SNP marker related to vallisneria identification and application of SNP marker
A technology of labeling and licorice, which is applied in the field of SNP markers related to the identification of licorice, can solve the problems of naming and classification confusion, long cycle of morphological identification methods, low reliability of morphological identification results, etc., to achieve improved efficiency, high accuracy, cost saving effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0130] Example 1 Screening of polymorphic SNP site markers
[0131] (1) Primer design
[0132] The Primer 3 software was used to develop SNP primers for the first 100 SNP sites of Erytheria miltiorrhiza from Taihe Water Co., Ltd., and the primer sequences are shown in Table 3. Sanger sequencing was used to verify the SNPs obtained by RAD-seq sequencing. A total of 5 samples of GS1a, GS4a, TH7, SH14, and HH23 were selected for sequencing verification of 100 sites. Tailing primers were used for amplification, and the general Common- F(AGTCACGACGTTGTAAAACGAC), the amplification system and procedure are as follows:
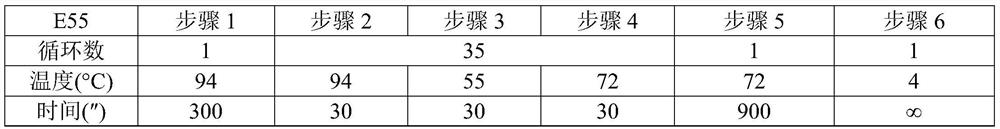
[0133] Table 1 Amplification program
[0134]
[0135] Table 2 Amplification system
[0136]
[0137] (2) Development test
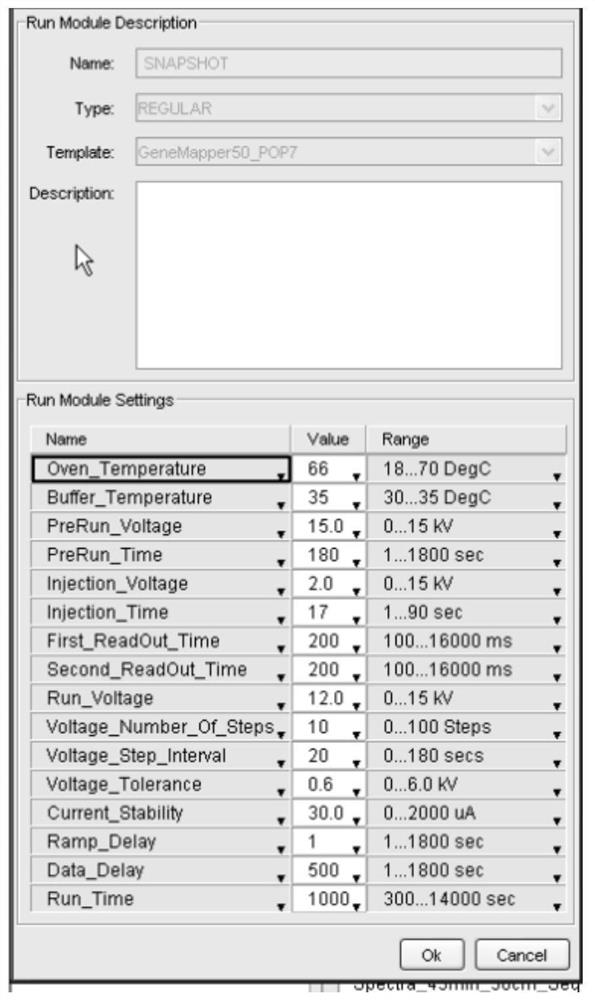
[0138] 29 loci with preliminary polymorphisms were obtained through Sanger sequencing screening, and then population verification was performed using SNAPSHOT. The experimental procedure is as follows:
[0139] Take 1 μl of DNA sampl...
Embodiment 2
[0162] Embodiment 2 and 3 are paired with the dwarf type bitter grass (GS) and 14 wild bitter grass groups (Taihu Lake TH, Honghu HH, Shanghai SH, Huai'an HA, Huangshan HS, Hangzhou HZ, Guangzhou GZ, Dali to the dwarf type bitter grass (GS) selected and bred by Taihe Water Company, Dali DL, Kunming KM, Guiyang GY, Liuzhou LZ, Changsha CS, Yingtan YT, Jingdezhen JDZ) as examples, use the 22 SNP polymorphic sites screened in Example 1 to carry out the identification process and build its phylogenetic tree.
[0163] (1) Sample collection and storage: collected the dwarf bitter grass (GS) bred by Taihe Water Company and 14 wild bitter grass populations (Taihu TH, Honghu HH, Shanghai SH, Huaian HA, Huangshan HS, Hangzhou HZ, Guangzhou GZ, Dali DL, Kunming KM, Guiyang GY, Liuzhou LZ, Changsha CS, Yingtan YT, Jingdezhen JDZ), in the laboratory for three days, soak in 5‰potassium permanganate dilution for 15min to remove microorganisms on the leaf surface , to avoid contamination caus...
Embodiment 3
[0249] Embodiment 3 constructs phylogenetic tree
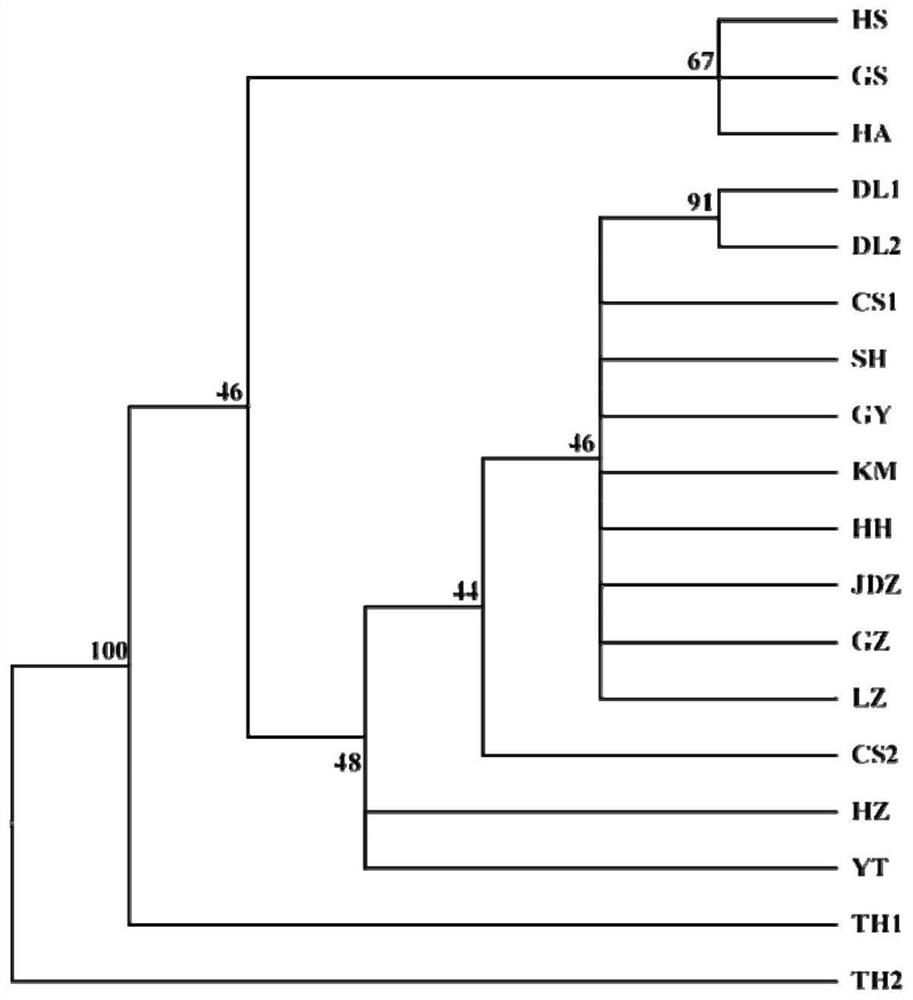
[0250] Sample collection, genomic DNA extraction, and PCR amplification procedures are the same as in Example 2. The PCR amplification products were sequenced. According to the sequencing results, a phylogenetic tree was constructed for 15 populations (18 samples) using the 22 polymorphic SNP sites described in this application, and Phylip.695 was used to construct the ML according to the Maximum Likelyhood Method. cluster plot ( figure 2 ). According to the constructed phylogenetic tree, we can intuitively see the population kinship relationship between the tested Elephantia miltiorrhiza and the dwarf Elephantiae elegans strains bred by Taihe Water Co., Ltd.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com