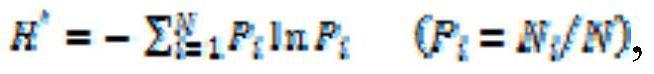Method for evaluating micro-plastic pollution level of marine sediments
A technology for marine sediments and pollution levels, applied in the field of risk assessment of marine pollutants, can solve the problems of no one to evaluate and compare the level of microplastic pollution, and achieve the effects of consistent collection time, good stability and accurate research results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] A method for assessing the pollution level of microplastics in marine sediments, said method comprising the steps of:
[0025] (1) Microplastic collection: All samples were collected from the upper 10cm of the sediment at each station. Sediments were collected using grab mud extractors, transferred to aluminum foil sampling bags, and immediately stored in an ice-filled freezer until further analysis. Prior to sampling at each station, the grabs and associated sampling tools were thoroughly rinsed with ethanol and seawater. Three replicate samples were randomly collected at each site, and each sample had a mass of approximately 3 kg.
[0026] (2) Separation of microplastics: All sediment samples were carefully homogenized under a clean glass vessel, and dried at 60°C for at least 72 hours to obtain a constant weight. The abundance of microplastics was therefore determined from the dry weight of the sediment samples. 800 ml of saturated NaCl solution was stirred with 5...
Embodiment 2
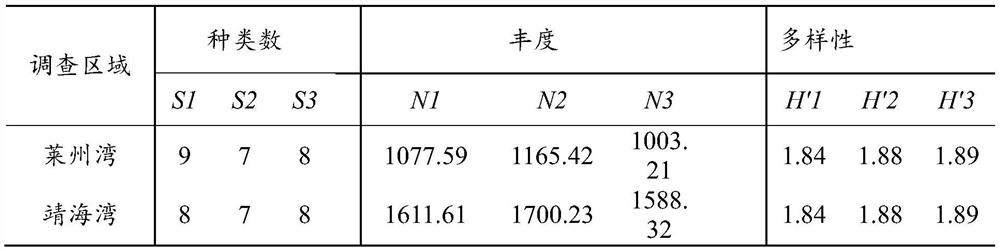
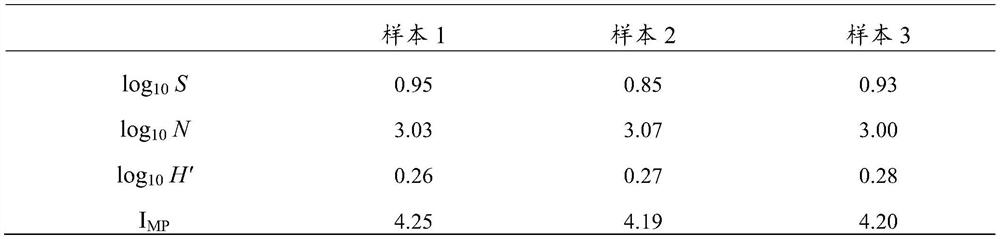
[0033] In this example, two coastal bays (Laizhou Bay and Jinghai Bay) near the Shandong Peninsula were used to investigate the pollution level of microplastics. Laizhou Bay is located in the northern part of Shandong Peninsula, China. It is a large bay with a water area of about 6000km 2 . The inflow of more than a dozen rivers, including the Yellow River, the second largest river in China, is surrounded by frequent human activities, including aquaculture, industry and tourism. Located in the east of Shandong Peninsula, Jinghai Bay is a small relatively closed bay with a water area of about 140km 2 . Jinghai Bay is responsible for the discharge of domestic and industrial sewage from surrounding villages and towns in Weihai City. Its population and types of human activities are much smaller than those of cities around Laizhou Bay.
[0034] Describe in detail below.
[0035] A method for assessing the pollution level of microplastics in marine sediments, the specific st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com