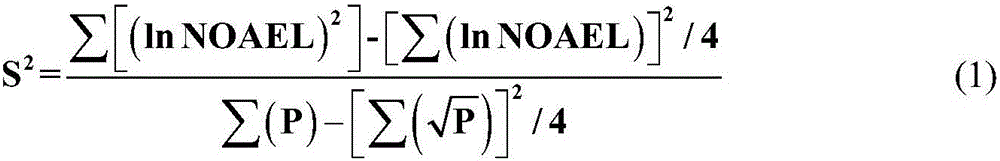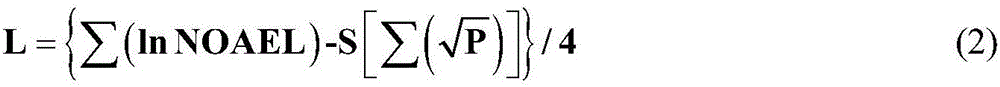Patents
Literature
30 results about "Tissue residue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tissue residue is the concentration of a chemical or compound in an organism's tissue or in a portion of an organism's tissue. Tissue residue is used in aquatic toxicology to help determine the fate of chemicals in aquatic systems, bioaccumulation of a substance, or bioavailability of a substance, account for multiple routes of exposure (ingestion, absorption, inhalation), and address an organism's exposure to chemical mixtures. A tissue residue approach to toxicity testing is considered a more direct and less variable measure of chemical exposure and is less dependent on external environmental factors than measuring the concentration of a chemical in the exposure media.
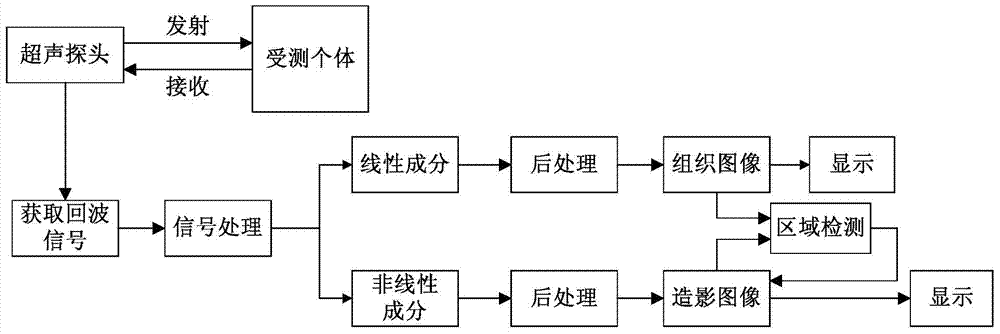
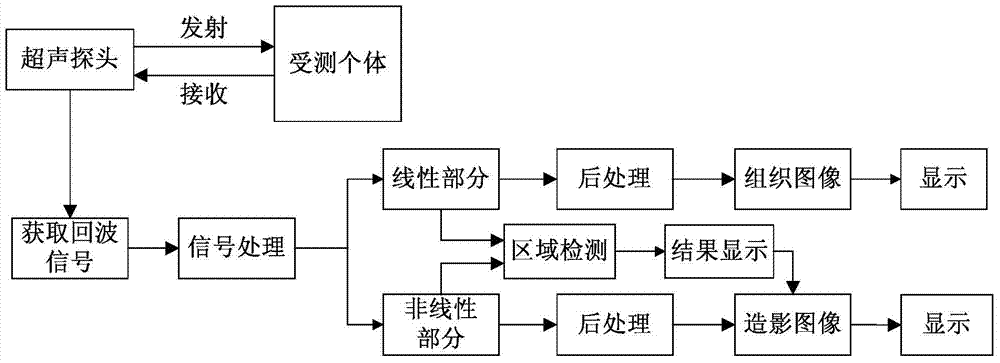
Ultrasound contrast imaging method and region detection and development methods for contrast images
ActiveCN104720850AImprove CTREnhanced signalImage enhancementWave based measurement systemsSonificationContrast enhance ultrasound
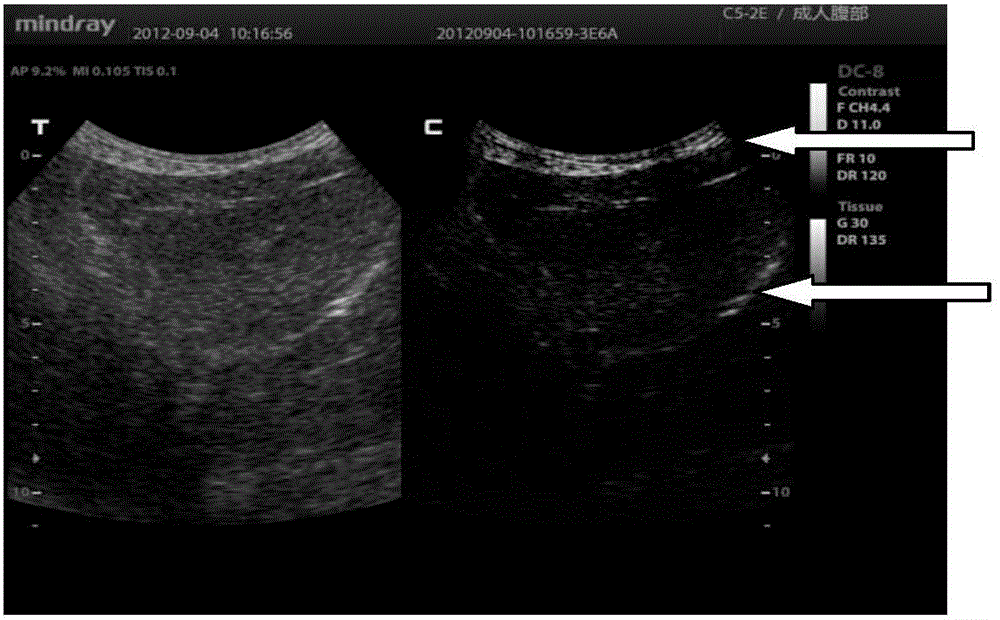
A contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging method and a method for regional detection and development of a contrasted image. The method for regional detection of a contrasted image comprises: acquiring a tissue signal and a contrast signal in a contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging process (S201); preprocessing respectively the tissue signal and the contrast signal (S202); comparison processing the preprocessed tissue signal and the contrast signal (S203); by means of a threshold segmentation approach, segmenting an image formed when comparison processed into a contrast agent effect region, a tissue residue effect region, and a noise effect region (S204); and, respectively marking corresponding positions on the contrasted image as a contrast agent region, the tissue residue effect region, and the noise effect region (S205). The regional detection method greatly increases the CTR of a contrast-enhanced ultrasound image, facilitates clinical observation, and enhances the contrast agent signal, thus allowing for a reduced contrast agent dosage injected during contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging and effectively reduced examination costs.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
One-step seedling culture method of wheat anther
InactiveCN101554136AReduced induction of adventitious budsEasy to operatePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsLate phasePollen
The invention discloses a one-step seedling culture method of wheat anther, which comprises the following steps of: selecting young spike of wheat with wheat pollen cells developing to mononuclear metaphase to late phase, and pretreating for 2 days at low temperature (2-4 DEG C); after conventional disinfection, stripping anther tissue from the pretreated young spike of wheat, and inoculating the anther tissue on one-step seedling culture medium for shade culture; and when growing visible callus, placing the cultured anther tissue under 1500Lx lighting conditions and culturing for a week, and then increasing the light intensity to 3000Lx-4000Lx and continuously culturing for two weeks to produce pollen plants with vigorous roots and seedlings. The method omits two necessary technical operation links of induction of adventitious buds and induction of adventitious roots by the pollen callus, the culture cost is reduced by nearly 50%, the culture days are shortened by 40-50 days, the average induction rate of green seedlings is equivalent to that of multistep seedling, the albino seedling rate is generally reduced by 10 percent, and test-tube seedlings are vigorous and has developed root system, connecting parts of rootstalks have little or no callus tissue residues, and the transplantation survival rate of the test-tube seedlings is high.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
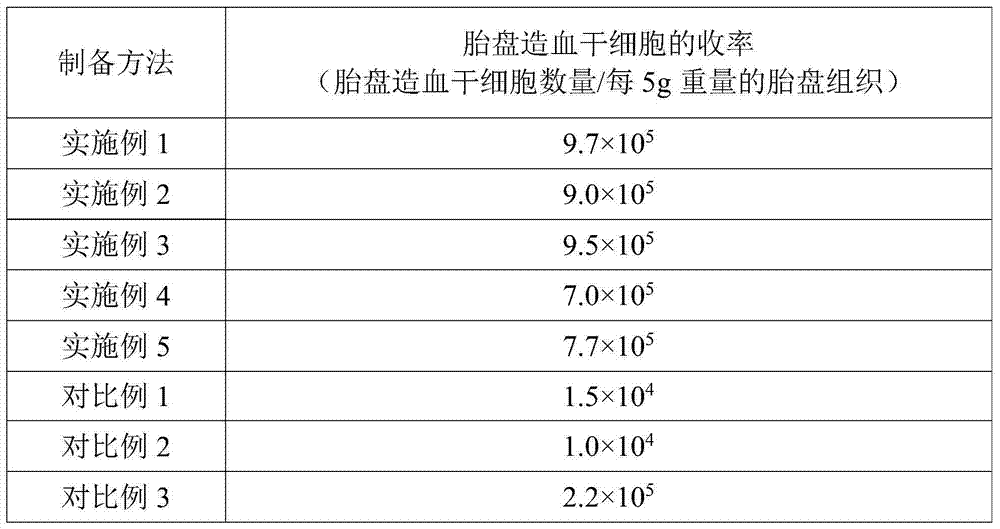
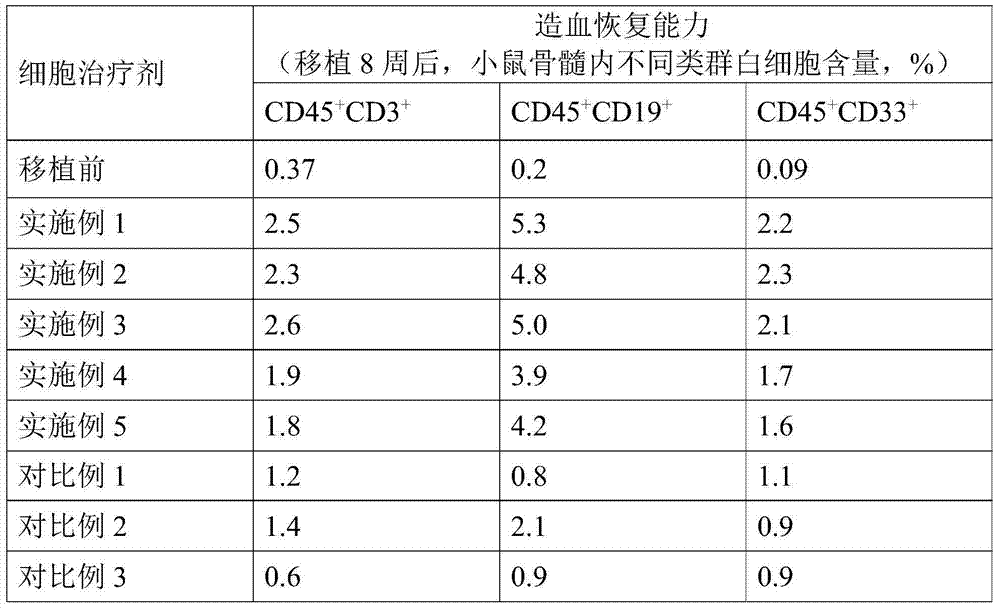
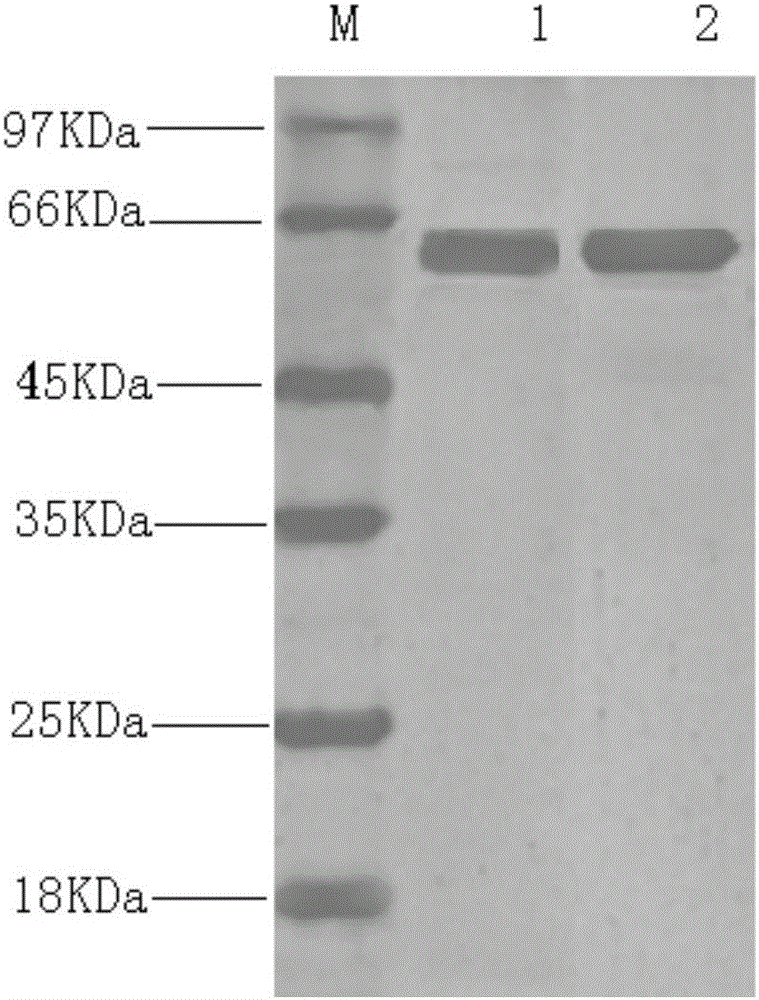
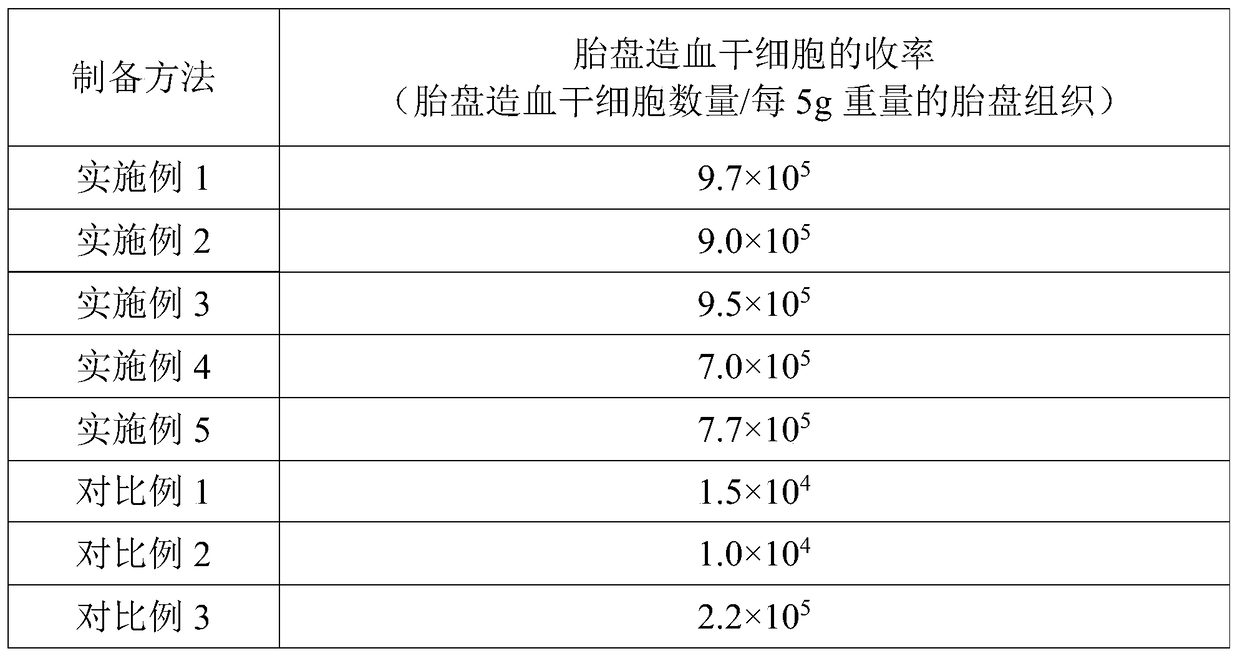
Method for preparing placenta hematopoietic stem cell preparation
ActiveCN104739865AImprove separation efficiencyMammal material medical ingredientsHydroxyethyl starchHydrolysate
The invention provides a method for preparing a placenta hematopoietic stem cell preparation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) digesting placenta tissues with an enzyme solution so as to obtain a digestive product and removing tissue residues in the digestive product to obtain enzymatic hydrolysate; (2) mixing the enzymatic hydrolysate with a hydroxyethyl starch solution, and layering the mixed materials to obtain a nuclear cell suspension; and (3) mixing the nuclear cell suspension with a frozen stock solution, wherein the enzyme solution contains type I collagenase, DNA enzyme I, dispase and hyaluronidase, and the frozen stock solution contains dimethyl sulfoxide, hydroxyethyl starch, human albumin and dextran. According to the technical scheme, the separation efficiency of the placenta hematopoietic stem cell can be improved; and the frozen placenta hematopoietic stem cell can be directly applied to stem cell treatment when heated to a room temperature.
Owner:HANGZHOU S EVANS BIOSCI LTD
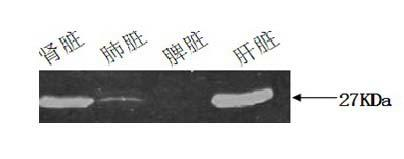
Method for efficiently extracting sheep viscus tissue protein
InactiveCN102443046AHigh purityQuality improvementPeptide preparation methodsBiological testingInsoluble proteinTissue protein
The invention provides a method for efficiently extracting sheep viscus tissue protein, i.e. a frozen crushing homogenate method and a vortex mixing method are adopted, the protein quantification is carried out on the extracted viscus tissue protein of livers, spleens, lungs, kidneys and the like of the sheep, the extracted protein is separated through polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and the expression of the transgenosis sheep green fluorescent protein (GFP) genes is detected by western blot. The method has the technical characteristics that: 1, the concentration of the extracted protein is high, and the cost is low; 2, the method is applicable to the extraction of viscus tissue protein of adult or young sheep; and 3, insoluble protein is little, the abandoned tissue residue is little, and important practical values are realized.
Owner:新疆维吾尔自治区畜牧科学院中国-澳大利亚绵羊育种研究中心
Method for coproduction of pistacia chinensis bunge essential oil and polyphenol
InactiveCN103301172AIncrease valueImprove use valueEssential-oils/perfumesPlant ingredientsForest industryPolyphenol
The invention discloses a method for coproduction of pistacia chinensis bunge essential oil and polyphenol. The method comprises the following steps of: naturally airing pistacia chinensis bunge leaves; extracting the pistacia chinensis bunge essential oil by adopting a supercritical CO2 fluid extraction method; crushing pistacia chinensis bunge tissue residues obtained by extracting the essential oil; and carrying out polyphenol extraction. According to the method disclosed by the invention, source forest fostering residues are used as raw materials to carry out the coproduction of the pistacia chinensis bunge essential oil and the polyphenol; in a process of obtaining the high-quality essential oil, the subsequent extraction of the polyphenol is carried; two substances with high value and good application prospect are dug from forestry wastes, so that the comprehensive utilization value of an important energy plant pistacia chinensis bunge is greatly improved; the method has the very important meanings in accelerating the development of a biological energy source industry and improving the economic and social benefits of energy source plants.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method utilizing environmental sediment samples to monitor freshwater benthic animals
PendingCN111593099AGuaranteed uniformityOvercome the defect of low accuracy of monitoring resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementCentrifugationFishery
The invention belongs to the technical field of benthic animal identification, and discloses a method utilizing environmental sediment samples to monitor freshwater benthic animals. The method includes the following steps: 1) collecting an environmental sediment sample to preserve after cleaning; 2) adding anhydrous ethanol in the preserved environmental sediment sample to perform extraction treatment, taking uniformly mixed extract liquid after treating for a period of time, performing vacuum centrifugation on the extract liquid, and discarding supernatant to obtain dried tissue residues so as to perform DNA extraction; 3) utilizing the extracted DNA barcode fragment to perform amplification so as to obtain an amplified product; and 4) sequencing and analyzing the amplified product. The method performs extraction on the sample by adopting the anhydrous ethanol so as to make the DNA of a benthic animal uniformly released in the solution, so that a homogeneous state can be achieved; andthrough the collection of the ethanol solution containing the DNA sample and the extraction of the DNA after centrifugal concentration, the accurate monitoring of a wide range of environmental samples can be realized.
Owner:南京易基诺环保科技有限公司
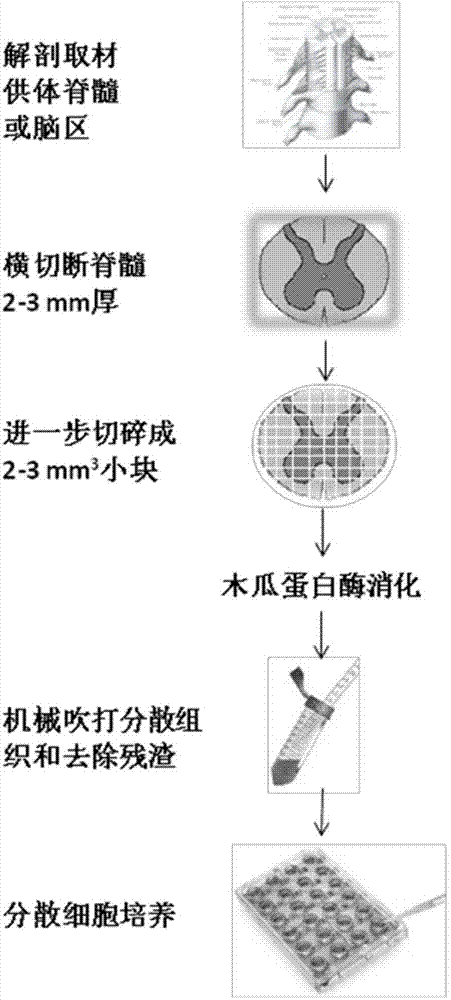
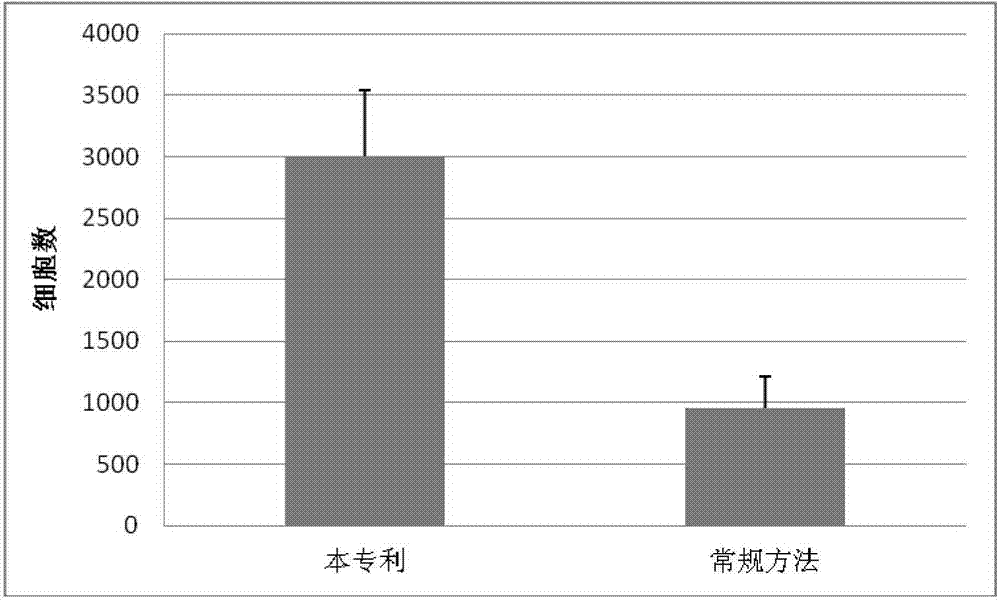
Method for increasing yield of neural stem cells in adult nerve tissues by utilizing organotypic culture
ActiveCN104726407AIncrease the totalEasily and thoroughly digestedNervous system cellsEnzymatic digestionCytotoxicity
The invention relates to a method for increasing the yield of neural stem cells in adult nerve tissues by utilizing organotypic culture. The method is characterized in that the method comprises organotypic culture and cell culture, and all the operations are completed on an aseptic operating platform. The method has the advantages and positive effects that organotypic culture is adopted and then papain digestion and blowing and beating dispersion are carried out seven days later, so that the quantity of obtained living cells is higher than that of the living cells obtained through direct enzymatic digestion by more than three times; another participation factor is mass multiplication of the neural stem cells in the organotypic culture process, thus increasing the total of the stem cells; another technological improvement is that the cells are directly inoculated in a poly-L-ornithine (PLO) coated cell culture plate after tissue dispersion, and tissue residues (including cell debris) are removed several hours later by changing a culture solution, thus omitting the time-consuming and tedious step of gradient centrifugation and also avoiding the cytotoxicity caused by most gradient centrifugation solutions.
Owner:斯坦姆(天津)生物技术研究有限公司
Bioactive tissue fluid separating and filtering device and working method thereof
PendingCN106731093ASimple structural designCompact designGravity filtersStationary filtering element filtersSingle stageTissue fluid
The invention relates to a bioactive tissue fluid separating and filtering device, which comprises a base, wherein the base is provided with a fluid bearing funnel; at least one separating and filtering assembly is arranged at the upper part of the fluid bearing funnel; the bottom of the fluid bearing funnel is connected to a storage tank through a pipe; the separating and filtering assembly comprises a separating and filtering drum; a stirring paddle, a filter net and a porous support plate are sequentially arranged in an inner cavity of the separating and filtering drum from top to bottom; and a transfer bar for driving the stirring paddle to rotate is arranged in the separating and filtering drum in a penetrating manner. The invention further relates to a working method of the bioactive tissue fluid separating and filtering device. The defects of existing single-stage filtering and multi-stage filtering are overcome; the filter net is not easily blocked, effective tissue is completely filtered, the tissue residues are few, the product quality is high, the operation is convenient and fast, and a filtered fluid is not in contact with air.
Owner:派生特(福州)生物科技有限公司
Method for synchronously separating chloroplast and mitochondria of high purity plant
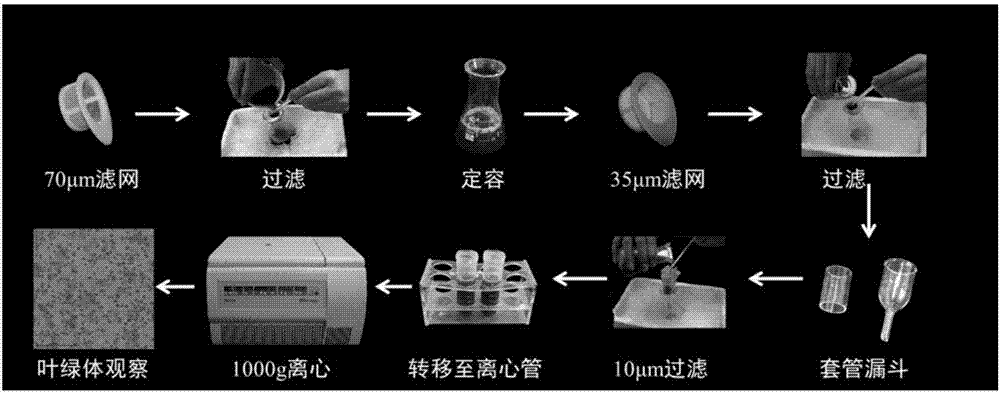
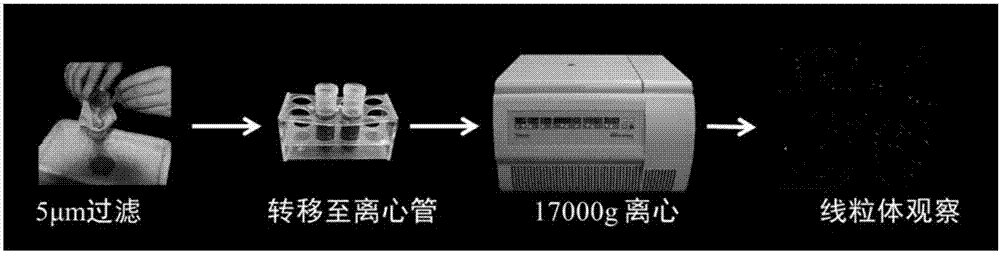
The present invention discloses a method for synchronously separating chloroplast and mitochondria of a high purity plant. The method comprises: A, adding leaf to a CIB buffer liquid, grinding, filtering sequentially with a 70 [mu]m filtration screen, a 35 [mu]m filtration screen and a 15 [mu]m filtration screen, and carrying out centrifugation on the filtrate for 5 min at 200*g to remove tissue residue and cell debris; B, carrying out centrifugation on the filtrate for 10 min at 1000*g, and collecting chloroplast-rich precipitate; C, collecting the supernatant after the centrifugation in the step B, filtering with a 5 [mu] filtration screen, carrying out centrifugation on the filtrate for 10 min at 2000*g, removing the precipitate, carrying out centrifugation on the supernatant for 10 min at 17000*g, and collecting mitochondria-rich precipitate; D, washing the precipitates respectively with a washing buffer liquid, and digesting with DNase I to remove background genome contamination; and E, carrying out centrifugation on the chloroplast precipitate for 10 min at 1000*g, removing the supernatant, carrying out centrifugation on the mitochondrial precipitation for 10 min at 17000*g, removing the supernatant, and washing the precipitates with a washing buffer liquid.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Chemotactic antibacterial nanometer material, and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN111529682AImprove adsorption capacityRealize unionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyChemical reaction
The invention discloses a chemotactic antibacterial nanometer material which comprises graphene oxides and polydopamine coating the surfaces of the graphene oxides, wherein antibacterial peptides areadsorbed on the surface of the polydopamine; and a chemotactic agent is loaded on the antibacterial peptides through a chemical reaction. The problems that bacteria invade organisms, and bacteria andmedicines are remained in tissues are solved. The invention also discloses a preparation method and application of the chemotactic antibacterial nanometer material.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
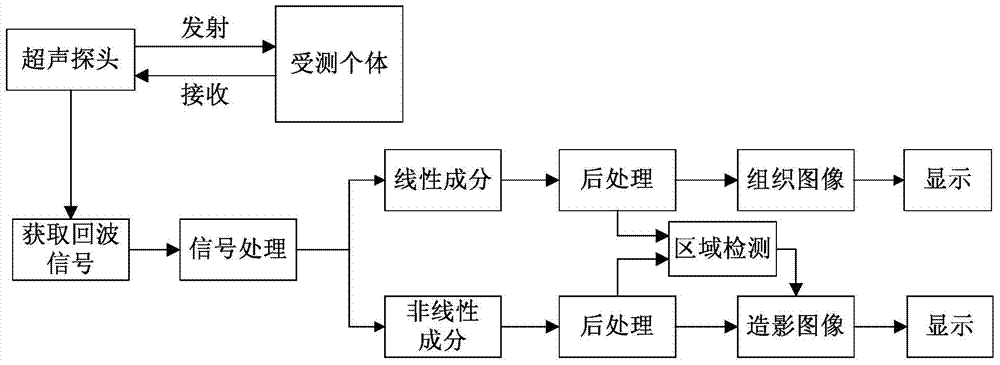
Ultrasound contrast imaging method and apparatus
ActiveCN106061396AIncrease CTRHigh resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsLinear componentSonification
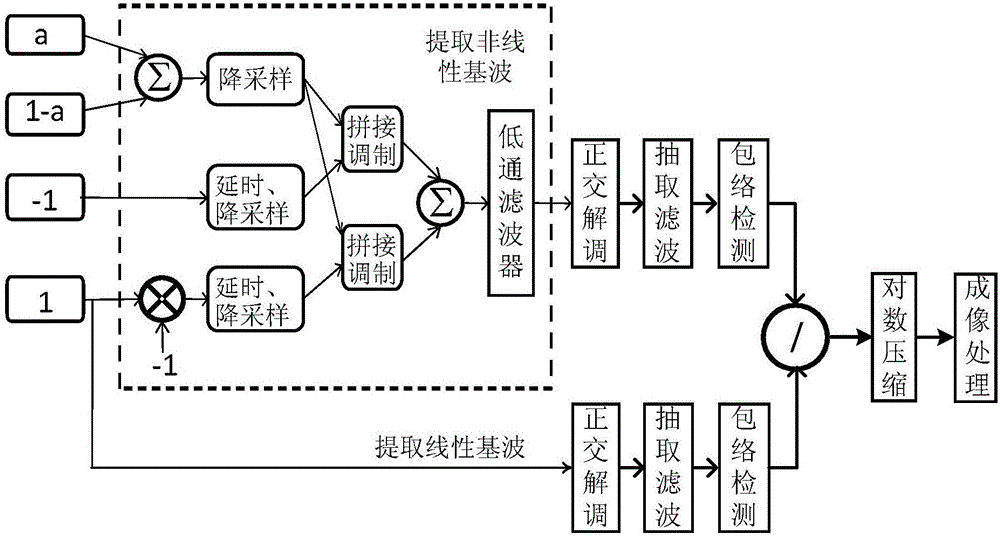
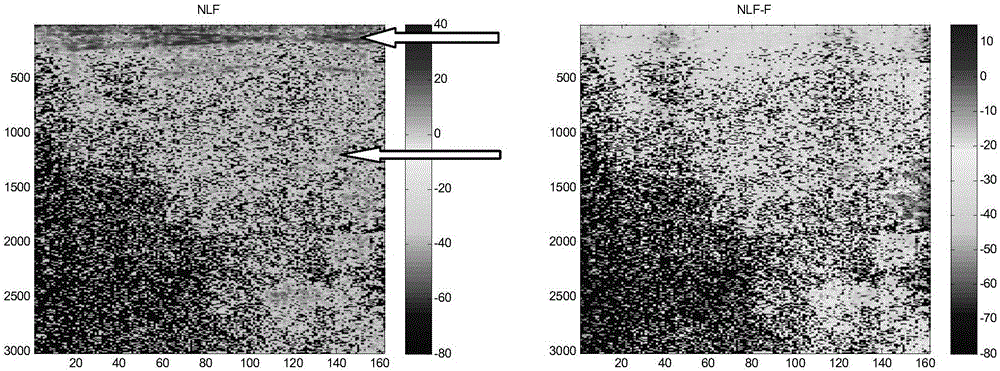
The invention provides an ultrasound contrast imaging method and apparatus. The method comprises: S1. transmitting a plurality of pulse waveform sequences, and acquiring echo signals of various pulses; S2. processing echoes of the various pulses to extract non-linear components of the echoes, and acquiring amplitude information about the non-linear components; S3. selecting echoes of any one or more pulses for processing to extract linear components of the echoes, and acquiring amplitude information about the linear components; S4. using the amplitude information about the non-linear components and that of the linear components to generate a non-linear parameter; and S5. performing imaging processing on the non-linear parameter. In the method, by simultaneously using amplitude information about linear components and non-linear components of an echo to generate a non-linear parameter, and performing imaging after processing this parameter, tissue residues can be effectively inhibited, and the dynamic range of a contrast agent signal is increased, thereby improving the CTR and contrast resolution of a contrast image.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
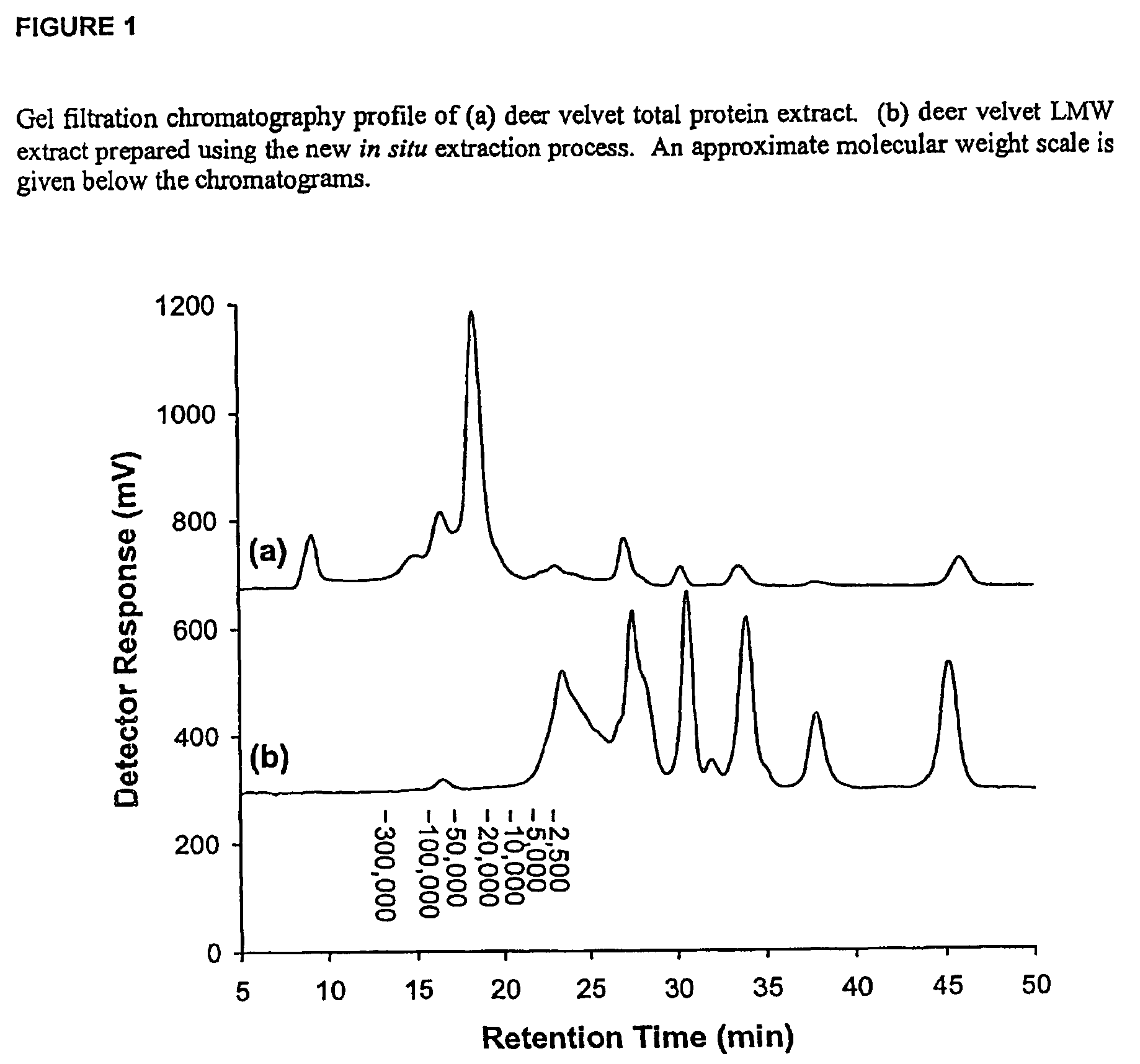
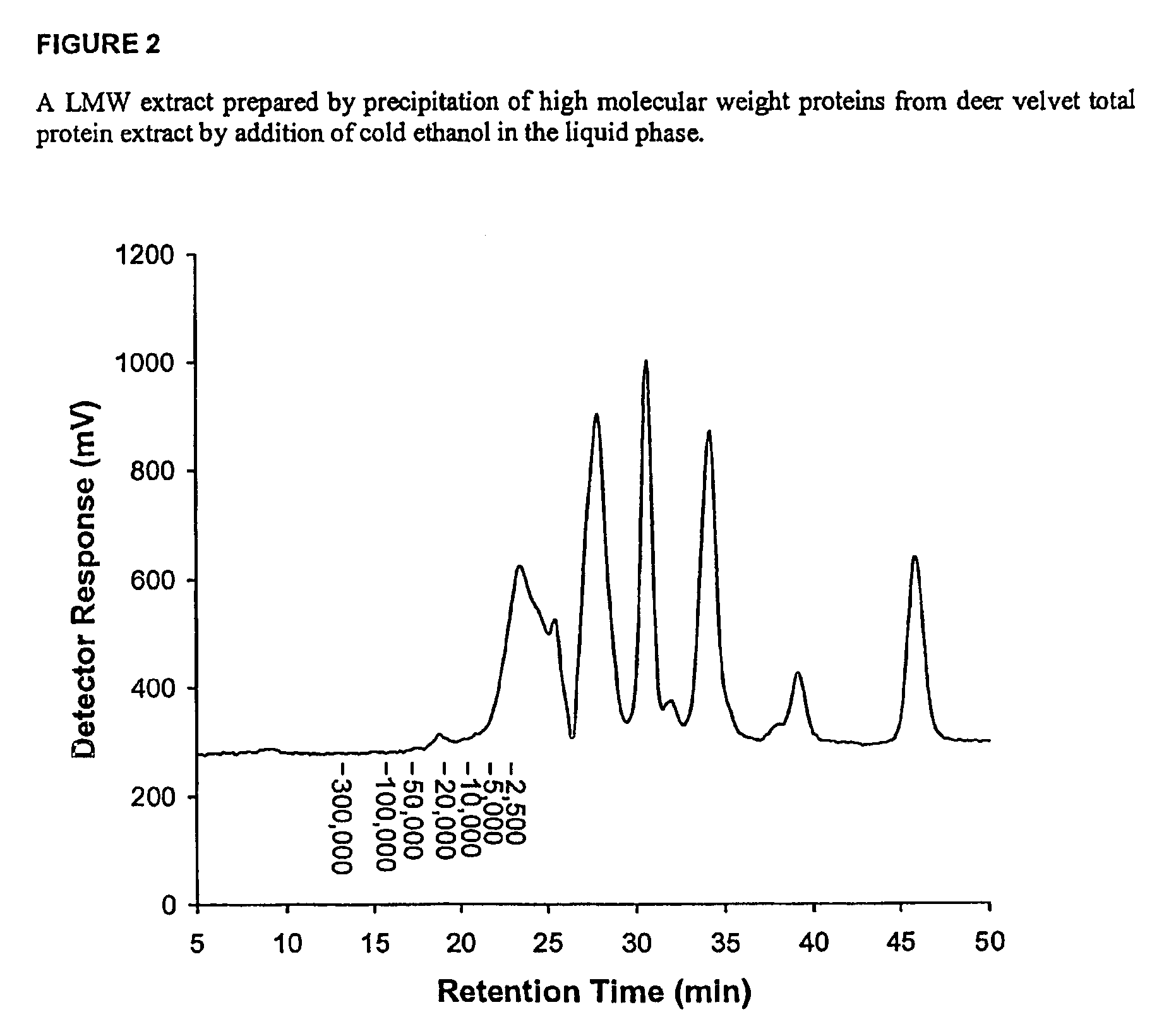
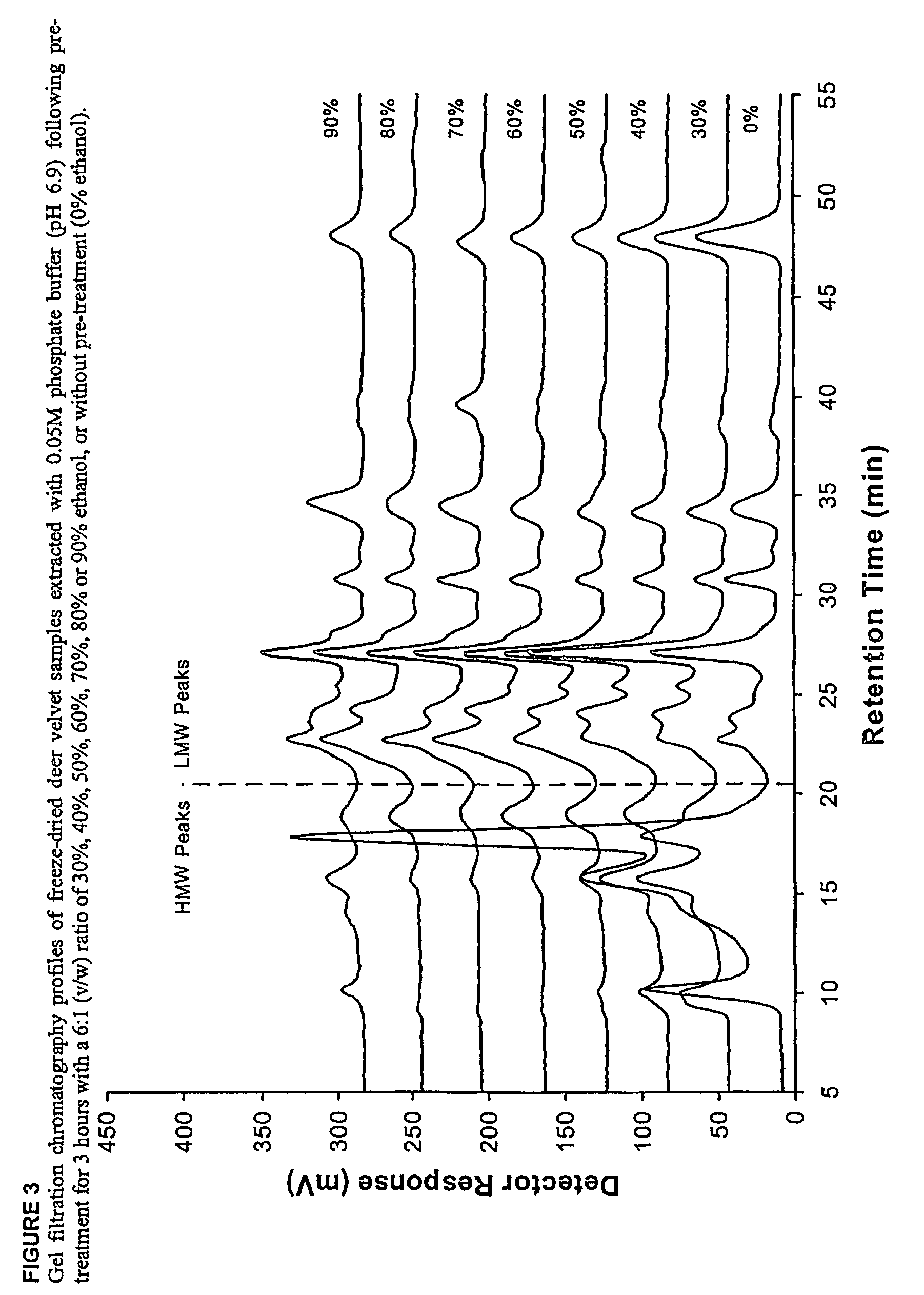
Low molecular weight extraction process
InactiveUS7547761B2Reduce microbial loadIncrease productionOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganic solventSlurry
Owner:VELVET ANTLER RES NEW ZEALAND
Derivation method for wildlife protection water quality standard of dieldrin
The invention discloses a derivation method for a wildlife protection water quality standard of dieldrin.The method comprises the steps that firstly, a tissue residue standard of cumulative substances is derived through a toxicity percentage ranking method; secondly, a biological cumulative factor of a representative species is selected, and the tissue residue standard is converted into a water quality standard; finally, the water quality standard for wildlife protection in China is determined according to the content level of the substance in a water body in China.According to the method, the biological cumulativity and effectiveness of the dieldrin are taken into account, and a direct support role can be supplied to water environment management and risk evaluation in China.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Microdissection technology of tobacco chromosomes
The invention discloses a microdissection technology of tobacco chromosomes. The microdissection technology is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) preparing a chromosome specimen: after immersing ripe and full seeds of tobaccos, putting the seeds into a culture dish and germinating; after roots grow to 0.5cm to 1cm, scissoring fresh root tips from 9:00 to 11:00 in the morning; putting the roots into a saturated alpha-bromnaphthalene solution and pre-treating at room temperature; washing and fixing by Carnoy I stationary liquid for one night; washing and putting the roots into distilled water and carrying out low percolation; treating with cellulose-pectinase mixed enzyme liquid and washing; putting the roots into the distilled water and carrying out the low percolation; putting root tip meristems on a slide and dropwise adding the stationary liquid; crushing materials and coating, and removing large tissue residues; then adding the stationary liquid; dyeing and washing to remove a dyeing solution; marking a good metaphase of microscope inspection for later use; (2) carrying out microdissection on the chromosomes: putting the specimen slide onto an objective table of a laser microdissection system and setting a cutting path; mounting a centrifugal tube with a viscous tube cover on an automatic recycling device of the laser microdissection system; treating the viscous centrifugal tube for later use after the chromosomes are cut and recycled.
Owner:GUIZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing sulphated glycosaminoglycans from biological tissues
InactiveUS7943764B2Quality improvementIncrease productionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAcetic acidSulfation
A method for isolating sulphated glycosaminoglycans washes a mechanically cleaned tissue, exposes tissue in a solution of 0.1M phosphate pH 5.8-6.0 buffer heated to a temperature of 65° C. for 30 minutes, overcooks the tissue in activated 0.1-0.4% papain at 65° C. for 6-24 hours, cools the papain digest to 4° C., removes fats and undigested tissue residues, selectively isolates the sulphated glycosaminoglycans for 4-10 hours on a solid carrier, obtained from bone tissue collagen with particle sizes ranging from 0-01 to 0.35 cm3, washes the carrier with 0.05-0.1 N-hydrochloric acid, degreases and eluates the carrier with a solution of 0.6-0.15 N-mineral salt in 0.8 N-acetic acid or in 0-01-0-025 N-alkali liquor, precipitates the sulphated glycosaminoglycans with ethanol, centrifuges with 1500 r.p.m. for 15 minutes at a temperature of 4° C., washes the precipitate with ethanol or acetone, and dries and sterilizes the precipitate.
Owner:SAVASCHUK DMITRY ALEKSEEVICH +1
Method for rapidly extracting RNA from animal tissue
InactiveCN108118049AQuick extractionLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationTwo stepGene expression level
The present invention relates to the field of molecular biology, and particularly to a method for rapidly extracting RNA from animal tissues. The method mainly comprises two steps such as rapid separation of cells from tissue and rapid extraction RNA from cells with a nucleic acid extraction reagent, wherein the step 1 comprises: cutting tissue into small blocks, weighing, adding PBS, uniformly grinding to obtain tissue homogenate, carrying out low-speed centrifugation to precipitate large tissue residue so as to make the single cell suspend in the supernatant, taking the supernatant with thesuspended cells, adding PBS, uniformly mixing, and carrying out centrifugation to remove the supernatant to obtain precipitate, ie., the separated cells, and the step 2 comprises: adding a nucleic acid extraction reagent to the cells, uniformly mixing, carrying out room temperature standing to lysing the cells, heating for 10 min at a temperature of 75 DEG C, and cooling the sample by placing on ice so as to obtain the prepared RNA for gene expression level detection or gene cloning and other works. According to the present invention, the method has advantages of simple operation, high speed,low reagent cost, no toxicity and no odor.
Owner:上海怡泽生物科技有限公司 +1
Method of generating an enhanced perfusion image
A method of generating an enhanced perfusion image comprising the use of a blind deconvolution algorithm and the adiabatic approximation to the Johnson and Wilson model (aaJW) and generation of an image, wherein the blind deconvolution algorithm and the aaJW model are used in the generation of values of the following parameters: voxel specific arterial input function cp[t] and voxel specific tissue residue function r[t].
Owner:STIFTELSEN UNIVTSFORSKNING BERGEN
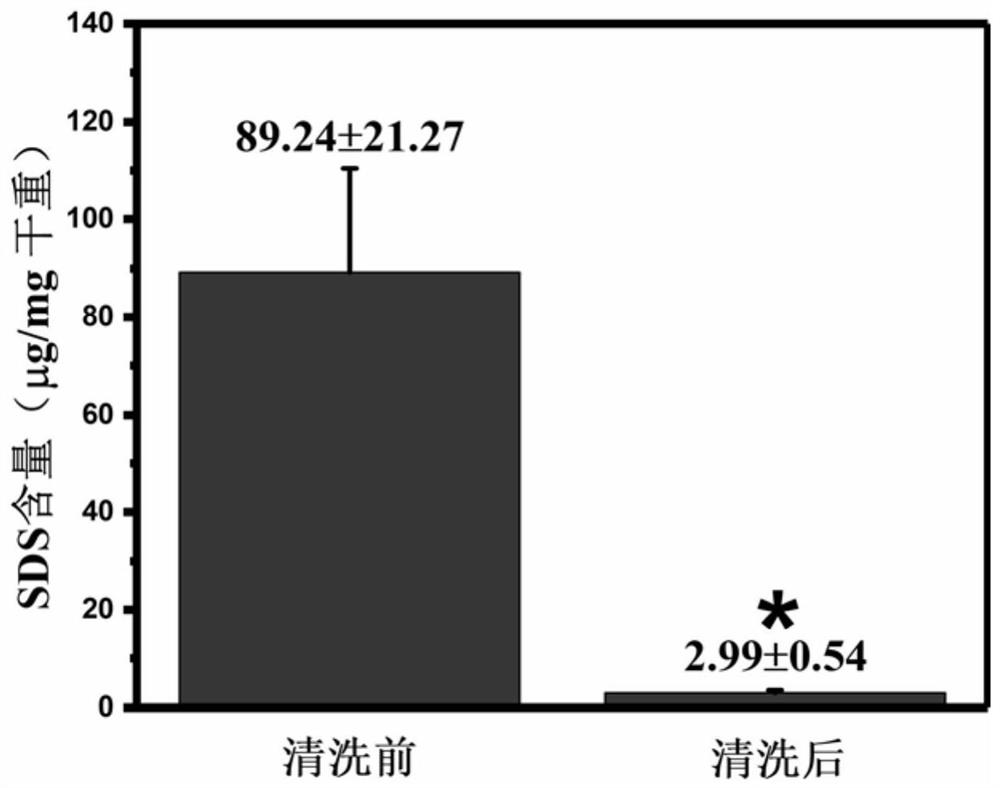
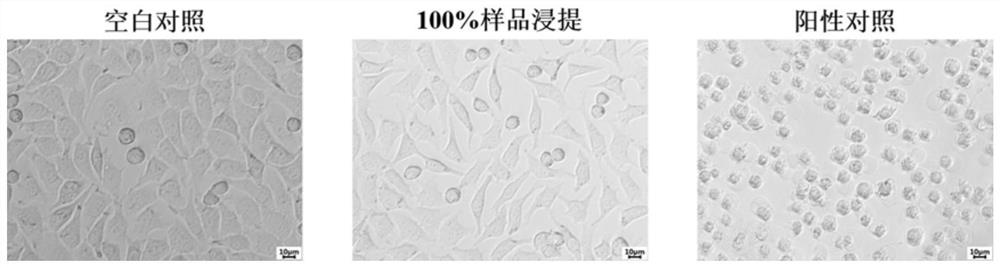
Method for cleaning decellularization reagent SDS
InactiveCN112354014AImprove cleaning and removal efficiencyEfficient removalTissue regenerationProsthesisPotassium ionsCytotoxicity
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for cleaning an decellularization reagent SDS, and belongs to the technical field of decellularization reagent post-treatment. The invention discloses a method for cleaning a decellularization reagent SDS, wherein decellularized tissues obtained by performing decellularization treatment by using SDS are sequentially soaked in an ethanol solution and a potassium ion solution. According to the invention, SDS decellularized tissues are sequentially soaked in an ethanol solution and a potassium ion solution, so that residual SDS in the decellularized tissue can be effectively removed, the content of the residual SDS is controlled to be free of cytotoxicity limit, the treatment time is shortened to 2-4 h, the SDS cleaning and removing efficiency is greatly improved, safety guarantee is provided for decellularization treatment of the SDS for the tissue, and industrial development is promoted; and the method disclosed by the invention is short-time and efficient, does not introduce other toxic substances, is safe and reliable, and is suitable for cleaning most SDS with decellularized allogeneic and xenogeneic tissue residues.
Owner:上海亚朋生物技术有限公司
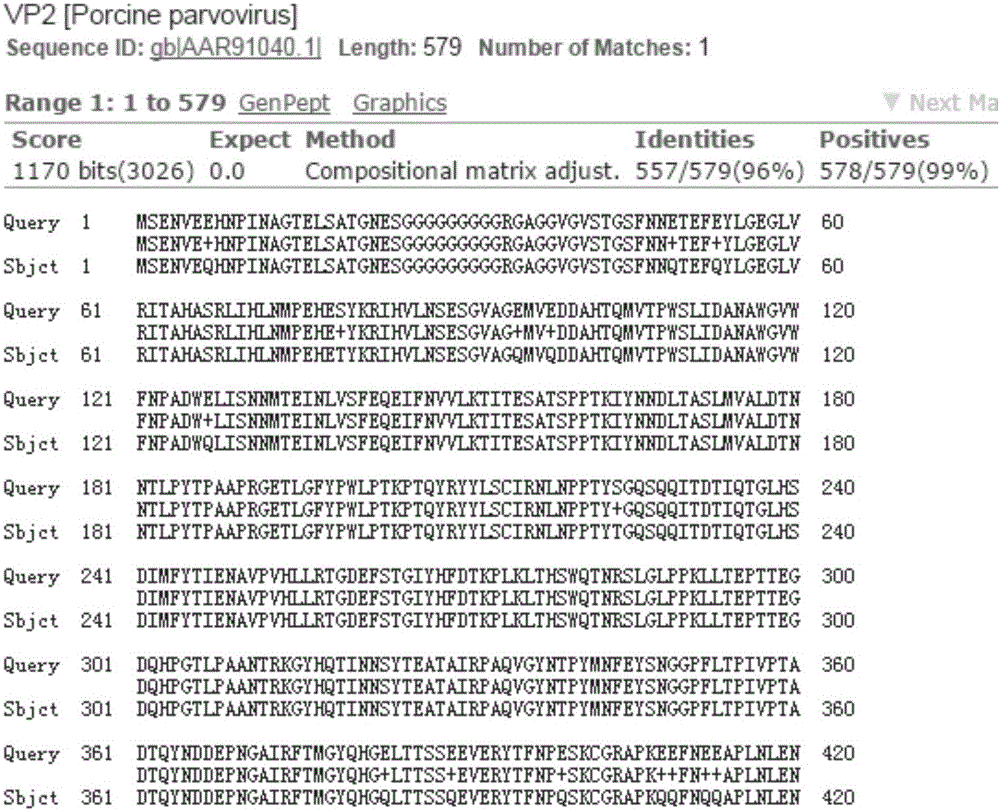
Porcine parvovirus VP2 protein
InactiveCN105820216AHigh antigen stabilityHigh purityViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesConceptusAmino acid
The invention aims at providing porcine parvovirus VP2 protein which is used for preparing a subunit vaccine so as to overcome deficiencies in the prior art .The amino acid sequence of the porcine parvovirus VP2 protein is SEQ ID NO:1 .The invention provides novel VP2 protein which lays a firm foundation for industrialized production of the porcine parvovirus subunit vaccine; the vaccine prepared through the protein is high in antigenic stability, high in purity, high in specificity and high in sensitivity, no other uncorrelated antibody is produced, an immune effect detection method is convenient and accurate, and production is very easy .Production is conducted without using animal bodies or embryoid bodies, tissue residues do not exist, and the safety is high.
Owner:YEBIO BIOENG OF QINGDAO
Derivation method of water quality standard for protection of wild life by dieldrin
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Method for Producing Sulphated Glycosaminoglycans from Biological Tissues
InactiveUS20080262218A1Quality improvementIncrease productionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAcetic acidInorganic salts
A method for isolating sulphated glycosaminoglycans washes a mechanically cleaned tissue, exposes tissue in a solution of 0.1M phosphate pH 5.8-6.0 buffer heated to a temperature of 65° C. for 30 minutes, overcooks the tissue in activated 0.1-0.4% papain at 65° C. for 6-24 hours, cools the papain digest to 4° C., removes fats and undigested tissue residues, selectively isolates the sulphated glycosaminoglycans for 4-10 hours on a solid carrier, obtained from bone tissue collagen with particle sizes ranging from 0-01 to 0.35 cm3, washes the carrier with 0.05-0.1 N-hydrochloric acid, degreases and eluates the carrier with a solution of 0.6-0.15 N-mineral salt in 0.8 N-acetic acid or in 0-01-0-025 N-alkali liquor, precipitates the sulphated glycosaminoglycans with ethanol, centrifuges with 1500 r.p.m. for 15 minutes at a temperature of 4° C., washes the precipitate with ethanol or acetone, and dries and sterilizes the precipitate.
Owner:SAVASCHUK DMITRY ALEKSEEVICH +1
A method for preparing placental hematopoietic stem cell preparation
ActiveCN104739865BImprove separation efficiencyArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsHydroxyethyl starchHydrolysate
The invention provides a method for preparing a placenta hematopoietic stem cell preparation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) digesting placenta tissues with an enzyme solution so as to obtain a digestive product and removing tissue residues in the digestive product to obtain enzymatic hydrolysate; (2) mixing the enzymatic hydrolysate with a hydroxyethyl starch solution, and layering the mixed materials to obtain a nuclear cell suspension; and (3) mixing the nuclear cell suspension with a frozen stock solution, wherein the enzyme solution contains type I collagenase, DNA enzyme I, dispase and hyaluronidase, and the frozen stock solution contains dimethyl sulfoxide, hydroxyethyl starch, human albumin and dextran. According to the technical scheme, the separation efficiency of the placenta hematopoietic stem cell can be improved; and the frozen placenta hematopoietic stem cell can be directly applied to stem cell treatment when heated to a room temperature.
Owner:HANGZHOU S EVANS BIOSCI LTD
Method for efficiently extracting sheep viscus tissue protein
InactiveCN102443046BHigh purityQuality improvementPeptide preparation methodsBiological testingTissue proteinInsoluble protein
The invention provides a method for efficiently extracting sheep viscus tissue protein, i.e. a frozen crushing homogenate method and a vortex mixing method are adopted, the protein quantification is carried out on the extracted viscus tissue protein of livers, spleens, lungs, kidneys and the like of the sheep, the extracted protein is separated through polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and the expression of the transgenosis sheep green fluorescent protein (GFP) genes is detected by western blot. The method has the technical characteristics that: 1, the concentration of the extracted protein is high, and the cost is low; 2, the method is applicable to the extraction of viscus tissue protein of adult or young sheep; and 3, insoluble protein is little, the abandoned tissue residue is little, and important practical values are realized.
Owner:新疆维吾尔自治区畜牧科学院中国-澳大利亚绵羊育种研究中心
Container special for operating room nursing isolation instruments
InactiveCN113081301AKeep dryEasy to disinfectSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsBacterial virusOperating theatres
The invention provides a container special for operating room nursing isolation instruments, and relates to the technical field of medical instrument containing. The container special for the operating room nursing isolation instruments comprises a box body, a support is fixedly connected to the upper inner wall of the box body, a supporting plate is fixedly connected to the inner wall of the support, a drawer is slidably connected to the upper surface of the supporting plate, and the lower side wall of the drawer and the left and right side walls of the support are all fine-hole steel wire meshes; the inner wall of the upper portion of the box body is fixedly connected with an upper partition plate, and the left side face of the upper partition plate and the left inner wall of the upper portion of the box body are each provided with a first ultraviolet lamp and an excimer discharge lamp. The medical instruments placed in the drawer are sterilized and disinfected through the excimer discharge lamp and the ultraviolet lamp, air is pumped outwards through the exhaust fan, the space where the drawer is located can be kept dry, microwave pyrolysis equipment is used for conducting microwave carbonization treatment on blood stains, tissue residues and germs on the surfaces of disposable articles and metal medical instruments after a hand operation, and the medical instruments are placed in the drawer. Bacterial viruses can be prevented from being infected and attached everywhere.
Owner:褚晓霞
A method for determining residual benzimidazoles in animal tissue
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
A method for separating soluble boron in plants
InactiveCN105203367BAchieve separationEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationWater immersionBiogeochemistry
Owner:LINYI UNIVERSITY
A method for synchronously isolating high-purity plant chloroplasts and mitochondria
The present invention discloses a method for synchronously separating chloroplast and mitochondria of a high purity plant. The method comprises: A, adding leaf to a CIB buffer liquid, grinding, filtering sequentially with a 70 [mu]m filtration screen, a 35 [mu]m filtration screen and a 15 [mu]m filtration screen, and carrying out centrifugation on the filtrate for 5 min at 200*g to remove tissue residue and cell debris; B, carrying out centrifugation on the filtrate for 10 min at 1000*g, and collecting chloroplast-rich precipitate; C, collecting the supernatant after the centrifugation in the step B, filtering with a 5 [mu] filtration screen, carrying out centrifugation on the filtrate for 10 min at 2000*g, removing the precipitate, carrying out centrifugation on the supernatant for 10 min at 17000*g, and collecting mitochondria-rich precipitate; D, washing the precipitates respectively with a washing buffer liquid, and digesting with DNase I to remove background genome contamination; and E, carrying out centrifugation on the chloroplast precipitate for 10 min at 1000*g, removing the supernatant, carrying out centrifugation on the mitochondrial precipitation for 10 min at 17000*g, removing the supernatant, and washing the precipitates with a washing buffer liquid.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
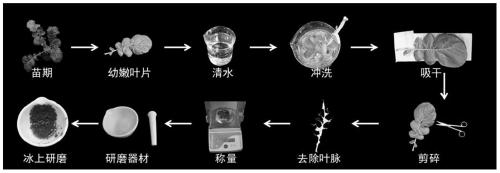
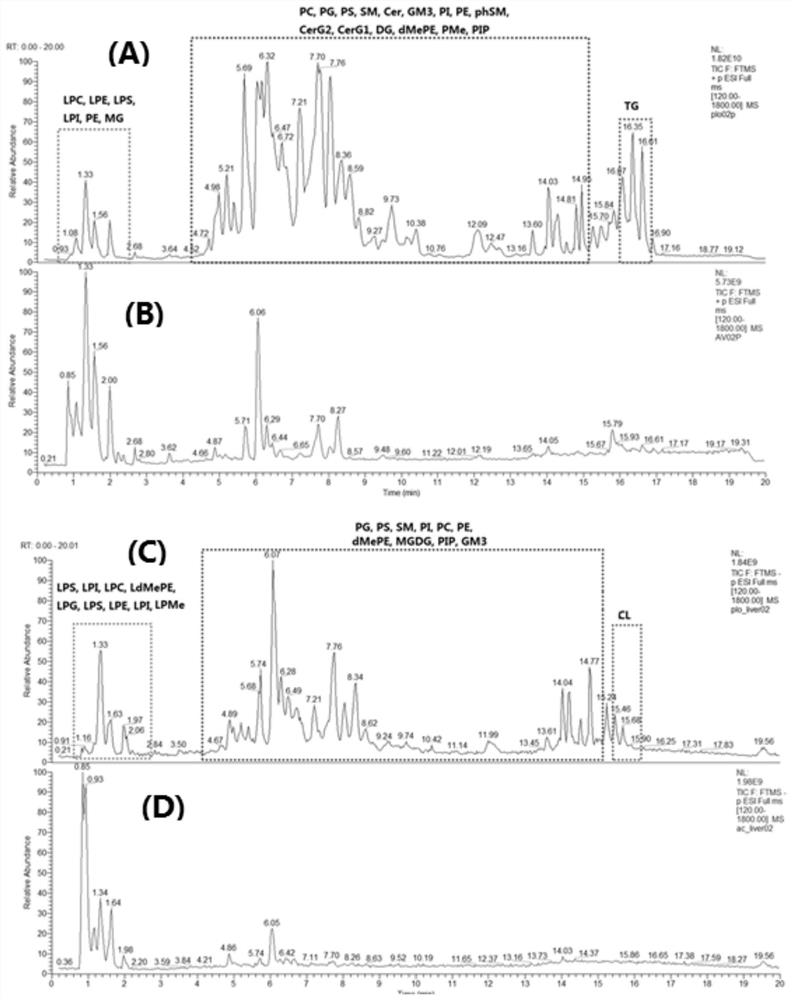
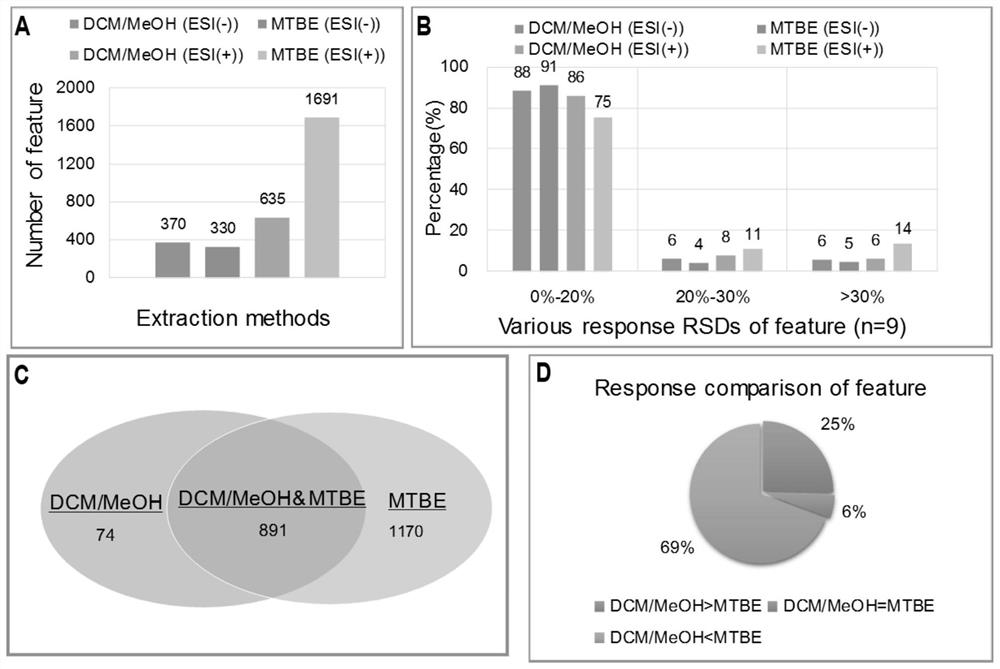
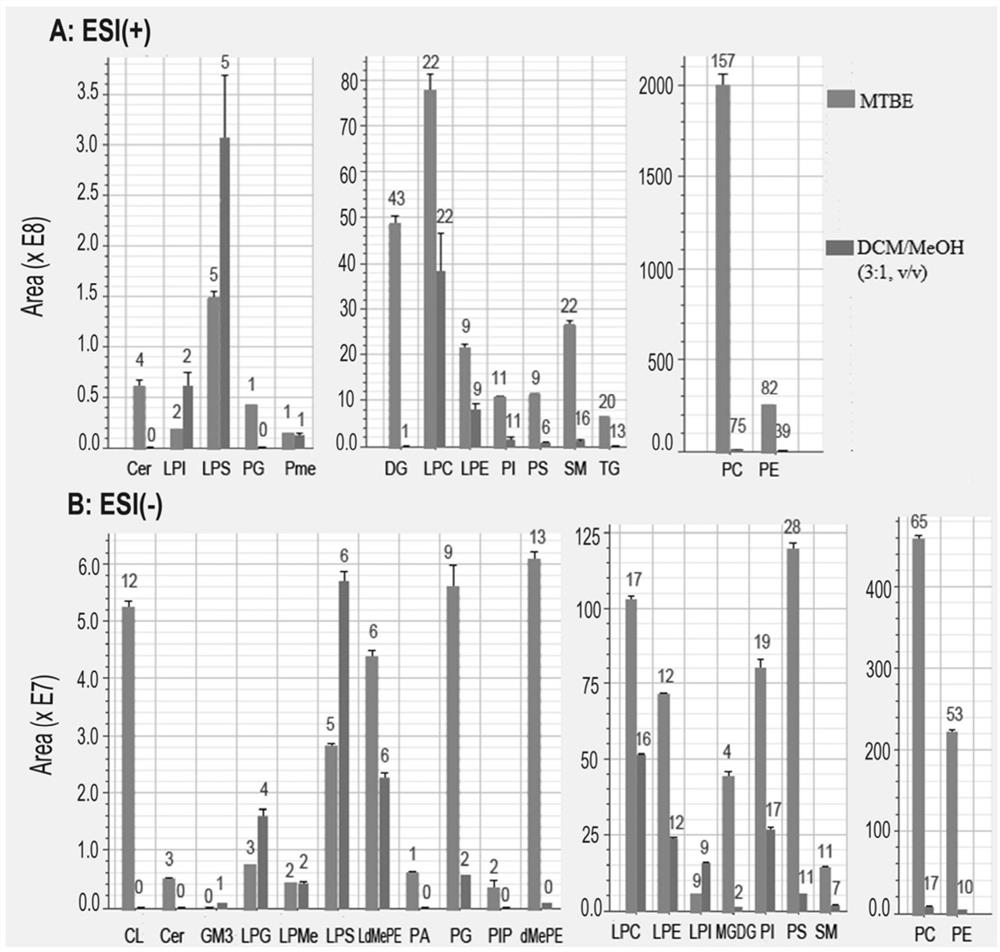
A sample extraction method for metabolomics and lipidomics studies of tissue samples
ActiveCN108593821BReduce degradation lossGood water solubilityComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationLipidomeMetabolite
The invention discloses a sample extraction method for metabolomics and lipidomics research of tissue samples. Trace tissue samples are taken in pre-frozen methanol-water solution, homogenized by low temperature beads, centrifuged to take supernatant The solution was used for metabolomics research, and the tissue residue was added to pre-frozen tert-butyl methyl ether, homogenized and centrifuged again for lipidomics research. The present invention can realize the simultaneous extraction of hydrophilic and lipophilic endogenous metabolites through a small amount of tissue, which are respectively used in the research of metabolomics and lipidomics. Compared with the method reported in the literature, the two-step extraction avoids mixing Solvent one-step extraction followed by two-phase separation to achieve hydrophilic and lipophilic metabolites in the extraction process. It is difficult to achieve full spectrum coverage of lipids with a single extraction system, and some hydrophilic metabolites are partially distributed to the lipid extraction layer during the phase separation process. Technical problems, while using MTBE extraction has higher lipid extraction efficiency and more convenient experimental operability than dichloromethane-methanol.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Separation method of soluble boron in plants
InactiveCN105203367AAchieve separationEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationBiogeochemistryBody fluid
The invention discloses a separation method of soluble boron in plants. The separation method comprises the following steps: (1) washing, drying, crushing and sieving plant samples; (2) weighing a certain amount of powder sample and putting the powder sample into a needle cylinder with a sieve plate and an end cap; adding water to immerse the sample and ultrasonically vibrating; (3) taking off the end cap of the needle cylinder of an injection syringe and putting the needle cylinder of the injection syringe into a screw-cap centrifugal pipe; centrifuging, separating and collecting filtrates; and (4) repeating the step (2) of adding the water and vibrating, and the step (3), totally separating for 5-10 times, and combining all the filtrates so as to completely separate the soluble boron in the plant samples. The invention establishes the separation method of the soluble boron in the plants; the method can be used for separating the soluble boron in plant sample fluid from non-soluble boron in tissue residues; the method has the characteristics of simplicity and reliability, and wide application prospect, and provides new technical supports for researches in the fields including plant boron nutrition, physiology and biochemistry of the boron, biogeochemical cycles of the boron and the like.
Owner:LINYI UNIVERSITY
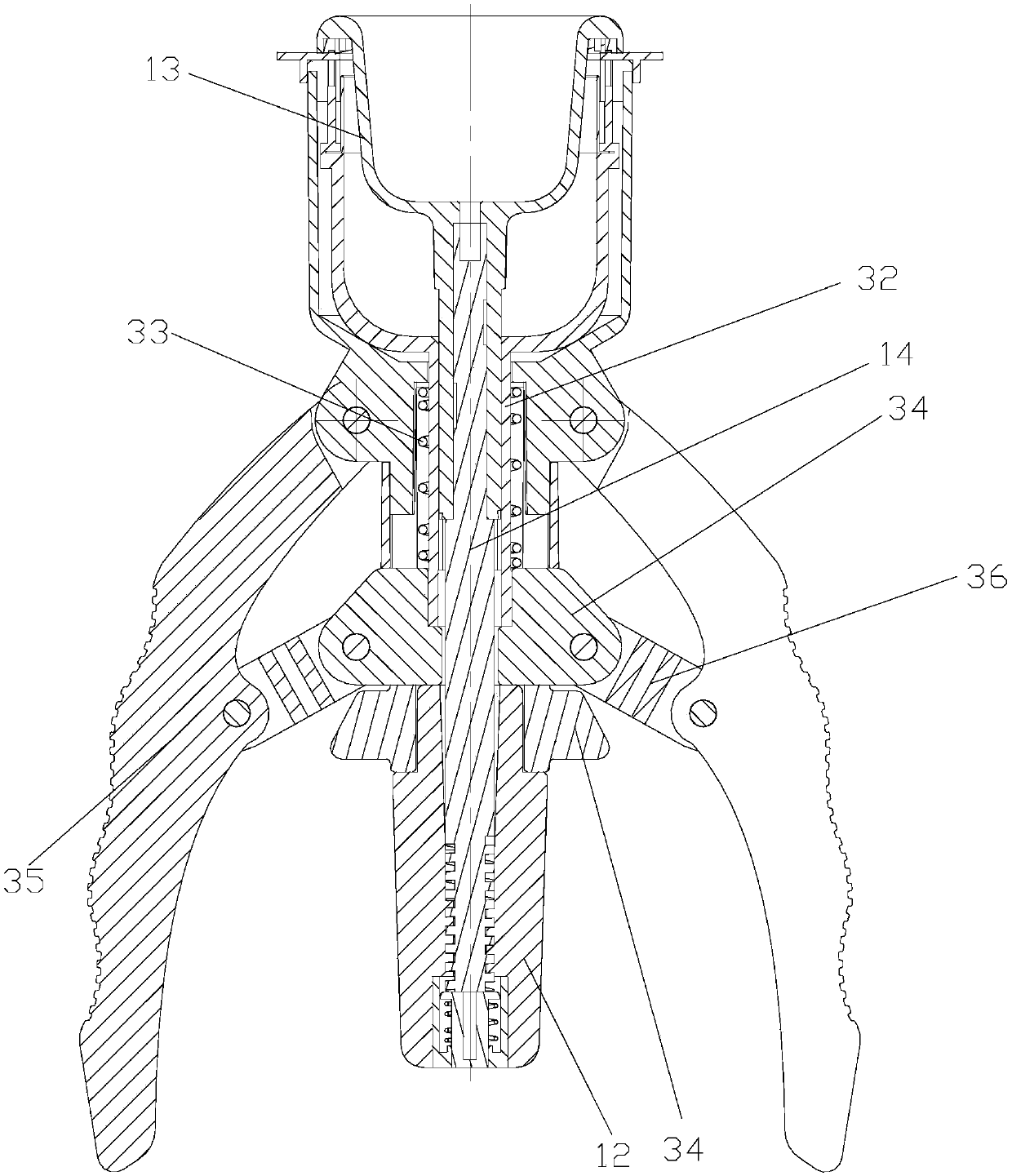
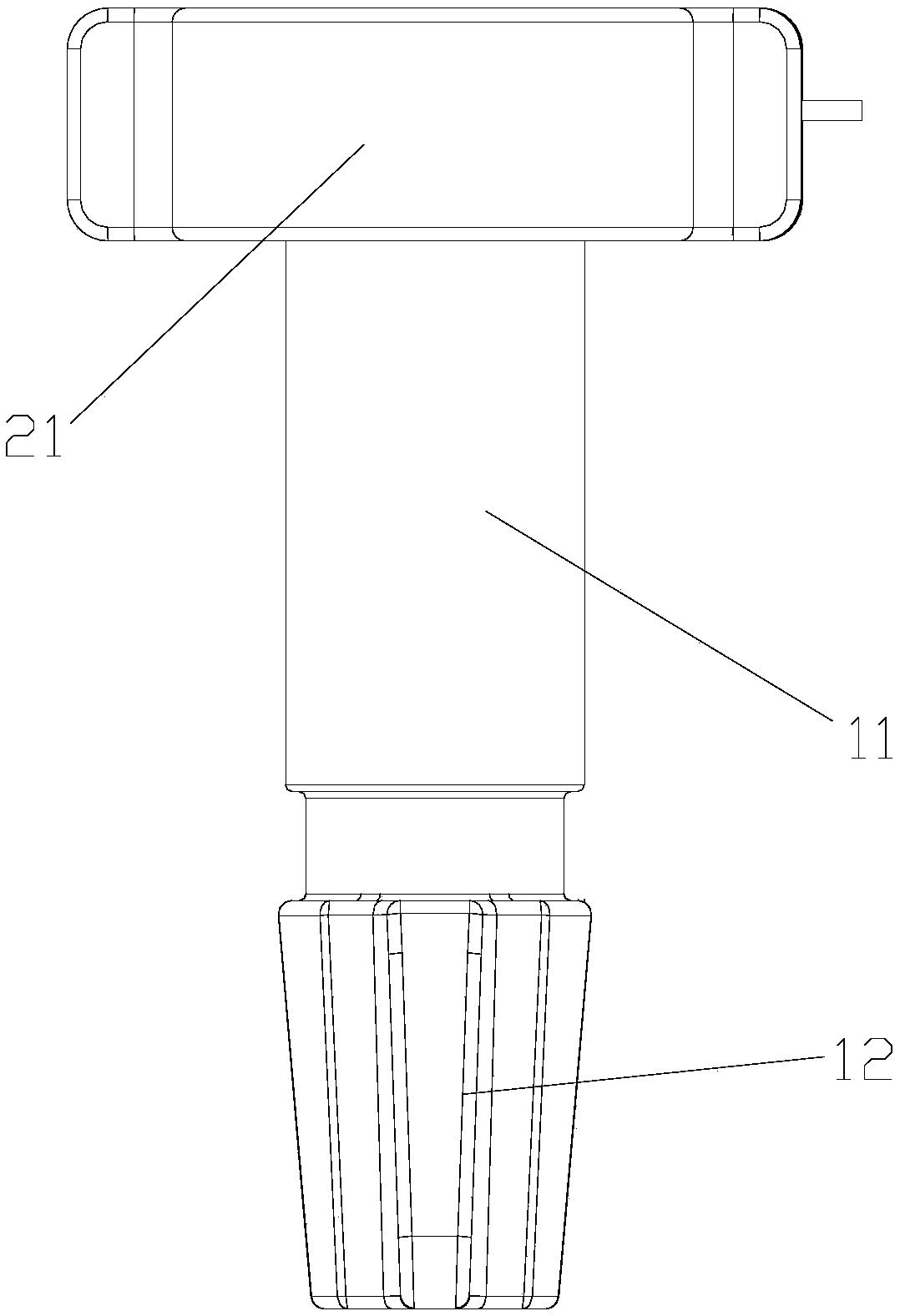
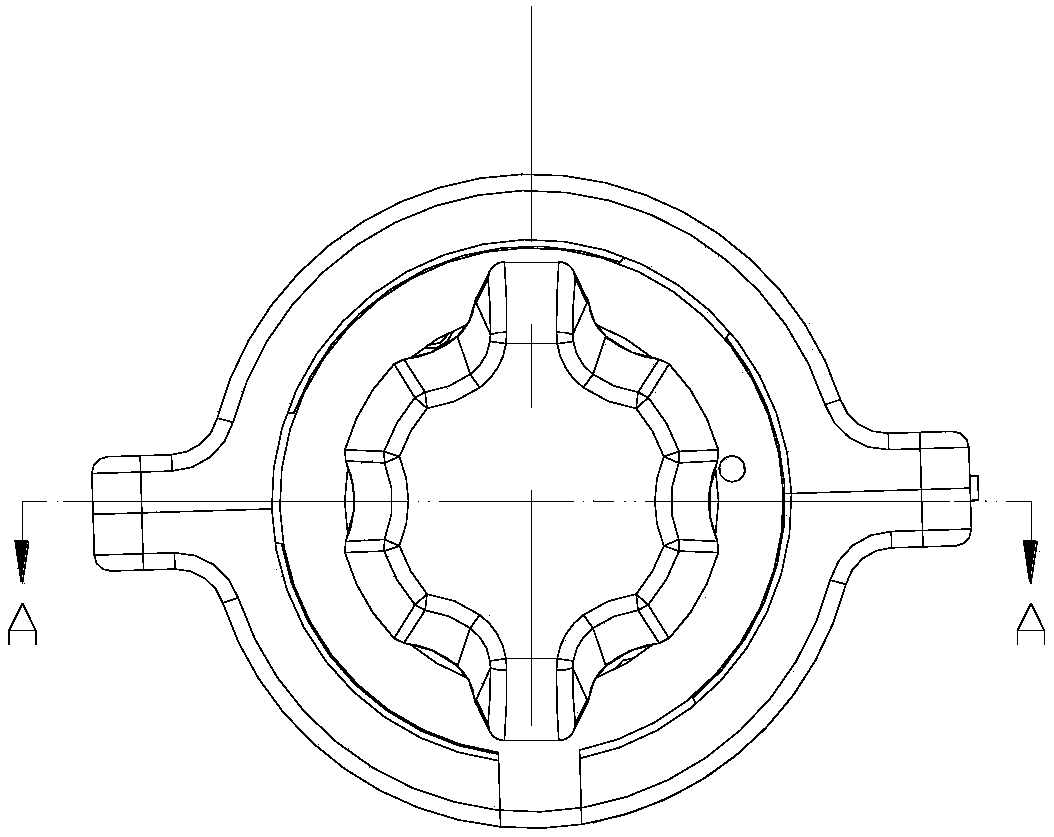
Side-nail anastomat
The invention discloses a side-nail anastomat. The anastomat includes a hand-held part and a functional part; the hand-held part includes a handle and a balanus shield which is arranged on the front end of the handle and is capable of moving front and back; the functional part comprises a side nail assembly, and the side nail assembly includes a cutting wheel shell group, pushing blocks, a jackingstructure and a nail chamber provided with multiple nail placing channels in an annular mode; the cutting wheel shell group is rotatably connected to the front part of the handle, and the annual nailchamber is arranged on the balanus shield in a sleeving mode and mounted in an inner cavity of the cutting wheel shell group; the jacking structure is located below the nail chamber and connected with the cutting wheel shell group; the nail placing channels are provided with anastomosing nails and the pushing blocks from inside to outside, and a pushing bevel is arranged on the wall surface of the inner cavity of the cutting wheel shell group. The side-nail anastomat has the advantages that 1. when the nailing positions of the anastomose nails are close to the junction between a prepuce and abalanus and the annular incision position is close to the nailing positions, the optimal prepuce incision effect is obtained; 2, incision and anastomosis are conducted from the side edge of tissue, tissue residues can be better prevented, the anastomosing conditions can be determined more easily, and the anastomosis can be conducted more easily.
Owner:SURGAID MEDICAL XIAMEN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com