Method for analyzing and identifying clinical difficult strains by 16S rRNA gene sequence
An analysis method and gene sequence technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc., can solve the problem of low sensitivity, unstable phenotypic expression, automatic bacterial identification instrument Can not give identification results and other problems, to achieve the effect of expanding the identification spectrum and meeting the identification needs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] This embodiment discloses a method for identifying difficult clinical strains. Specifically, the 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis method is used, including:
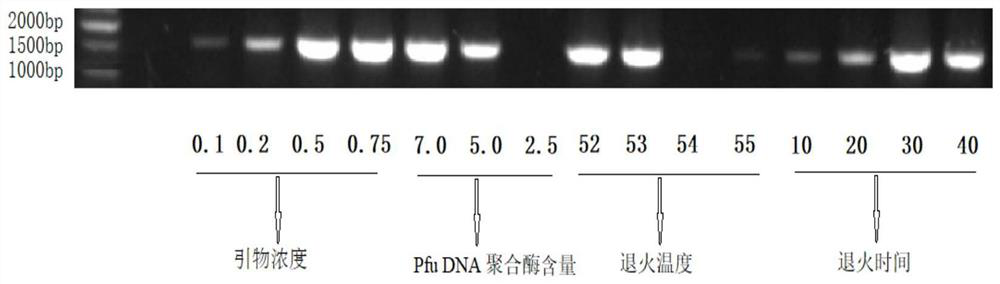
[0038] S1: Extract the bacterial DNA of the strain to be identified, select bacterial universal primers, and establish a PCR method for amplifying bacterial 16S rRNA;
[0039] S2: Optimizing the PCR reaction system and reaction conditions to obtain amplification products;
[0040] S3: Sequence comparison of the amplified product with the gene database to obtain the bacterial species to be identified.
[0041] Specifically, the following steps are included:
[0042] 1. Genomic DNA extraction
[0043] The specimens were from bacteria that could not be identified by conventional methods in the Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University from 2015 to 2019. Take the activated clinical isolate strain 4 and inoculate it on the blood plate, at 35°C, supplemented with 5% CO 2 Colonies were collected after 24-48 hours of a...
Embodiment 2
[0058] This embodiment studies the detection and analysis of some clinical difficult bacterial species, and the results are as follows:
[0059] 2.1 Detection and analysis results of Bordetella holmesii (B.holmesii)
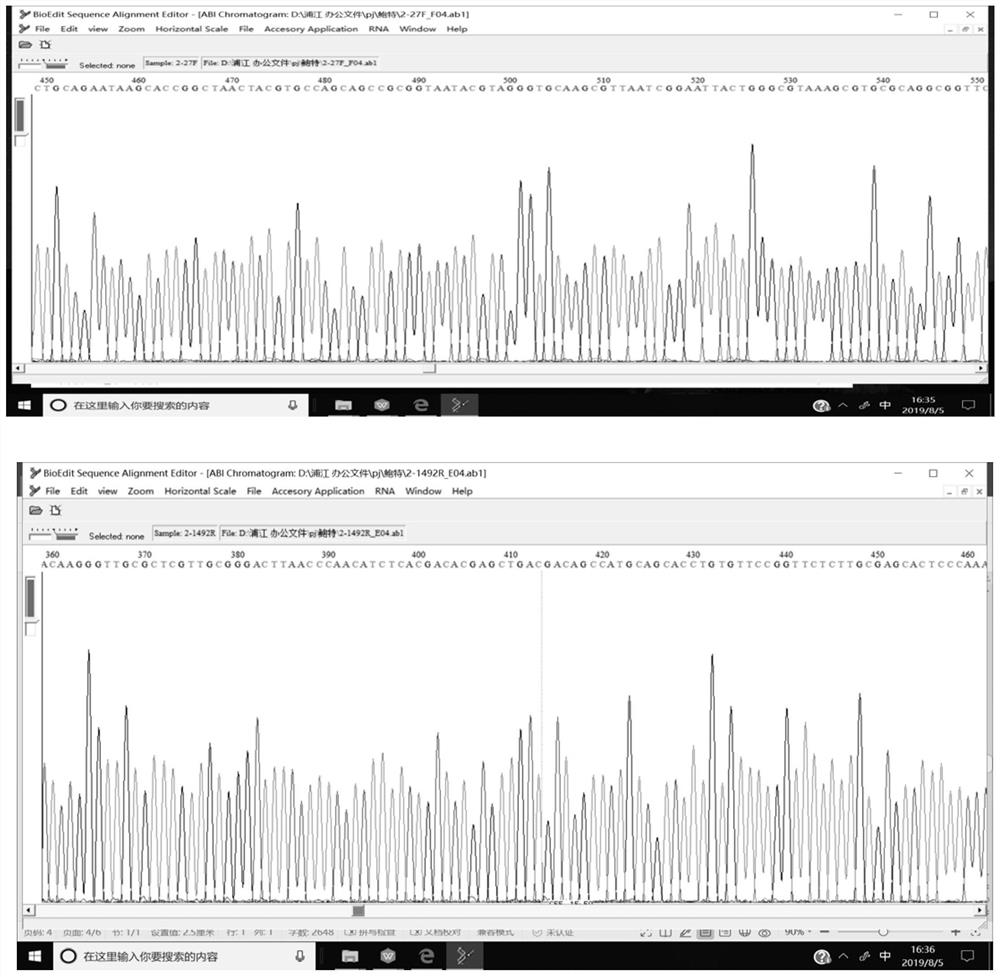
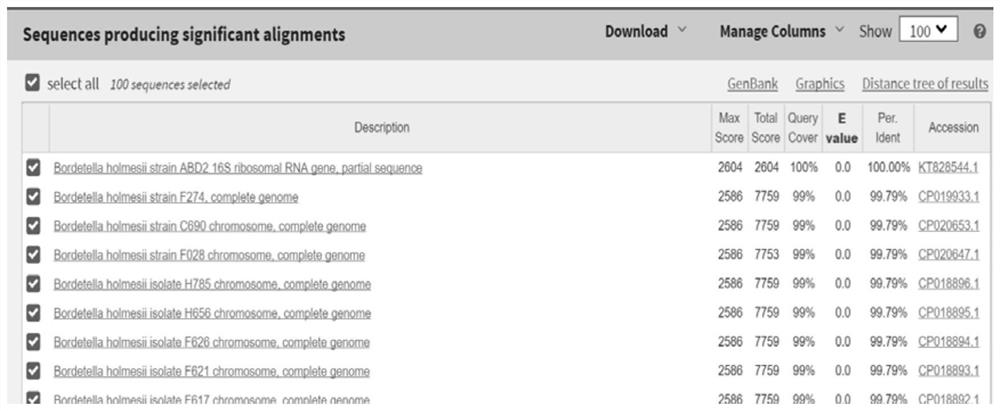
[0060] The total DNA of the isolated bacteria was extracted as a template, amplified using the optimized PCR reaction system and conditions, and the product was bidirectionally sequenced (see figure 2 ), and then carried out BLAST comparison with the Genebank database, the results showed that the 16S rRNA sequence of the isolate was similar to the 16S rRNA sequence of B.holmesii reported in the database, and the similarity reached 99% ( image 3 ), so the strain was identified as B.holmesii. The 16S rRNA gene sequence of the isolate was uploaded to NCBI GenBank with access number KT828544.1. The isolation of B.holmesii has not been reported in China, so the strain was uploaded to the China General Microorganism Culture Collection Management Center (CGMCC, stra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com