Rapid detection of antimicrobial resistance by microbial ribosome immunoprecipitation
A drug resistance, microbial technology, applied in the field of biomedicine and diagnostics, can solve undisclosed or proposed problems, and achieve the effect of increased test sensitivity, reduced variability and degradation rate, increased variability and degradation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
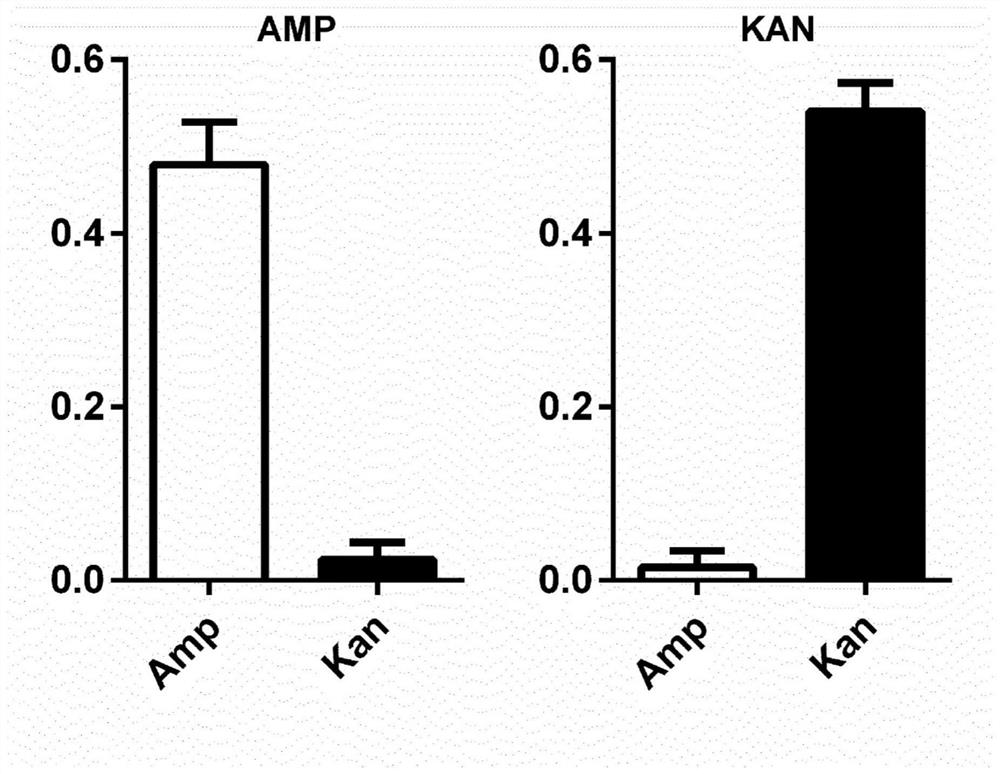
[0092] Example 1: Selective detection of antibiotic resistance in transformed bacterial cultures
[0093] To assess the efficiency of immunoprecipitation of bacterial ribosome-associated transcripts, Escherichia coli cultures transformed with plasmids conferring resistance to the antibiotics ampicillin (AmpR positive) or kanamycin (KanR positive), respectively, were genotyped. Control settings. Ribosomal immunoprecipitates were tested with ampicillin and kanamycin primers to identify the presence or absence of antibiotic resistance genes. Experiments were performed using two technical replicates and five biological replicates (standard error mean SEM).
[0094] Enriched antibiotic resistance genes in transformed E. coli cultures can be specifically identified by qRT-PCR by ribosomal immunoprecipitation using antibodies against bacterial ribosomal subunits (see figure 1 ).
example 2
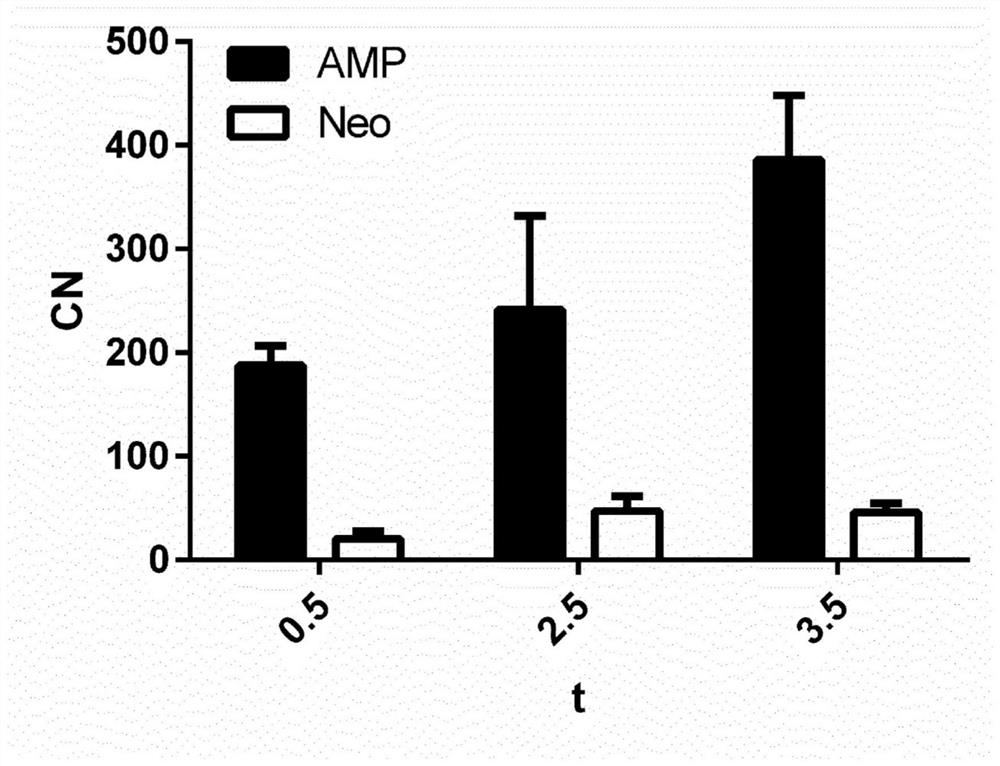
[0095] Example 2: Selective increase of AmpR expression in ampicillin-transformed E. coli cultures
[0096] To assess whether this method allows for the discrimination of increases in active versus inactive translated genes, E. coli cultures were transformed with plasmids containing resistance cassettes against two antibiotics (ampicillin and neomycin), while only applying ampicillin selective pressure.
[0097] Using this method, it is possible to detect a selective increase in the expression of the ampR gene, especially during exponential growth, while substantially not affecting neoR (see figure 2 ), thus highlighting the ability of the method to provide a higher detection range for transcriptionally active genes.
example 3
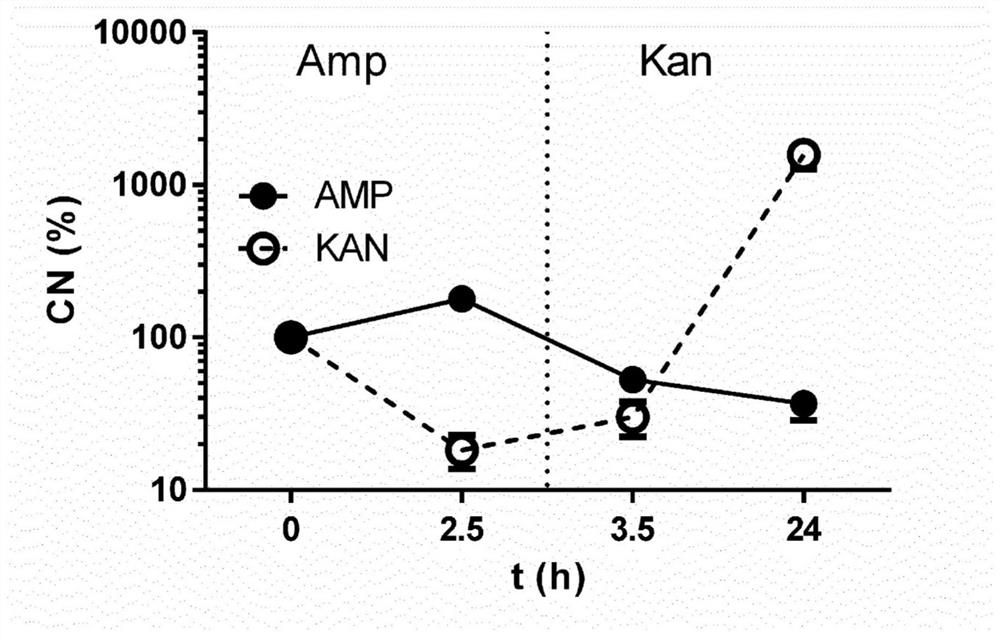
[0098] Example 3: Monitoring of antibiotic-induced dynamic expression changes in mixed cultures
[0099] To test the ability of this method to determine dynamic changes in selective pressure and transcriptional state, we used mixed E. coli cultures containing both kanamycin- and ampicillin-resistant cells and subjected them to different antibiotic stresses (ampicillin-resistant Xilin for 2.5h, and then switch to kanamycin for up to 24h). Subsequent qRT-PCR results for the ampR and kanR genes allowed us to closely monitor the associated changes in gene expression of these AMR genes in the recovered immunoprecipitated transcripts (see image 3 ), thus highlighting the diagnostic potential of this method.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com