Application of 3, 4, 5-O-tricaffeoylquinic acid as cell protective agent in radiotherapy
A technology of caffeoylquinic acid and 5-O-, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of limited clinical application and serious adverse reactions, and achieve the effects of inhibiting apoptosis and improving proliferation inhibition.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
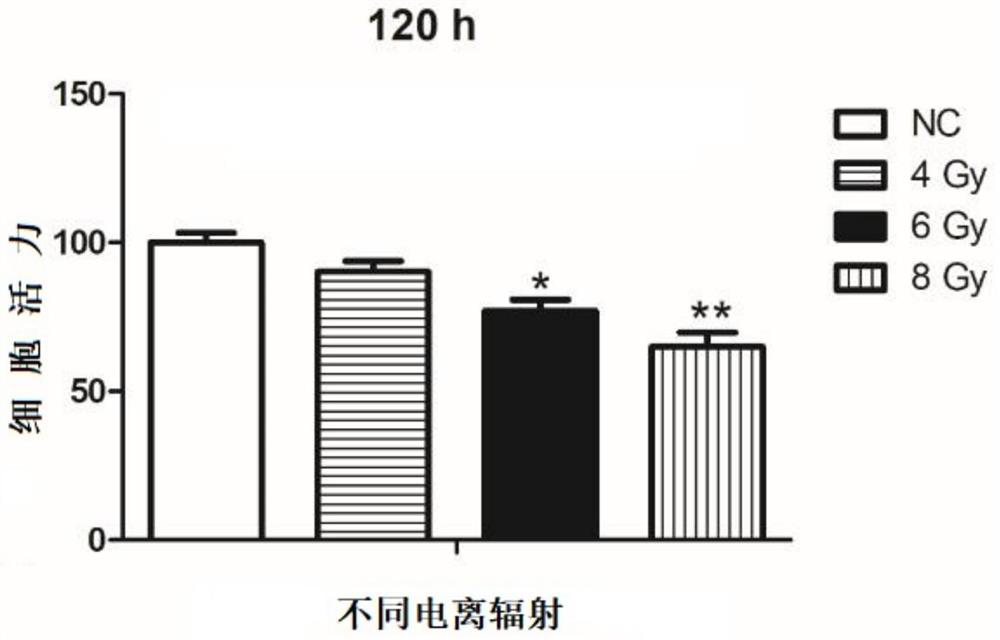
[0075] In this example, normal colonic epithelial cells NCM460 were irradiated according to different radiation doses (0, 4, 6, 8 Gy), and the cell survival rates of NCM460 cells under different radiation doses were detected.
[0076] Method: In order to construct a radiation injury model, the normal colonic epithelial cells in this example were irradiated by Gammacell-40 low-dose rate research radiation instrument at room temperature at 0.70Gy / min, and the irradiation doses were 4Gy, 6Gy, and 8Gy, respectively. Recorded as irradiation groups 1, 2, and 3 in sequence; normal cultured colonic epithelial cells without irradiation were taken as the control group (NC group); 120 hours after irradiation, the cell viability of the irradiation group and the control group was detected to understand the cell viability of the cells. Survival rate and comparative observation. Each experiment was repeated three times. Cell viability was measured by MTT method, expressed as the mean ± SD o...
Embodiment 2
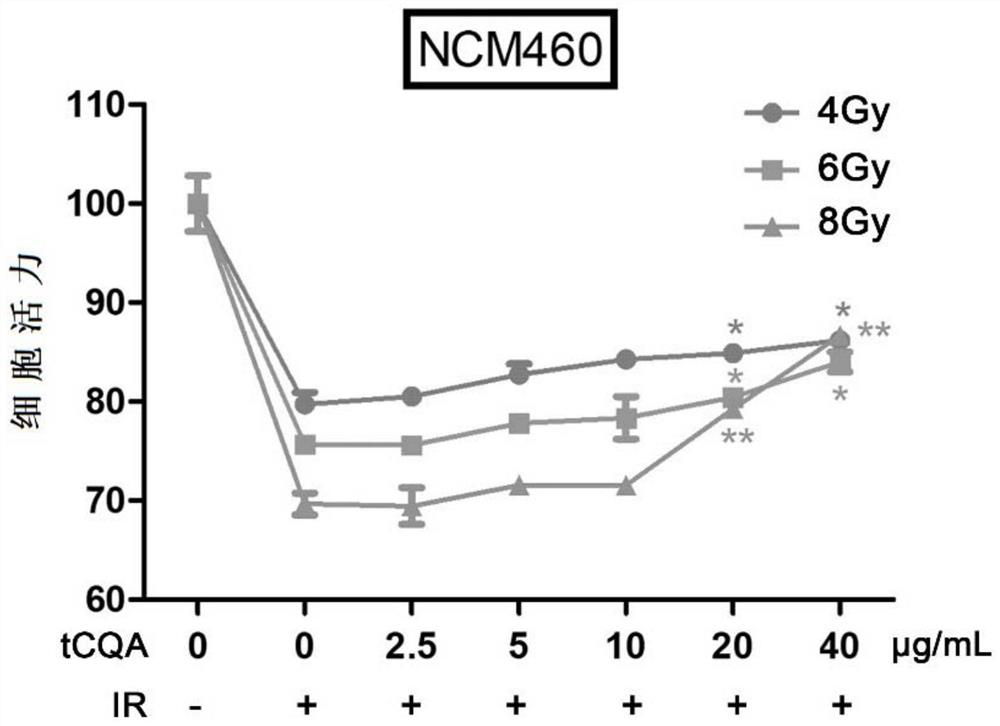
[0081] In this example, tCQA was added before the normal colonic epithelial cells NCM460 were irradiated, the cell viability was detected by the MTT method, and the cell proliferation was observed.
[0082] METHODS: Samples were dissolved in serum-free medium and added to final doses of tCQA containing 0 μg / mL, 2.5 μg / mL, 5 μg / mL, 10 μg / mL, 20 μg / mL and 40 μg / mL 4 hours before irradiation Then, they were irradiated with 4Gy, 6Gy and 8Gy respectively, and then the cells were cultured for 120h, and the cell proliferation was observed by MTT method. In this experiment, 0 μg / mL, normal cultured cells without radiation were used as the blank control group. Each experiment was repeated three times. The cell viability was detected by MTT method, and the results were as follows: figure 2 shown.
[0083] The data from these experiments were visually analyzed with Student's t-test to analyze the significance of the difference between the IR treatment group and the 0 μg / mL group: *p<...
Embodiment 3
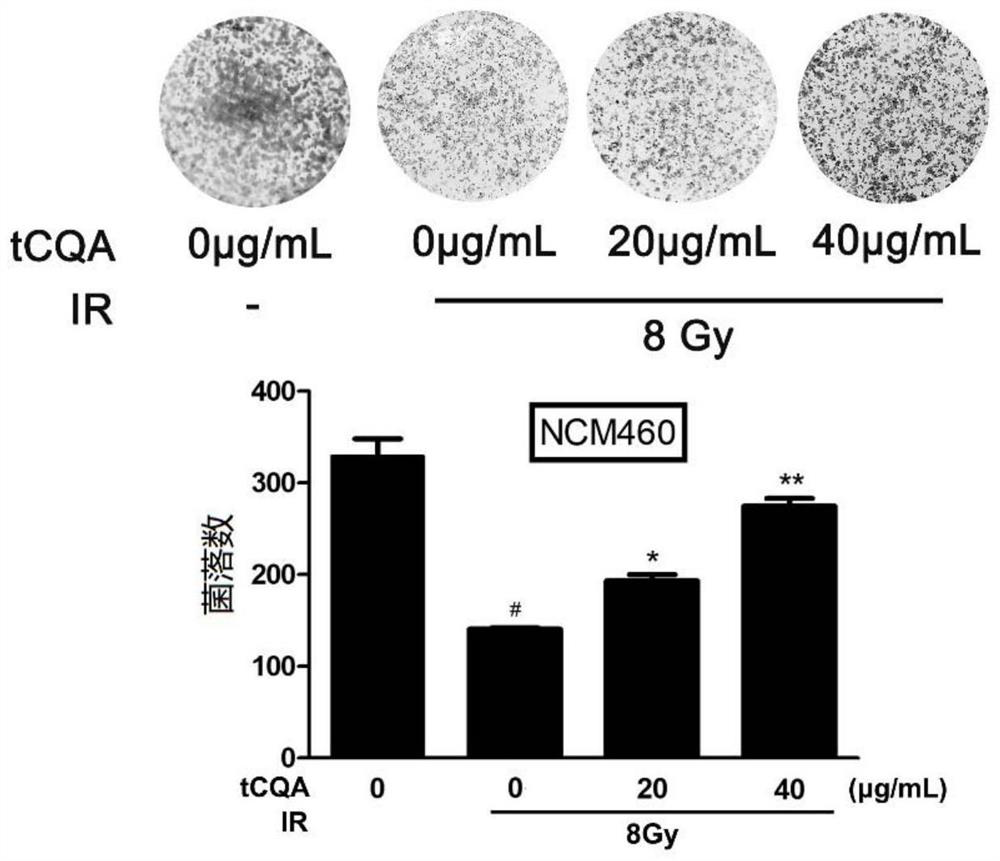
[0088] In this example, the colony formation of normal colonic epithelial cells was used to determine the proliferation ability of the cells, so as to explore the effect of tCQA on IR-induced proliferation inhibition of normal colonic epithelial cells.
[0089] Method: 200 normal colonic epithelial cells were uniformly dispersed on a 24-well plate at a density of 200 per well, placed in media with final doses of tCQA of 0 μg / mL, 20 μg / mL and 40 μg / mL, and irradiated after 4 hours , the radiation dose was 8Gy, which were recorded as the experimental group (0μg / mL+8Gy), treatment group 1 (20μg / mL+8Gy) and treatment group 2 (40μg / mL+8Gy); then the cells were cultured for 7 days. In this experiment, 0 μg / mL, normal cultured cells without radiation were used as the blank control group. Each experiment was repeated three times. After the incubation, wash with PBS, visible colonies were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 minutes, and stained with crystal violet for 20 minutes at ro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com