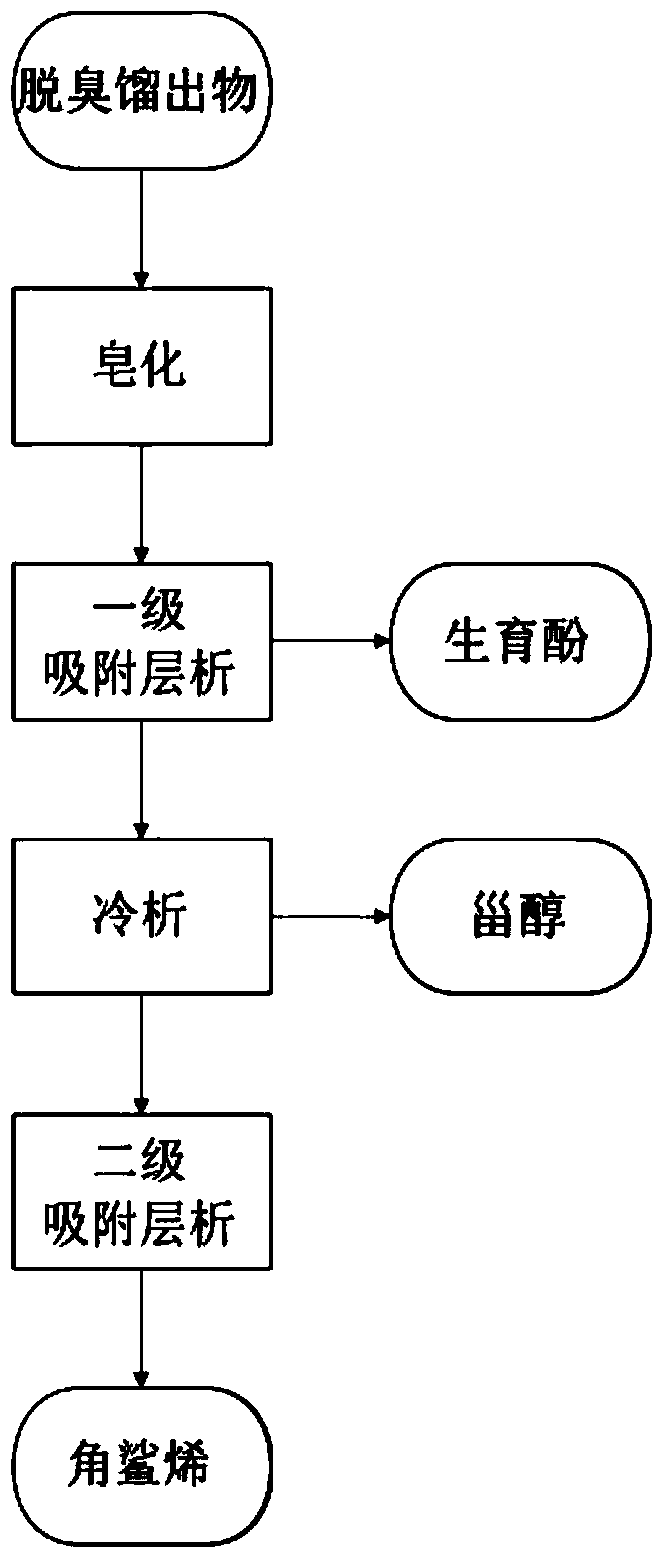
Method for extracting squalene in vegetable oil deodorizer distillate through two-stage column chromatography
InactiveCN103708992AIncrease contentGood choiceSteroidsAdsorption purification/separationSterolVegetable oil
The invention provides a method for extracting squalene in vegetable oil deodorizer distillate through two-stage column chromatography, which comprises the following processing steps: performing saponifying pretreatment to separate unsaponifiable matters, performing first-stage column chromatography to separate tocopherol and sterol, and performing second-stage column chromatography to purify squalene. Through the whole process, the squalene having a content of about 50% can be obtained, and meanwhile, the tocopherol having a content of 70% or above and the sterol having a content of 98% or above can be also obtained. Thus, the method provided by the invention overcomes the problem of low pertinence in the traditional squalene extraction process, achieves favorable selectivity of column chromatography and greatly increases the extraction efficiency. The process has the advantages of simple operation procedure, high separation efficiency, high squalene recovery rate, low investment and the like.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Hybrid autothermal catalytic process for converting alkanes to alkenes and catalysts useful for same
The present invention relates to a thermally integrated multi-zone process for conversion of alkanes to their corresponding alkenes, involving endothermically converting an alkane to its corresponding alkene by soft oxidant conversion in an endothermic reaction zone, in the presence of a weak oxidant, a suitable catalyst, and heat, to produce an intermediate product gas comprising the corresponding alkene and hydrogen. The weak oxidant may be, for example, carbon dioxide. The hydrogen is then removed from the intermediate product gas by contacting the intermediate product gas, in an exothermic reaction zone, with different second catalyst, and oxygen, to combust the hydrogen and produce a heated product stream comprising the corresponding alkene, water and heat. Heat is recovered from theheated product stream and recycled back to the endothermic reaction zone, while the resulting cooled product stream comprising the corresponding alkene may be subjected to further reaction and / or processing.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Process for refining C-4 hydrocarbon fluid
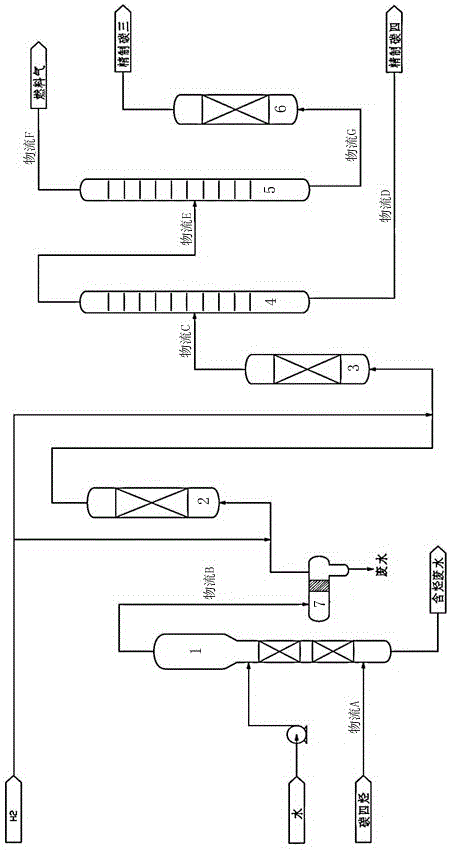
ActiveCN105152840AReduce Methanol ContentDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsDehydrogenation2-Butene
The invention discloses a process for refining C-4 hydrocarbon fluid. Preparation equipment includes a methanol removing tower, a first hydrogenation reactor, a second hydrogenation reactor, a depropanizing column, a dethanizing column and an adsorption tower, wherein the top of the methanol removing tower is connected with the bottom of the first hydrogenation reactor through a high-efficiency coalescer; the top of the first hydrogenation reactor is connected with the bottom of the second hydrogenation reactor through a pipeline; the top of the second hydrogenation reactor is connected with the depropanizing column through another pipeline; the top of the depropanizing column is connected with the dethanizing column through another pipeline; and the bottom of the dethanizing column is connected with the adsorption tower through another pipeline. The process mainly aims to a purification process of an alkylation raw material, and comprises the following steps: by taking mixed C-4 hydrocarbon as a raw material, extracting with water to remove methanol so as to reduce the content of methanol in C-4 hydrocarbon to be lower than 50ppm, selectively adding hydrogen and isomerizing so as to reduce the content of butadiene in C-4 hydrocarbon to be lower than 50ppm, converting more than 70% of 1-butene into 2-butene, and finally rectifying to remove dimethyl ether and C-3, thereby obtaining refined C-4 as the alkylation raw material, and a byproduct refined C-3 as a propane dehydrogenation propylene raw material.
Owner:CHINA CHENGDA ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com