Method for cleaning decellularization reagent SDS
A decellularized and decellularized tissue technology, applied in medical science, tissue regeneration, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable acellular tissue repair materials industrialized production, time-consuming, high cytotoxicity, etc., to promote the development of the industry, The effect of improving the cleaning and removal efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
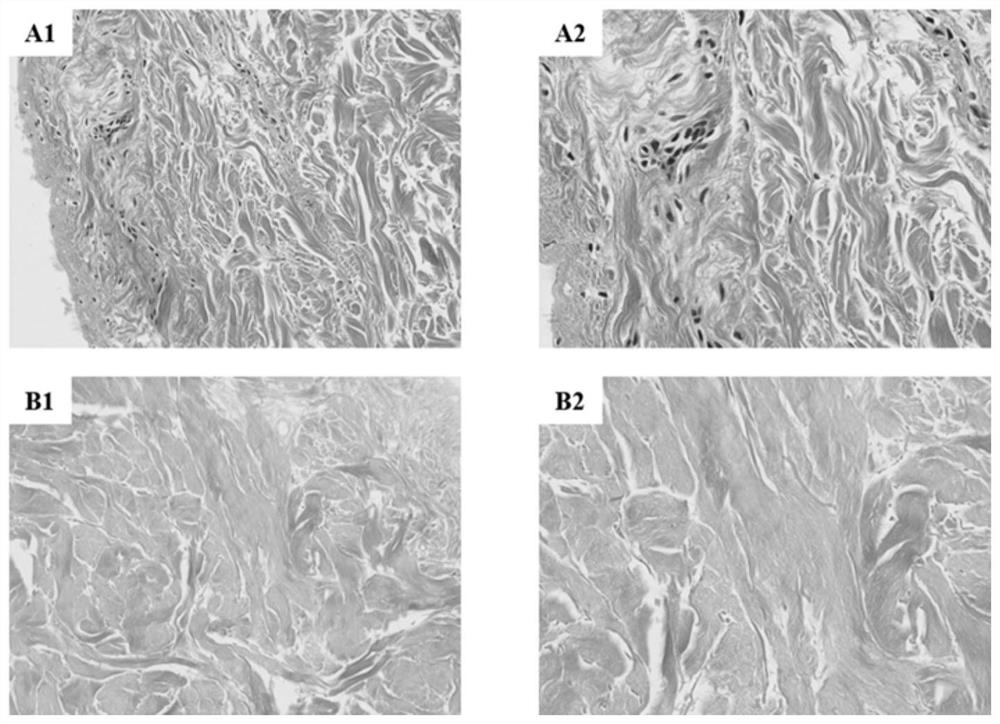
[0031]The allogeneic skin in this example is human skin tissue with the dermis retained, with a thickness of 0.2-1.5mm and a surface area of 10mm×10mm. It is shaken and immersed in a 0.5% SDS aqueous solution for 24 hours to ensure SDS It penetrates completely into the tissue, and then uses the method of the present invention to clean the residual SDS. The specific operations are as follows:
[0032]The acellular allogeneic skin obtained above was immersed in a 75% ethanol solution with a volume fraction, and the shaker was shaken for 1 hour, during which the liquid was changed every 20 minutes. Then take out the allogeneic skin, immerse it in a 0.5M KCl aqueous solution with a molar concentration of potassium ions, shake the shaker for 1 hour, and change the liquid every 20 minutes. Ensure that the SDS deposited on the surface of the allogeneic skin is completely washed away.
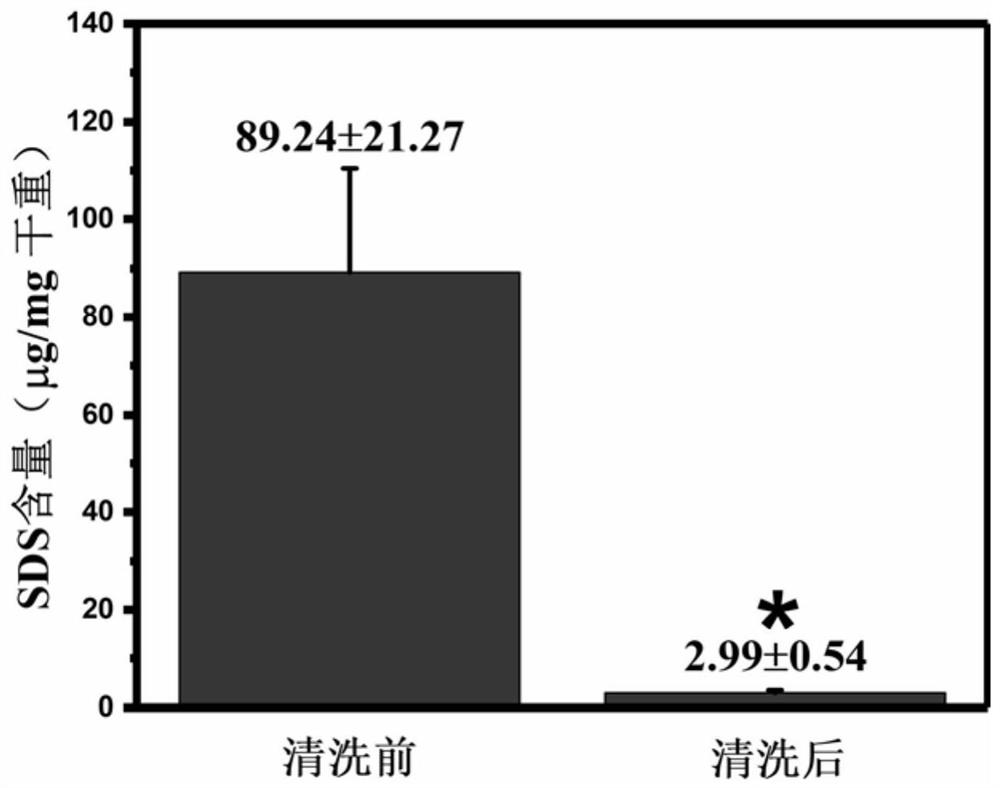
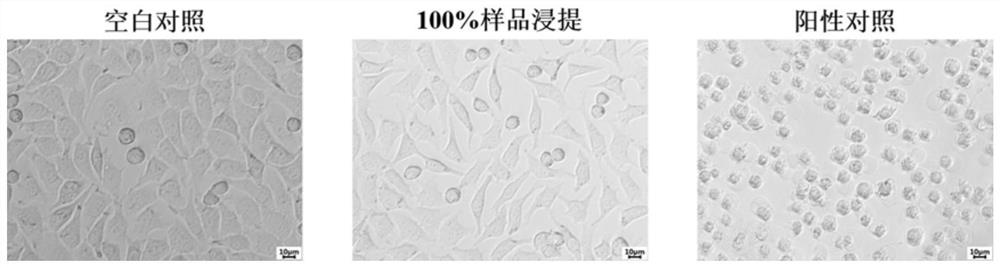
[0033]In order to illustrate the feasibility of the method of this embodiment, the following verification is ...
Embodiment 2
[0042]The allogeneic tendon in this example is the tendon tissue taken from a human donor. The dense ends at both ends of the tendon bundles have a diameter between 3-15 mm. They are shaken in a 0.5% SDS aqueous solution. After immersing for 24 hours, it is ensured that the SDS completely penetrates into the tissue, and then the method of the present invention is used to clean the residual SDS. The specific operations are as follows:
[0043]The decellularized allogeneic tendon obtained above was immersed in a 75% ethanol solution with a volume fraction, and the shaker was shaken for 2 hours, during which the liquid was changed once every 40 minutes. Then take out the allogeneic tendon, immerse it in a KCl aqueous solution with a potassium ion molar concentration of 0.5M, shake the shaker for 2 hours, and change the liquid every 40 minutes. Ensure that the SDS deposited on the surface of the allogeneic tendon is completely washed off.
[0044]In order to illustrate the feasibility of this...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com