Heavy metal contaminated soil ecological risk assessment method
A technology for soil pollution and ecological risk, which is applied in the fields of soil pollution risk control and ecological risk assessment to achieve the effect of reducing uncertainty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
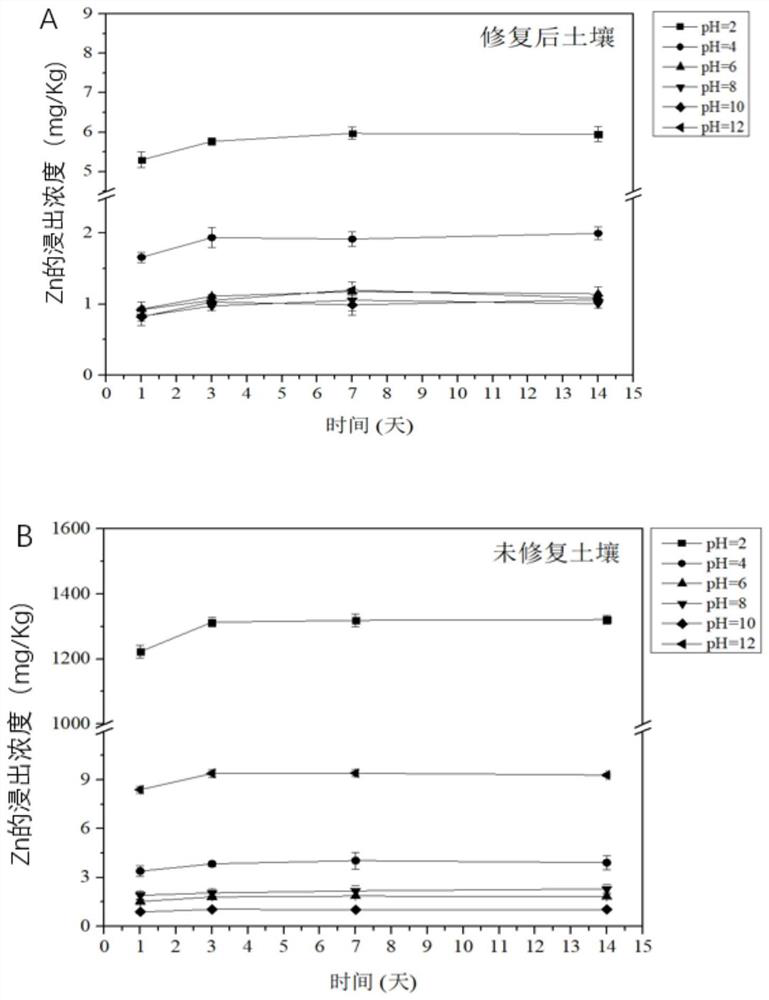
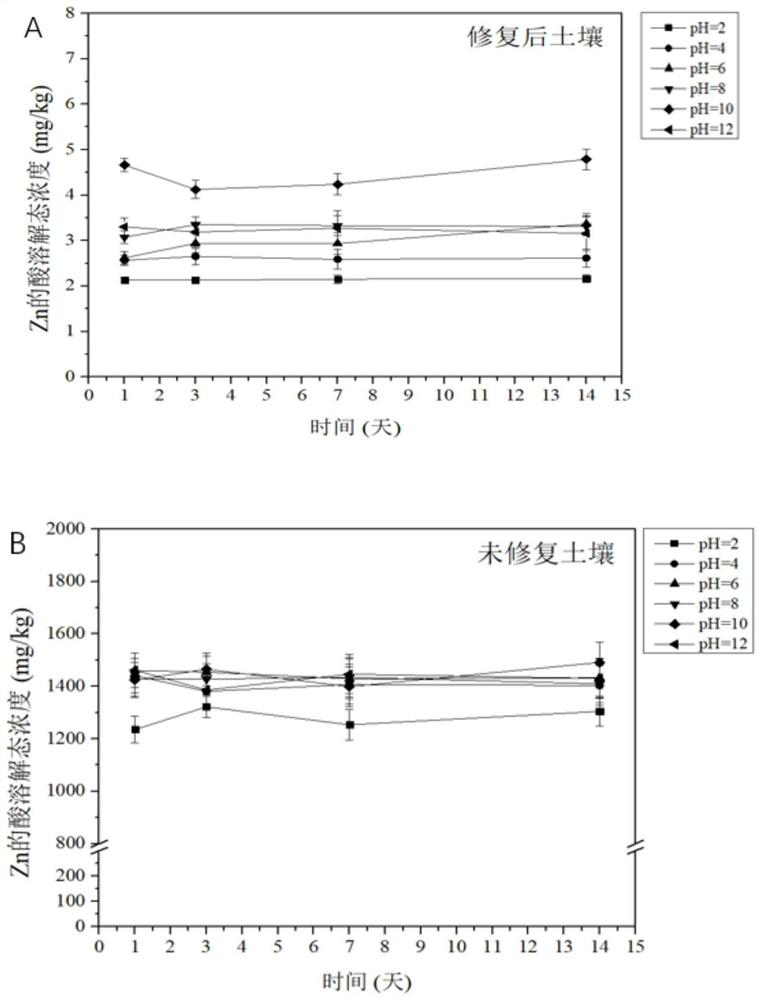
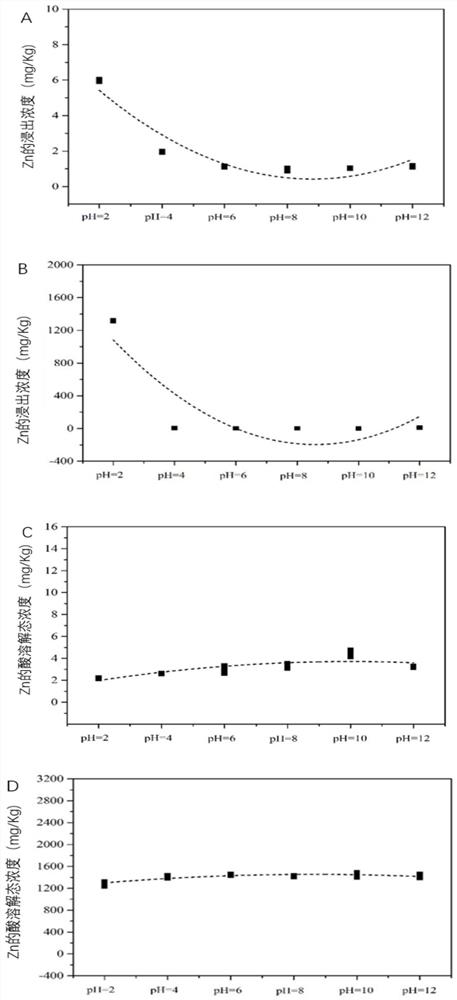
[0058] Example 1 Zinc (Zn) Contaminated Soil Ecological Risk Assessment Method
[0059] In this example, a laboratory is used to simulate heavy metal-contaminated soil. The non-polluted soil was collected from a green space in a park in Tianhe District, Guangzhou City. It was the surface soil of 30cm, the soil pH was 5.4, and the concentration of Zn in the non-polluted soil was 27.7mg / kg. ZnO powder was artificially added and fully ground to make the polluted soil The Zn content in the medium reaches 3413.7mg / kg; with the addition of Cr 2 o 3 way to form ZnCr 2 o 4 High temperature curing reaction by way of spinel, ZnO and Cr 2 o 3 It is prepared in such a way that the molar ratio is Zn:Cr=1:2. Then, coal gangue and shale were added to the mixed contaminated soil as auxiliary materials. The mass ratio of coal gangue to shale in the auxiliary material was 1:2, and the mass ratio of auxiliary material to contaminated soil was 2:1. The fully mixed and ground sample was pre...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Embodiment 2 Copper (Cu) contaminated soil ecological risk assessment method
[0068] In this example, a laboratory is used to simulate heavy metal-contaminated soil. The non-polluted soil was collected from a green space in a park in Tianhe District, Guangzhou City. It was the surface soil of 30 cm. The pH of the soil was 5.6, and the concentration of Cu in the non-polluted soil was 15.2 mg / kg. The Cu content in the medium reaches 4656.4mg / kg; with the addition of Cr 2 o 3 CuCr 2 o 4 High temperature curing reaction by means of spinel, CuO and Cr 2 o 3 The molar ratio is Cu:Cr=1:2 for preparation. Then, coal gangue and shale were added to the mixed contaminated soil as auxiliary materials. The mass ratio of coal gangue to shale in the auxiliary material was 1:2, and the mass ratio of auxiliary material to contaminated soil was 2:1. The fully mixed and ground sample was pressed into a cylindrical sample at 350MPa, and after sintering in a muffle furnace at 1000°C...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Example 3 Cadmium (Cd) Contaminated Soil Ecological Risk Assessment Method
[0077] In this example, a laboratory is used to simulate heavy metal-contaminated soil. The non-polluted soil was collected from a green space in a park in Tianhe District, Guangzhou City. It was the surface soil with a surface layer of 30 cm. The pH of the soil was 5.6, and the concentration of Cd in the non-polluted soil was 0.019 mg / kg. The Cd content in the medium reaches 8412.6mg / kg; with the addition of Cr 2 o 3 form CdCr 2 o 4 High temperature curing reaction by way of spinel, CdO and Cr 2 o 3 The molar ratio is Cd:Cr=1:2 for preparation. Then, coal gangue and shale were added to the mixed contaminated soil as auxiliary materials. The mass ratio of coal gangue to shale in the auxiliary material was 1:2, and the mass ratio of auxiliary material to contaminated soil was 2:1. The fully mixed and ground sample was pressed into a cylindrical sample at 350 MPa, and after sintering in a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com