Organic fertilizer stack type fermentation method taking mushroom dregs as substrate
A fermentation method and organic fertilizer technology, applied in the direction of organic fertilizer, organic fertilizer preparation, bio-organic part treatment, etc., can solve the problems of difficult large-scale processing and utilization, poor utilization of nutrients, unfavorable packaging and sales, etc., to achieve suitable for large-scale Effects of processing, improving quality, and avoiding waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in combination with specific embodiments and with reference to the accompanying drawings. It should be understood that these descriptions are exemplary only, and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention. Also, in the following description, descriptions of well-known structures and techniques are omitted to avoid unnecessarily obscuring the concept of the present invention.
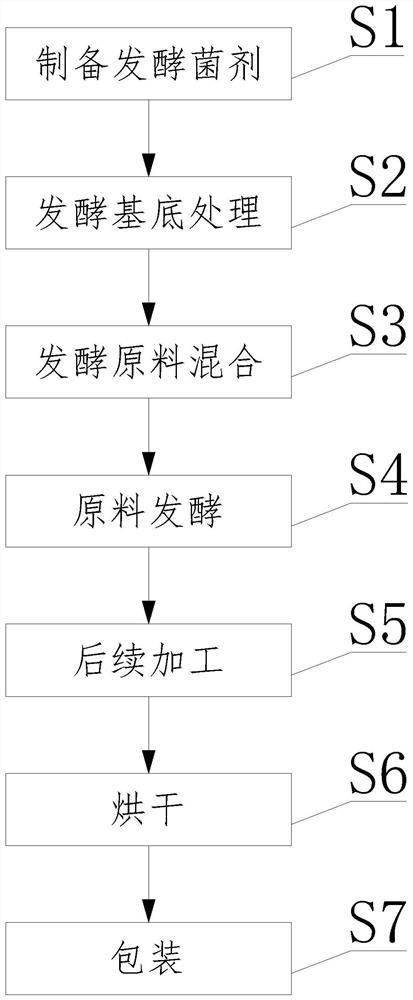
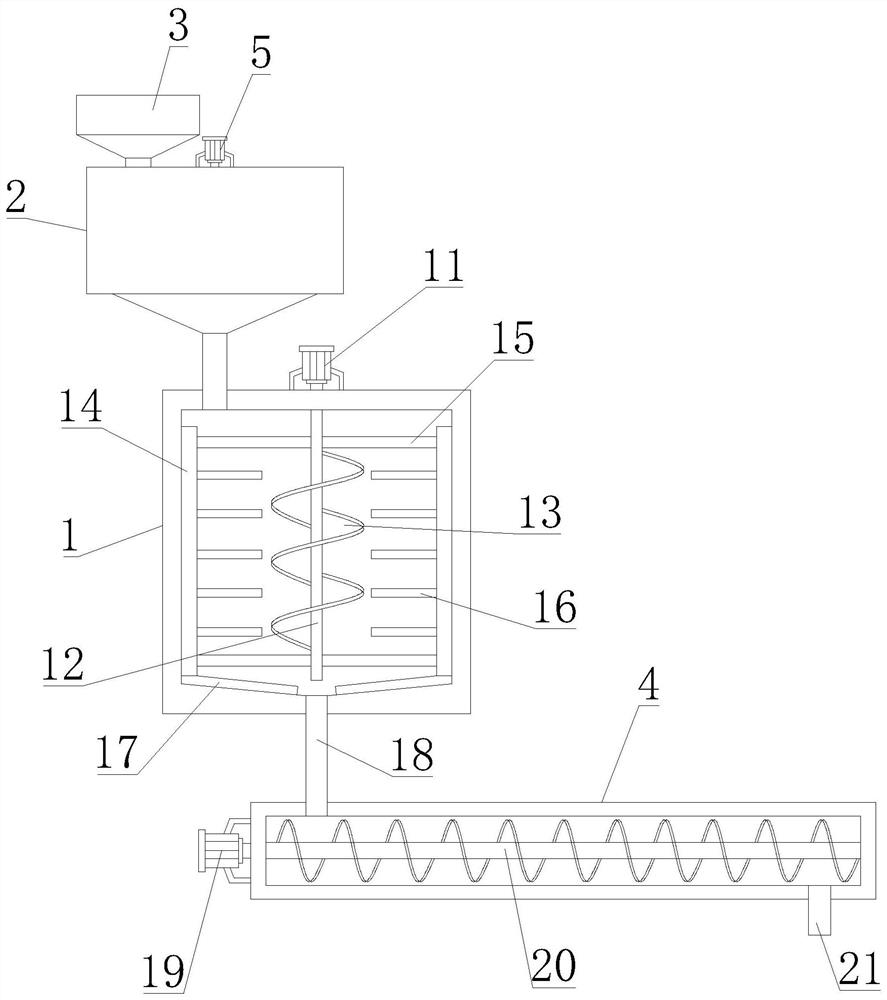
[0038] Such as Figure 1-2 Shown, a kind of organic fertilizer pile type fermentation method that the present invention proposes is that bacterium slag is base, comprises the following steps:
[0039] S1. Preparation of fermentation inoculum: select the strains required for fermentation and mix them, then expand the culture after mixing, and after expansion to a certain density, ferment for 16 hours at a temperature of 3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com