Method for detecting concentration of free radicals in sodium hypochlorite aqueous solution
A sodium hypochlorite and aqueous solution technology, applied in the field of chemical detection, can solve the problems of expensive equipment, complicated reaction process, expensive instruments, etc., and achieve the effects of low degree of natural oxidation, high product stability, and good linear relationship.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] A method for detecting free radical concentration in aqueous sodium hypochlorite solution, comprising the steps:
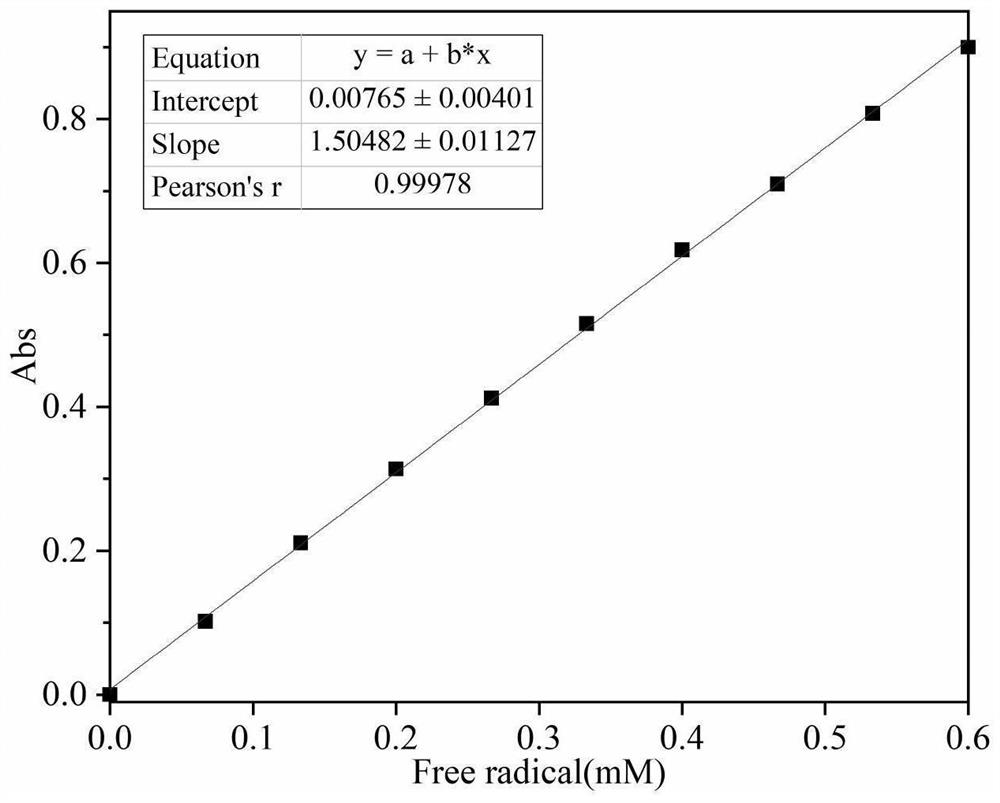
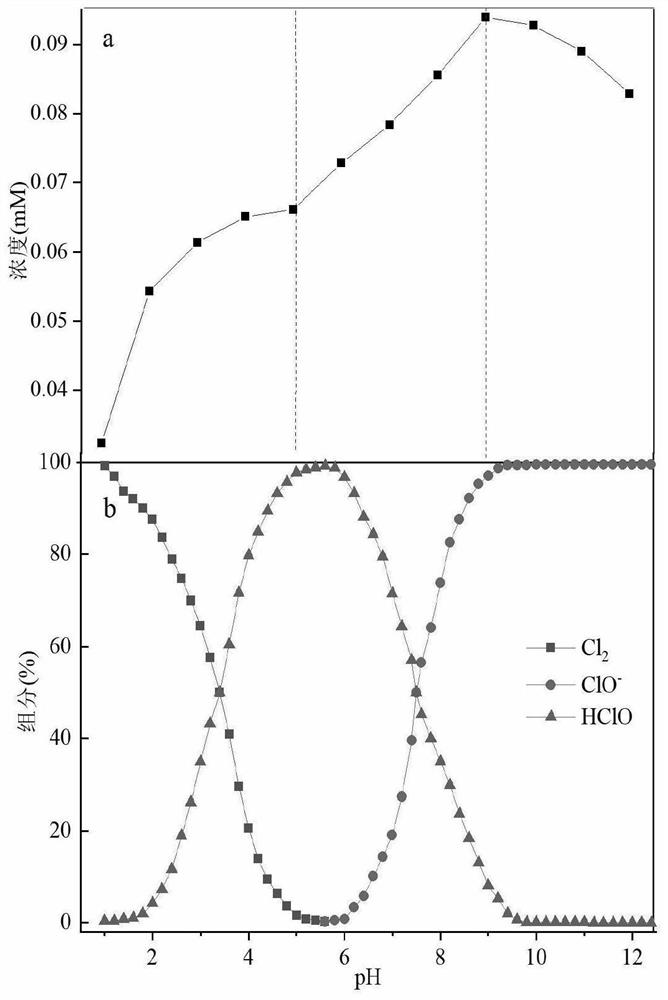
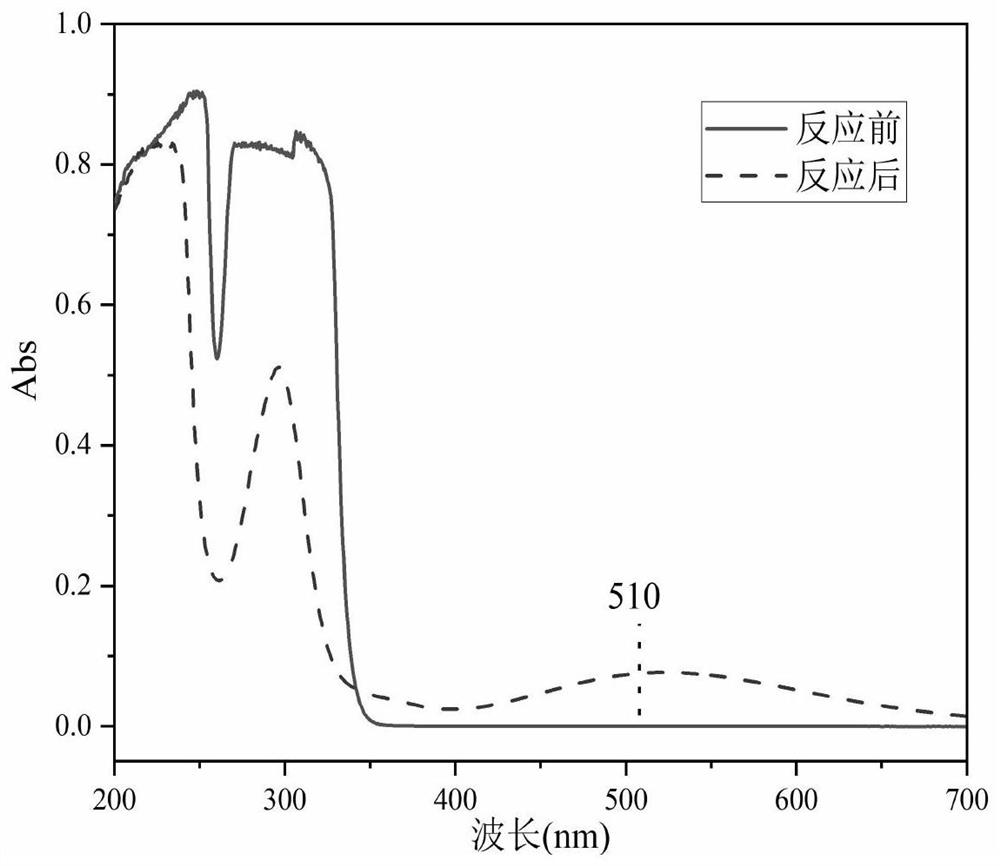
[0020] (1) Add 2ml of capture agent, 2ml of 10mM ferrous sulfate aqueous solution, 3ml of sodium hypochlorite aqueous solution (pH 7, exposed in air) to a 25mL plugged colorimetric tube, add deionized water to 15ml, and ultrasonically For 20 minutes, heat in a water bath at 37°C for 20 minutes, observe that the solution in the colorimetric tube appears purple, and if purple appears, free radicals are generated, and the absorbance measured at a wavelength of 510nm by a spectrophotometer is 0.658;
[0021] (2) Add 2ml capture agent respectively in 11 colorimetric tubes, then add 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1ml, pH=3 10mM ferric chloride aqueous solution, Add deionized water to 15ml (at this time, the concentration of ferric chloride aqueous solution in the colorimetric tube is 0, 0.067, 0.133, 0.2, 0.267, 0.333, 0.4, 0.467, 0.533, 0.6, 0.6...
Embodiment 2
[0025] A method for detecting free radical concentration in aqueous sodium hypochlorite solution, comprising the steps:
[0026] (1) Add 2ml capture agent, 1ml concentration of 8mM ferrous sulfate aqueous solution, 0.5ml sodium hypochlorite aqueous solution (pH is 1, exposed in air) to be tested in 25mL stoppered colorimetric tube, add deionized water to 15ml, Sonicate for 10 minutes, heat in a water bath at 37°C for 10 minutes, observe whether the solution in the colorimetric tube is purple, if purple appears, free radicals are generated, and the absorbance measured at a wavelength of 510nm by a spectrophotometer is 0.281;
[0027] (2) Add 2ml capture agent respectively in 11 colorimetric tubes, then add 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1ml, pH=4 8mM ferric chloride aqueous solution, Add deionized water to 15ml, (at this time, the concentration of ferric chloride aqueous solution in the colorimetric tube is 0, 0.053, 0.107, 0.16, 0.213, 0.267, 0.32, 0.373, 0.42...
Embodiment 3
[0030] A method for detecting free radical concentration in aqueous sodium hypochlorite solution, comprising the steps:
[0031] (1) Add 2ml of capture agent, 3ml of 8mM ferrous sulfate aqueous solution, 5ml of sodium hypochlorite aqueous solution (pH 12, exposed in air) to a 25mL plugged colorimetric tube, add deionized water to 15ml, and ultrasonically For 30 minutes, heat in a water bath at 37°C for 30 minutes, observe whether the solution in the colorimetric tube is purple, which will produce free radicals, and measure the absorbance at a wavelength of 510nm with a spectrophotometer to be 0.573;
[0032] (2) Add 2ml capture agent respectively in 11 colorimetric tubes, then add 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1ml, pH=2 10mM ferric chloride aqueous solution, Add deionized water to 15ml, (at this time, the concentration of ferric chloride aqueous solution in the colorimetric tube is 0, 0.067, 0.133, 0.2, 0.267, 0.333, 0.4, 0.467, 0.533, 0.6, 0.667mM), ultrason...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com