Gene therapeutics for treating bone disorders
A transgenic and viral technology, applied in gene therapy, bone diseases, genetic engineering, etc., can solve problems such as increasing the risk of stroke and increasing bone tissue destruction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
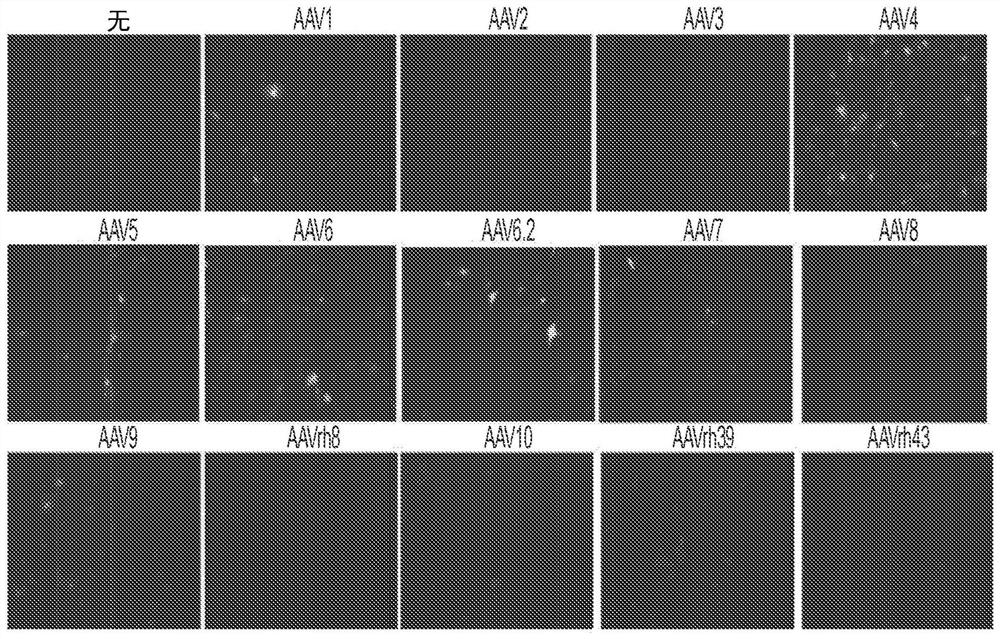
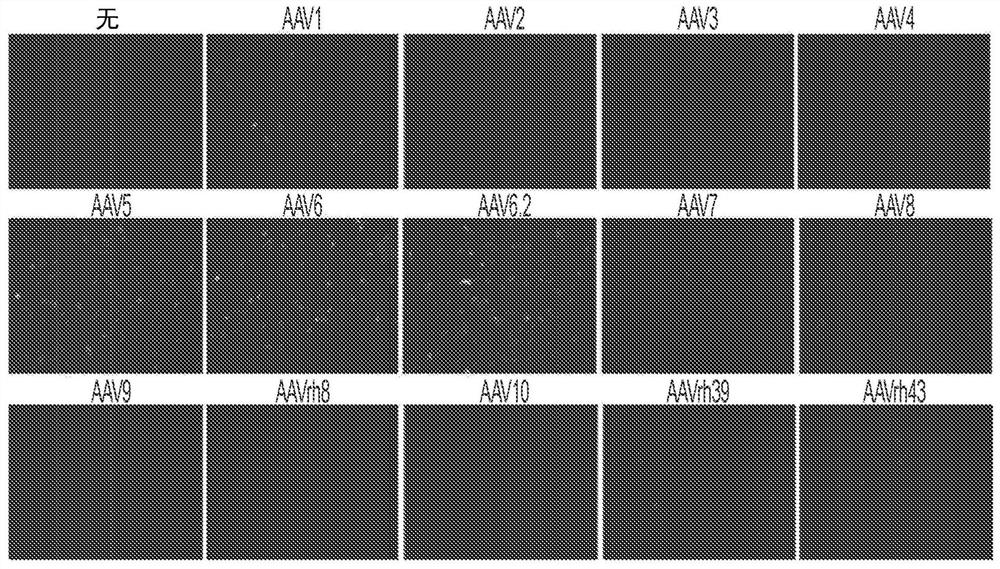
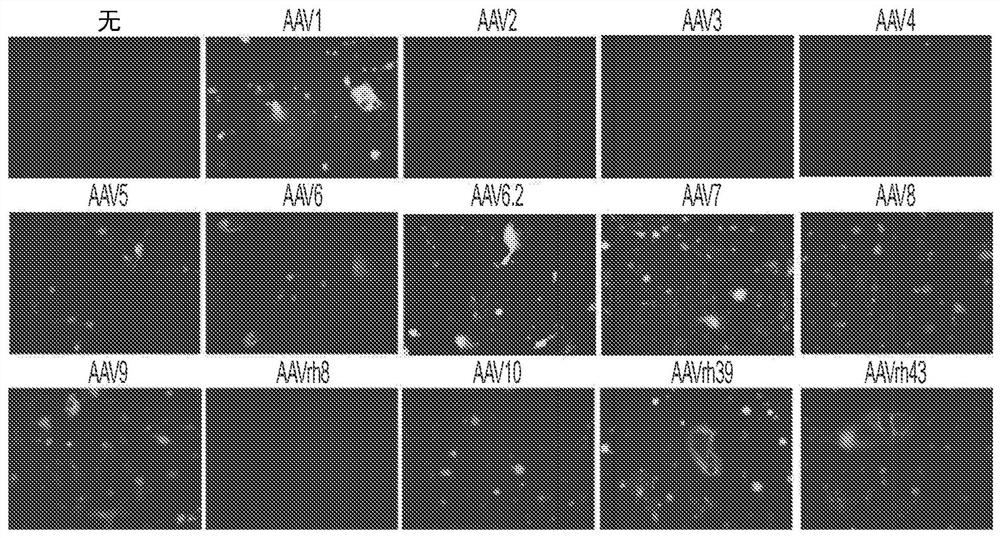
[0180] Several key regulators of bone formation have been identified as therapeutic targets for osteoporosis. For example, inhibition of the naturally occurring bone formation inhibitor sclerostin (SOST) or the adapter protein schnurri-3 (SHN3, also known as HIVEP3) leads to a progressive increase in bone mass due to increased OB activity. Unlike SHN3 and SOST, which mainly function in OB, cathepsin K (CTSK) is highly expressed in OC, and its inhibition increases bone mass by blocking OC activity. Finally, treatment with bone anabolic factors including PTH, PTH-related protein (PTHrP) or DJ-1 promoted bone formation. In this example, gene therapy agents that can manipulate the expression of these candidate genes through the use of bone-targeting adeno-associated virus (AAV)-mediated gene silencing or addition are described. In some embodiments, therapeutic agents (e.g., compositions described in this disclosure) have only limited activity on bone remodeling and regeneration b...
Embodiment 2
[0223] Example 2: Development of Novel Gene Therapeutics for Osteoporosis Using AAV-Mediated Gene Addition
[0224] In some embodiments, intermittent treatment with subcutaneously injected recombinant PTH peptide (1-34aa) or recombinant PTHrP peptide (1-36aa) increases OB activity and promotes bone formation. These peptides (teriparatide, abaloparatide) are FDA approved and are currently used in human patients with osteoporosis. In some embodiments, the secreted factor DJ-1 acts as a mediator of cross-sensing between OB and endothelial cells. In some embodiments, treatment of DJ-1 promotes OB differentiation in human MSCs and angiogenesis in human endothelial cells, while it inhibits OC differentiation.
[0225]This example describes the delivery of scAAV9 serotypes encoding secreted osteogenic factors to animals via intramuscular (IM) injection, whereby the injected muscle acts as a biological pump, providing a steady high level of these factors in the blood circulation. ...
Embodiment 3
[0228] Example 3: Inducible deletion of Shn3 in osteoblasts promotes bone formation in adult mice
[0229] To examine the effect of short-term inhibition of SHN3 on bone formation, the Shn3 fl / fl mice and mature osteoblasts (Shn3 Ocn-Ert ) to generate inducible, osteoblast-specific Shn3-knockout mice. These mice were further combined with the Cre reporter gene Rosa mT / mG Mouse crosses to visualize Cre-expressing cells (Shn3 Ocn-Ert ;Rosa mT / mG ). Treatment of Shn3 with tamoxifen Ocn-Ert ;Rosa mT / mG Mice resulted in GFP expression in mature osteoblasts located on the trabecular and cortical bone surfaces, indicating an osteoblast-specific deletion of Shn3 (Fig. 23). Thus, these mice showed a significant increase in trabecular bone mass compared to tamoxifen-treated control mice (Figure 23). These results demonstrate that inducible deletion of Shn3 in mature osteoblasts is sufficient to increase bone mass in adult mice.
[0230] Cre-encoding scAAV9 vector (scAAV9-Cre,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com