Method for recovering dichloromethane in acesulfame potassium synthesis
A technology of acesulfame potassium and dichloromethane is applied in the disproportionation separation/purification of halogenated hydrocarbons, organic chemistry and other directions, which can solve the problems of inability to directly apply, influence, and high recovery costs, and achieves improved production efficiency and improved rectification effect. , the effect of reducing labor intensity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
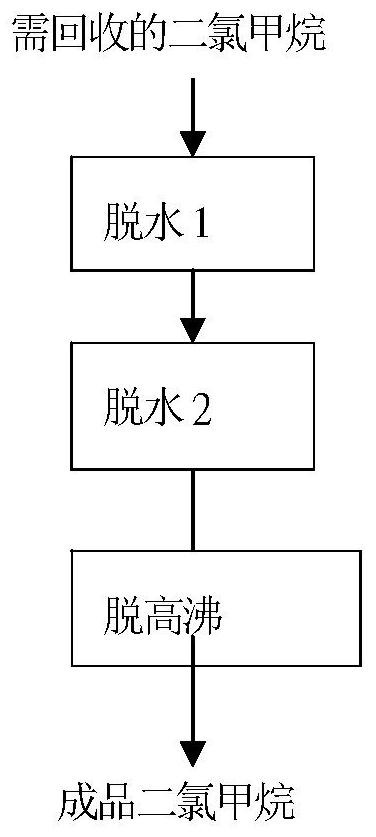
[0039] Dichloromethane and water-binding agent (a mixture of n-hexanol and m-xylene with a mass ratio of 7:3) that need to be recovered from the synthesis of acesulfame potassium are continuously fed into the rectification column from the tower at a mass ratio of 1:0.001. Carry out rough dehydration, continuously discharge materials from the tower kettle, control the pressure at the top of the tower to 0.5MPa, and the dichloromethane material whose moisture in the top of the tower reaches the specified index ≤ 0.1% enters the rectification tower ② from the top of the tower continuously for dehydration again, and control the pressure at the top of the tower to 1MPa , the top of the tower is connected to the water separator and condenser, the upper stratified water in the water separator is continuously discharged, and the lower dichloromethane layer is refluxed to the rectification tower ②Continue dehydration, the water in the tower kettle reaches the specified index ≤0.003% dich...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The dichloromethane and water-binding agent (a mixture of ethylene glycol and toluene each accounting for 50%) that need to be recovered from the synthesis of acesulfame potassium are continuously entered into the rectification tower ① from the tower for crude dehydration at a mass ratio of 1:0.005 , the tower kettle is continuously discharged, the pressure at the top of the tower is controlled to 0.3MPa, and the dichloromethane material with the moisture in the top of the tower reaching the specified index ≤0.1% enters the rectification tower ② for dehydration again, and the pressure at the top of the tower is controlled at 0.5MPa. The top is connected to the water separator and the condenser, the upper stratified water in the water separator is continuously discharged, and the lower layer of methylene chloride is refluxed to the rectification tower ② to continue dehydration, and the moisture in the tower kettle reaches the specified index ≤ 0.003% of the methylene chlor...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Dichloromethane and water-binding agent (a mixture of ethylene glycol and m-xylene each accounting for 50%) that need to be recovered from the synthesis of acesulfame potassium are continuously entered into the rectification tower ① from the tower at a mass ratio of 1:0.003 Coarse dehydration, continuous discharge from the tower kettle, control the pressure at the top of the tower to 0.5MPa, and the dichloromethane material whose moisture in the top of the tower reaches the specified index ≤0.1% enters the rectification tower ② from the top of the tower continuously for dehydration again, and controls the pressure at the top of the tower to 0.2MPa , the top of the tower is connected to the water separator and condenser, the upper stratified water in the water separator is continuously discharged, and the lower dichloromethane layer is refluxed to the rectification tower ②Continue dehydration, the water in the tower kettle reaches the specified index ≤0.003% dichloromethan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com